UARK BIOANTHRO EXAM 3 Delezene
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
What evolutionary scenario was envisioned by early thinkers that linked brain size, canine size, diet, locomotion, and tool use?
They believed humans have a larger brain therefore they need more calories. Meat has more calories so they have sharper canines. Apes had to use tools to acquire meat.
Which feature was expected to appear first and drive the evolution of the remaining features?
Big brains
Historically speaking, which species of extinct hominin was first discovered in Europe? When?
Neandertals, 1829
How was Homo neandethalensis reconstructed by Marceline Boule?
As caveman like
How did this affect interpretations of Neandertals and potential human ancestors?
Not based on hard science but slanting the data to fit preconceived notions of how early man was supposed to look so they would accept that's where humans came from
Why are so many fossils found in limestone caves in Europe?
Neandertal bones and artifacts were well preserved in these caves
What is taphonomy?
the study of fossils
How did Piltdown fit into the expectations of early evolutionary thinkers?
Large brains like humans, "missing link", intelligence evolved first
Who was involved in the hoax?
Charles Dawson
What anatomical elements were mixed into the Piltdown specimen?
Large human like brain case and an ape mandible ( and large chimp canines)
What's the historical context for the Piltdown "discovery"
Can be an example of scientific racism
What real hominin fossils were known at the time of Piltdown's discovery?
Homo Erectus, Homo neanderthalensis
Where were these other fossils found?
