SCIENCE - Energy
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SUMMARY OF LIGHT, ENERGY & SOUND.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Definition Of Energy
Energy is the ability to do work or make things change. It is used to create light, heat, or to power machines.
Units for energy
Joules or kilojoules.
What do we call the two main categories that energy can be classified under?
Potential energy and kinetic energy.
Examples of energy transformation
The chemical energy in food gives us kinetic energy.
Plants convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
Chemical energy stored in batteries is transformed into electrical energy when used to power devices.
In a car engine, chemical energy from fuel is transformed into mechanical energy to move the vehicle.
Electrical energy is transformed into thermal energy (heat) to toast bread.
(Note: your answer does not have to be one of these examples, if you can please make up your own)
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
Two things that can affect the amount of gravitational potential energy an object has.
Height & Mass. The higher and larger the mass of an object, the greater the gravitational potential energy it is
How is heat transferred? Define each type of heat transfer and give an example.
Conduction, Convection & Radiation
Define & give eg of: Conduction
Conduction is the process of heat transfer through direct contact
Eg. When you touch a hot pan, heat moves from the pan to your hand.
Define & give eg of: Convection
Convection is how heat moves through fluids (liquids or gases) by the fluid's movement.
Examples:
- Boiling water—hot water rises, and cooler water sinks, making a circular motion.
- Air conditioners use fans to circulate cool air, promoting heat transfer and cooling a room.
Define & give eg of: Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of energy in the form of waves/particles through space (heat moves through space in waves)
Example: Feeling warmth from the sun on your skin, even though you’re not touching it.
Energy that is stored within an object is called _________ energy.
POTENTIAL
Energy in moving objects is called _______ energy.
KINETIC
Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands have _______ _________ energy.
ELASTIC POTENTIAL
The energy stored in the centre of atoms is called _______ energy.
NUCLEAR
The movement of electrons is called __________ energy.
ELECTRICAL
Wind is an example of _______ energy.
KINETIC
The energy in petroleum and food is called ________ energy.
CHEMICAL
The energy an object possess depends on its location in the air is called _____________ _________ energy.
GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL
The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the ___ __ ____________ of energy.
LAW OF CONSERVATION
The difference between energy transfer and energy transformation.
The movement of energy from one object or system to another. Eg. heat moving from a hot object to a cooler one.
The process of changing energy from one form to another. Eg. chemical energy turns into electrical energy in a battery.
Chemical energy is a form of _________ energy.
POTENTIAL
Why is chemical energy considered a form of potential energy?
It can be converted into other forms of energy
Types of potential energy
Gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and chemical potential energy.
FLOW DIAGRAM EXAMPLE (CLICK TO SEE)

Sound energy is a form of _______ energy.
KINETIC
Why is sound energy considered a form of kinetic energy?
Because there is particle motion
Forms of kinetic energy.
Thermal energy, sound energy, electrical energy and mechanical energy. (only memorise 3)
A light bulb transforms 200J of electrical energy into 140J of light and 60J of heat. Calculate the energy efficient of the light blub.
140/200×100
=70%
Potential Energy is…?
STORED ENERGY
Kinetic Energy is…?
THE ENERGY OF A MOVING OBJECT
Sound wave definition.
A sound wave is a vibration that travels through a medium (like air or water) and can be heard when it reaches our ears.
Distinguish between the two types of waves.
LONGITUDINAL WAVES: Waves that move parallel to travel. Eg. Light waves.
TRANSVERSE WAVES: Waves that move perpendicular. Eg. Sound waves.
What is the difference between a compression and a rarefaction?
COMPRESSION: Close
RAREFACTION: Far apart

Explain why sound cannot travel through space.
Sound cannot travel through space because it needs a medium (like air or water) to propagate, and space is a vacuum with very few particles.
What is loudness? What is it measured in?
Loudness is how strong or intense a sound feels to us. It is usually measured in DECIBELS.
What is amplitude?
How far a wave moves from its rest position.

what is a wavelength?
The distance between one wave crest to the next.
