Chapter 2- Prokaryotic Cell Structures
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Components of a cell
- cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA
- viruses don't have ribosomes
- all viruses contain cytoplasm
- some viruses have DNA and cell membrane
- all microbes that are cellular have these components
Cell components
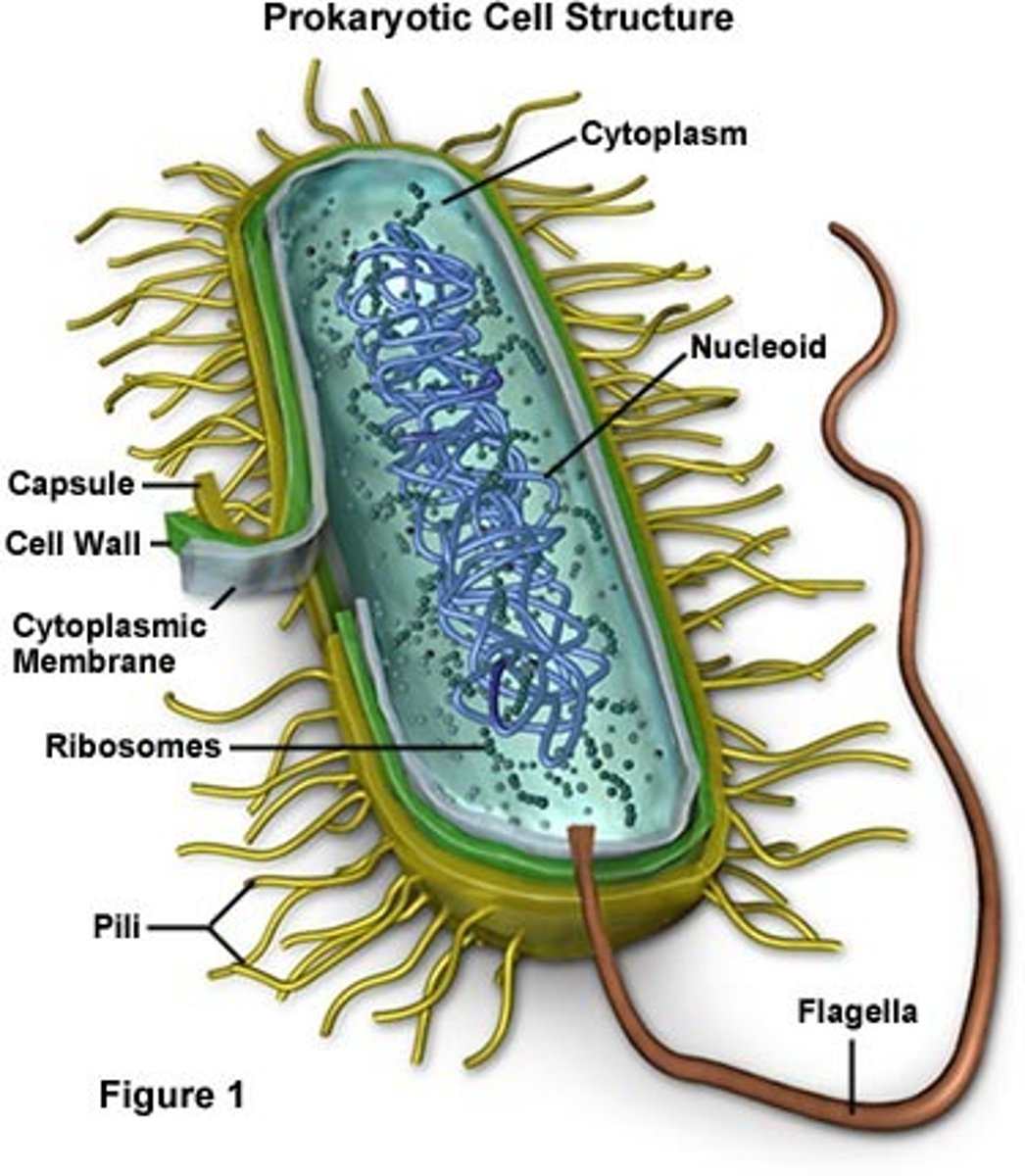
nucleoid, plasmid, ribosomes, inclusions, endospores, plasma membrane, cell wall, capsule, fimbriae, pili, flagellum
Nucleoid
- contains chromosome (s) and nuclear associated proteins
- chromosomes are usually haploid (1 set of chromosomes) and circular
- eukaryotes: usually diploid, linear chromosomes (not circular)
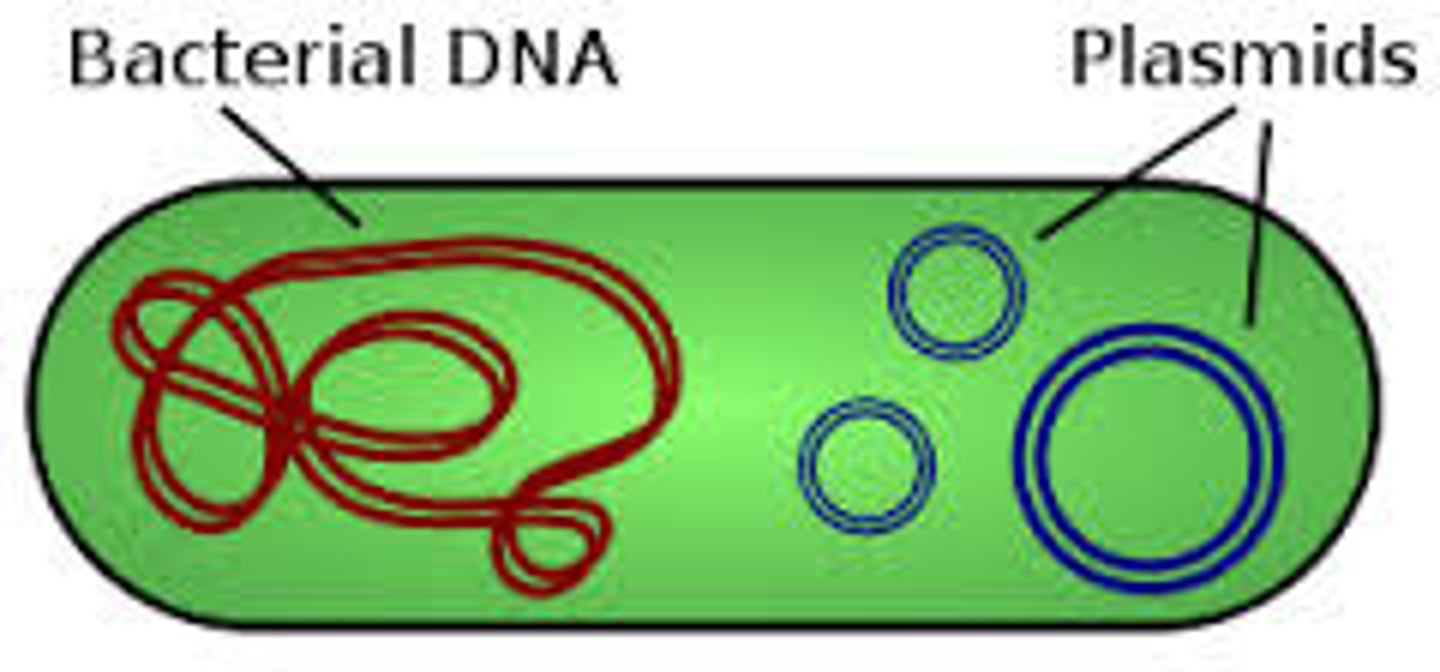
Plasmid
- circular double-stranded DNA
- not part of the chromosome
- can have 1-100s; multiple different plasmids or multiple of the same plasmid (they share)
- non-chromosomal DNA (bonus DNA)
- located outside nucleoid in cytoplasm
