CHEM final exam (grade 12)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
SOme rules of naming compounds
-fINd the longest chain
-name so you have the smallest numbers possible
- //: -#- enes
- ///: - # - ynes
alphabetical order (chaines)
naming format
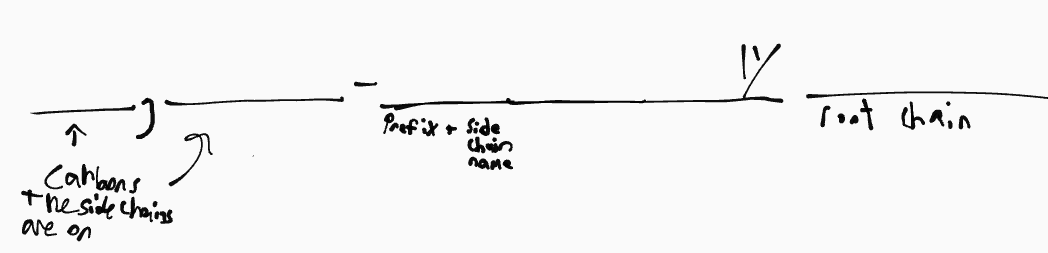
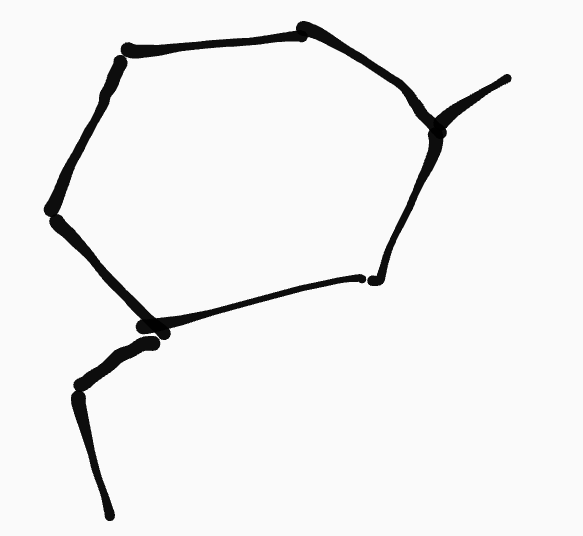
cycloalkane
__ ,__- ____ylcyclo____
ex. 1-methyl-3-ethylcyclohexane
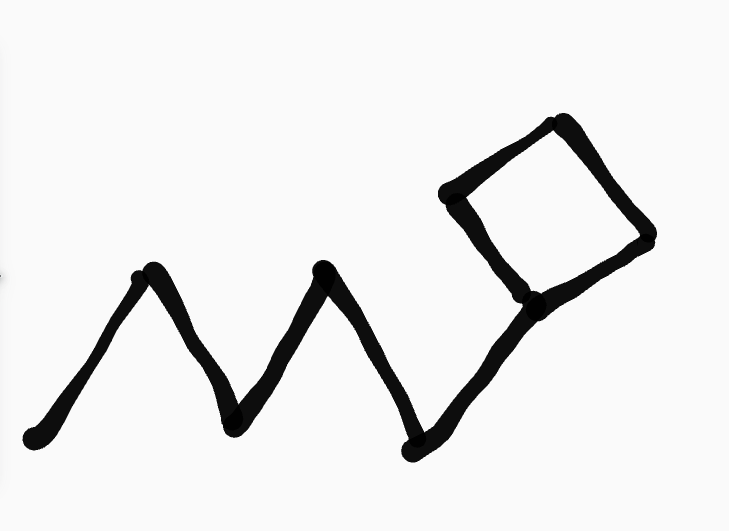
cycloalkane
_ ,__- _cyclo____yl ______
ex. 1-cyclobutylpentane
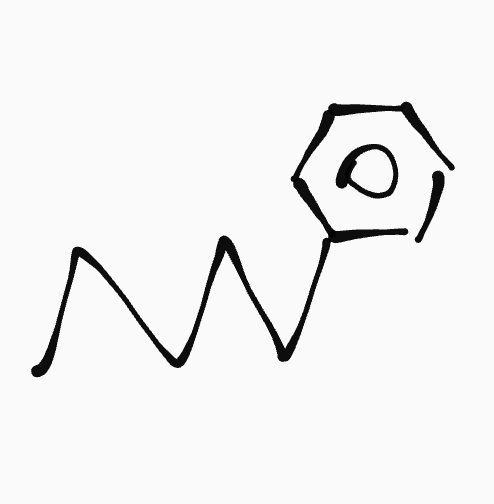
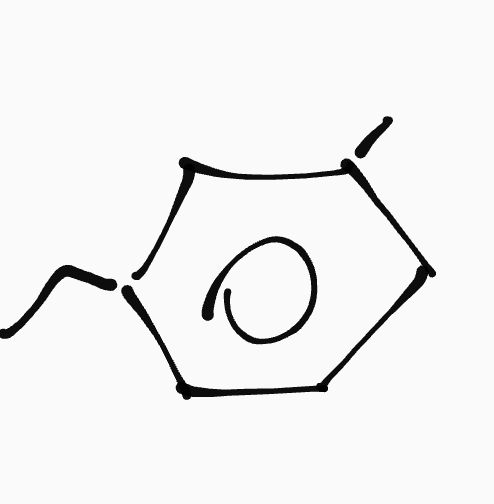
Aromatic hydrocarbon
_ ,__- ____ylbenzene
ex. 1-ethyl-3-methylbenze
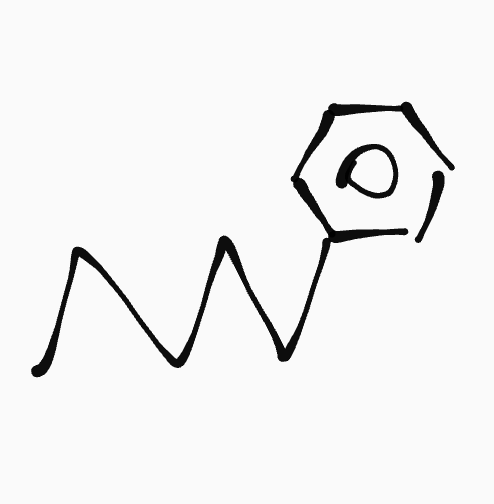