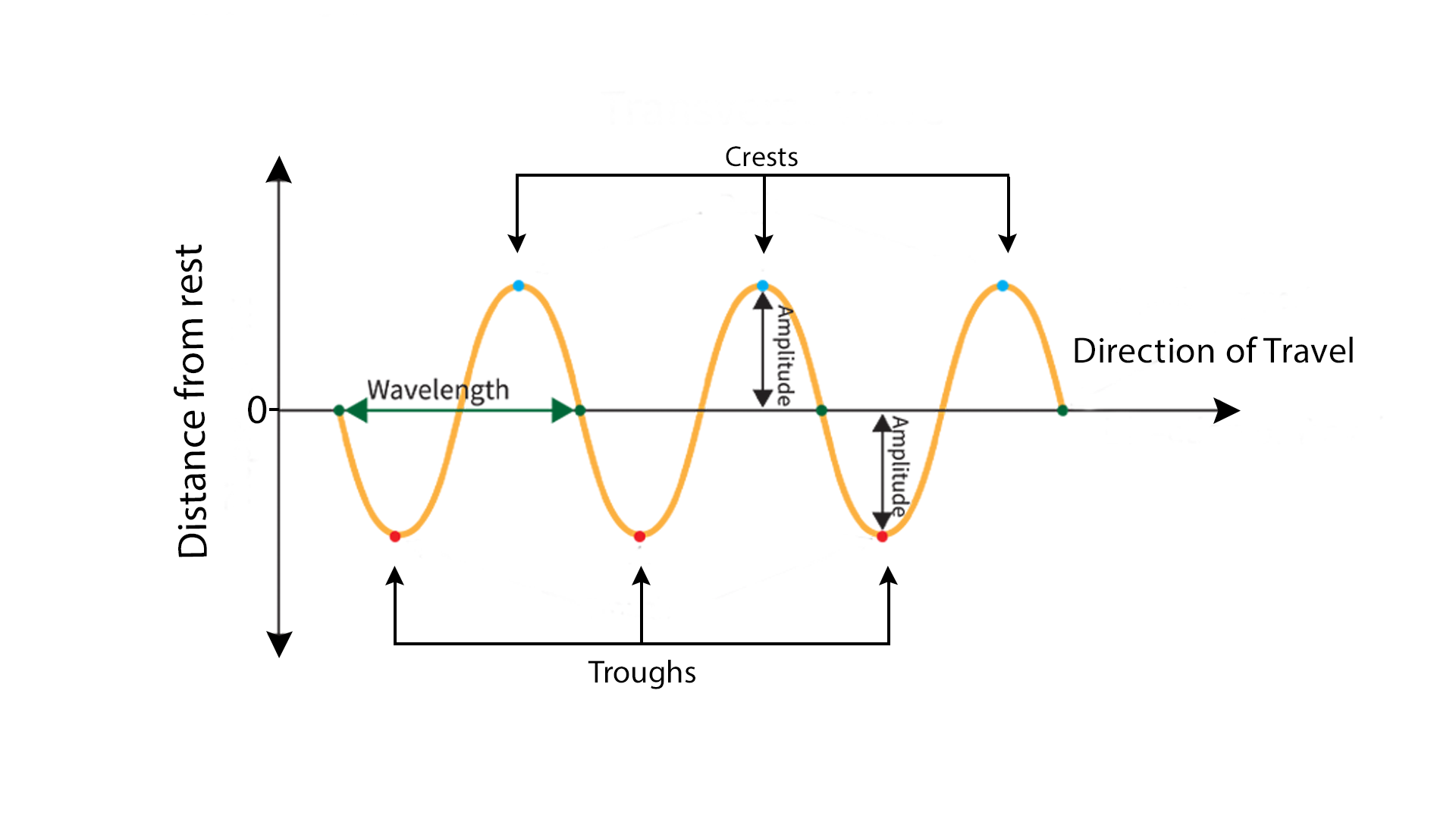
what is frequency?
The number of waves that pass a point in one second, measured in hertz (Hz).

An object which is unable to emit its own light is said to be:
A NON-LUMINOUS OBJECT
An object which can emit its own light is said to be:
A LUMINOUS OBJECT
Reflection of Light
Bouncing of light rays off a surface.
Refraction of Light
Bending of light as it passes between different media.
What is the difference between reflection and refraction of light?
REFLECTION: Bouncing of light rays off a surface.
REFRACTION: Bending of light as it passes between different media.
The process used to produce colours on the visible light spectrum is called:
DISPERSION
The speed of light is:
300,000,000 m/s OR 3×10⁸ m/s
m/s: meters per second
Law of Reflection
When a light ray strikes a reflective surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
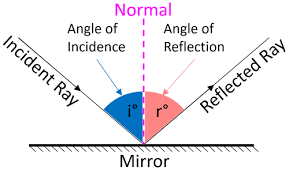
Incident Ray
The incoming ray of light before it hits a surface.