- encode antibiotic resistance & virulence factors (help bacteria infect us better)
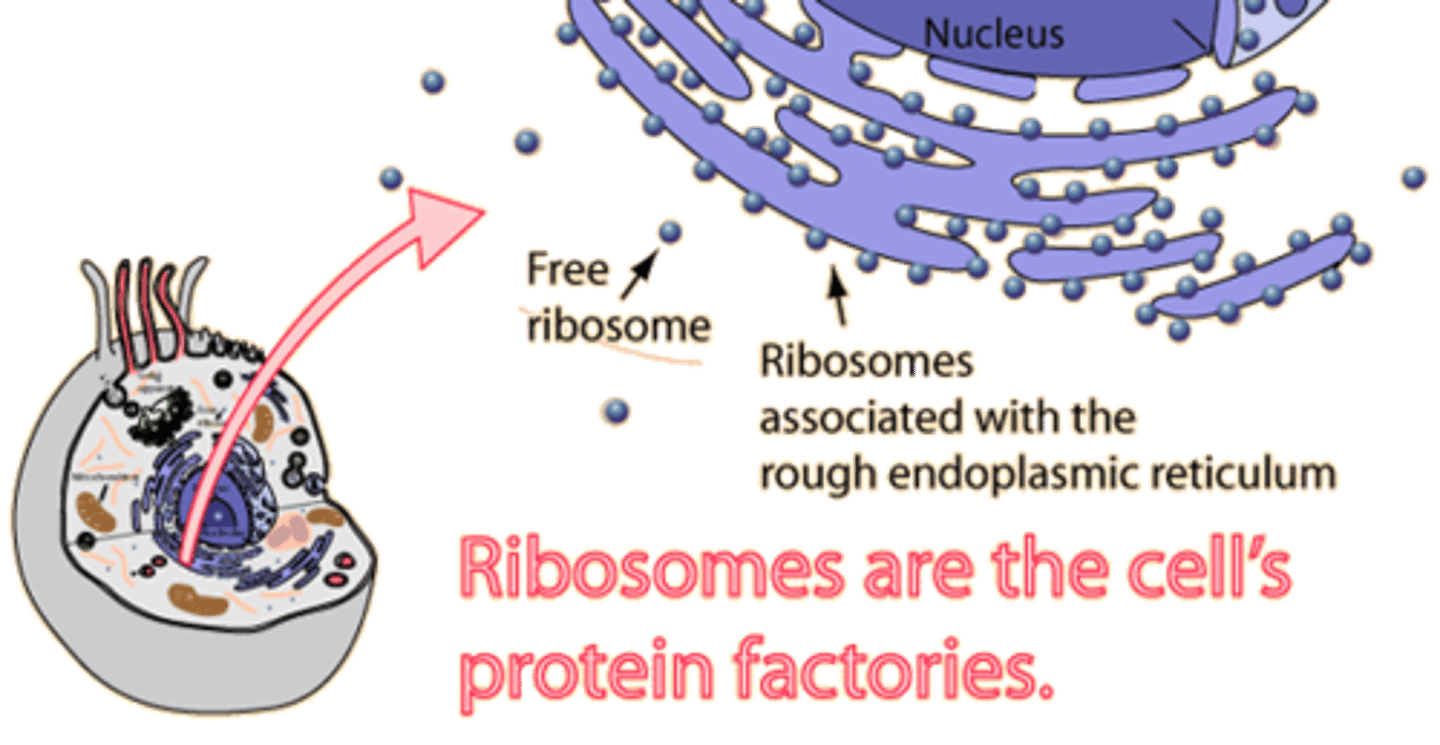
Ribosomes
- protein synthesis
- made up of proteins and RNA
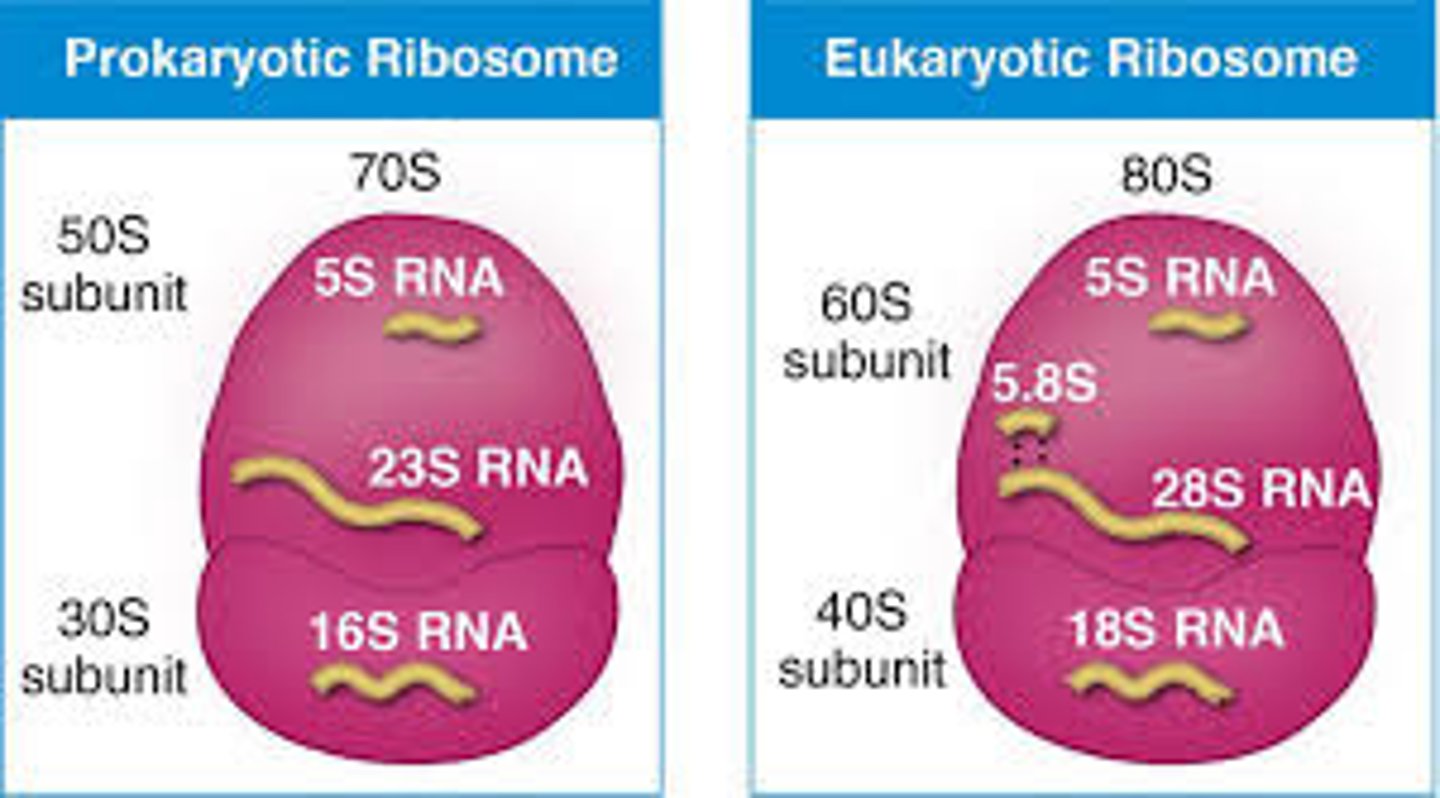
- prokaryotes: 70S (50S+30S)
- eukaryotes: 80S (40S+60S)- larger
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Ribosomes
Prokaryotic: use mRNA to make protein, composed of both protein and RNA, 30S+50S=70S, 16S for sequencing, free-floating (don't have ER)
Eukaryotic: use mRNA to make protein, composed of both protein and RNA, 40S+60S=80S, 18S for sequencing, free-floating or attached to ER membrane
Inclusions (not all bacteria)
- storage of nutrients, etc.
- have protein shells instead of lipids
Inclusion bodies
1. Lipid droplets: microbes use lipids to make new membranes; lipids used in metabolism
2. Volutin: store inorganic phosphates (need ATP for energy)
3. Sulfur inclusions: store sulfur; sulfur used in metabolism in bacteria
