Chapter 5 - Price Controls and Quotas
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ECON:1100 Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are price controls?
they are legal restrictions on how high or low a market price may go
What are two of the main price controls?
price ceilings and price floors
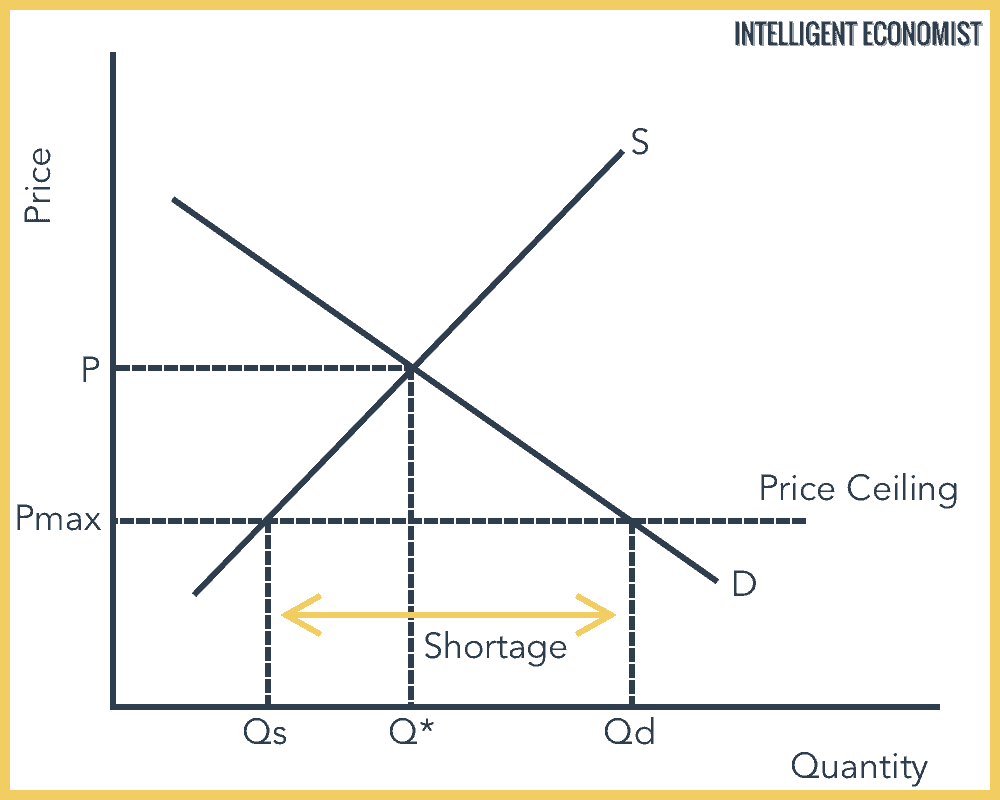
What are price ceilings?
they are the maximum price sellers are allowed to charge
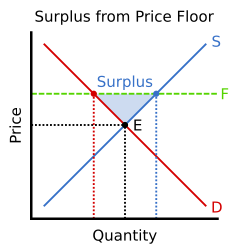
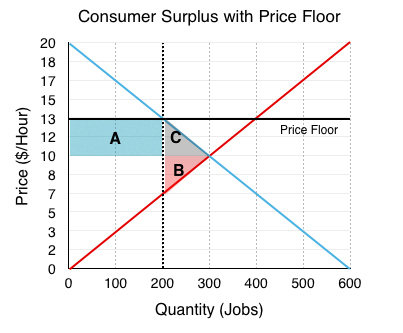
What are price floors?
they are the minimum price buyers are allowed to pay for a good
What do price controls cause?
deadweight loss
What is deadweight loss?
it is the loss in total surplus that happens when the amount transacted below efficient equilibrium quantity is reduced
Where is deadweight loss on a graph, in terms of price controls?
It is the triangle where total surplus would be
Nonbinding
if a price is set above equilibrium it will have no effect
Binding or effective
only price ceilings set below equilibrium will have an effect
What are some predictable side effects of these price controls?
inefficiently low quality
wasted resources
inefficient allocation to customers
black markets
Why is inefficiently low quality a side effect of price controls?
sellers have more consumers than goods at a controlled price and in response there is reduced quality and service
Why are wasted resources a side effect of price controls?
money is expended as well as effort and time to cope with shortages caused by PCs
What are shadow/black markets?
when goods are bought and sold illegal, as a whole they make society worse
Why are there price ceilings?
they benefit some people
when they have been in effect for a while they have an affect on buyers, they have adapted
gov. officials usually do not understand supply and demand analysis
What does controlling quantities mean?
sometimes governments control quantity instead of price
What is an example of a controlling quantity?
quota
What is a quota?
it is a limit on quantity of a goos that can be bought or sold
Quota limit
the total of a good under a quota or quantity control that can be legally transacted
License
the right to supply a good, it is given by the government
The “wedge”
it is the difference between the demand price and the supply price at the quota limit
How does a quota show up on a graph?
it is a vertical line further left than the equilibrium, it creates a wedge between consumer and producer surplus
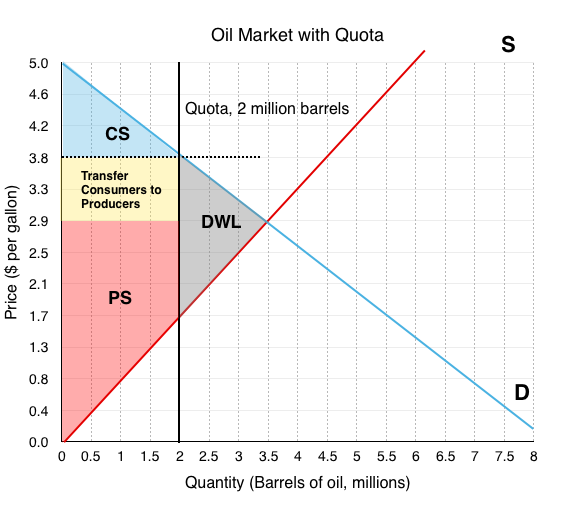
What type of cost is there on society with quantity controls?
deadweight loss
incentive for illegal activities