Bio H Semester 1 Final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
1
New cards
independent variable
the variable being changed
2
New cards
dependent variable
the variable changing as an effect of the independent variable
3
New cards
control variables
variables that do not change throughout the experiment
4
New cards
characteristics of life: MRGGORME
made of cells
reproduces
genetic code
grows and develops
obtains energy
responds to environment
maintains homeostasis
evolves over time
reproduces
genetic code
grows and develops
obtains energy
responds to environment
maintains homeostasis
evolves over time
5
New cards
objective lens (microscope)
main lens; magnifies object
6
New cards
stage (microscope)
where the slide is placed
7
New cards
diaphragm (microscope)
adjusts light level; below the stage
8
New cards
light source (microscope)
provides light
9
New cards
ocular lens/eyepiece (microscope)
10x magnification
10
New cards
stage clip/slide clamp (microscope)
holds slide in place on stage
11
New cards
coarse focus (microscope)
moves stage up/down - low and medium objectives
12
New cards
fine focus (microscope)
moves stage back and forth - all objectives
13
New cards
magnification of low objective lens
4x
14
New cards
magnification of medium objective lens
10x
15
New cards
magnification of high objective lens
40x
16
New cards
magnification of eyepiece
10x
17
New cards
field of view using low objective lens
4\.5mm
18
New cards
field of view using medium objective lens
2mm
19
New cards
field of view using high objective lens
0\.5mm
20
New cards
prokaryote
small, simple organisms
no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
eubacteria and archaebacteria
no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
eubacteria and archaebacteria
21
New cards
eukaryote
larger, more complex organisms
contains nucleus that holds genetic material
animals, plants, protists, fungi
contains nucleus that holds genetic material
animals, plants, protists, fungi
22
New cards
unicellular organism
rely on one cell to perform all functions
bacteria and protists
bacteria and protists
23
New cards
multicellular organisms
organisms contains different cells to perform different functions
animals, plants, fungi
animals, plants, fungi
24
New cards
autotrophs
make their own food
plants, fungi, some bacteria via photosynthesis
plants, fungi, some bacteria via photosynthesis
25
New cards
heterotroph
consume or eat other organisms to supply themselves with energy
animals, carnivourous plants, protists, certain bacteria
animals, carnivourous plants, protists, certain bacteria
26
New cards
bacteria
prokaryotic
unicellular
hetero+autrotrophic
unicellular
hetero+autrotrophic
27
New cards
protista
eukaryotic
mostly unicellular
hetero+autrophic
mostly unicellular
hetero+autrophic
28
New cards
fungi
eukaryotic
multicellular (exception: yeast)
heterotrophic
multicellular (exception: yeast)
heterotrophic
29
New cards
plantae
eukaryotic
multicellular
autotrophic
multicellular
autotrophic
30
New cards
animalia
eukaryotic
multicellular
heterotrophic
multicellular
heterotrophic
31
New cards
taxonomy
the classification of animals by characteristics and genetics
32
New cards
binomial nomenclature
aka scientific name - first part: genus (name for family), second part: species (specific)
33
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
that eukaryotic cells resulted from evolution and combination of prokaryotic cells
34
New cards
evidence of endosymbiotic theory
chloroplasts and mitochondria conduct binary fission
similar DNA
similar size
electron transport chain in outer membranes
small like prokaryotes
prokaryotes appeared before chloroplasts and mitochondria through fossils
similar DNA
similar size
electron transport chain in outer membranes
small like prokaryotes
prokaryotes appeared before chloroplasts and mitochondria through fossils
35
New cards
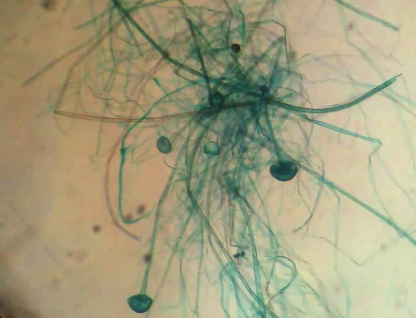
what kingdom?
