Module 9 and 10 Chemical Reactions and Moles Diagram | Quizlet
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Subscript
A number in a chemical formula that tells the number of atoms in a molecule or the ratio of elements in a compound
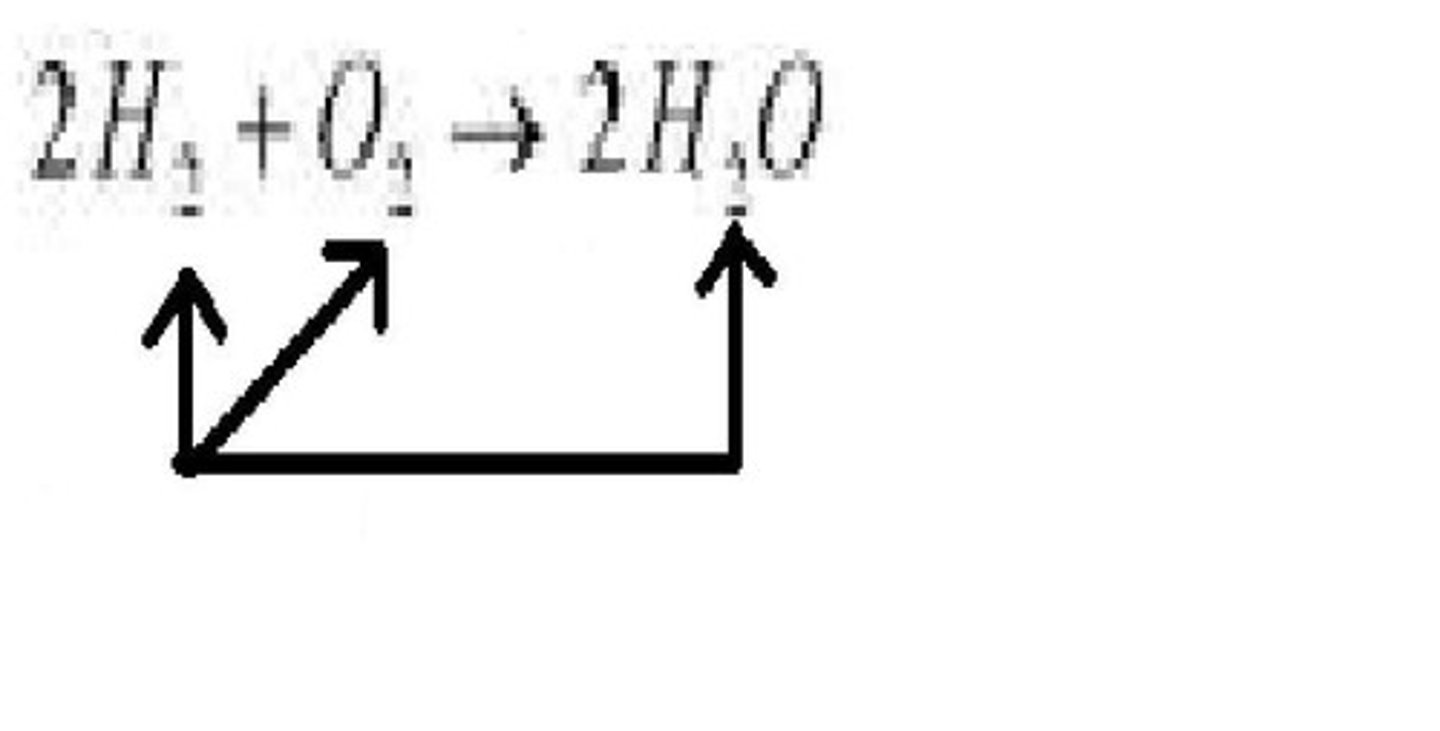
TERM
Coefficient
DEFINITION
A number in front of a chemical formula in an equation that indicates the relative number of moles of reactants and products involved in a reaction.