Aromatic hydrocarbon
_ ,__- _phenyl______
ex. 1-phenylpentane
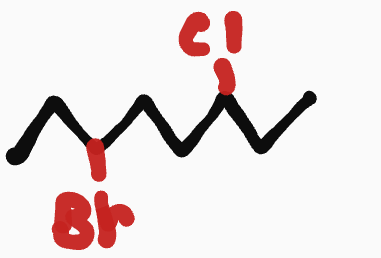
haloalkanes
__- _(F/Cl/Br/I)_____
fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo
ex. 3-bromo-6-chlorooctane
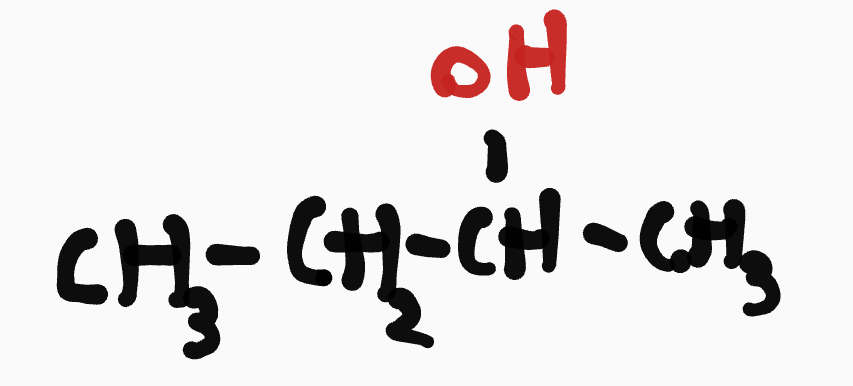
Alcohol (R-OH)
__- ____yl___- (c #0)- ol
ex. butan-2-ol
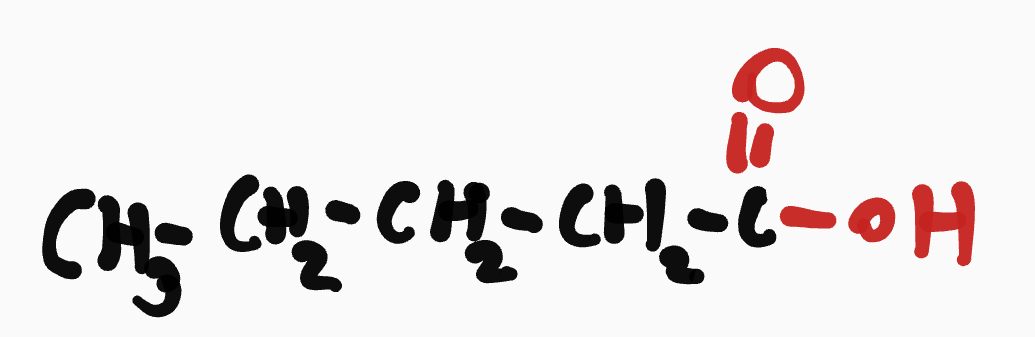
Carboxylic acid
__- ___yl_____oic acid
ex. pentanoic acid

Aldehyde
__- ____yl___al
O= determines the root chain
alwayd on the end so no numbers needed (At end)
ex. 2-methylbutanal
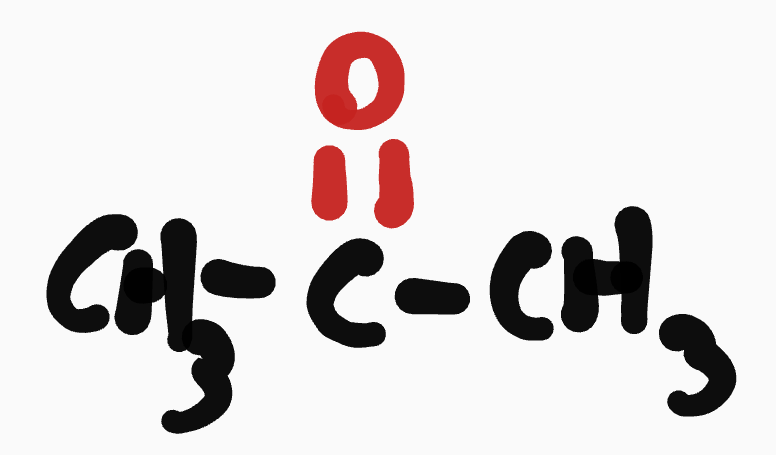
Ketone
O= determines root chain
O is prioritized
drop the e at the end
__- ____yl___- (c #0)- one
ex. propanone