fungi
spores, no obvious cell/nucleus
spores, no obvious cell/nucleus
36
New cards
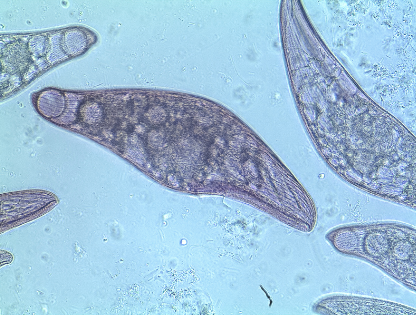
what kingdom?
protista
can be parasites, have mitochondria, have nucleus
can be parasites, have mitochondria, have nucleus
37
New cards
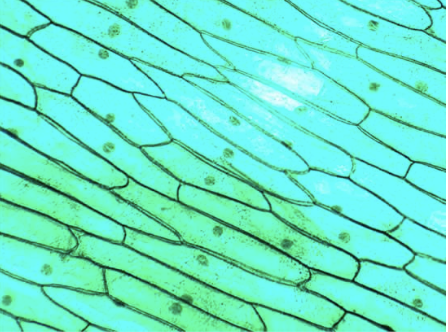
what kingdom?
plantae
green (chlorophyll), chloroplasts, grid-like cell wall, nucleus
green (chlorophyll), chloroplasts, grid-like cell wall, nucleus
38
New cards
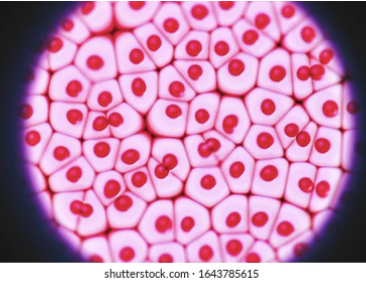
what kingdom?
animalia
red blood cells, no cell wall, round with membrane, obvious nucleus
red blood cells, no cell wall, round with membrane, obvious nucleus
39
New cards
what kingdom?
bacteria
unicellular, small bits, no nucleus
unicellular, small bits, no nucleus
40
New cards
protons
\+1 charge
located in nucleus
located in nucleus
41
New cards
neutron
0 charge
located in nucleus
located in nucleus
42
New cards
electron
\-1 charge
located electron cloud
located electron cloud
43
New cards
covalent bond
form when electrons are shared between atoms
44
New cards
ionic bonds
formed when ions bond together due to charge differences
45
New cards
entities formed after the big bang
matter, energy, space, time
46
New cards
evidence for the big bang
hubble’s law - the universe is constantly expanding from a single point
cosmic microwave background radiation
cosmic microwave background radiation
47
New cards
how the planets formed
gas and dust particles formed an accretion disk which formed into the solar system
48
New cards
polar covalent bond
bonds formed where one atoms is more electronegative than the other, sharing/unevenly distributing the valence electrons
49
New cards
electronegativity
the property where an atom attracts more electrons to itself; forming polar covalent bonds
50
New cards
electronegativity in water
oxygen is partially positive
hydrogen is partially negative
hydrogen is partially negative
51
New cards
cohesion
water sticking to itself
52
New cards
adhesion
water sticking to other substances
53
New cards
hydrophilic
“water loving”, attracts water
54
New cards
hydrophobic
“water loving”, repel water
55
New cards
density in water
ice is less dense than liquid water because extra hydrogen bonds form when it is frozen, increasing the volume
56
New cards
ions in acidic solutions
low PH = high conc. of hydroxide ions \[OH-\]
57
New cards
ions in basic solutions
high PH = high conc. of hydrogen \[H+\] ions
58
New cards
pH range of acids
0-7
59
New cards
pH of basic solutions
7-14
60
New cards
products of mixing strong acid and base
acid-base reaction creates salt and water
61
New cards
pH buffer
special solution that controls the pH of a solution
neutralizes or maintains steady pH level
neutralizes or maintains steady pH level
62
New cards
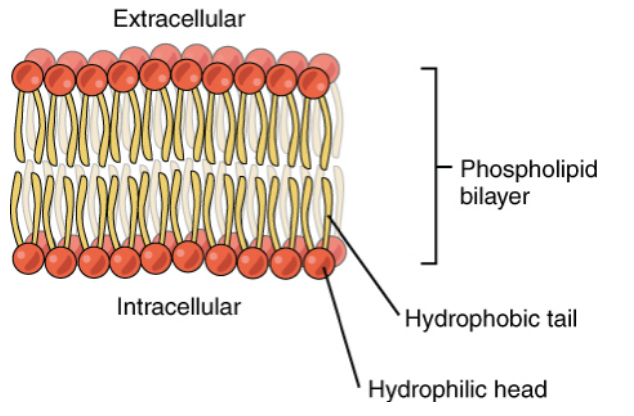
phospholipid bilayer
makes up the cell membrane
hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic head
hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic head
63
New cards
plasma membrane = fluid mosaic
mosaic = mixture of lipids and proteins in the membrane
fluid = its components (phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins) move around laterally
helps maintain its role as a barrier between inside/outside of the cell
fluid = its components (phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins) move around laterally