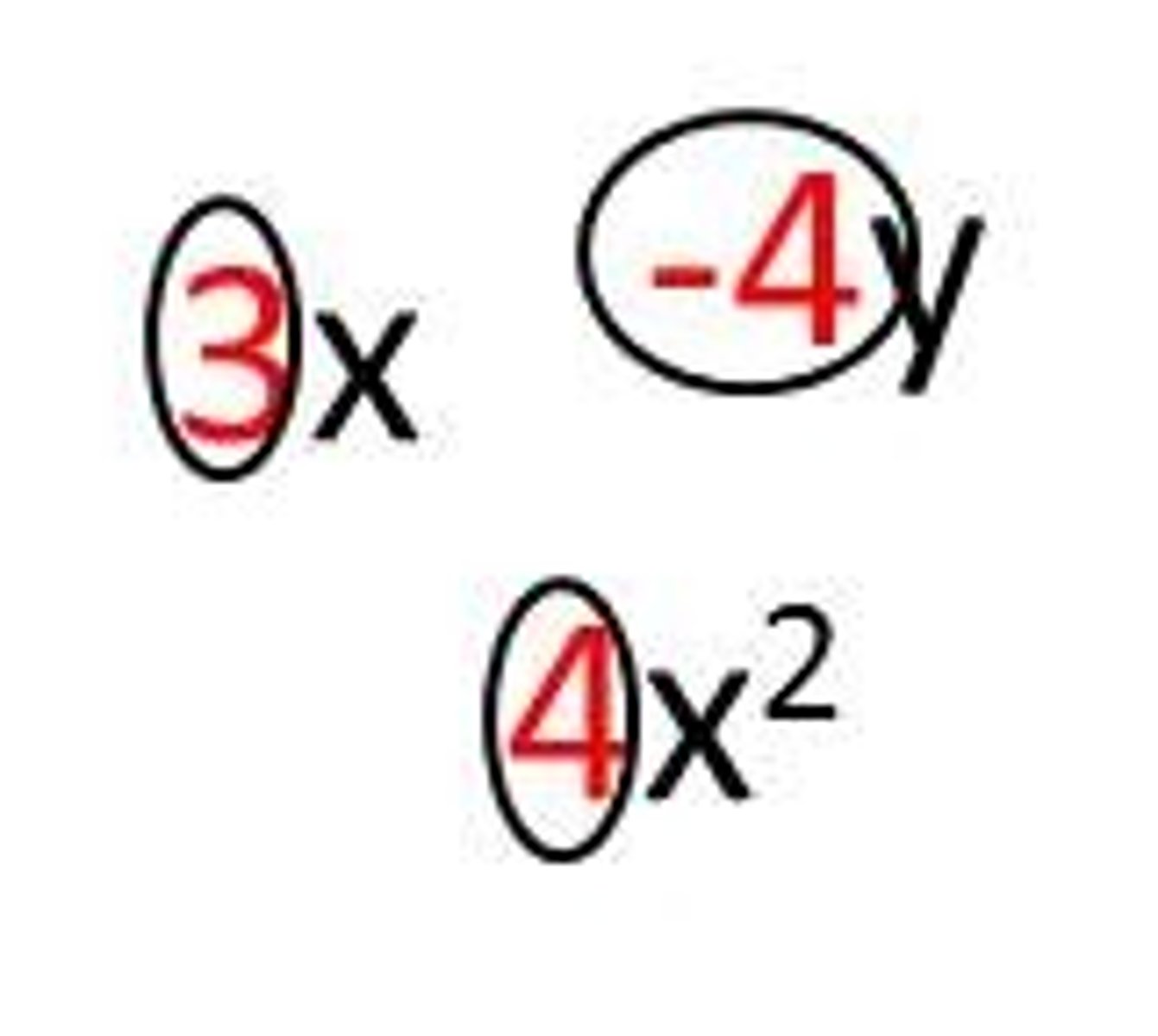
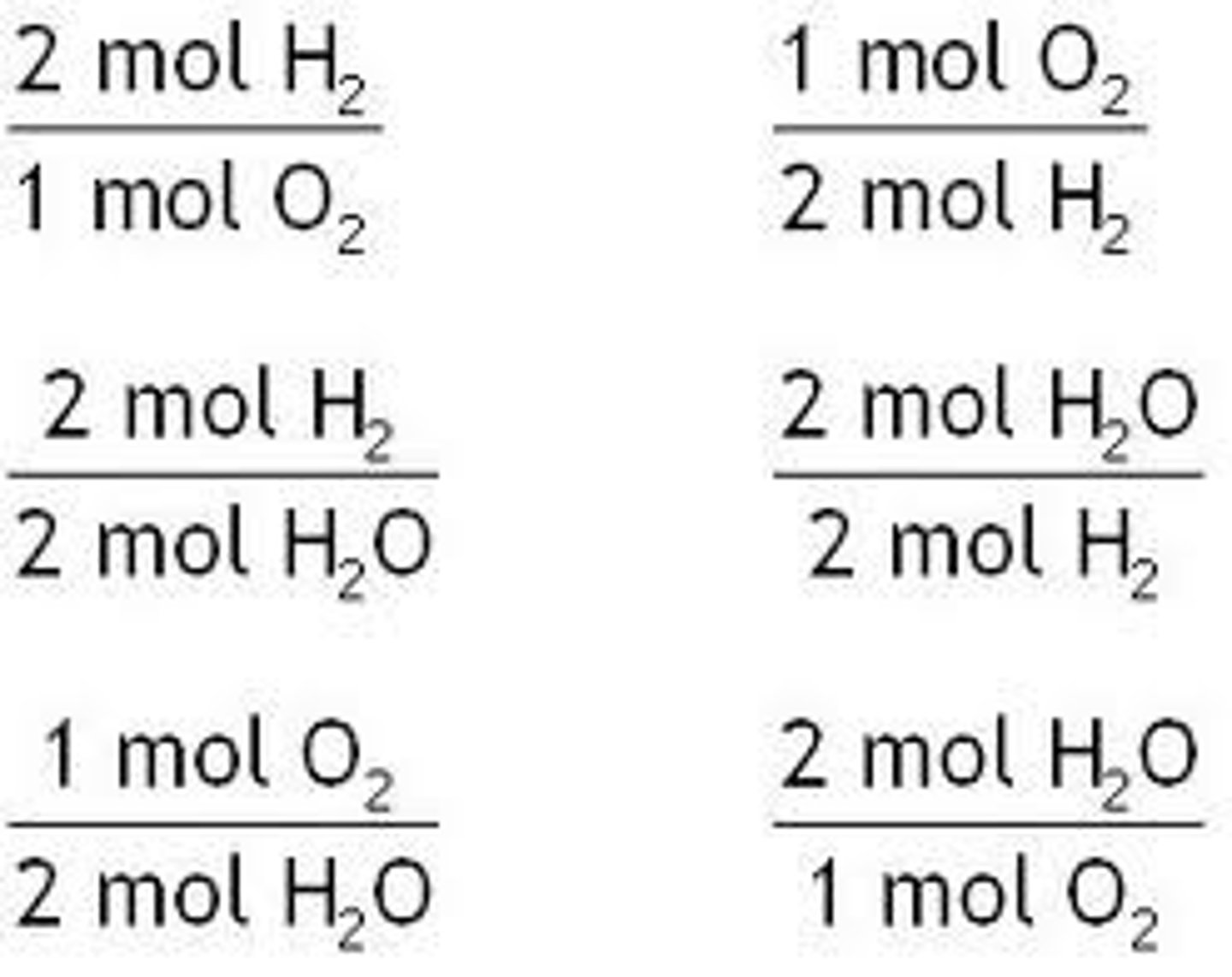
Molar ratio
fraction formed from the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation.