4. Gas bubbles: gives them buoyancy (they float); in aquatic prokaryotes
5. Magnetosomes: storage of iron oxide or iron sulfide; movement
Endospore (not all bacteria)
- inside the bacteria
- protects bacteria in a dormant state
- sporulation: process of becoming dormant (becoming endospores)
- germination: process of becoming active
- vegetative: active/replicating
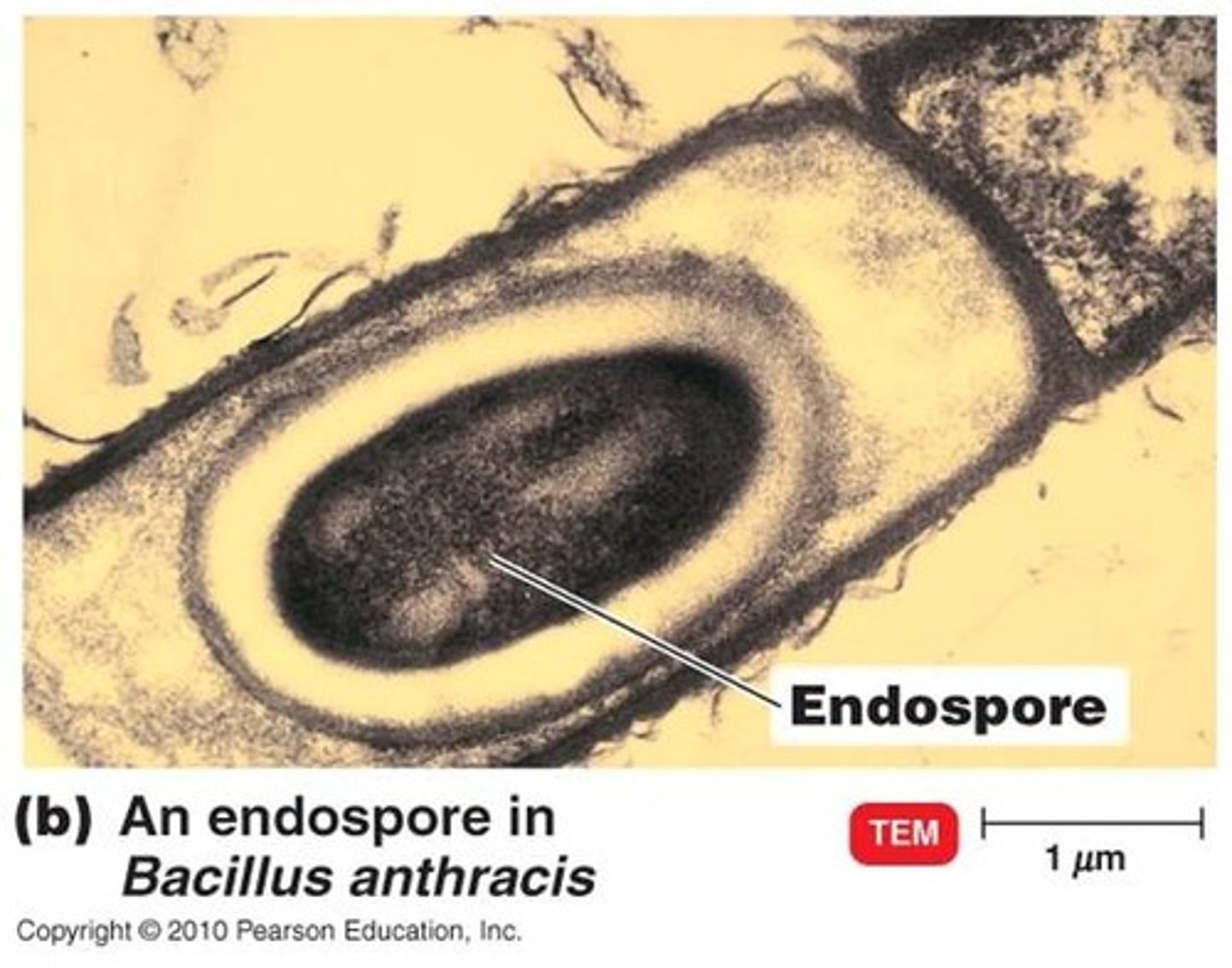
Endospore Formation (Sporulation)
Endospores are not reproductive
1. DNA replicates
2. membranes form around the DNA (DNA moves to end and membrane added)
3. forespore forms additional membranes
4. protective cortex (protein layer) forms around the spore
5. protein coat forms around the cortex (additional protein coat); on outside of membrane because they are more stable
6. spore is released (through cell lysis- bursts open- and the original dies in process
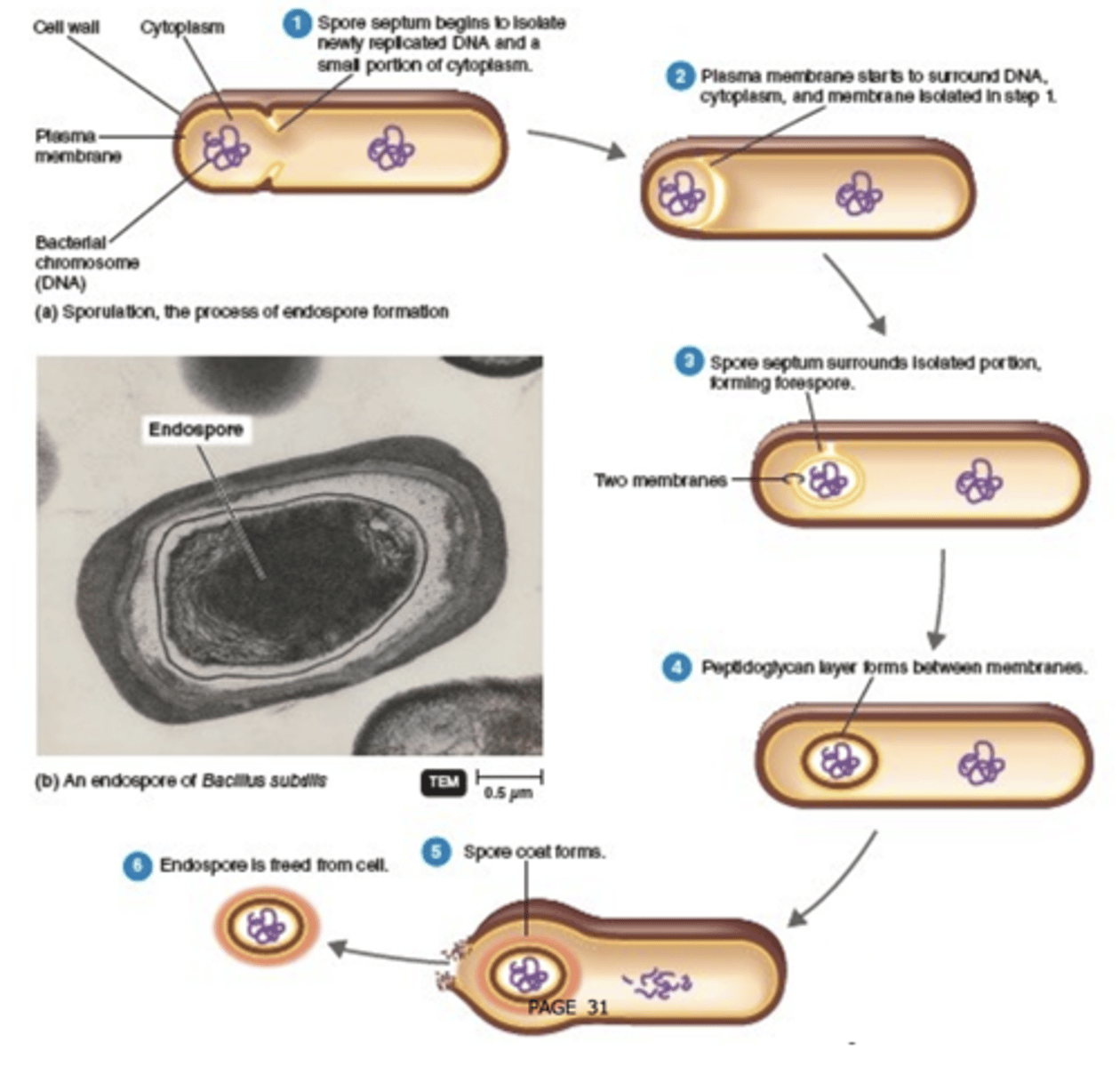
Plasma membrane
- like eukaryotic membranes
- semi-permeable
- composed of lipids and proteins