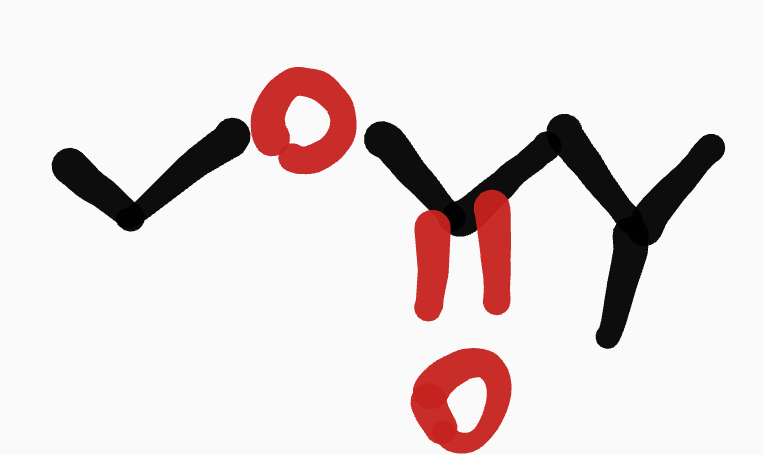
Ester
root chain is determined by O=
short chain-_-____yl rootcahin oate
ex. ethyl-3-methylbutanoate

Ether
(the # C that O is attached too on the longest chain) short chain oxy-_-____yl root chain
O is prioritized
ex. 1-methoxy-4-methylpentane
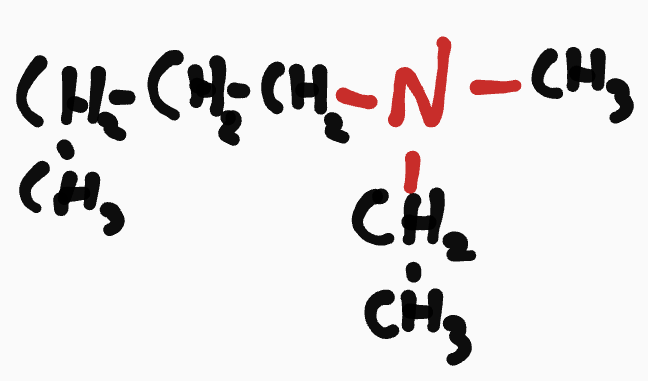
Amine
N-_chain_-N- chain root chain - (the # C that N is attached too on the longest chain) - amide
ex. N-ethyl-N-methylbutanamine
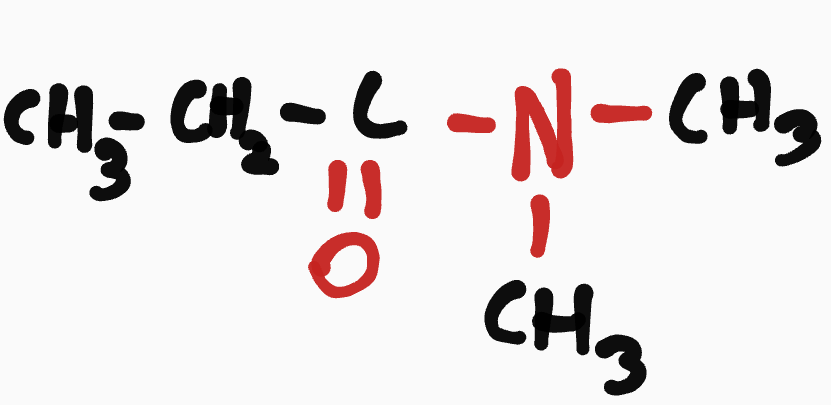
Amide
N-_____-__-______________________amide
ex. N,N-methylbutanamide
what happens in an addition reaction?
the double / triple bonds break
Alkenes
C=C + X-Y —> X-C-C-Y