Avogadro's Number
number of representative particles in a mole, 6.02 X 10^23
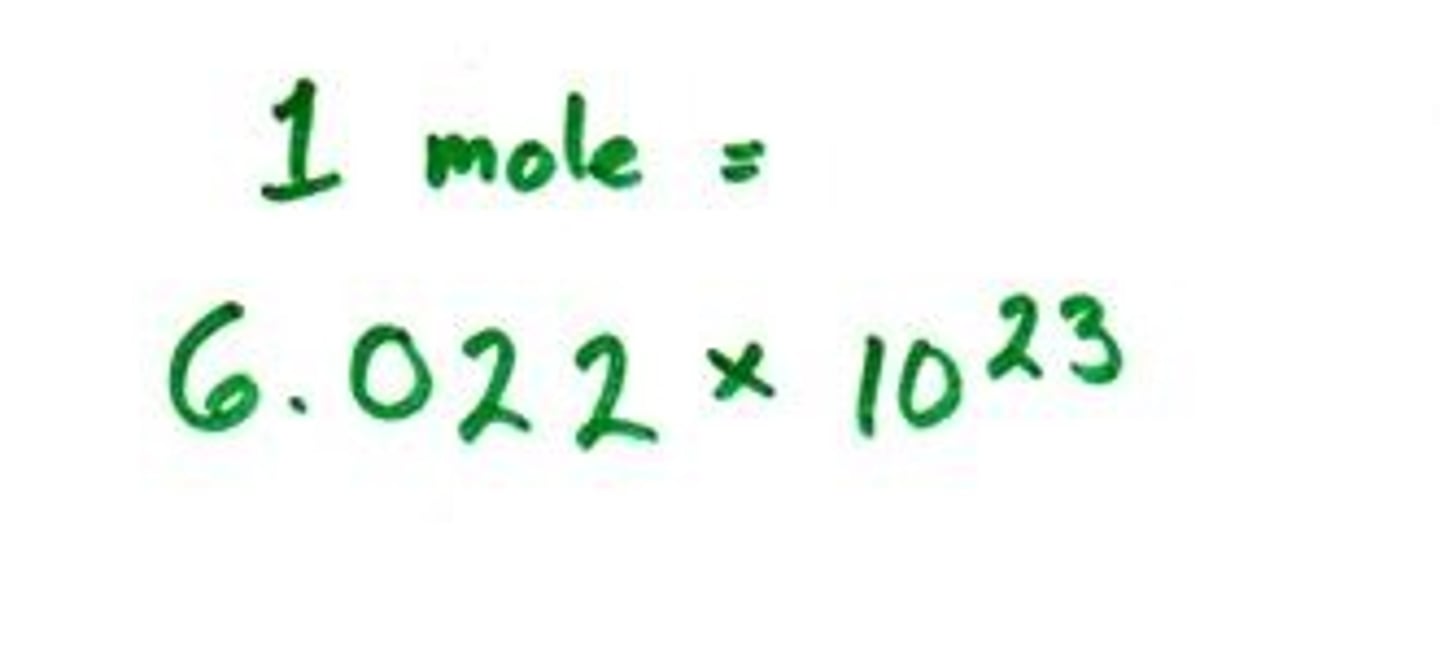
Synthesis
A+B=AB

Decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.