- controls transport into and out of the cell
Membrane transport:
- diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis (eukaryotes- bacteria can't use vesicles)
- bilayer with hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Sterols- unique to eukaryotes (ex. cholesterol or ergosterol)
Diffusion
- simple diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
- facilitated diffusion: need a protein channel (bigger molecules), solutes moving from high to low concentration
- active transport: solutes moving from low to high concentration; requires energy
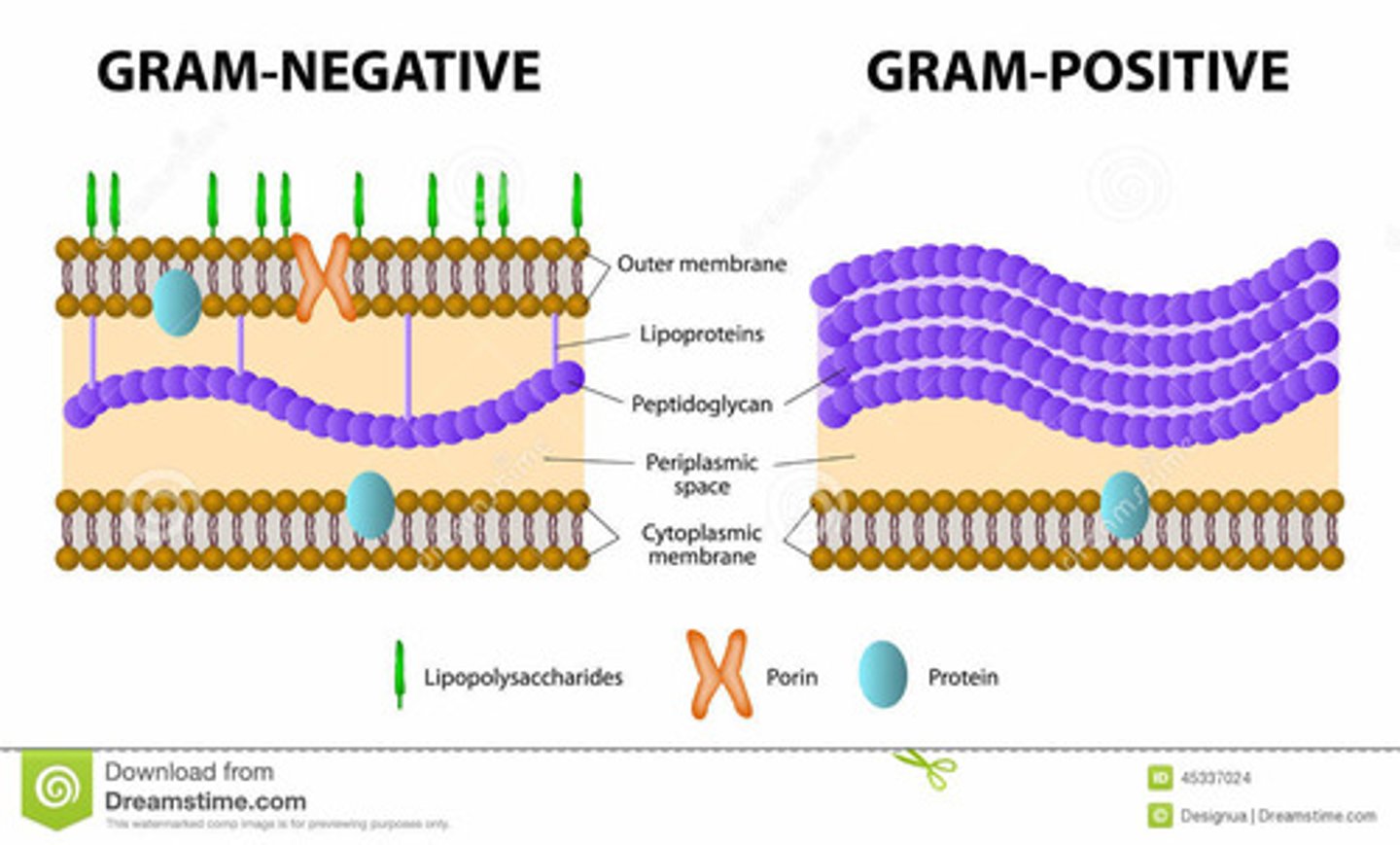
Cell Wall
- protects the cell from harsh (changing) environments
- contains peptidoglycan (bacteria)
- gram-negative vs gram-positive
Gram positive
- purple
-have a cell wall that is structurally less complex and contains more peptidoglycan than the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria (thick cell wall)
- usually less toxic than gram-negative bacteria
