Biological Bases and Behaviour
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Preconscious
anything that could potentially be brought into the conscious mind.
Nonconscious
any mental process that goes on in which the individual is unaware and which he/she cannot become aware of, even with introspection
Unconscious
feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that are outside of our conscious awareness.
contents that are unacceptable or unpleasant, such as feelings of pain, anxiety, or conflict.
Dual Proccessing
process info on conscious and unconscious level at same time
Hypothalamus
regulate body temp, blood pressure, pulse, blood sugar levels, hormone levels
Circadian Rhythm
regulate sleep wake cycle
influences when wake up/fall asleep
responds to light and darkness
Sleep
Complex combo of states of consciousness
Hypnagogic state
relaxed, fail to respond to outside stimuli
first stage of sleep: Non-Rem-1
REM sleep
90 mins after falling asleep
NIghtmares
frightning dreams occuring during REM sleep
Lucid dreaming
aware of and directs one dreams
Insomnia
inability to fall asleep/stay asleep
Narcolepsy
awake person suddenly and uncontrollably falls asleep
directly into REM
Sleep apnea
temporary cessations of breathing that wake the sufferer up
Nigh Terrors
frequent childhood sleep distruptions
deepest part of NREM-3
Sleepwalking
aka somnambulism
NREM-3
Trips out of bed completing complex activities
Hypnosis
altered state of reality
Focused attention
Heightened suggestibility
Used for stress, pain, habits
Dissociation theory
a mental process where a person disconnects from their thoughts, feelings, memories or sense of identity
Meditation
focus concentration away from thoughts/feelings to create calmness
Pyschoactive drugs
chemicals that pass thru blood brain barrier to alter perception, thinking, behaviour, mood
Freud analysis of dreams
uncover the unconscious desire and fears
Manifest content
story line of dream
Latent content
underlying meaning
Activation synthesis theory
Dreams are the brain’s way of making sense of random neural activity during sleep
Behavioural geneticists
Study the role of genes and environment
Look at the causes of individual differences
Identical twins
2 individual who share the same gene/heredity
develop from same fertilized egg/zygote
monozygotic
Fraternal twins
siblings sharing half of same genes
develop from 2 fertilized eggs/zygote
dizygotic
Heritability
proportion of variation among individuals in a population due to genetics
Gene
DNA segment of chromosome determining a trait
Chromosome
Carry info stored in genes to new cells
humans have 46
egg and sperm have 23
Turner Syndrome
chromosomal disorder in females where one X chromosome is missing or incomplete (XO)
Klinefelters syndrome
chromosomal disorder in males where they have an extra X chromosome (XXY)
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Caused by three copies of chromosome 21
Genotype
An individual’s genetic makeup for a trait.
Phenotype
The physical expression of genes.
Dominant vs. Recessive Genes
When genes differ, the dominant gene is expressed, and the recessive gene is hidden.
Tay-Sachs Syndrome
genetic disorder where the body can’t break down fat in the brain, causing nerve damage.
Albinism
Caused by failure to produce pigment (melanin)
abnormal nerve pathways to brain
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
genetic disorder where the body cannot break down phenylalanine
leading to brain damage unless treated with a special low-phenylalanine diet early in life
Huntingtons disease
dominant gene disorder causing nervous system degeneration in adulthood.
Endocrine system
secrete chemical messengers (hormones) into blood
travel to target organs to bind to specific receptors
Endocrine glands
H – Hypothalamus
P – Pituitary
T – Thyroid
P – Parathyroid
A – Adrenal
P – Pancreas
G – Gonads (testes/ovaries)
Pineal Gland
Releases melatonin → regulates sleep and circadian rhythm
associated w/ seasonal affective disorder
Hypothalamus
Controls the endocrine system by signaling the pituitary gland to release hormones.