AB = A + B
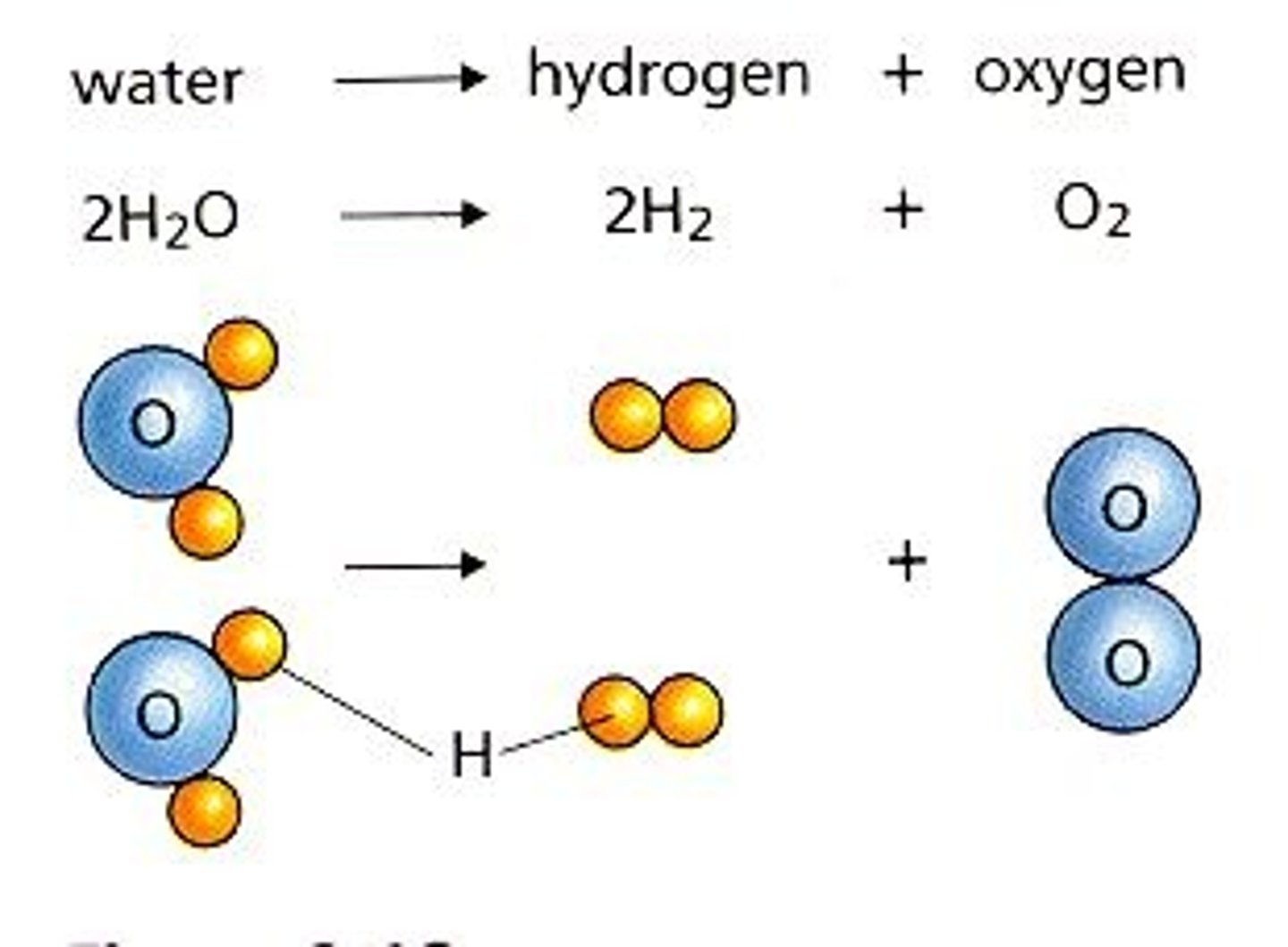
Single Replacement
A + BC --> B + AC
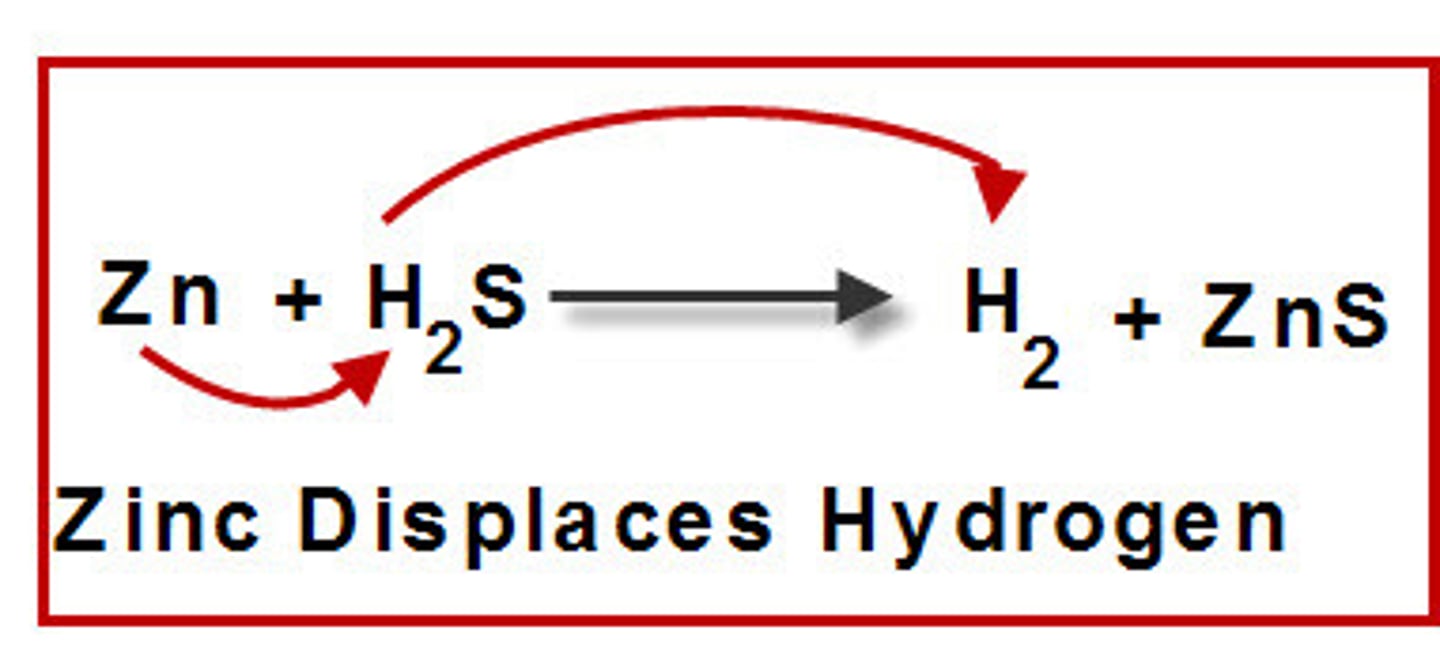
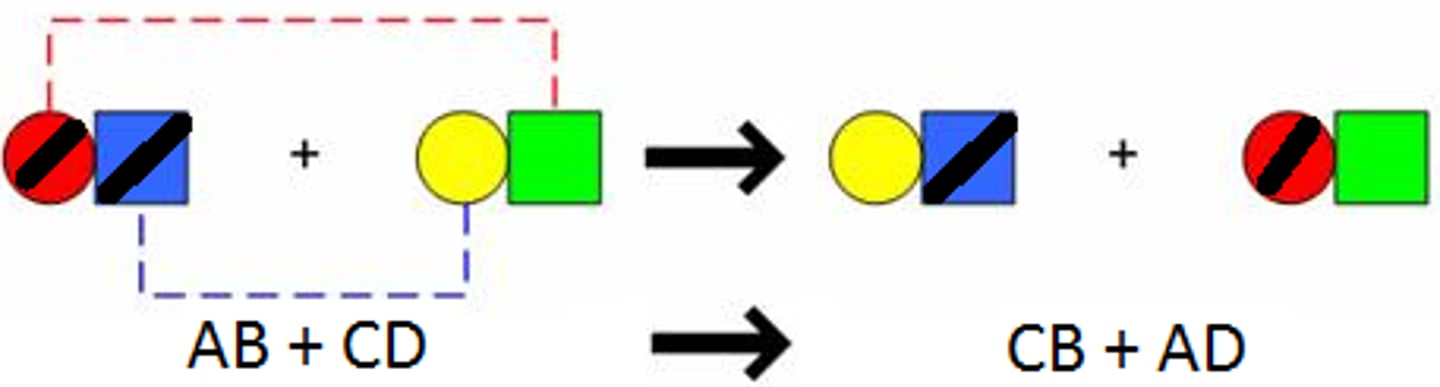
Double Replacement
a chemical reaction where two elements in different compounds trade places
Combustion
Burning. Oxygen gas is one of the reactants and water is one of the products.