helps maintain its role as a barrier between inside/outside of the cell
64
New cards
extremophile
organisms that thrive in extreme conditions (weather, climate, pH, environments)
65
New cards
common trait between lipids
fatty, waxy, or oily
insoluble in polar solvents (water)
soluble in organic solvents
insoluble in polar solvents (water)
soluble in organic solvents
66
New cards
monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharide (immediate energy use, eg. glucose)
polymer: disaccharide/polysaccharide (short-term energy storage, eg. glycogen)
polymer: disaccharide/polysaccharide (short-term energy storage, eg. glycogen)
67
New cards
additional use for carbohydrates
cellulose (eg. plant cell walls)
68
New cards
monomer of all nucleic acids
nucleotides
69
New cards
monomer of proteins
amino acids
70
New cards
functions of proteins
repair + build cells and tissue
helps body grow
enzymes - digestion, muscle contraction
messenger (hormones)
provides structure (keratin, collagen)
maintain pH in body
helps body grow
enzymes - digestion, muscle contraction
messenger (hormones)
provides structure (keratin, collagen)
maintain pH in body
71
New cards
order or protein folding structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary (not in all proteins)
72
New cards
primary folding structure
the sequence of amino acids that make up a protein, a polypeptide chain
held with peptide bonds
held with peptide bonds
73
New cards
secondary folding structure
actual “folding” occurs, the sequences of amino acids fold into either a-helix or b-pleated sheet
hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bonds
74
New cards
tertiary folding structure
occurs in the 3d shape of the protein, either hydrophobic or hydrophilic depending on the “r-group”
ionic, disulphide and hydrogen bonds
ionic, disulphide and hydrogen bonds
75
New cards
quaternary folding structure
NOT IN ALL PROTEINS
proteins consisting of multiple polypeptide chains
proteins consisting of multiple polypeptide chains
76
New cards
denaturation
when proteins lose its shape due to either heat, organic compounds, change in pH, or heavy metal ions
77
New cards
benedict’s test
tests for carbs
negative - blue
positive - green → red
negative - blue
positive - green → red
78
New cards
iodine test
test for starch
negative - orange
positive - blue
negative - orange
positive - blue
79
New cards
bromothymol blue test
tests pH
basic - blue
acidic - green → yellow
basic - blue
acidic - green → yellow
80
New cards
concentration gradient
occurs when there are two areas of diff. concentration
81
New cards
diffusion
type of passive transport (no ATP required)
particles will spread out from a higher to lower concentration when there is a concentration gradient
particles will spread out from a higher to lower concentration when there is a concentration gradient
82
New cards
solute
particles being dissolved (salt, sugar)
83
New cards
solvent
solution that particles are being mixed with (water, hydrogen peroxide)
84
New cards
solution
mixture of solute and solvent (salt water)
85
New cards
osmosis
the process of a solvent passing through a semipermeable membrane to balance the solute concentrations on either side of the cell (eg. water)
86
New cards
facilitated diffusion
diffusion occurring the the assistance of carrier proteins if the particles are too large or charged
87
New cards
active transport
typically from low → high conc.