- pentapeptide: unique to gram +; it is the reason for the thick cell wall
Gram negative
- pink/red
- have a cell wall that is structurally more complex and contains less peptidoglycan than the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria (thin cell wall)
- often more toxic than gram-positive bacteria
- has lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that is toxic (infects healthy tissue)
Peptidoglycan
3 subunits: NAG, NAM, tetrapeptide (for gram + & -)
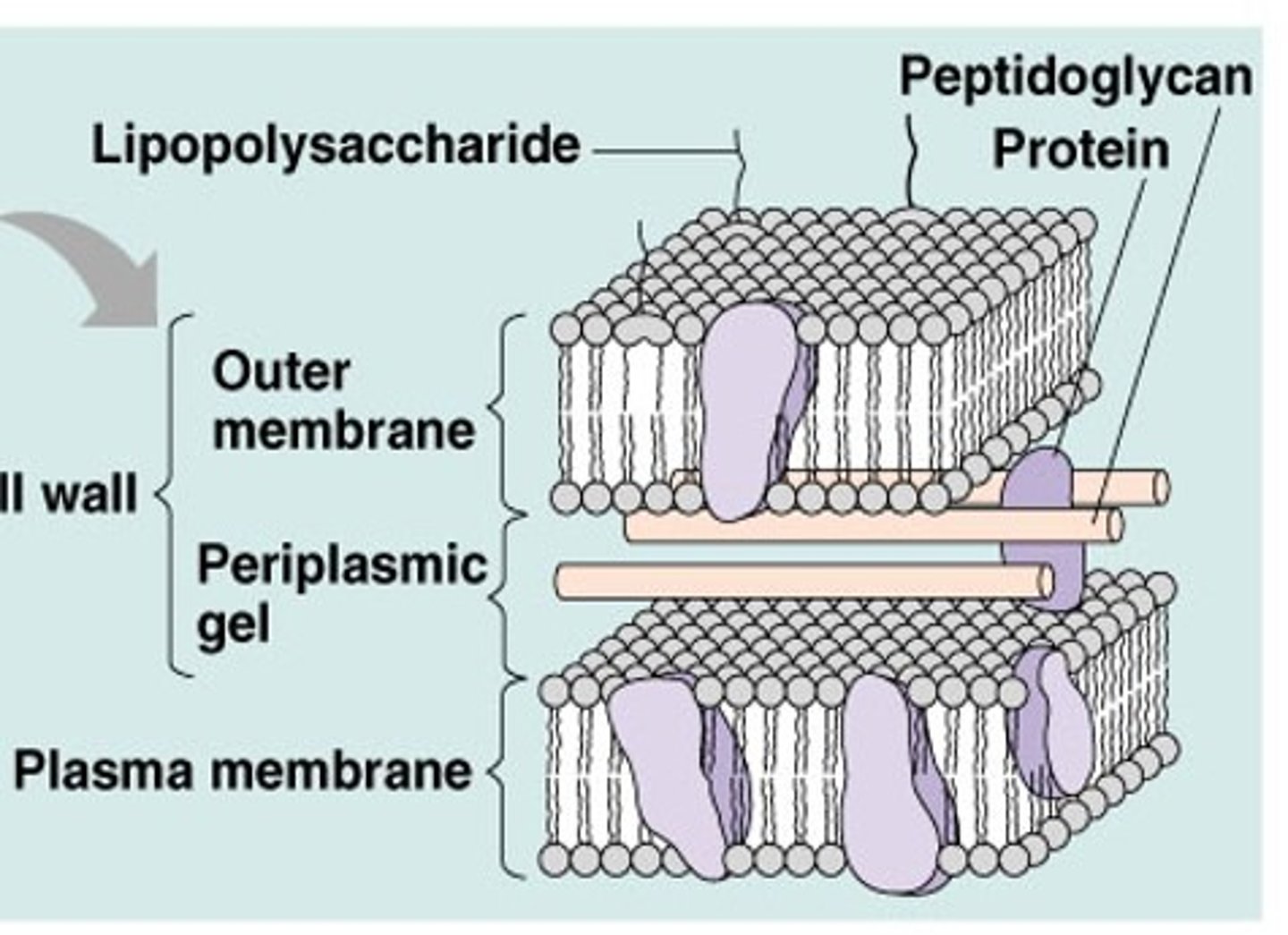
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
component of the gram-negative cell wall
- toxin
- structural component of outer membrane
Gram stain process
Step 1: Crystal violet- primary stain added to specimen spear - stains cell purple or blue
Step 2: Iodine- mordant makes dye less soluble so it adheres to cell wall- cell remains blue or purple
Step 3: Destain- (ethanol) decolorization washes away stain from gram negative cell walls- gram positive remains purple or blue and gram negative are colorless