Alkynes
if limited ≡ —> =
if excess ≡ —> -
Multiple Products
2 possible products
C=C-C + X-Y —> CX-CY-C or CY-CX-C
Markovmikov’s Rule
Unsymetrical:
Major (H is added to the carbon with the most H)
Minor (H is added to the carbon with the less H)
What happens in an elimination reaction?
forms double bonds
CH2X-CH2Y —> CH2=CH2 +X-Y
Alcochols perform with strong acids (H2SO4)
Haloalkanes preform under strong bases (NaOCH2CH3)
Major/Minor law / anti markovnikov rule
is the double bond can be formed in more then one place, then the H will be removed from the carbon with the most carbons attached to it (major)
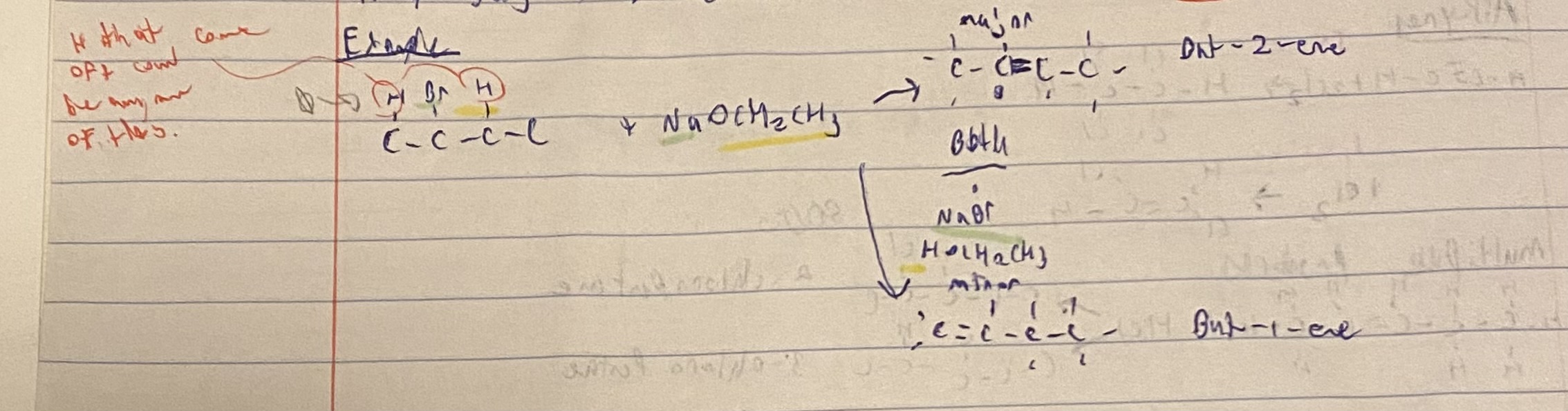
what happens in a substituons reaction?