Thyroid gland
produces thyroxine which maintains and stimulates metabolic activities
Adrenal glands
atop kidneys
Pancreas
secrets the hormones insulin and glucagon, regulating. blood sugar
Ovaries/Testes
produce hormones necessary for reproduction
Pituitary gland
Known as the “master gland”
Releases hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction, under the direction of the hypothalamus.
Endocrine system
secrete chemical messengers (hormones) into blood
travel to target organs to bind to specific receptors
Endocrine glands
H – Hypothalamus
P – Pituitary
T – Thyroid
P – Parathyroid
A – Adrenal
P – Pancreas
G – Gonads (testes/ovaries)
Pineal Gland
produce melatonin that helps regulate circadian rhythm
associated w/ seasonal affective disorder
Hypothalamus
Controls the endocrine system by signaling the pituitary gland to release hormones.
Thyroid gland
produces thyroxine which maintains and stimulates metabolic activities
Adrenal glands
atop kidneys
Pancreas
secrets the hormones insulin and glucagon, regulating. blood sugar
Ovaries/Testes
produce hormones necessary for reproduction
Pituitary gland
Known as the “master gland”
Releases hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction, under the direction of the hypothalamus.
Glial Cells
Guide growth of neurons
provide nutrition and get rid of waste
form insulation
Cell Body/Soma/Cyton
contains cytoplasm and nucleus
Processes information
Dendrites
receives info
neurogenesis
growth of new neurons
Glutamate
major excitatory neurotransmitter
information processing, especially memory formation in hippocampus
Endorphins
brains painkillers
GABA inhibits the firing of these neurons
Norepinephinre
attentiveness, sleeping, dreaming, and learnin
Agonists
bind to receptor site to produce the effect of neurotransmitter
antagonists
block receptor site inhibiting the effect of neurotransmitter
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain,
responsible for higher-order thinking, reasoning, perception, and voluntary movements.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of the cerebrum
divided into lobes
controls thinking, planning, sensory processing, and voluntary movement.
Frontal Lobe
Controls decision-making, problem-solving, planning, personality, and voluntary movement (contains motor cortex)
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information like touch, temperature, and pain (contains somatosensory cortex).
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for visual processing.
Temporal Lobe
Processes auditory information and is involved in memory and language.
Cerebellum
controls posture, equilibrium, and movement
Thalamus
directs incoming sensory signals to the correct brain areas (except smell).
Hypothalamus
Regulates hunger, thirst, body temperature, and hormones; links nervous and endocrine systems.
Pituitary Gland
“Master gland” of the endocrine system
controls hormone release.
Amygdala
Controls emotions, especially fear and aggression.
Hippocampus
Enables formation of new long term memories
Corpus Callosum
Connects the two hemispheres of the brain, allowing communication between them.
Medulla
Part of brainstem controlling heartbeat, breathing, and reflexes
Pons
Definition: Part of brainstem that helps coordinate movement and sleep/wake cycles
EEG (Electroencepgalogram)
Measures waves of electrical activity (brain waves) produced by neurons firing on the scalp
Where and when brain activity occurs
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
Shows brain activity by detecting where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a task.
Colored
fMRI (Functional MRI)
Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels.
Shows both structure and function
Magnetic Source Image (MSI)
EEG and MRI data to pinpoint the exact location of brain activity
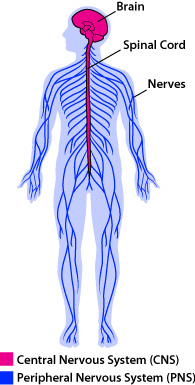
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous system
stimulate skeletal (voluntary muscle)
Autonomic Nervous system
Stimulate smooth (involuntary) and heart muscle
antagonistic sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic stimulation
response that help body deal w/ stressful events
eg dilated pupils, high heart rate, secretion of adrenaline
Parasympathetic stimulation
Calms body following sympathetic stimulation
Eg restore digestive function, returning pupil size
Spinal Cord
protected by membranes (meninges) and spinal column of bony vertebrae
start at base of back → base of skull → brain