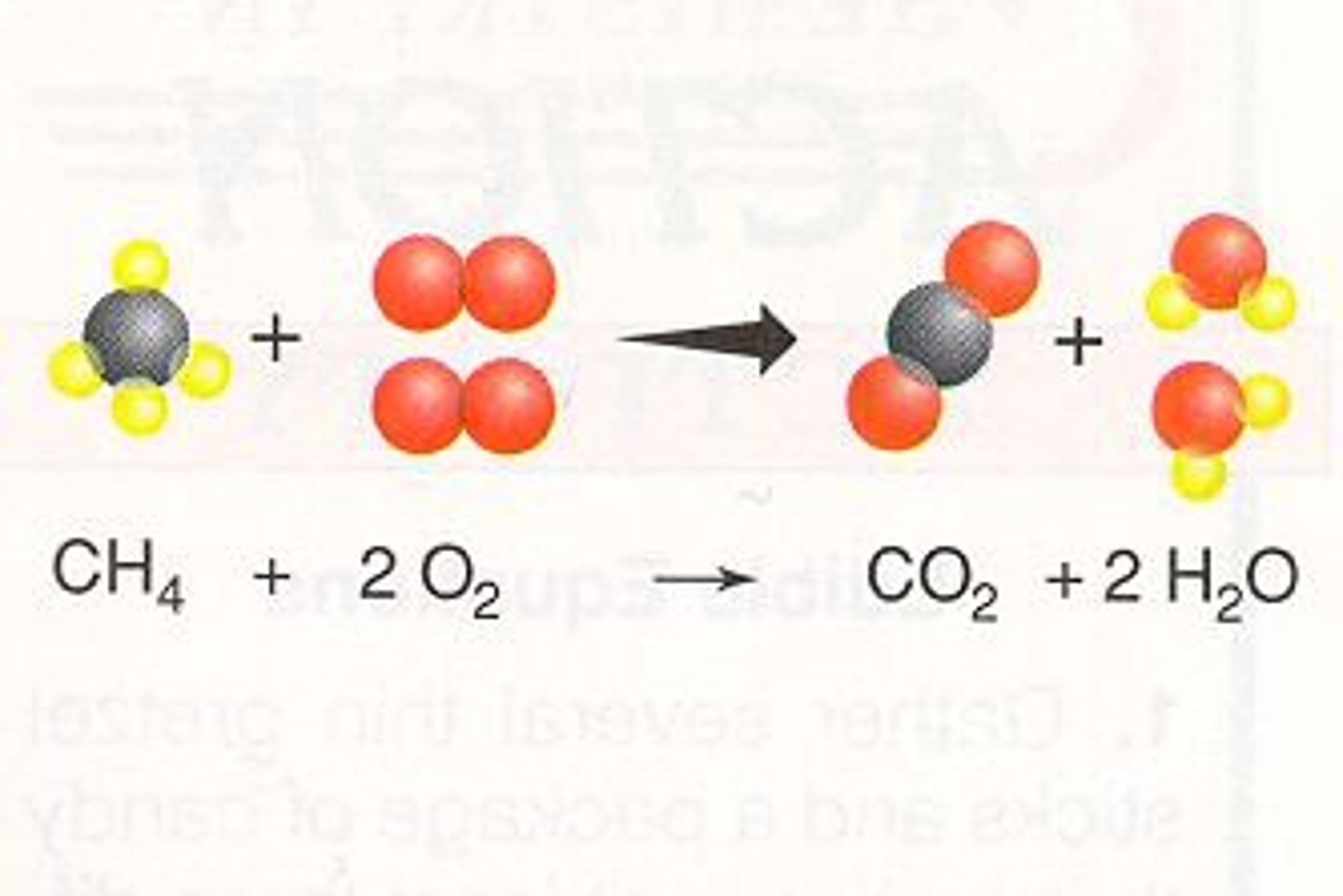
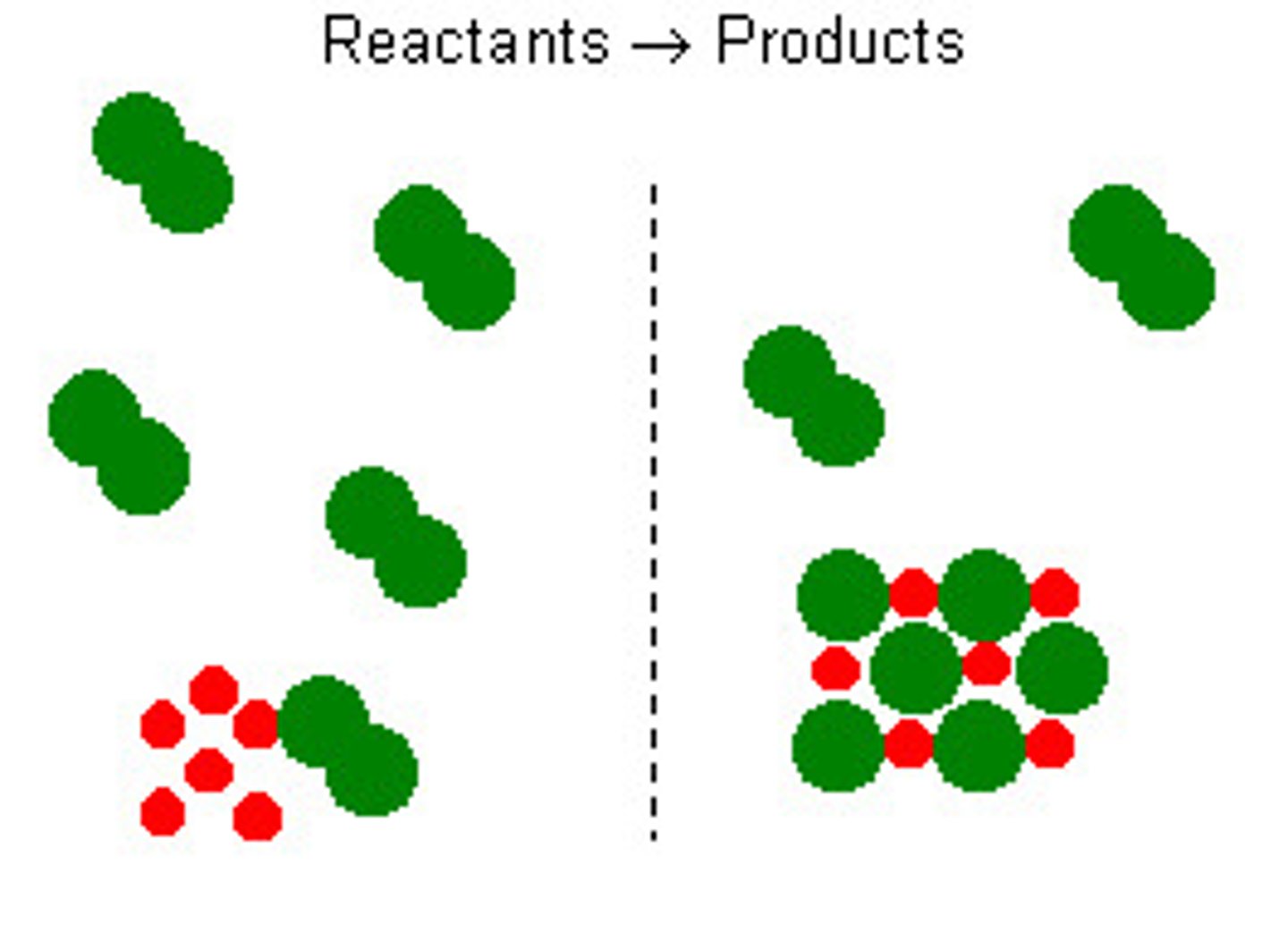
Products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction. On the right side of a chemical equation.