they swap
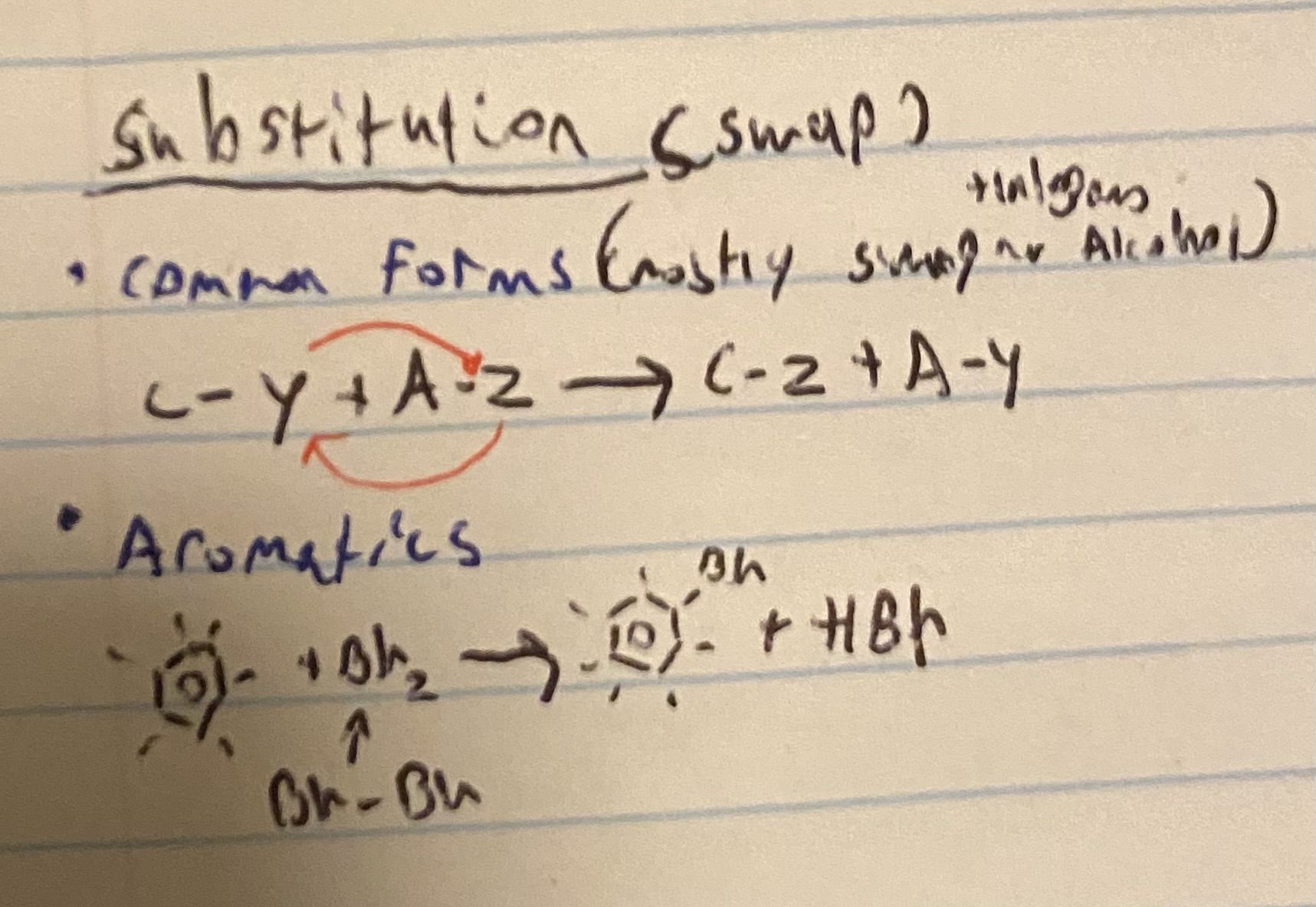
what happens in a condensation reaction?
