IB biology: topic 2: molecular biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:30 PM on 9/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
what are the four major organic molecules?
proteins, fats, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
2
New cards
what is the monomer of protein?
amino acid
3
New cards
what are the monomers of fat? (2)
fatty acids and glycerol
4
New cards
what are the monomers of carbohydrates? (2)
glucose and ribose (and more)
5
New cards
what is the monomer of nucleic acid?
nucleotides
6
New cards
what do functional groups do?
give organic compounds their different properties
7
New cards
what is the functional group of hydroxyl?
OH-
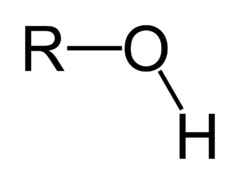
8
New cards
what is the functional group of methyl?
CH₃
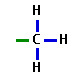
9
New cards
what is the functional group of carbonyl?
C=O
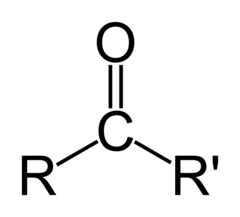
10
New cards
what is the functional group of carboxyl?
COOH
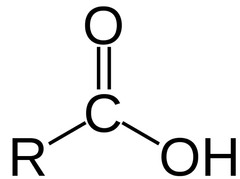
11
New cards
what is the functional group of amino?
NH₂
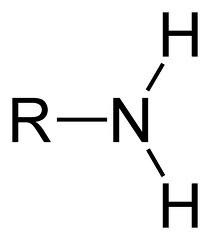
12
New cards
what is metabolidm?
the sum total of reactions within our cells
13
New cards
what is anabolism?
syntehsis of complex molecules (macromolecules) from simpler molecules (monomers) by condensation reaction
14
New cards
what is catabolism?
the break down of complex molecules (macromolecules) into simpler molecules (monoers) by hydrolysis
15
New cards
who was Friedrich Wohler?
the first person to artificially synthesise urea
16
New cards
what was Vitalism?
the belief that all organic compounds could only be formed by the presence of the Vital Principle (a mystic life force)
17
New cards
what was used as evidence to disprove Vitalism?
Friedrich Wohler's artificial synthesis of urea
18
New cards
what did disproving Vitalism tell us about life?
that it was just a series of chemical reactions
19
New cards
what is a key example of a condensation reaction?
peptide bond formation
20
New cards
what is a condensation reaction?
two molecules are joined together by a covalent bond with the loss of water
21
New cards
describe the formation of a peptide bond between amino acids
the covalent bond between the carboxyl end of one amino acid molecule is joined together with the amino acid end of another, many amino acids join together to form a polypeptide
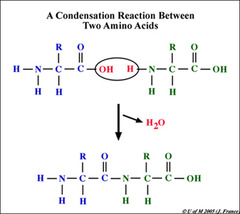
22
New cards
what is hydrolysis?
the addition of water to break down a large molecule into smaller ones
23
New cards
what is an example of a hydrolysis reaction?
a polypeptide is broken down into amino acids/dipeptides
24
New cards
what is delta?
a little bit

25
New cards
in water, what is delta positive?
hydrogen
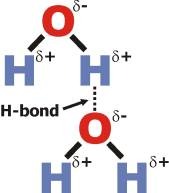
26
New cards
in water, what is delta negative?
oxygen
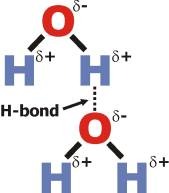
27
New cards
what is cohesion?
attraction between molecules of the same substance (water)
28
New cards
what is adhesion?
an attraction between molecules of different substances (water + other)