Reflected Ray
The ray of light that bounces off a surface.
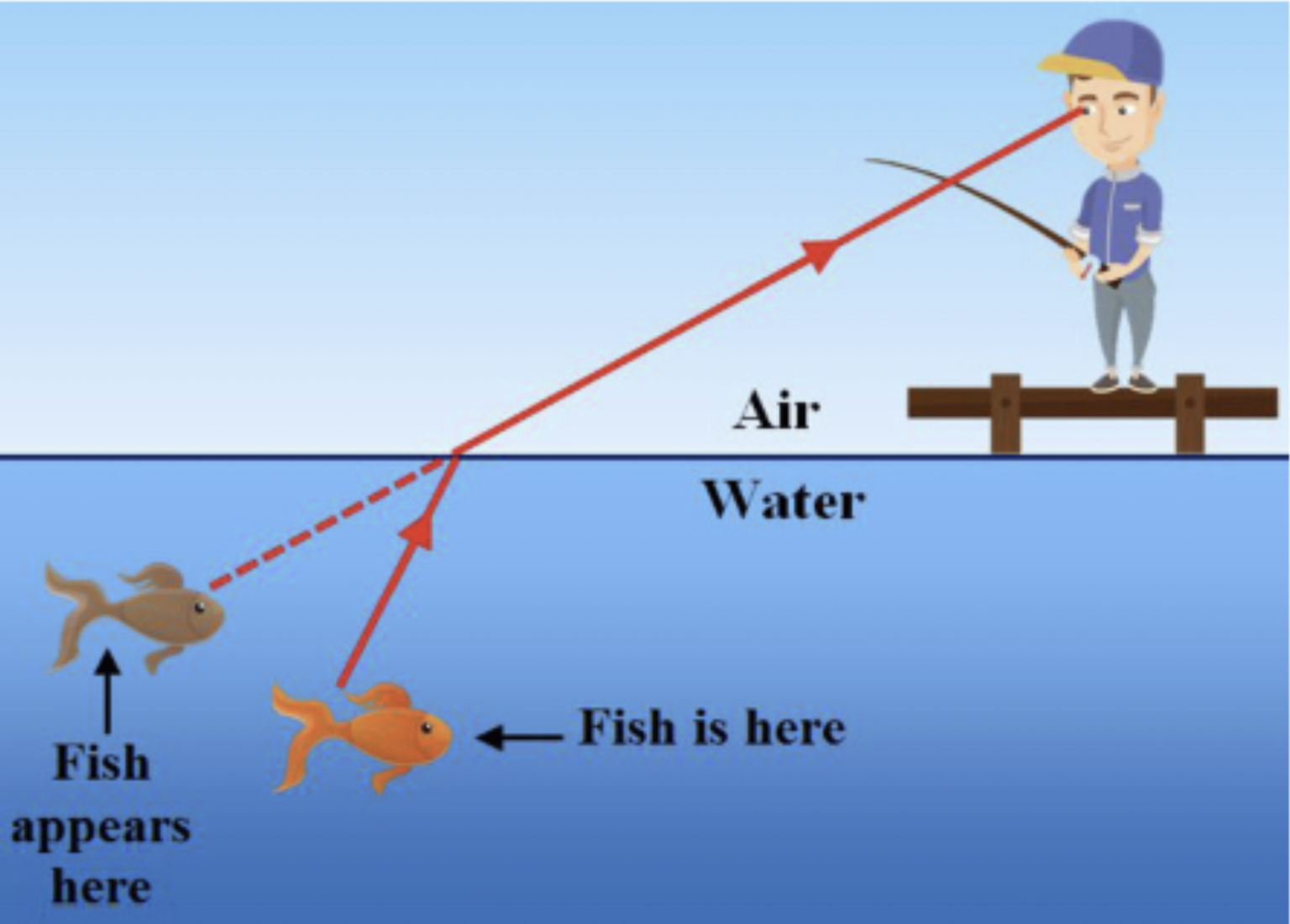
In the picture, the person sees the image of the fish in a different location than the actual fish. This happens because:
Refraction of Light: Light bends when it passes a denser medium.
Which medium does a light wave travel the fastest in?
A VACUUM.
Does light slow down or speed up when it passes from the air into the cornea? How do you know this?
Light travels fastest in a vacuum and slower in denser mediums, so when it enters a denser medium like the cornea, it slows down.
Lens
Focus the light onto a point on the retina.