requires ATP energy to occur
requires ATP energy to occur
88
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
where the conc. of a particle is balanced but the particles are still constantly moving
NET movement of 0
NET movement of 0
89
New cards
free water
water molecules not attached to a solute
are able to move through the membrane
high solute conc. = low amt. of free water
are able to move through the membrane
high solute conc. = low amt. of free water
90
New cards
hypertonic (plant cell)
plasmolyzed
water leaves the cell
water leaves the cell
91
New cards
isotonic (plant cell)
flaccid
balanced water conc. inside/outside of the cell
balanced water conc. inside/outside of the cell
92
New cards
hypotonic (plant cell)
turgid (normal - since plants need extra water to survive)
water moves into the cell
water moves into the cell
93
New cards
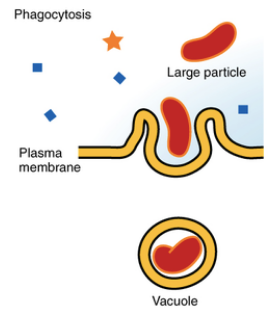
phagocytosis
“cell eating”
a form of endocytosis (bulk transport) where large particles are transported into the cell
the cell membrane engulfs particles from outside
a form of endocytosis (bulk transport) where large particles are transported into the cell
the cell membrane engulfs particles from outside
94
New cards
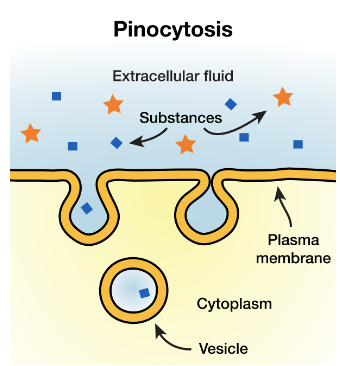
pinocytosis
“cell drinking”
a form of endocytosis where small amounts of fluid are taken into a cell’s cytoplasm into vesicles
a form of endocytosis where small amounts of fluid are taken into a cell’s cytoplasm into vesicles
95
New cards
receptor-mediated endocytosis
where receptor proteins on a cell’s surface capture specific target particles
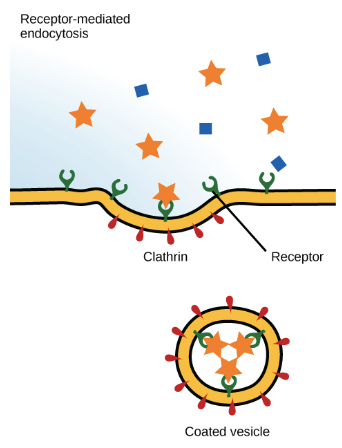
96
New cards
exocytosis
“cell exiting”
where cells move materials from inside to outside of the cell from the vesicle to the membrane
where cells move materials from inside to outside of the cell from the vesicle to the membrane
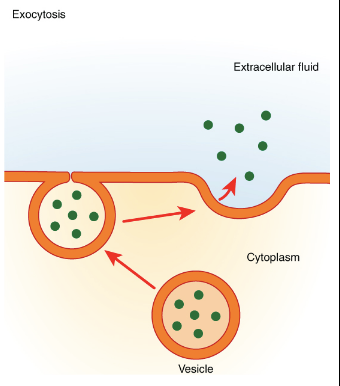
97
New cards
homeostasis
the process of maintaining equilibrium in the body
allows optimal conditions for the body to operate at
allows optimal conditions for the body to operate at
98
New cards
endotherm
“warm blooded”
maintain similar body temp. no matter the temp. of environment
mammals, birds
maintain similar body temp. no matter the temp. of environment
mammals, birds
99
New cards
ectotherm
“cold-blooded”
body temp changes with the environment temp
reptiles
body temp changes with the environment temp
reptiles
100
New cards
endothermic reaction
absorbs heat, cools surroundings