2 molecules combine and form larger molecule + H2O
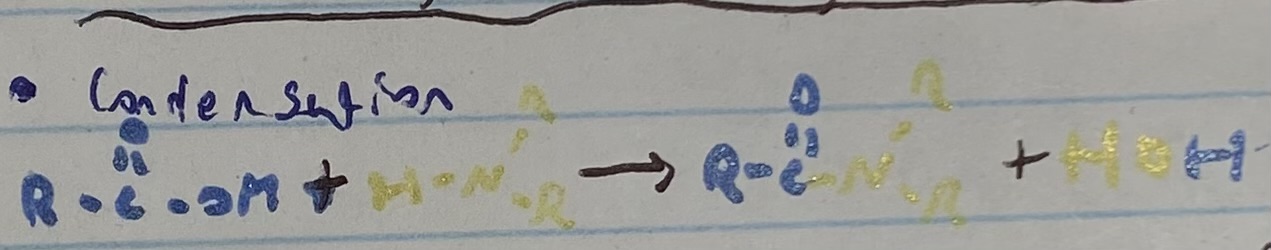
what happens in an estérification reaction
condensation reaction between carboxylique acid and alcohol
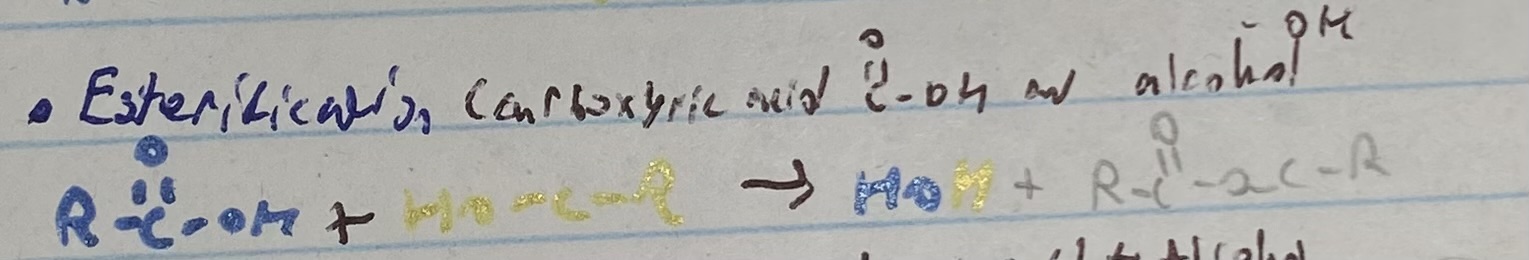
what happens in a hydrolysis reaction
ester + water —> carboxyic acid + alcohol

what happens in an oxidation reaction?
gains O lose H (alcohol + [O])
1^o. -OH + excess [O] —> aldehyde —> carboxylic acid
2^o. -OH + excess [O] —> ketone
3^o. -OH + [O] —> N.R.
![<p>gains O lose H (alcohol + [O])</p><p>1^o. -OH + excess [O] —> aldehyde —> carboxylic acid </p><p>2^o. -OH + excess [O] —> ketone</p><p>3^o. -OH + [O] —> N.R.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/33de1338-c3b6-48cb-90b2-576a9c0b3f6b.jpg)
what happens in a reduction reaction ?
gains [H] lose O (K,A, or CA + [H] makes -OH)
![<ul><li><p>gains [H] lose O (K,A, or CA + [H] makes -OH)</p></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f2d44b3b-f0e9-4861-8063-ec2501f53183.jpg)
what happens in combustion reactions?
complete: hydrocarbon + O2 —> CO2 + H2O + energy
incomplete: hydrocarbon + O2 (insufficient) —> C + CO + CO2 + H2O + energy
what happens in a polymer addition reaction?
reduces carbons double bond and makes a pattern
what happens in a polymer condensation reaction?
takes an OH off of one and H from the other to make H2O and a pattern
john dalton
described that matter is made up of small indestructible and indivisible shares (atoms)
JJ Thomson
used glass discharging tubes with trace amounts of gas and passed an electric current though it. rays appeared, which curved with a magnet showing they were negatively charged. (found out there was a + and - charge in a atom) (plum pudding boy)
Ernest Rutherford
Fired alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold surrounded by zinc sulfuric coated screen that light up when hit with alpha particles. some particles had a large particle deflection, meaning most of the mass and all positive charges surround a very dense center (nucleus) while electrons orbit around it.