Step 4: counter (secondary) stain allows dye adherence to gram negative cells- gram positive cells remain purple or blue and gram negative appear pink or red
Gram + (ish) with mycolic acid
- mycolic acids are waxy substances that prevent uptake of gram stain dyes
- acid fast stain: dye binds mycolic acid
- acid = red = positive
Glycocalyces (optional)
- capsule or slime layer
- adherence to surfaces
- aids in biofilm formation (community of bacteria)
S-layer (optional)
- substitute cell wall (often in archaea)
Fimbriae
- short bristle-like protein projections
- adherence to surfaces
- smallest size
- scattered around membrane surface
- not used for movement
Pili
- longer protein projections
- less numerous
- adherence to surfaces
- DNA transfer (plasmid); mediate transfer from 1 bacteria to another
- intermediate size
- not used for movement (?)
- plasmid movement leads to increase of antibiotic resistance
Flagellum
- long protein projections
- made of flagellin (protein)
- movement
- longest size
- flagella in eukaryotes made of actin or microtubules
Different flagella
- monotrichous: 1 flagella
- amphitrichous: 1 flagella on each end (2 total)
- lophotrichous: many flagella at 1 end
wrong in the picture
- peritrichous: many flagella all over
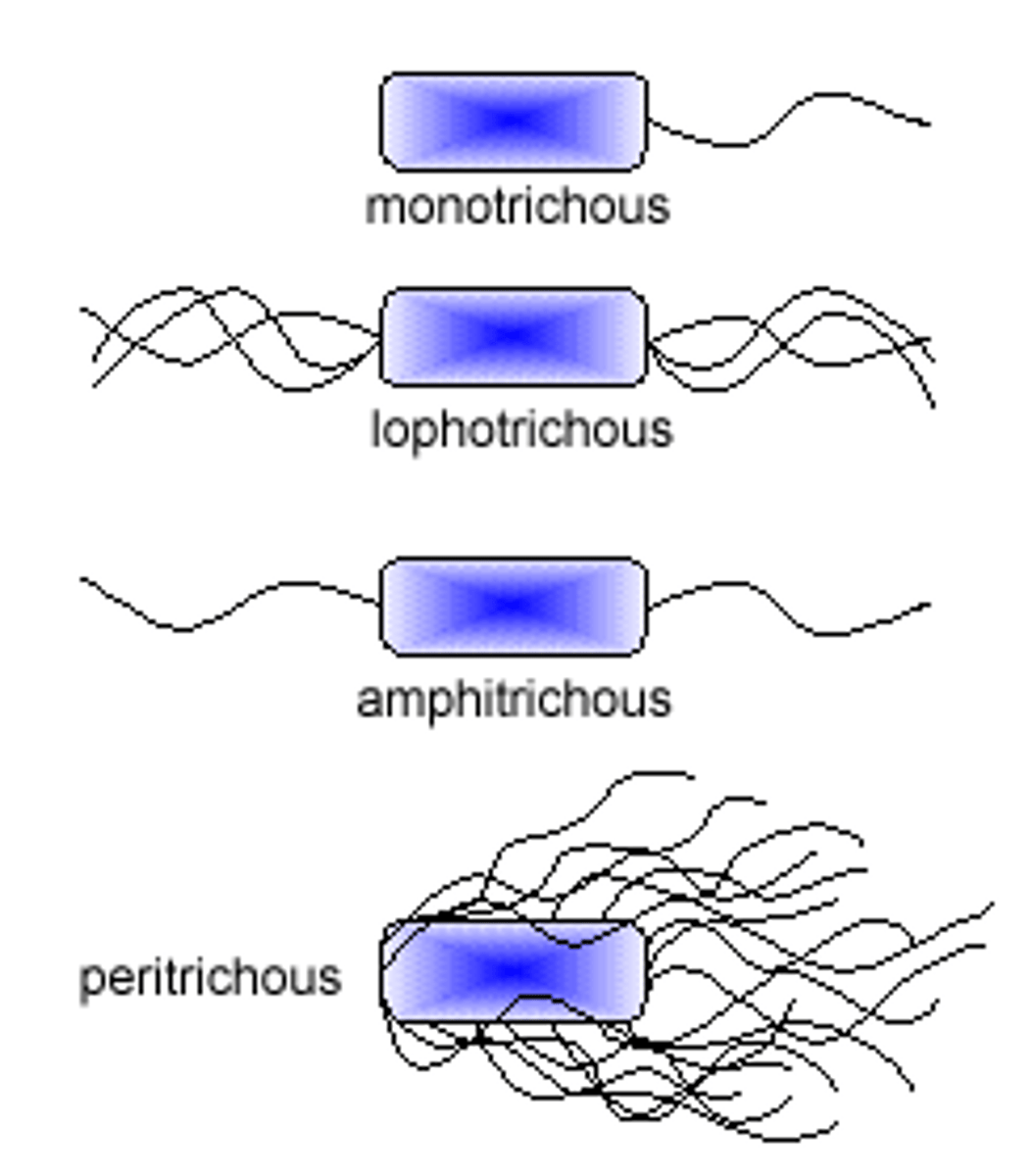
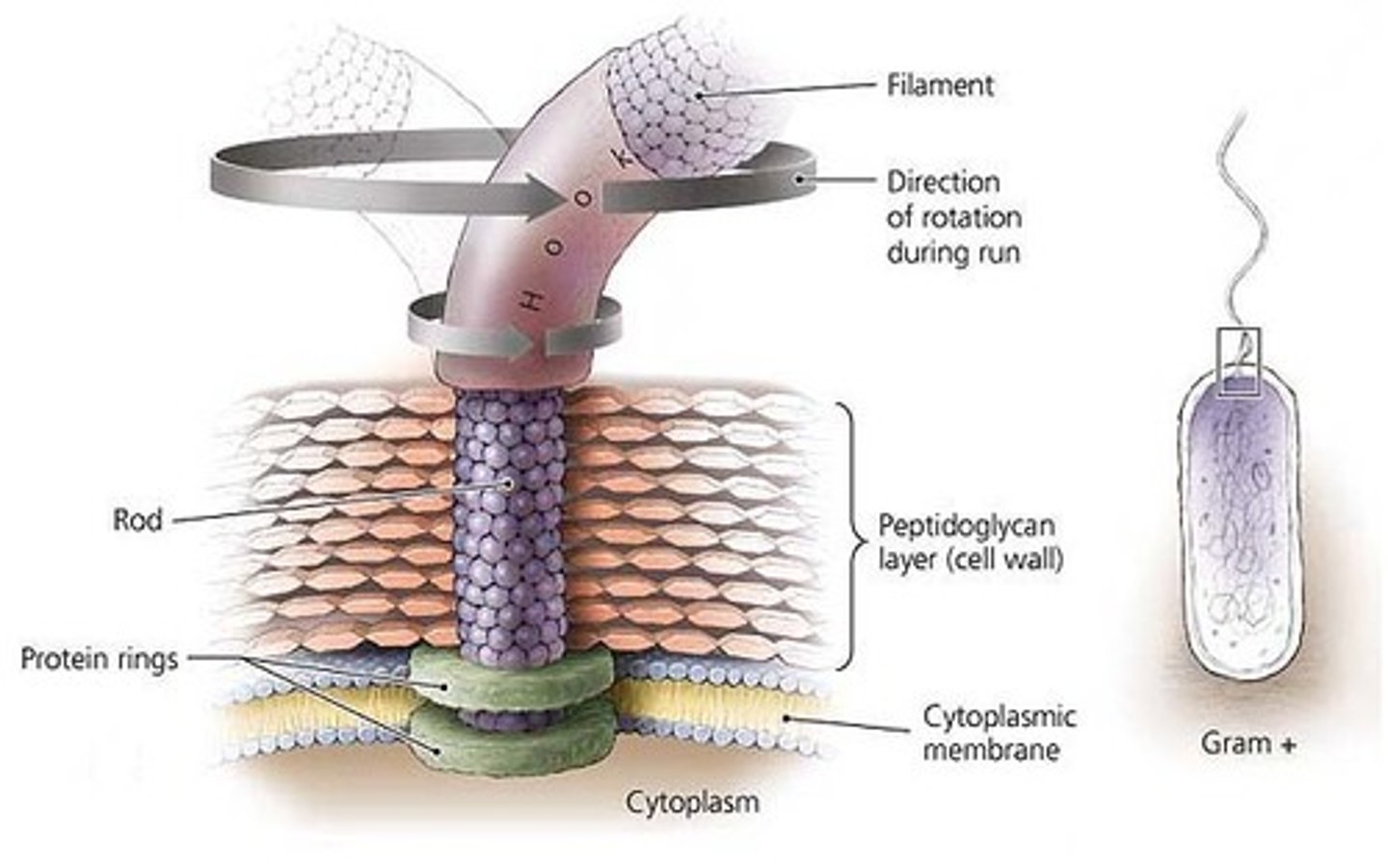
Gram positive flagella
Basal body composed of 2 rings
1. Inner ring (attached to plasma membrane)
2. Outer ring (attached to peptidoglycan)
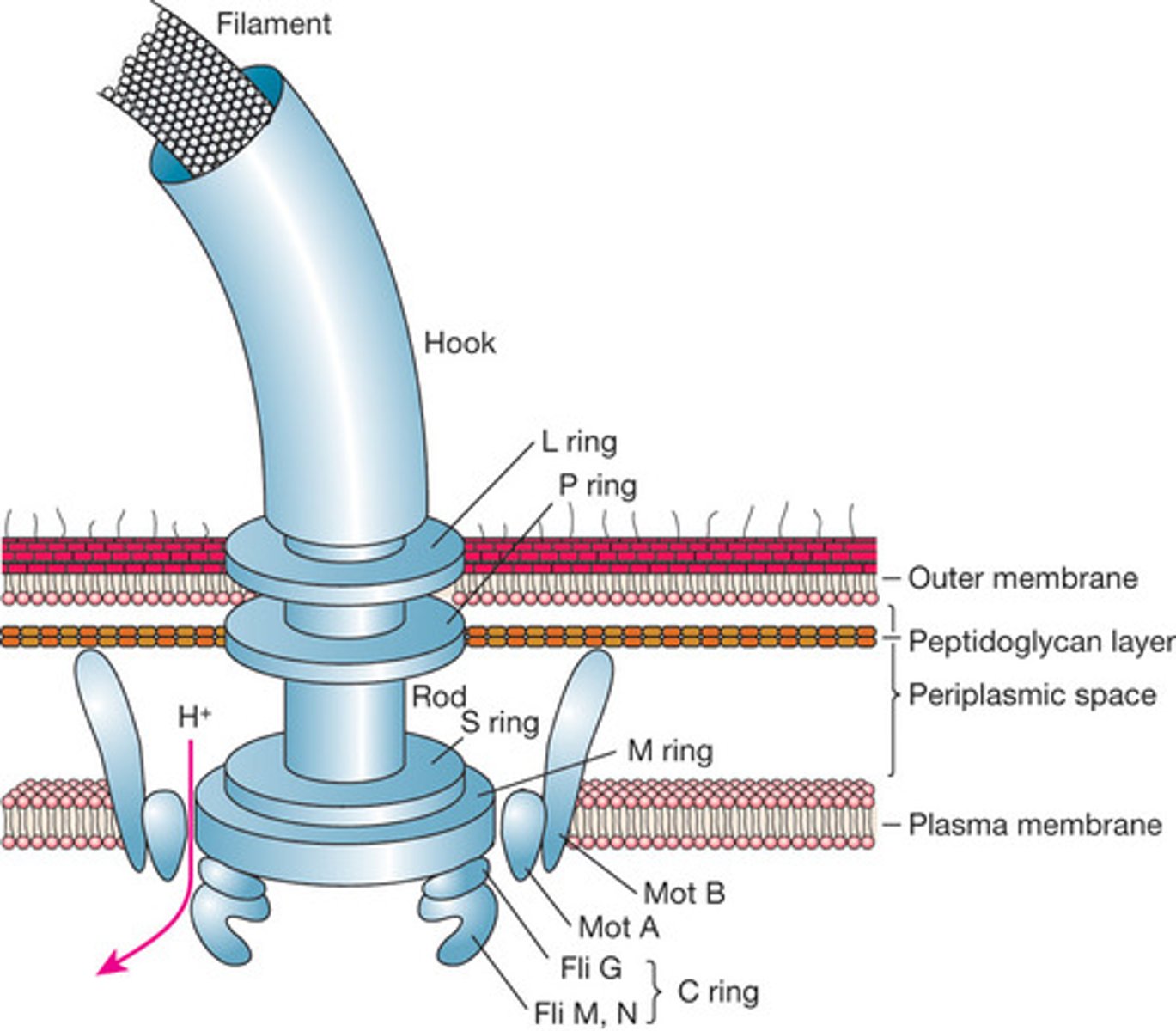
Gram negative flagella
Basal body composed of 4 rings
1. L-Ring (associated with LPS layer)
2. P-Ring (associated with peptidoglycan layer)
3. S-Ring
4. M-Ring (associated with plasma membrane)
- The MS-C ring acts as the rotor of the flagellar motor
Eukaryotic flagella and cilia
components: actin and tubulin
- cytoskeletal elements
Bacteria movement