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction. On the left side of a chemical equation.
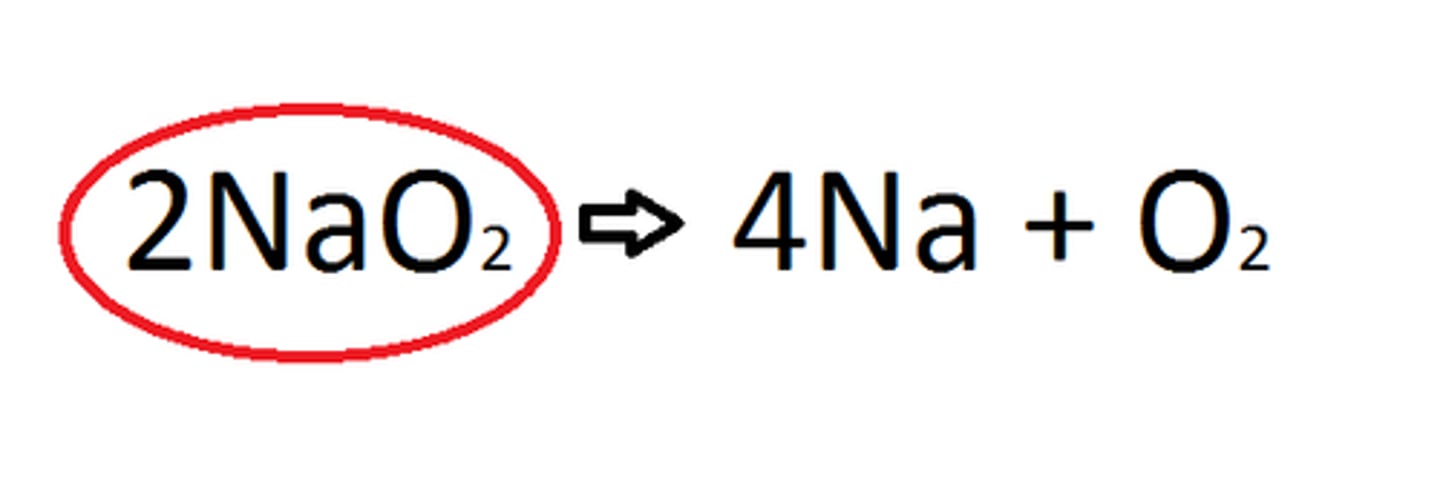
TERM
Stoichiometry
DEFINITION
(chemistry) expresses the quantitative relationship between reactants and products.

Excess reactant
The substance that is not used up completely in a reaction
Molar Mass
The mass of 1 mole of any substance. Must use the periodic chart to obtain this value by adding up the mass of all the atoms in the substance.