neanderthal: Germany, Erectus: Indonesia
What was the human fossil record like in England at that time?
In England, there were none
What role did Piltdown play in the acceptance of the Taung child as a fossil hominin?
It played on scientific racism as Piltdown had been "discovered" only 4 years before and scientists argued on if it was a young gorilla or a hominin because they preferred our ancestors be found in europe instead of africa
What evolutionary scenario did the Taung child imply that conflicted with the Piltdown remains?
Canine reduction before brain expansion, Bipedalixm before brain expansion, brain size is not the defining feature of hominins, it is either canine size or bipedalism
Which species does the Taung Child belong to?
Australopithecus africanus
Who, where, and when was it found?
Raymond Dart, South Africa, 1925,
What social/political factors played into the acceptance/rejection of the Taung child as a fossil hominin?
Scientific Racism and the scientists at the time wanting a european ancestor to be found instead of in africa
Kenya
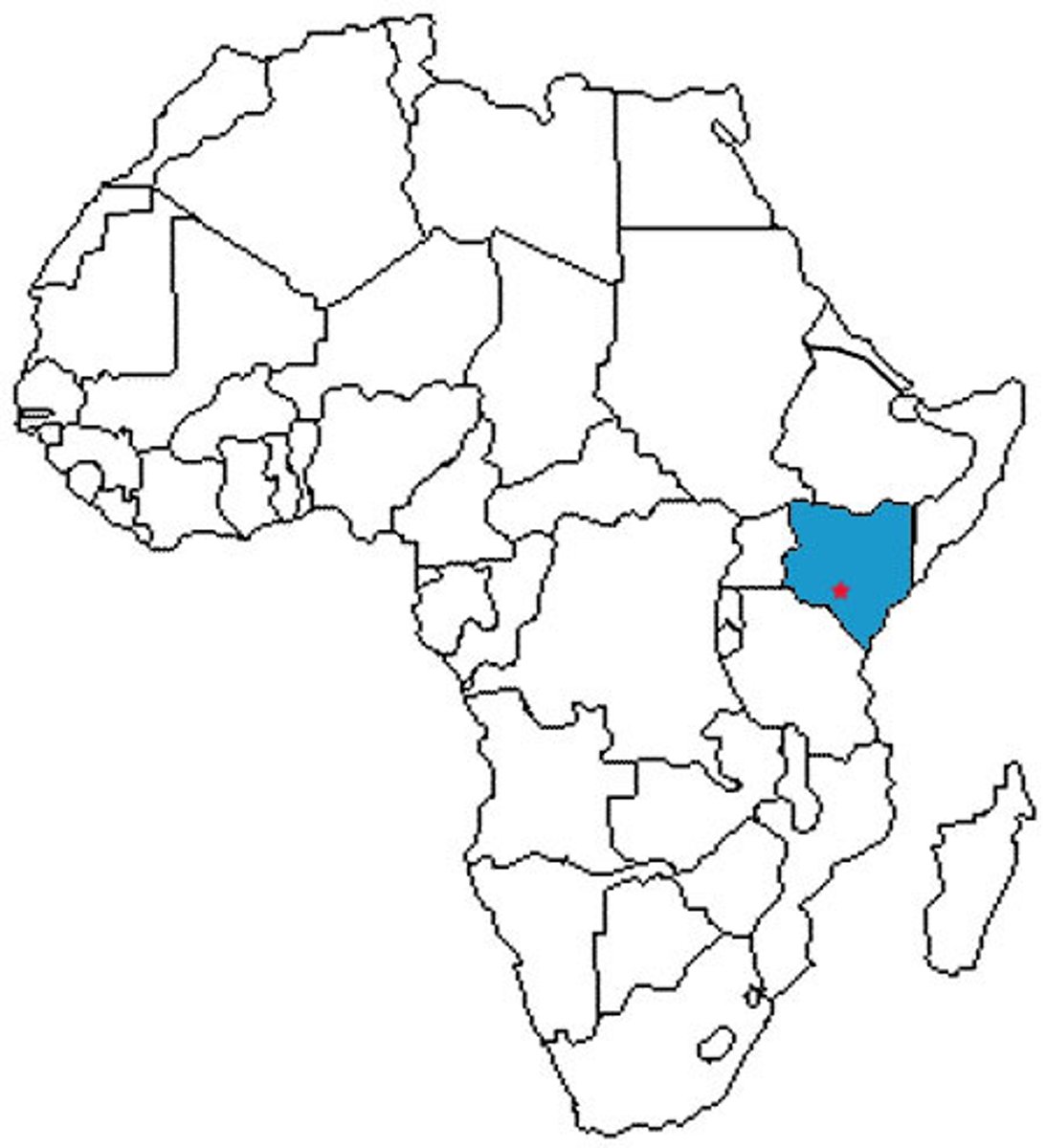
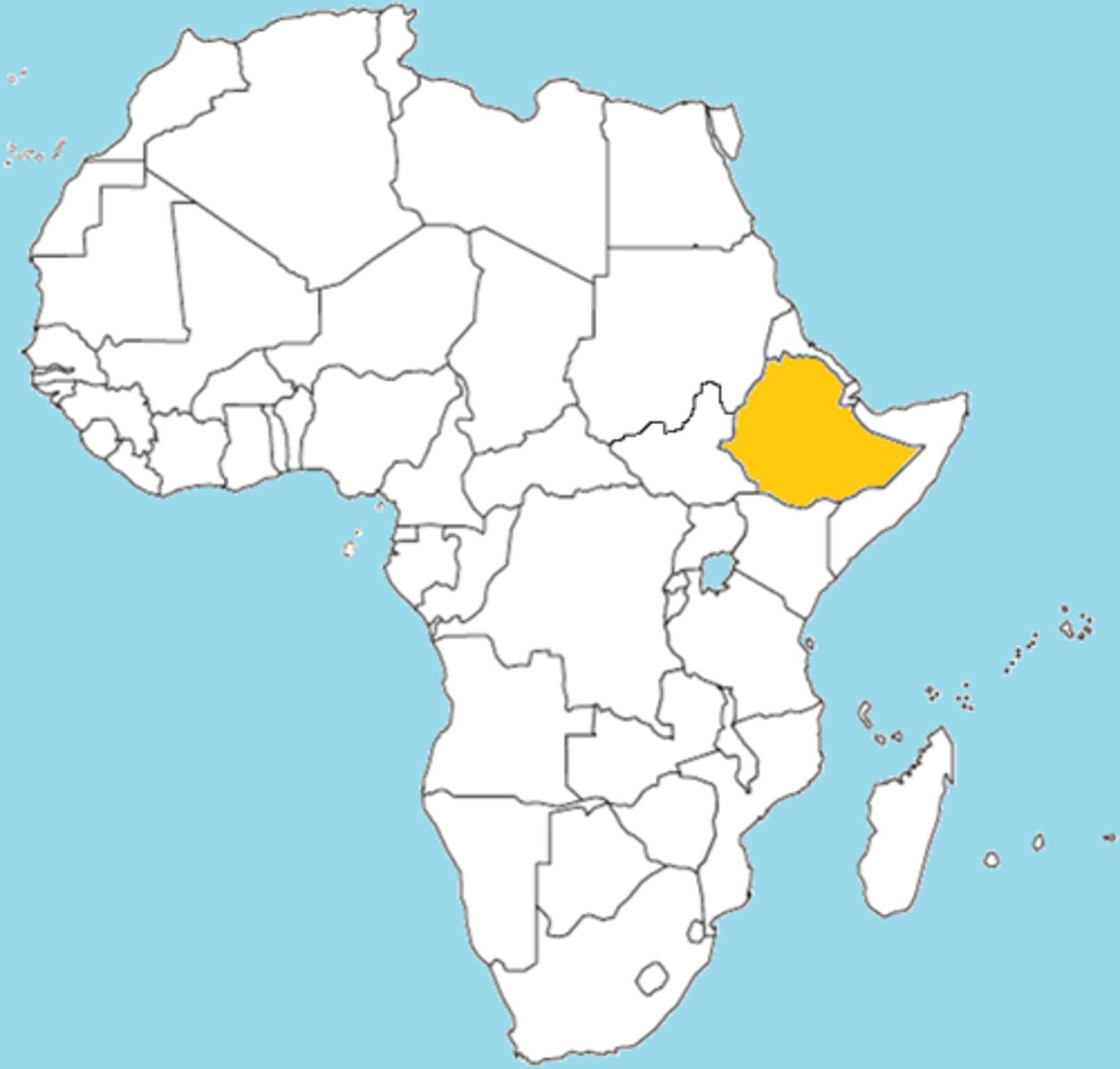
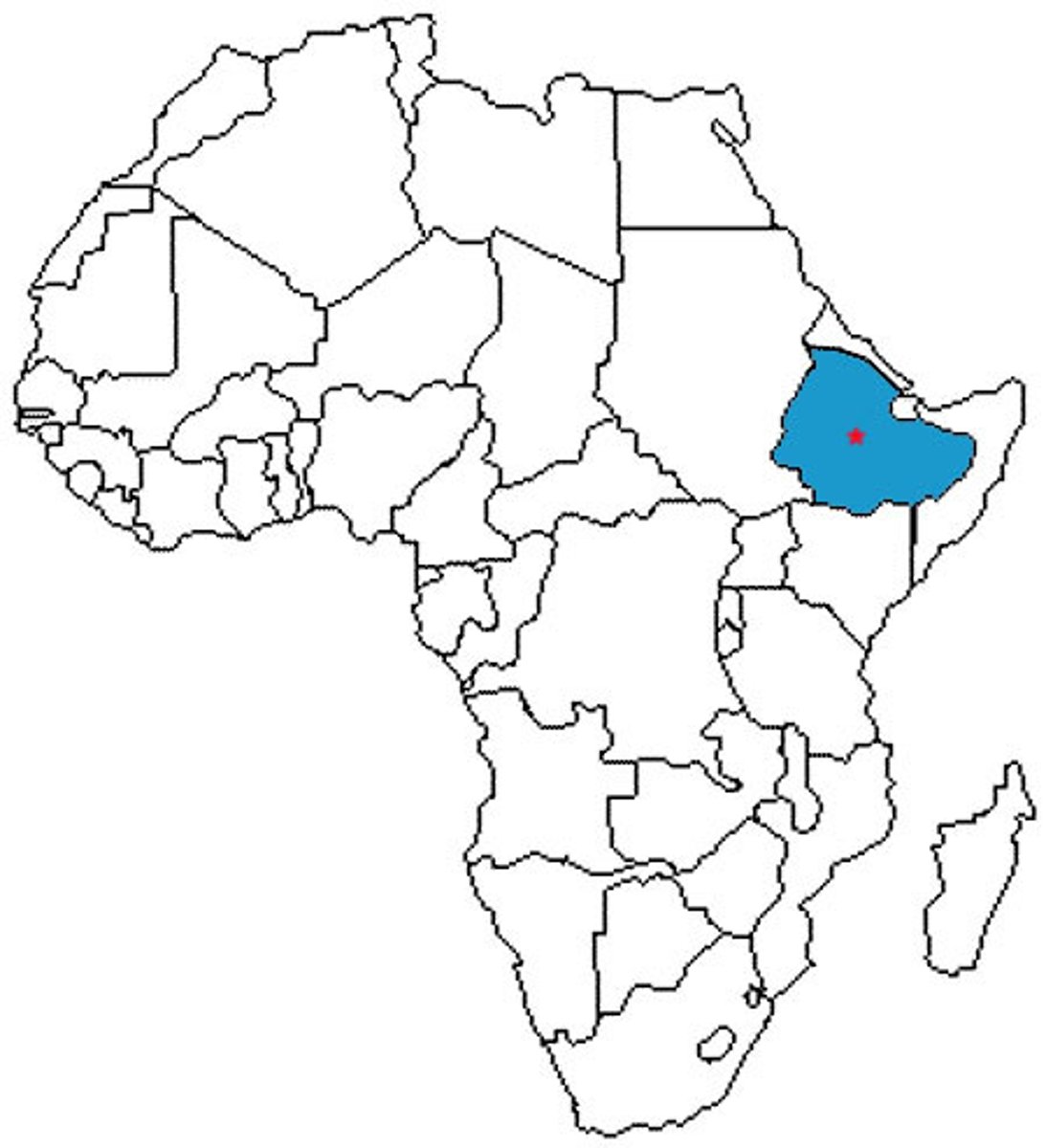
Ethipoia
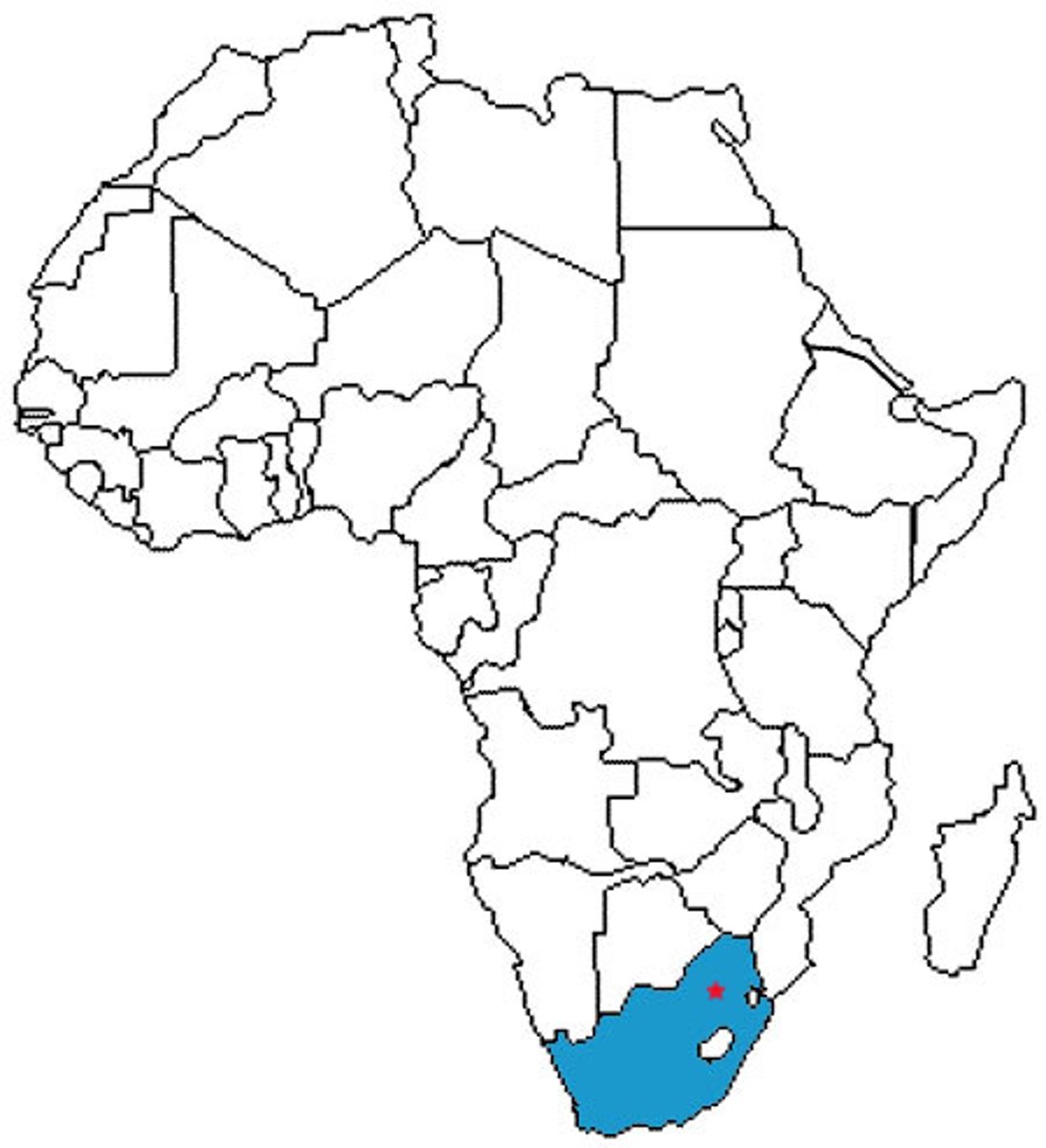
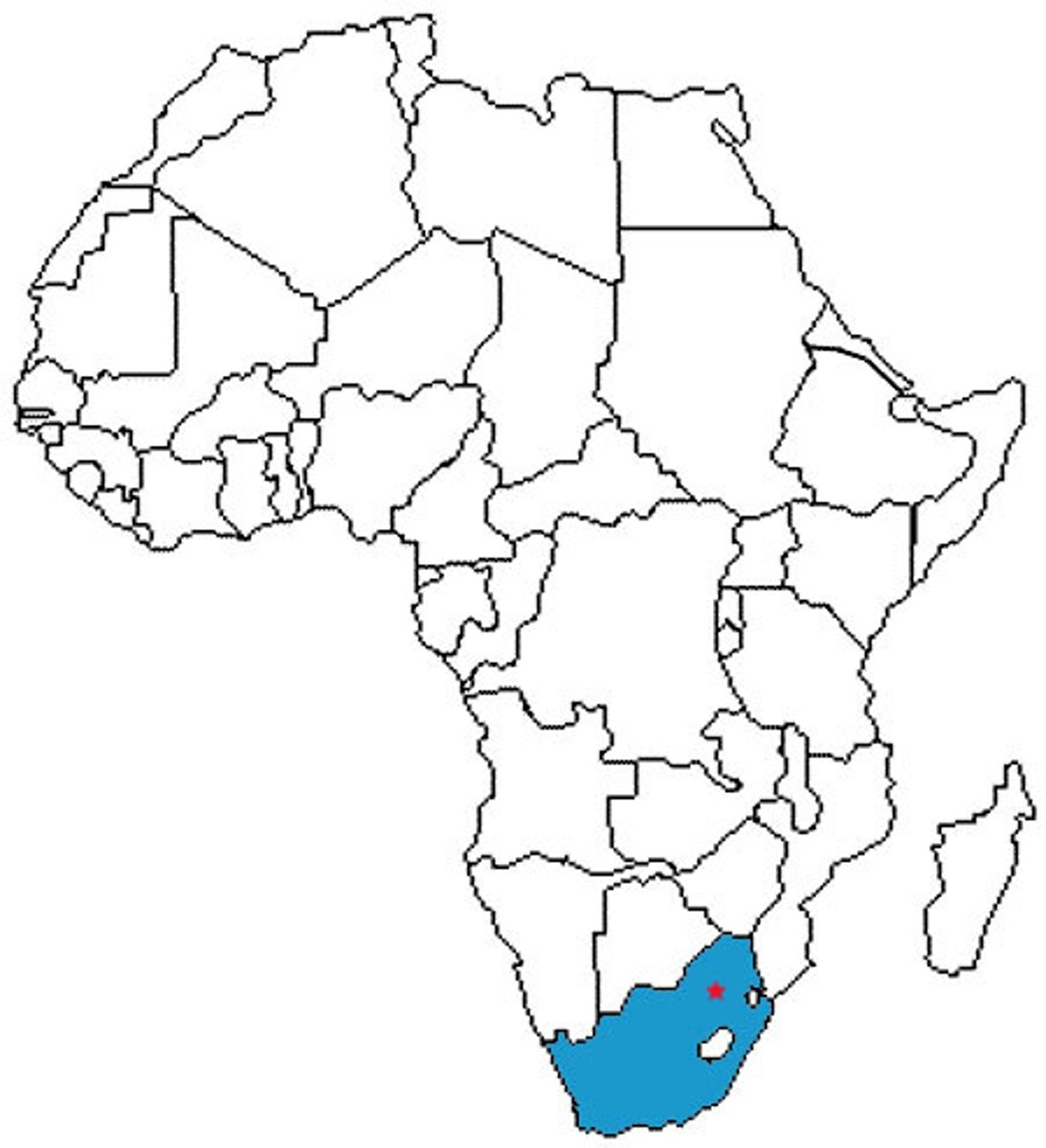
South Africa
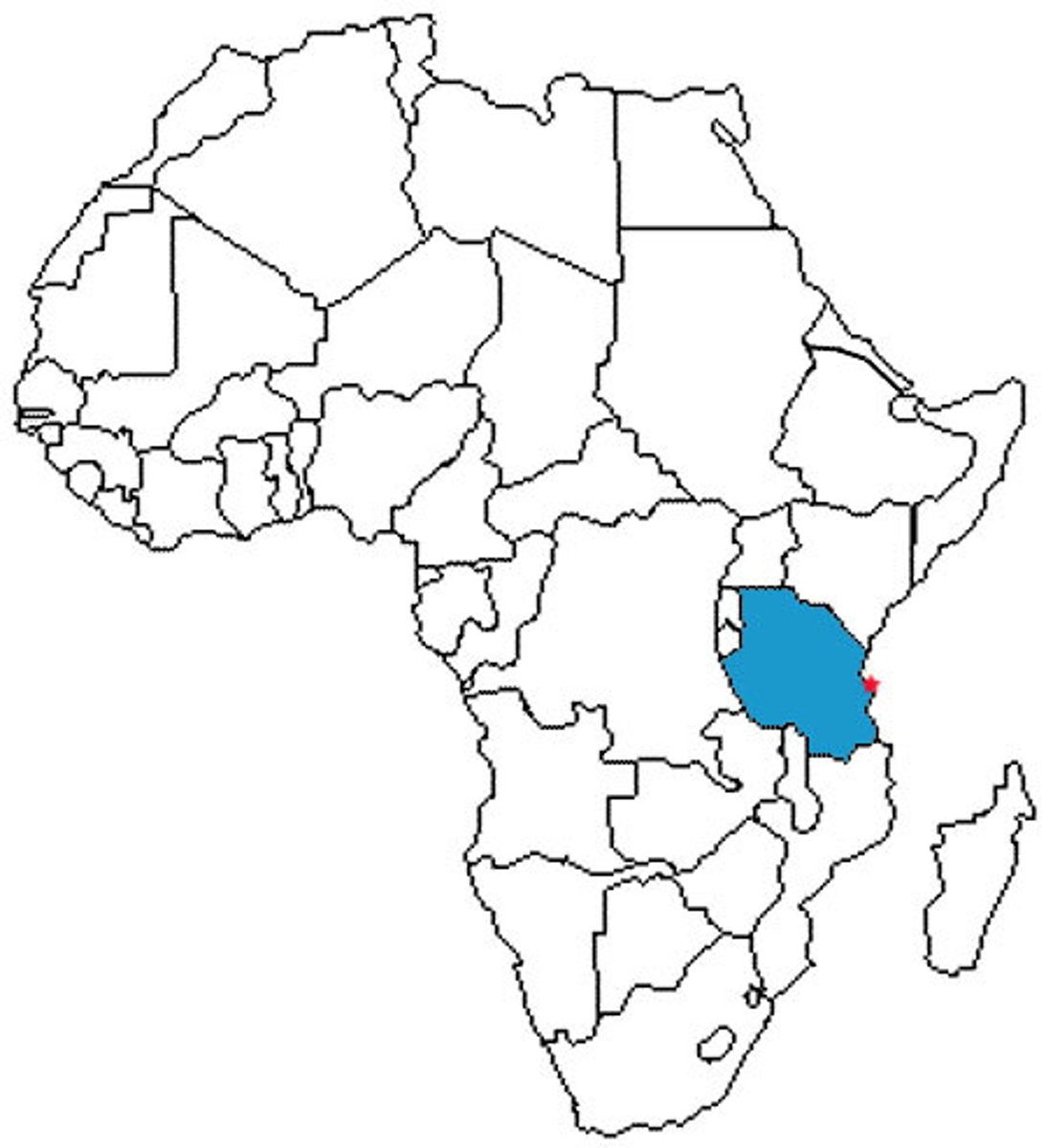
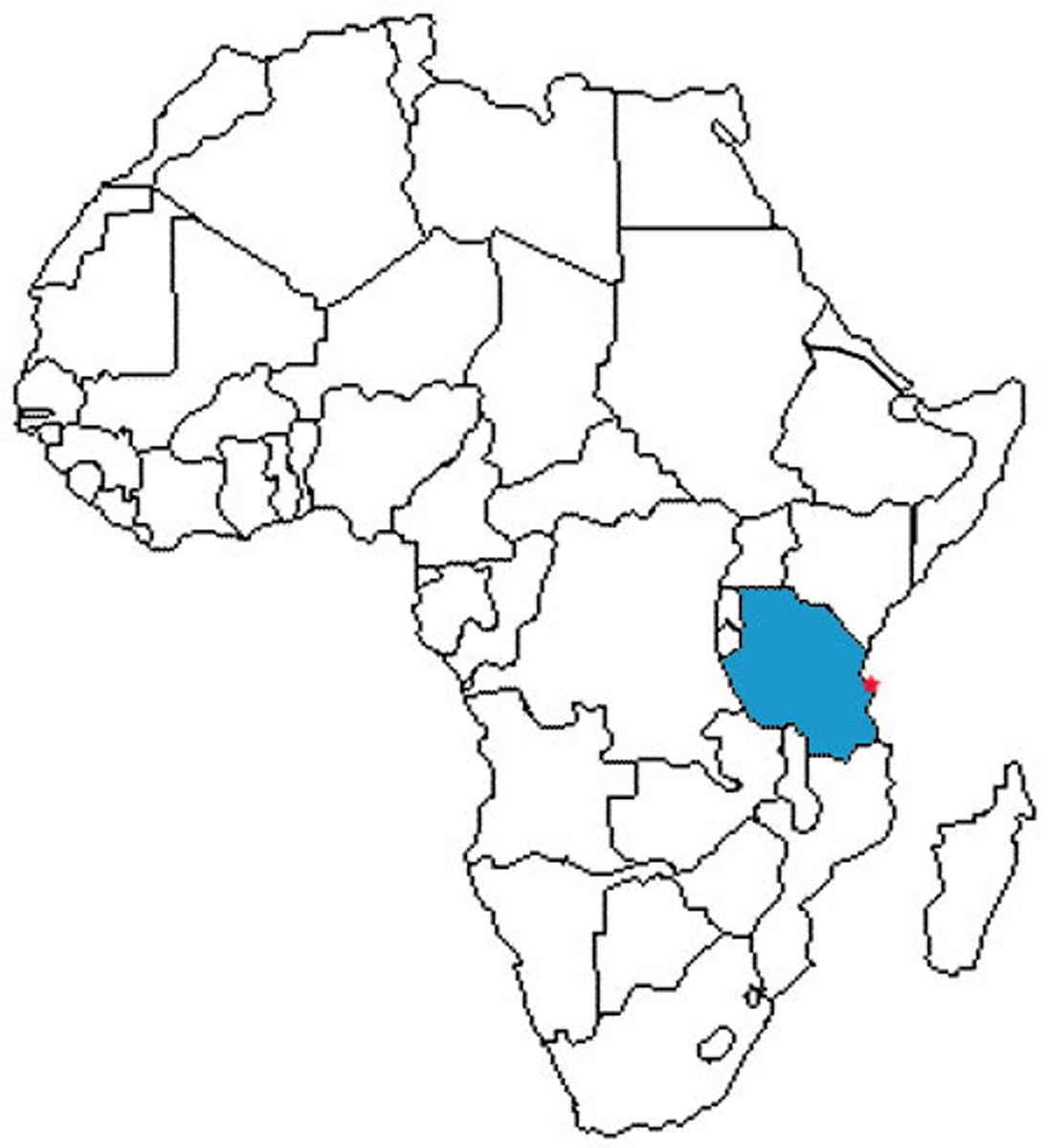
Tanzania
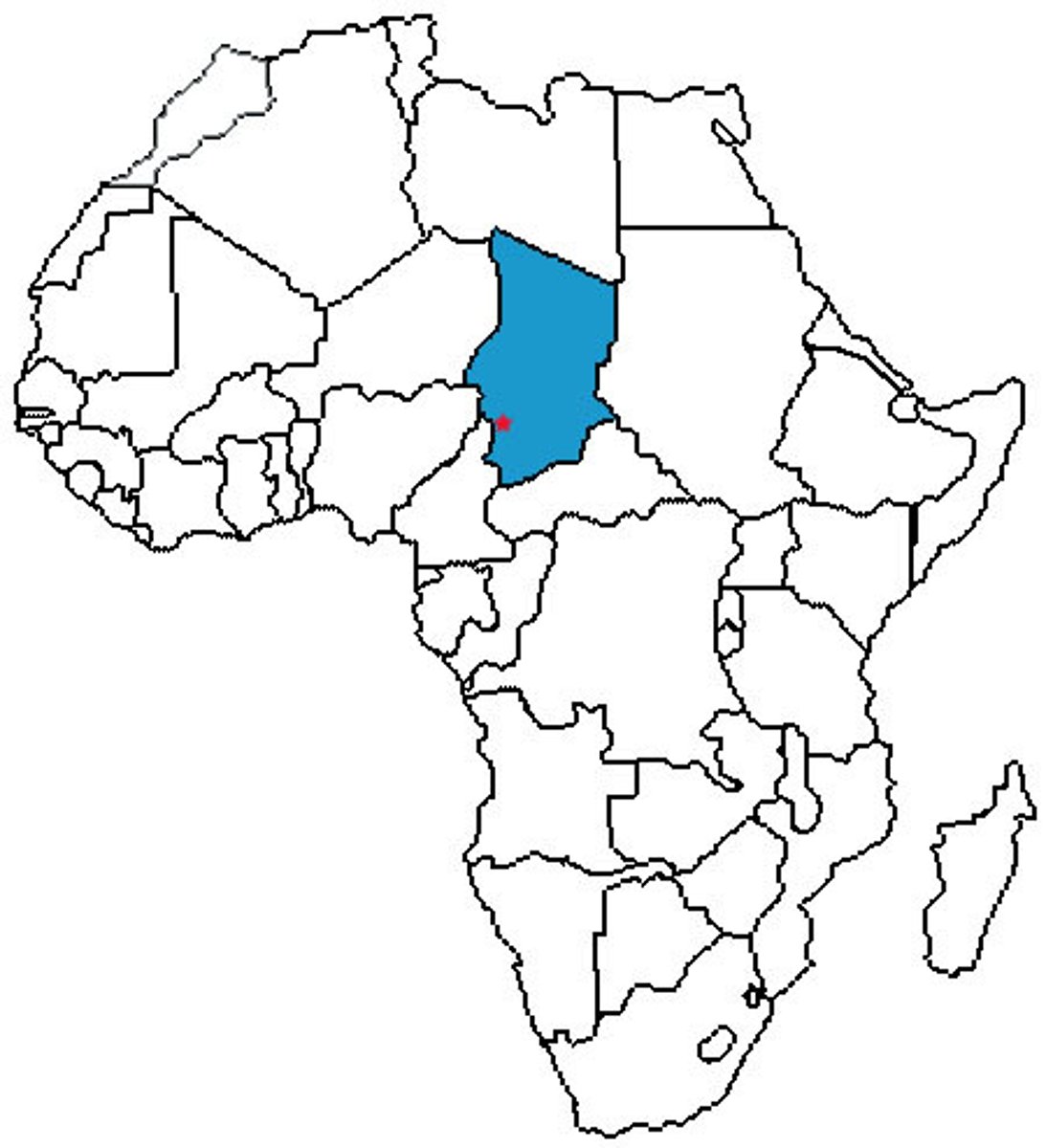
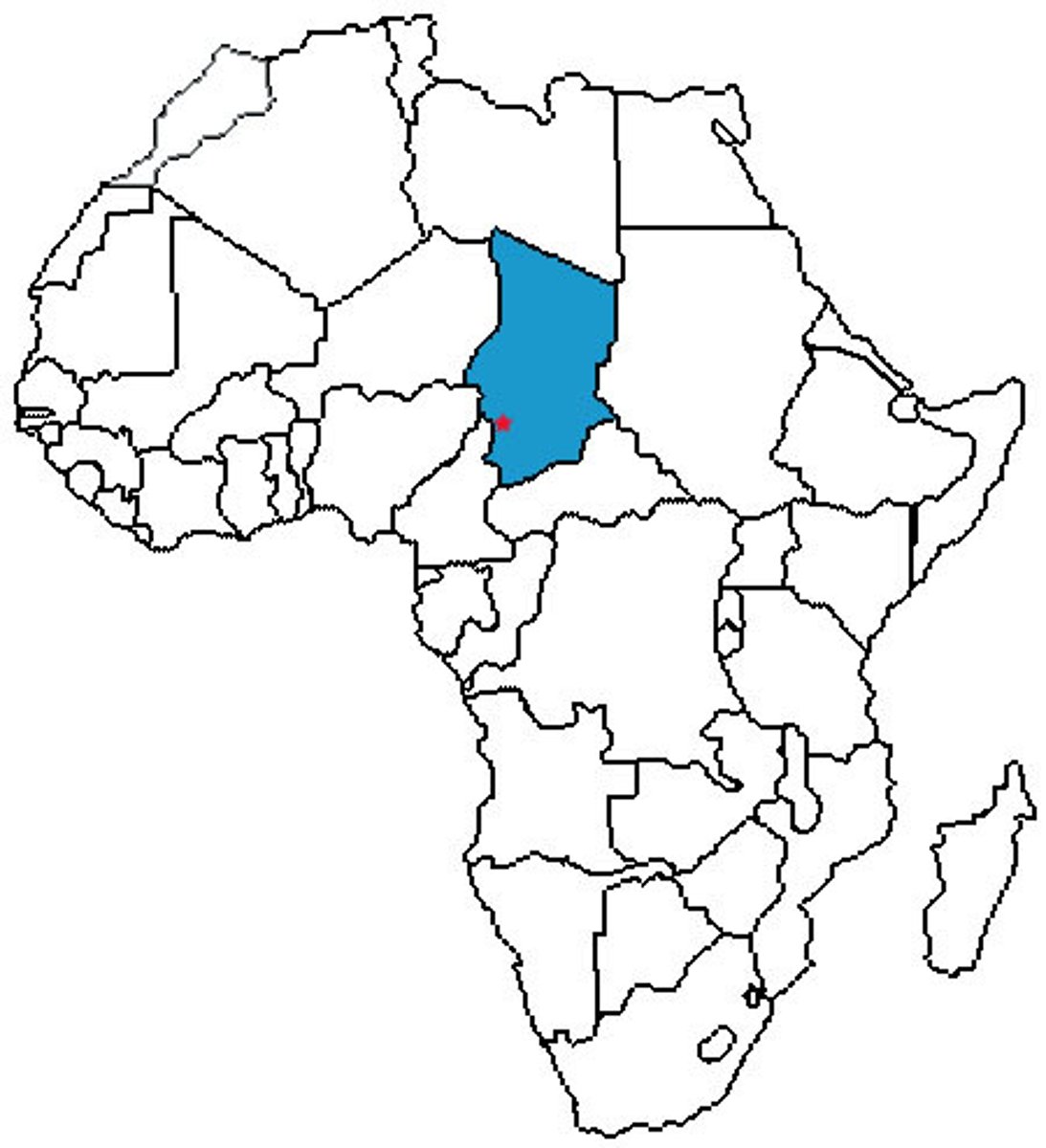
Chad
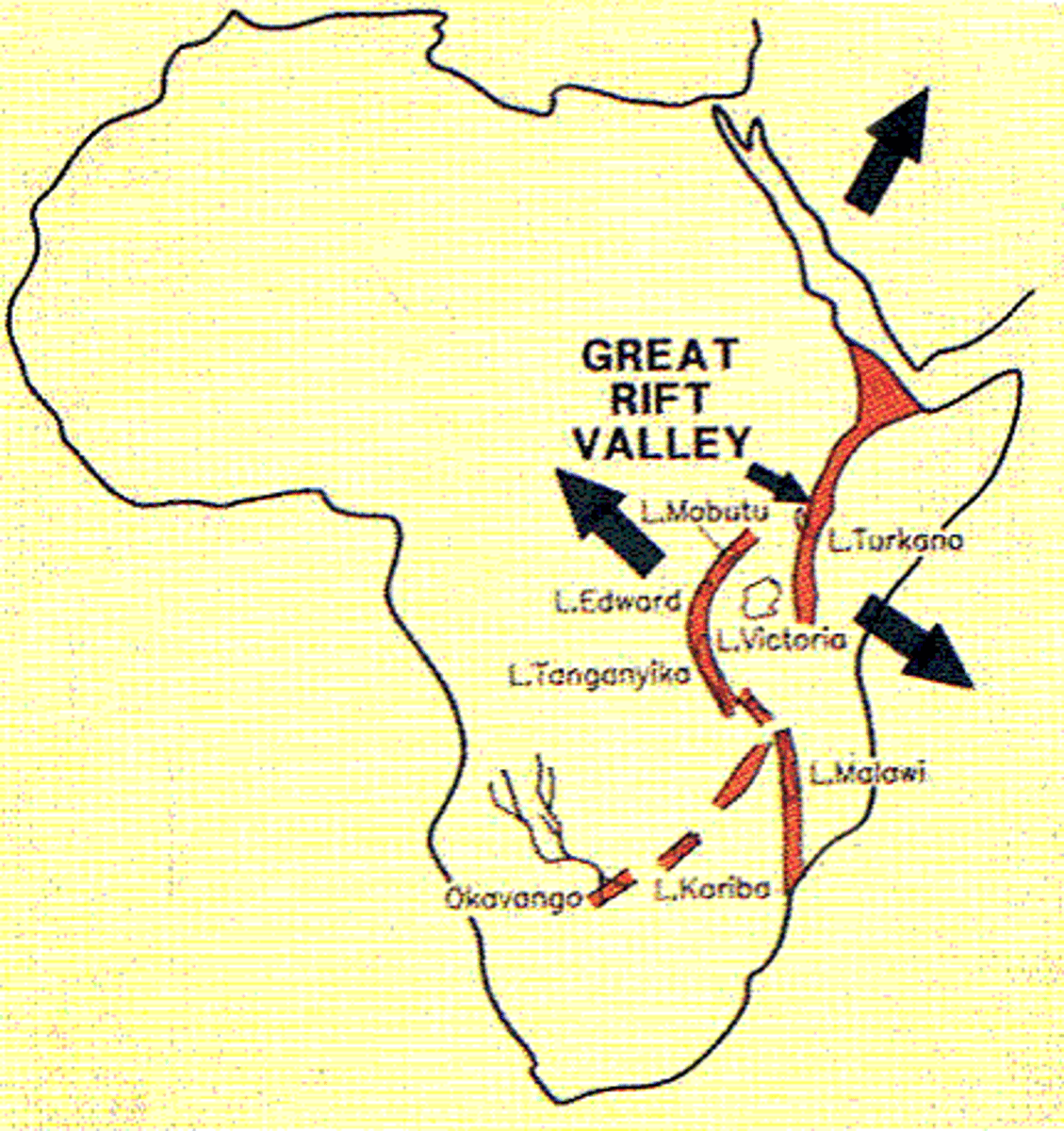
African Rift Valley
(It's in Kenya)
Hadar
(It's in Ethiopia)
Laetoli
(It's in Tanzania)
What is the African Rift Valley?