- tumbling: clockwise rotation of flagella- slowing down or stopping; "splayed" conformation
- running: counter-clockwise rotation of flagella- bundle the flagella and then move forward
- run -> tumble -> run -> attractant
Coccus (pl. cocci)
single coccus
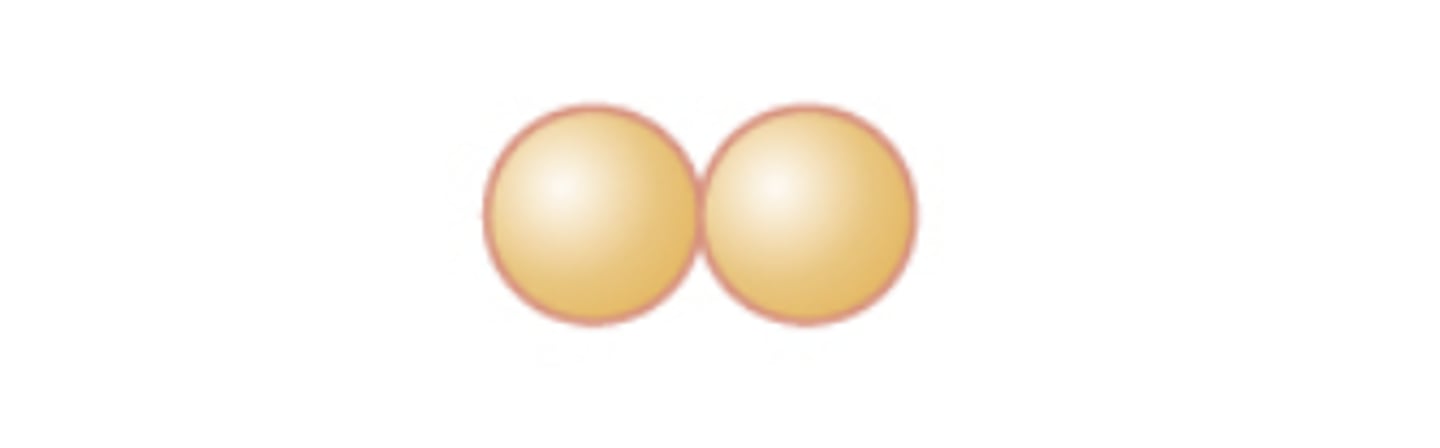
Diplococcus (pl. diplococci)
pair of two cocci

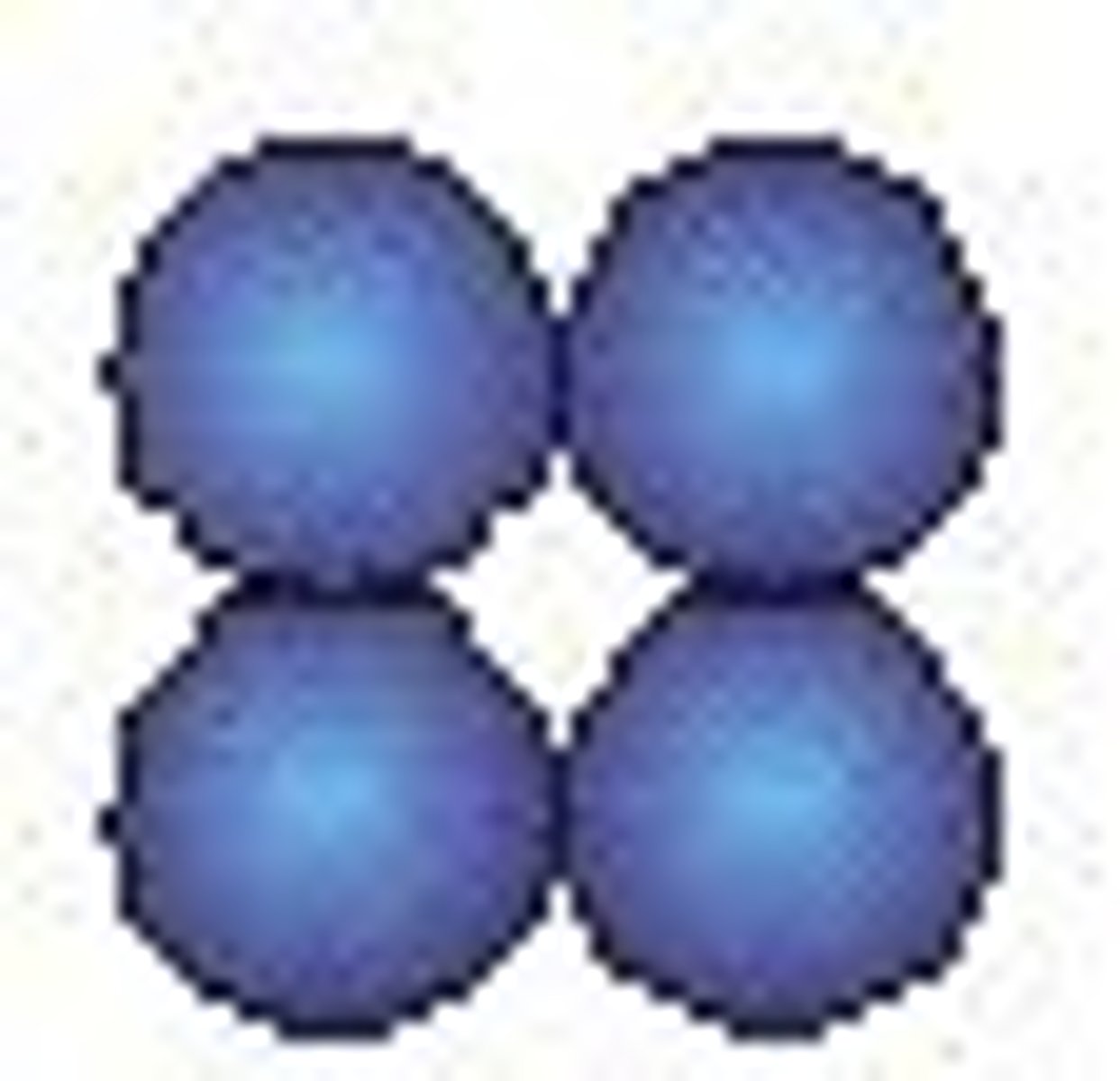
Tetrad (pl. tetrads)
grouping for four cells arranged in a square

Streptococcus (pl. streptococci)
chain of cocci
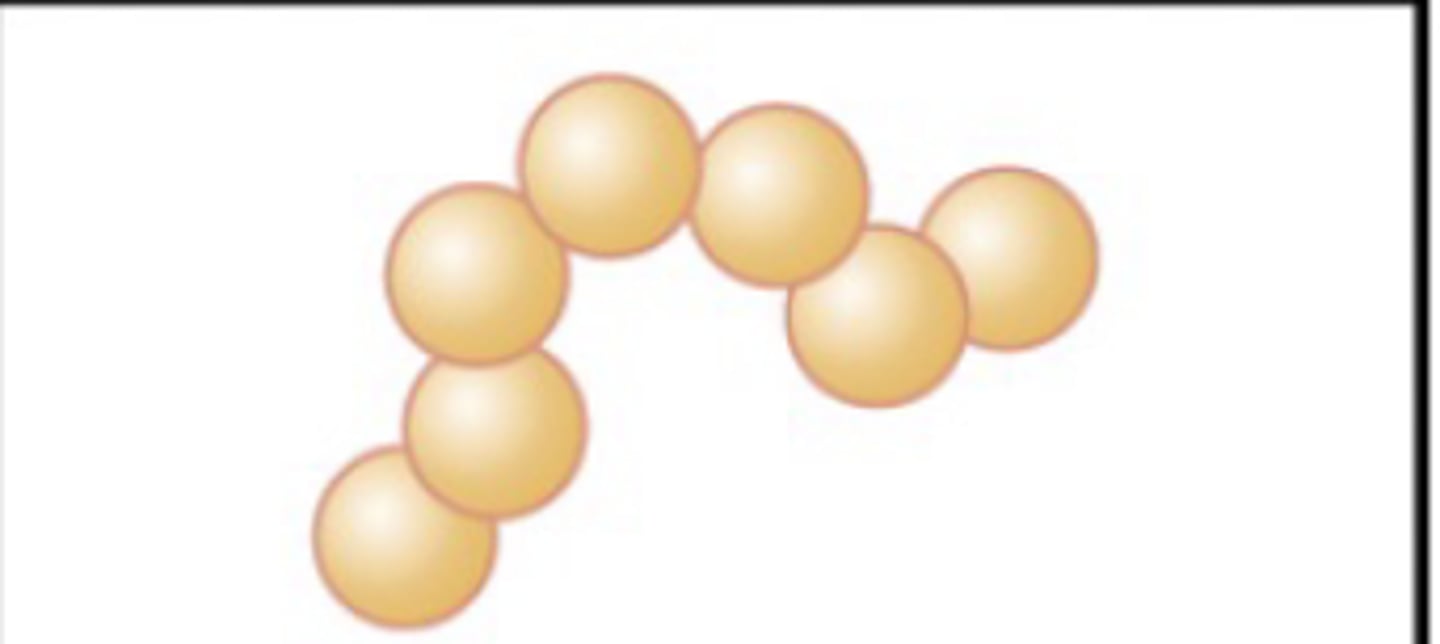
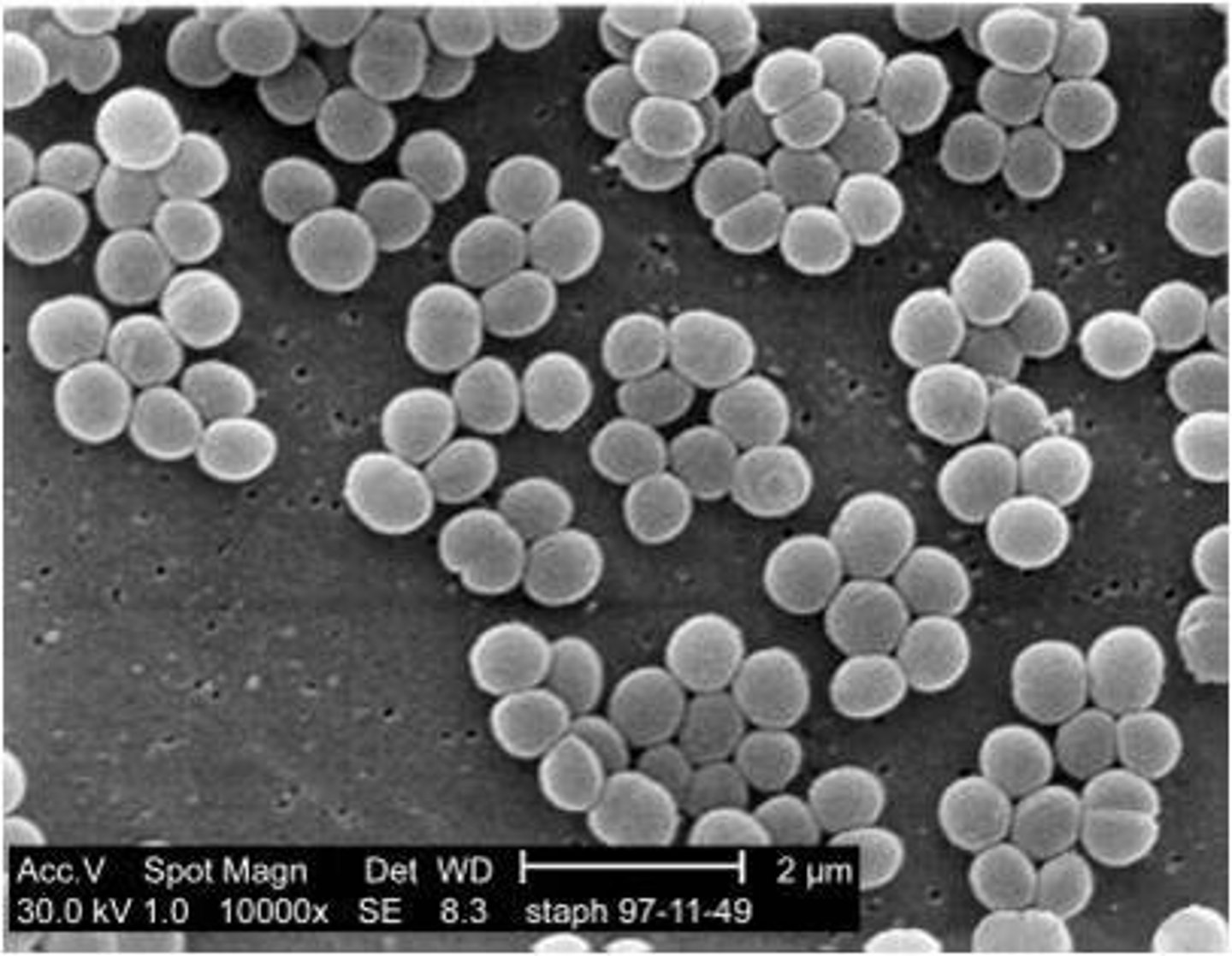
Staphylococcus (pl. staphylococci)
cluster of cocci

Bacillus (pl. bacilli)
single rod
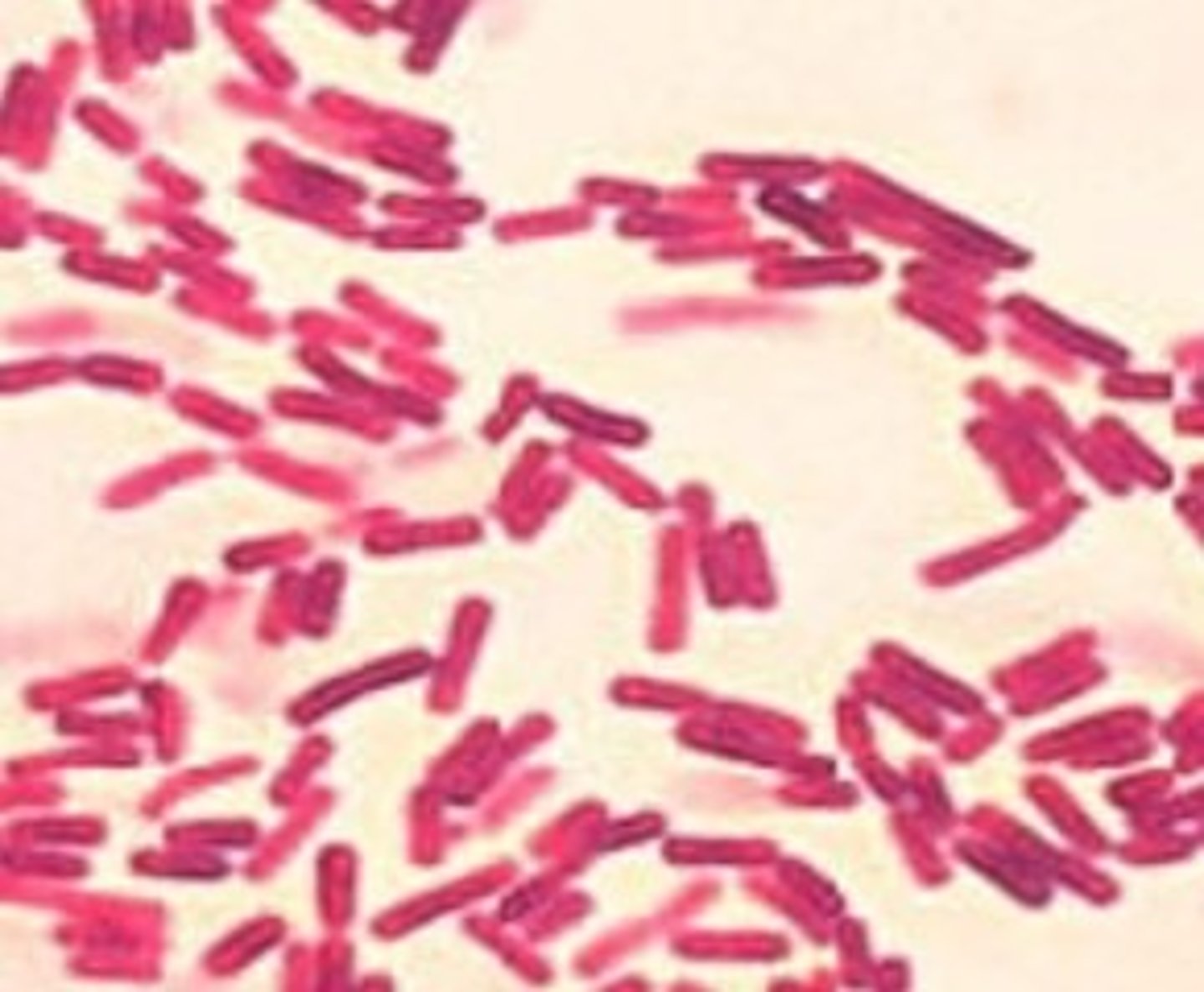
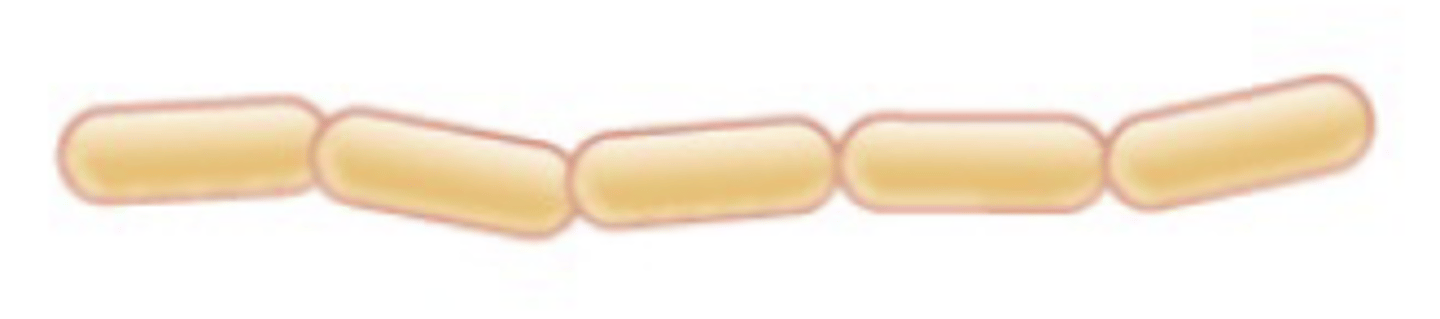
Streptobacillus (pl. streptobacilli)
chain of rods
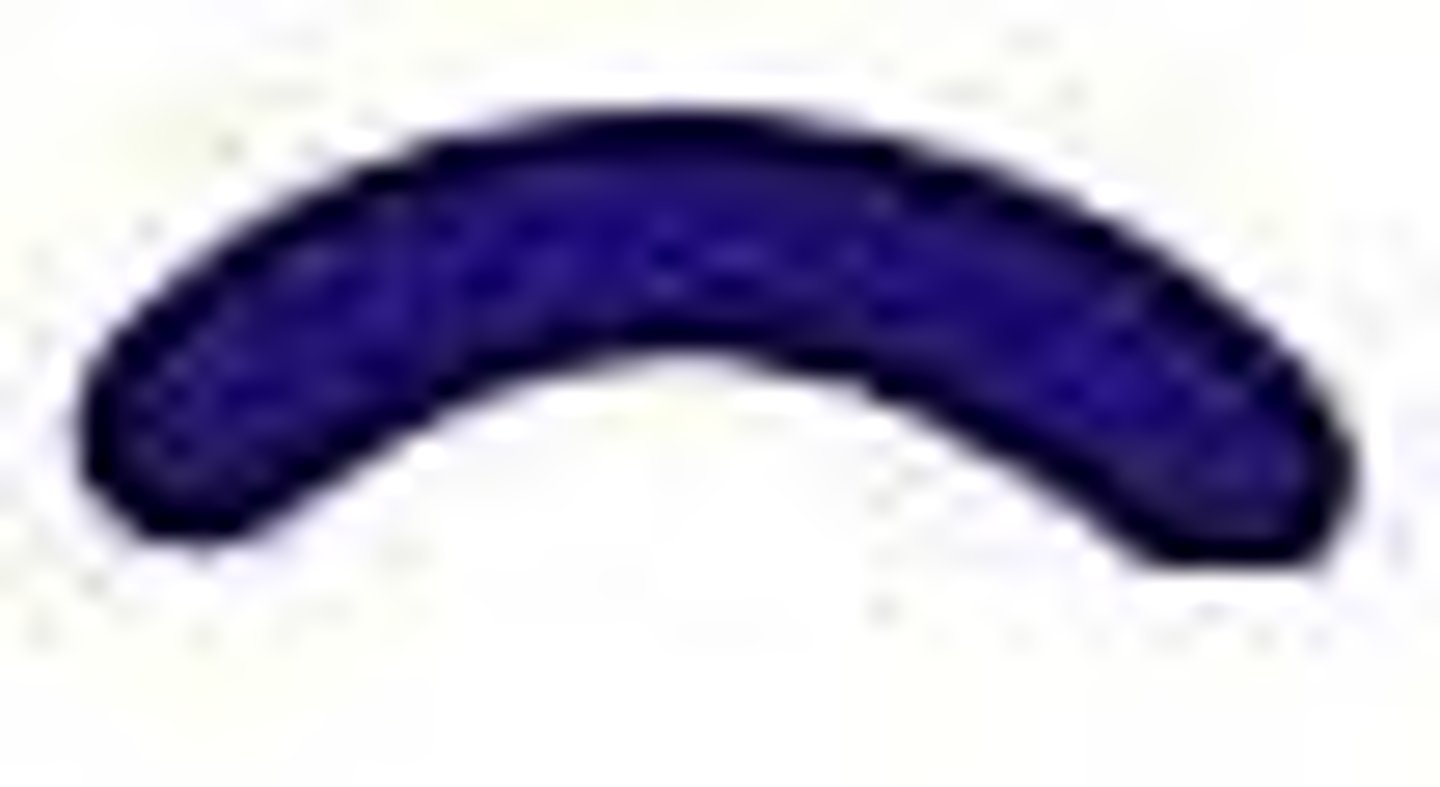
Vibrio
comma shaped

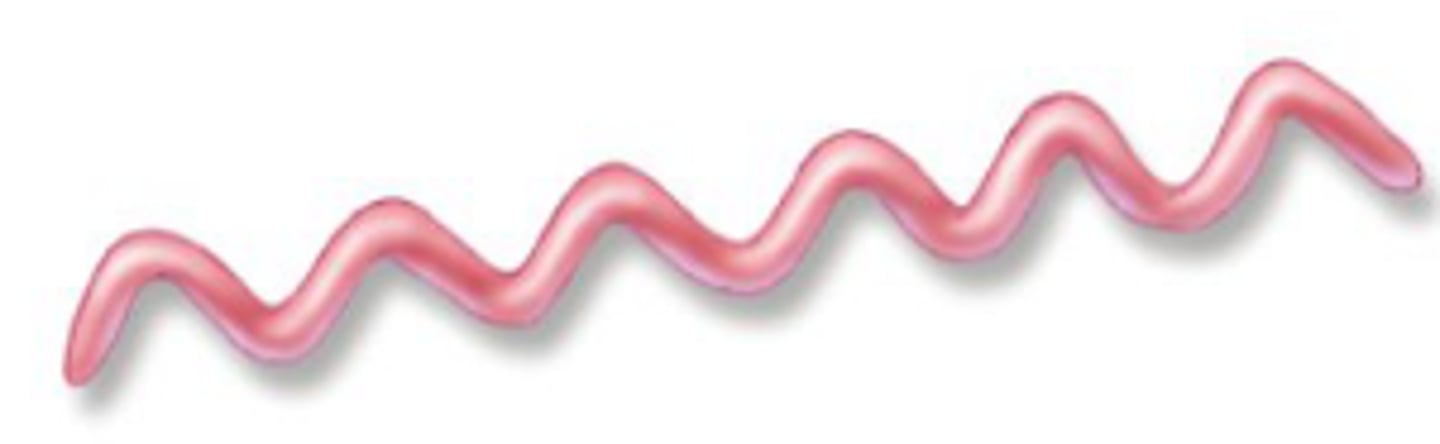
Spirillum
spiral (wavy) shaped bacteria
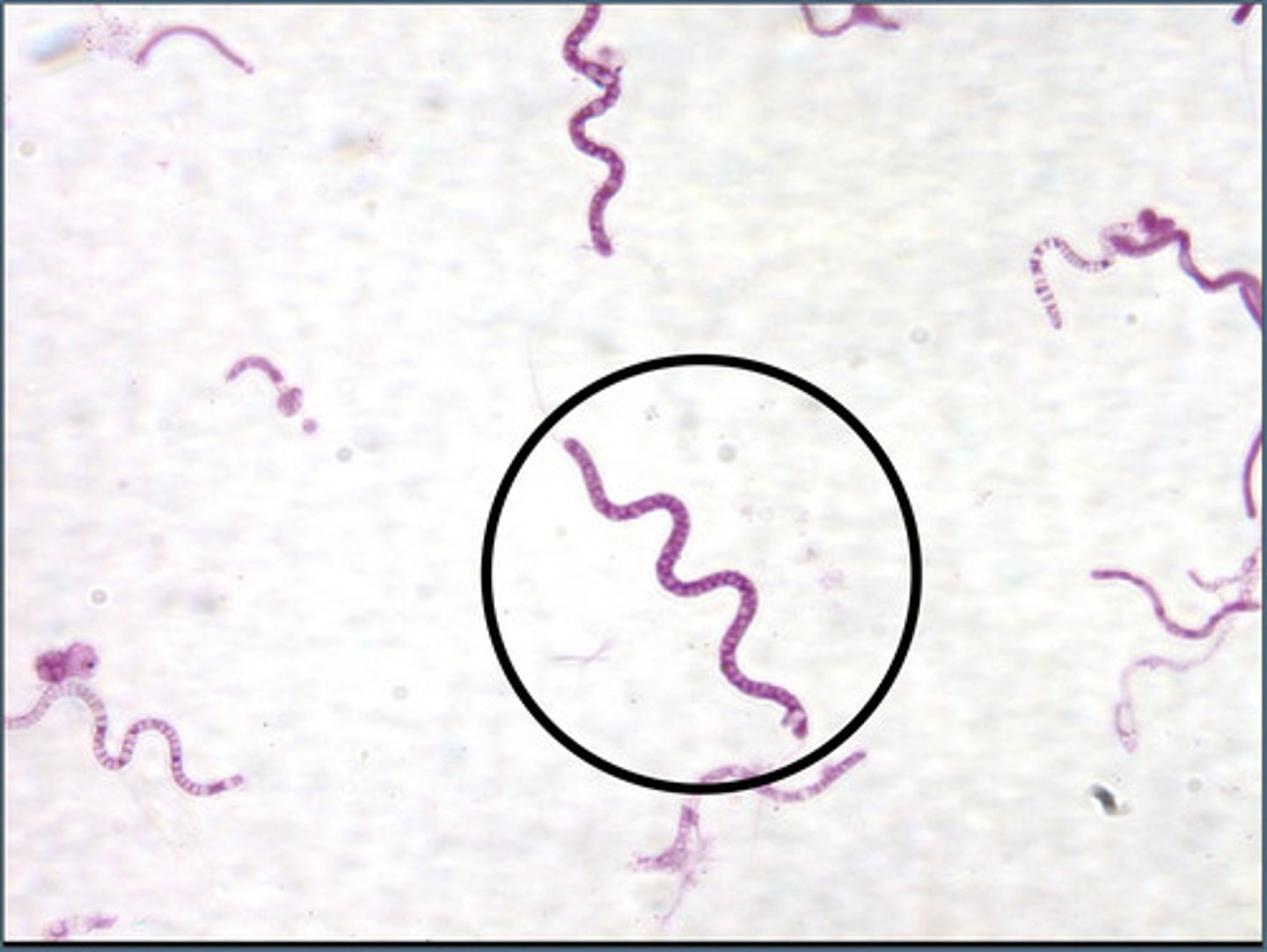
Spirochete
spiral (coiled) shaped bacteria