units: g/mol

Balanced Chemical Equation
Allows one to determine the mole ratio of any two substances in the reaction
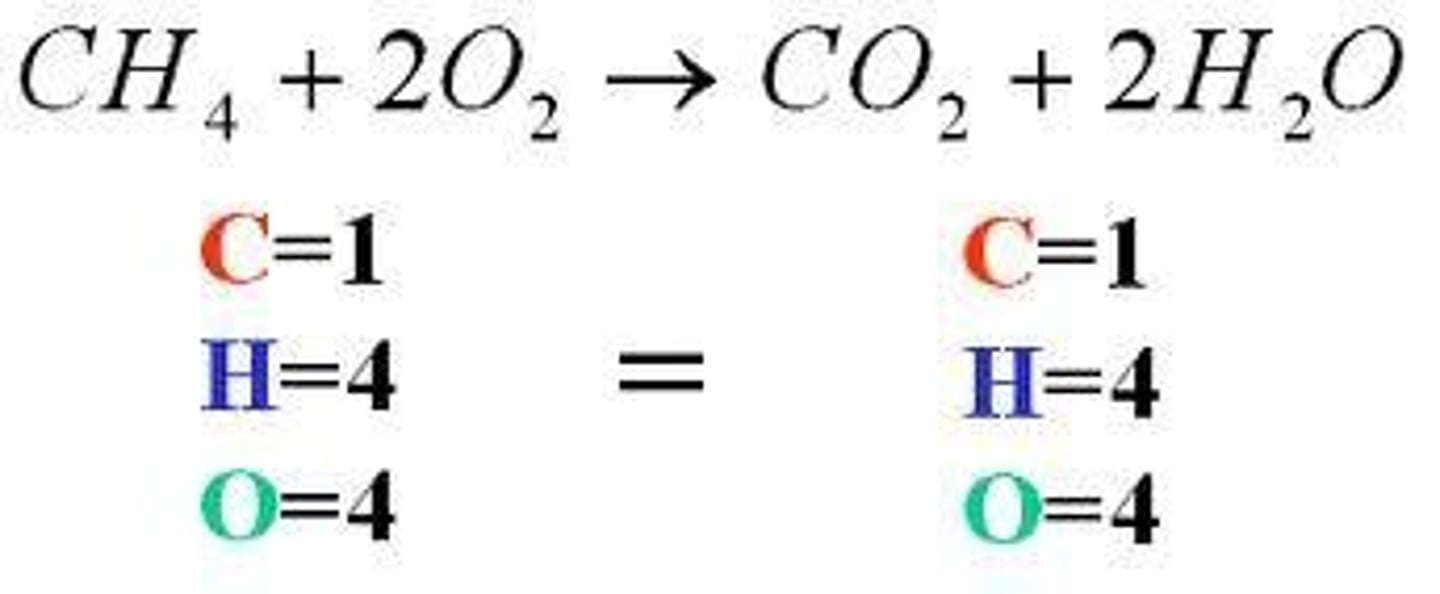
mass of one mole of a diatomic element (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine)
twice the mass listed for that element on the periodic chart
mass of one mole of a compound
the sum of the masses listed on the periodic chart of the atoms contained in it
Molecular Formula
A formula that gives the number of each atom that is present in any given compound.
Mole
the SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
6.022 x 10²³
Gram
Roughly the mass of 1 mole of Hydrogen atoms
Diatomic elements
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine
Polyatomic Ion
Covalent molecule with either has extra electrons or fewer electrons than the sum of the electrons in the neutral atom
phosphate
PO₄³−
carbonate
CO₃ ²⁻
Sulfate Ion
SO₄ ²⁻
Hydrogen phosphate ion
HPO₄²−
Dihydrogen phosphate ion
H₂PO₄¹−
Rules for naming molecular compounds with two elements
-Use the greek prefixes for the number of atoms in the subscripts plus the name of the element
-If there is only one atom for the first element drop the mono
mono
1 atom (prefix for covalent naming)
di
2 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
tri
three atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
tetra
4 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
penta
5 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
hexa
6 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
hepta
7 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
octa
8 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
nona
9 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
deca
10 atoms (prefix for covalent naming)
Naming compounds with polyatomic ions
Name of the metallic element + name of polyatomic ion
How to find the subscripts for metals and polyatomic ions in a salt
-Look up the charge of the polyatomic ion
-Get the charge of the metal from the name or the periodic table
-Use the criss-cross method.
-charges * sub must add up to zero
Hydrogen sulfate
HSO₄ ¹⁻
Hydrogen carbonate
HCO₃ ¹⁻
Bicarbonate
HCO₃ ¹⁻
Mass of 1 mole of an element in grams
Same number as the average mass of atom (decimal number on the periodic table)
Diatomic Elements
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine
limiting reactant
The reactant that is used up first in a reaction
The reactant that makes the least amount of product
excess reactant
the substance that is not used up completely in a reaction
the reactant that makes the most amount of a product
amount of product of a reaction
determined by the limiting reactant
Incomplete combustion
When a fuel burns in insufficient oxygen, producing carbon monoxide as a toxic product.
Complete combustion reaction
A reaction in which enough oxygen is supplied when burning a carbon-containing fuel to produce carbon dioxide and water
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
pollutants that are produced when carbon-containing fuels are combusted with excess oxygen at high temperature
catalytic converter
A device that uses catalysts to convert pollutant molecules in vehicle exhaust into less harmful molecules
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Fuel Contaminants
nitrogen and sulfur containing compounds that are found in carbon-containing fuels that created nitrogen oxides or sulfur oxides during combustion
sulfur oxides
(SOx) Pollutants primarily created by combustion of coal. Primary and secondary effects include acid deposition, respiratory irritation, plant damage. Reduction methods include: scrubbers, burn low sulfur fuel.
stoichiometric balance
when a reaction is set up using the same molar ratios found in the chemical equation.
Molar Volume
the volume occupied by 1 mole of a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP); 22.4 L