Crack in earth's crust from Lebanon to Mozambique, Divides Kenya into 2 sections, rich in fossils that allow study of human evolution
What's going on geologically
The rapidly eroding highlands have filled the valley with sediments, a favorable environment for the preservation of remains. The bones of several hominid ancestors of modern humans have been found here.
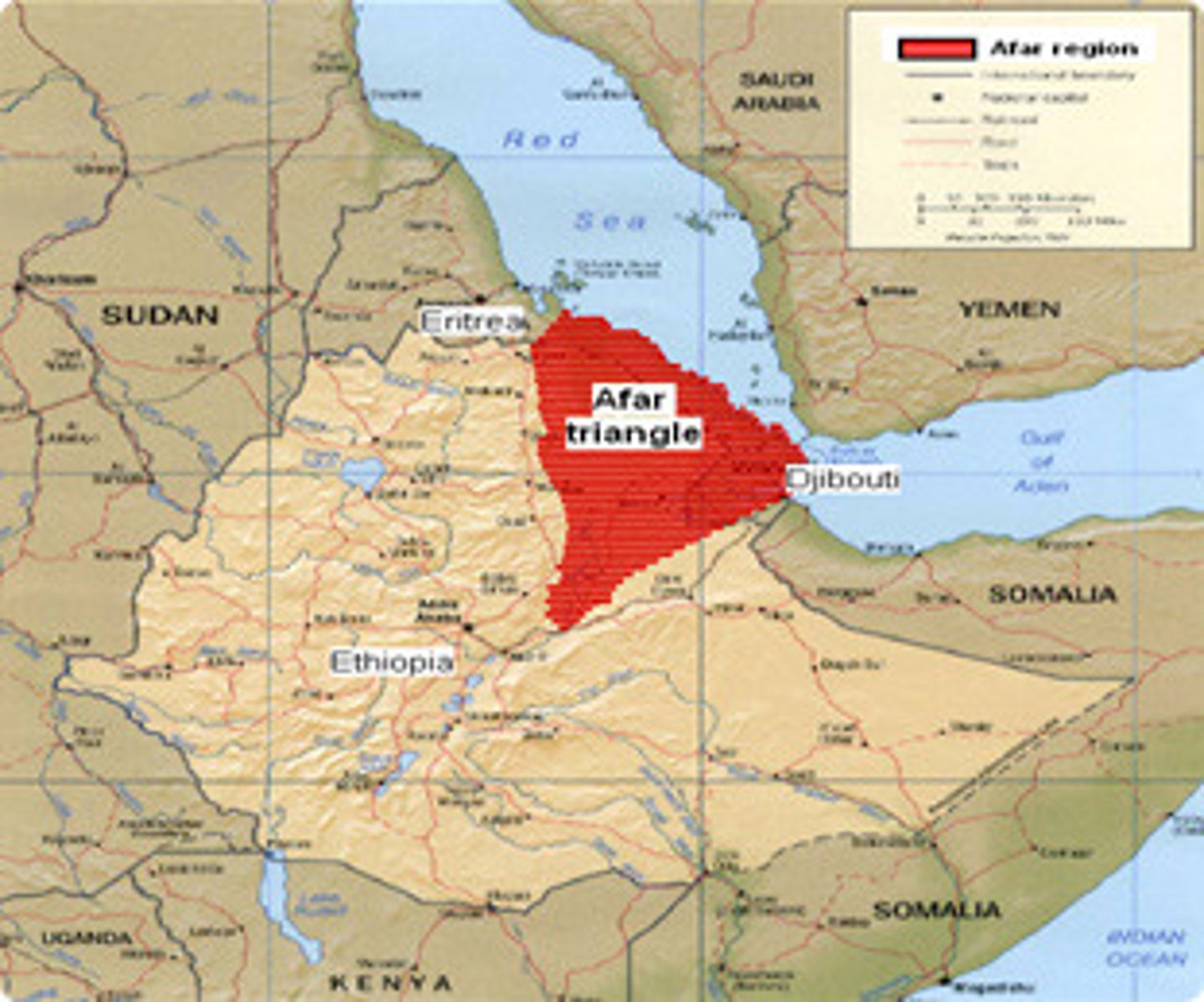
Afar Triangle
Taung
(It's in South Africa)
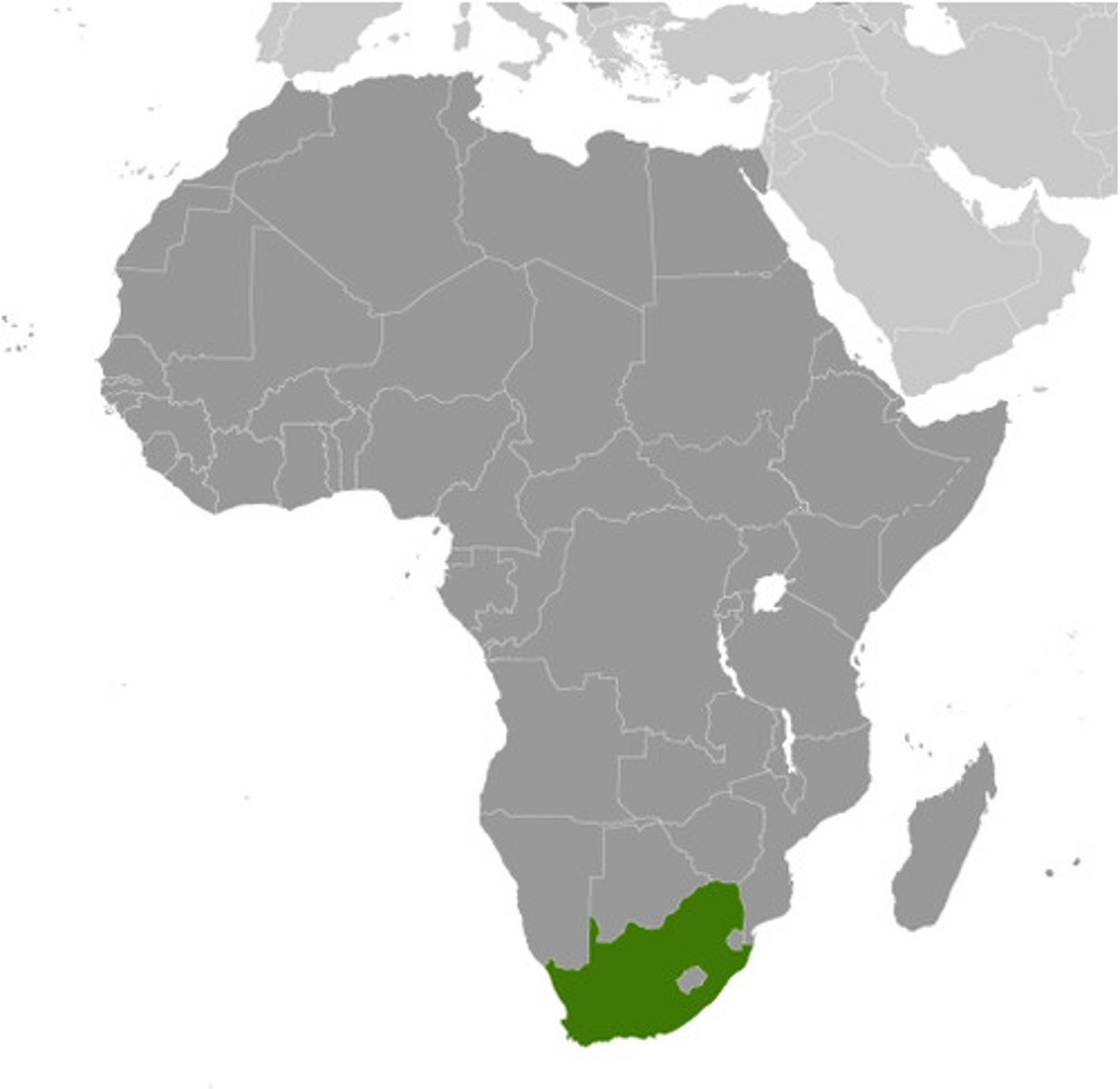
Sterkfontein, Swartkrans, Kromdraii
(It's in South Africa)
Djurab Desert
(It's in Chad)
Lake Turkana
(It's in Kenya)
A. afarensis and A. africanus Cranial morphology
Ape like
A. afarensis and A. africanus Brain size
small
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
Geographical area of discovery
Southern Chad
Geological age
7 MYA
The person(s) who discovered it
Michel Burnett
What does the name mean?
Sahel = sahara, anthropus = human, tchad= Chad, ensis = originating from
Why it may be a hominin
Foramen magnum may be forwardly placed, small unsharp canine
Why it may not be a hominin
Small cranial capacity (360cc),thick superorbital torus, thin enamel on post canine teeth. Large brow ridge
Orrorin tugenensis
Geographical area of discovery
Kenya
Geological age
6 MYA
The person(s) who discovered it
Martin Pickford and Brigette Senut
What the name means (nicknamed millemium man)
Orrorin = 1st human in Tugen, tugenesis = originating from Tugen Hills in Kenya
Why it may be a hominin
Shape of the femur head, canine not large and not honed, postcanine are argued to be thickly enameled
Why it may not be a hominin.
Femoral neck is argued to be human like but no good picture,
Ardipithecus ramidus
Geographical area of discovery
Afar triangle of Ethiopia
Geological age
4.4 MYA
The person(s) who discovered it
Tim White
What the name means (nickname Ardi)
Ardi = ground, Pithecus = ape, kadabba = oldest ancestor in Afar language
Why it may be a hominin
Anterior foramen magnum, less facial prognathism, no knucklewalking, biped pelvis, small canines, cranial capacity 300-350 cc., smaller face than chimps
Why it may not be a hominin.
Nose sticks out, curved arched fingers (suspensory),
Focus on the foot, the big toe (hallux) especially
Grasping feet with divergent hallux
Australopithecus afarensis
Geographical area of discovery
Hadar, Ethiopia, and Laetoli, Tanzania
Geological age
2.9-3.7 MYA
The person(s) who discovered
Don Johansen and Mary Leakey
What the name means
AUSTRALOPITHECUS = austral - southern, pithecus-ape, afar = triangle, ensis = from