(nuclear model)
what happens to element when they are energized
they give off specific wavelength of light
Niels Bohr
electrons orbit like planetary orbits
the force that holds electrons together is electrostatic force betweent and - charges on electrons
electrons only exist in energy levels
electrons can jump between energy levels by absorbing or emitting energy
planetary model (didn't explain larger atoms)
what are the quantum numbers and do they describe
n, 1, ml,: describes the distribution of electrons in atoms
n: energy levels and size
I : shape
ml: 3D orientation
ms: behaviour of specific electron
charaistics of n
• tells you the energy level and size of orbital
* (all orbitals with the same value of n are in the same shell/energy level)
greater value of n means greater probability of finding an electron farther from the nucleus
electrons can jumps to different levels of n (absorlos energy when it goes up, and releases it when goes down)
stuff about I
shape of orbital
also callEd sublevels or subshells
1 = n-1 (possible values)
0=5, 1=p, 2=d, 3=f
stud about ml
• Choose from -I to +l, indicating the 3D orientation of orbitals. The total number of orbitals for an energy level n is n²
pauli exclusion principle
• no 2 electrons around an atom can have the same 4 Q numbers (electrons in the same orbital have same 3 Q's but different spins)
Aufbau principle
electrons occupied the lowest energy orbitals first
hunds rule
the lowest energy level of a atom has the max amount of unpaired allowed
ionic bonds
metal + non-metal
metals lose there electrons and non metals gain
opposites attract and form a crystal lattice
covalent bonds
non metal + no metal
metallic bonds
metal + metal
since 2 metals have a valance shell that are less then 8, they create a sea of valence electrons
low EN
valence electrons move freely from one atom to the next
Valance bond theory
a covalent bond (share electrons) forms when the orbitals of 2 atoms overlap and share a common region in space where a pair of electrons are
Hybrid orbitals
formed by the combination of 2 or more orbitals in the valence shell of an atom.
PI bonds
covalent bonds formed by the overlap of P orbitals/formed from double bonds
VSEPR Theroy
valance shall electron pair repulse theory
electron groups around an atom are positioned as far away from each other
(electron groups are lone pairs, single, double and triple bonds)
first law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed only transferred
second law of thermodynamics
when objects are in thermal contact that heat will be transferred from the object will the higher temperature to the object with the lower infill both objects have the same temperature and reach thermal equilibrium
what are the 6 Factors Affecting Reaction Rate
Nature of the reactants
Concentration of solution
Temperature
Pressure of Gases
Surface area of the particles of a solid
Presence of a catalys
Keq’s relation to one
Keq >1 favoris products
Keq < favours reactants
change in concentration (product up and down)
product ⬆ more reactents formed
product ⬇ more product formed
change in pressure
pressure ⬆ more/shift towards side with fewer particles
pressure ⬇ shift to side with more particles
Temperature increase
Toward endothermic reaction → Endothermic forward reaction Keq Increases
Temperature decrease
Toward exothermic reaction → exo increase keq
Properties of Ionic compounds
◼ Crystal Lattices
◼ High MP and BP (In the range of metals [some above some below])
◼ Soluble (positive and negitve meds of ploles)
◼ Hard and Brittle (With enough force, the ions can “shift” and now repel.)
◼ Conductive if dissolved in water (so ions to move and conduct electricity)
Intramolecular bonds
exist within a molecule.
Intermolecular forces
Dipole-Dipole
Dipole induced dipole
Dispersion forces aka Van der Waals forces
Dipole-Dipole
When a covalent molecule is polar it has a permanent dipole
These dipoles can line up and cause attraction to each other
Induced Dipole
Bringing a polar molecule near a non-polar one can induced a dipole.
The molecules than have a small attraction to each other.
Dispersion Forces
Attractive forces between non-polar molecules.
Electrons orbit nuclei and cause brief momentary (but ongoing) moments of slight polarity.
Temporary dipole.
Very weak, but when many occur at the same time, can have a significant effect.
structure isomère
same formula diff shape
distereomer
same formula different properties
anti imores
mirror images