AFARENSIS: afar - triangle, ensis - from
Australopithecus africanus
Geographical area of discovery
Taung, Sterkfontein, Makapansgat
Geological age
3.2-2.2 MYA
The person(s) who discovered
Raymond Dart
What the name means
AUSTRALOPITHECUS = austral - southern, pithecus-ape, afar = triangle, ensis = from
AFRICANUS: of Africa
A. afarensis and A. africanus canine size
tiny canines
A. afarensis and A. africanus incisor size
tiny incisors
A. afarensis and A. africanus Postcanine Tooth Size
Large flat
A. afarensis and A. africanus Postcanine hypermegadontia
Enlarged large molars and premolars
A. afarensis and A. africanus Premolar molarization
Molarization is evolution of less specialized teeth into molars
A. afarensis and A. africanus Foramen Magnum position
anterior
A. afarensis and A. africanus Facial prognathism/orthognathism
Prognathism ( reduced to Australopithecus)
A. afarensis and A. africanus Flaring Zygomatics
Big muscles of mastication
A. afarensis and A. africanus Forwardly placed zygomatics
Over premolars, "dished" midface
A. afarensis and A. africanus Cranial Cresting : What muscle of mastication attaches to the sagittal crest?
Temporalis
A. afarensis and A. africanus Cranial Cresting : What muscle of mastication attaches to the broad zygomatic bones?
masseter
Homo Habilis
Geographical area of discovery
Eastern Africa (Olduvai, Lake Turkana area, Hadar)
Geological age
2.3-1.6 MYA
The person(s) who discovered it
Mary and Louis Leaky
What the name means
Homo - human, habilis - handy (nickname is handyman or Twiggy)
Homo Habilis Cranial morphology
No sagittal crest, more prominent forehead, projecting supraorbital torus, smaller face, is in between human and ape
Homo Habilis Brain size
large
Homo Habilis canine size
small canines
Homo Habilis Postcanine Tooth Size
Large post canine teeth
Homo Habilis Dental Arcade Shape
Large premolars and molars, small canines and incisors, parabolic
Homo Habilis Foramen Magnum position
Anterior
Homo Habilis Facial prognathism/orthognathism
Orthognathic face
Homo Habilis Cranial Cresting
No cresting
Homo Habilis Postcranial morphology
Small brow ridge, deep, flat cheeks, orthognathic face
Homo Habilis foot morphology
more suitable for bipedalism
Homo Habilis hand morphology
tool user
Which came first during human evolution: obligate terrestrial bipedalism, reduced nonhoning canines, large brains, or stone tools? (Assume that Ar. ramidus is a good guide for what hominins that predate Australopithecus would have looked like
Large brains, diet, tool use, locomotion, small canines
Lucy
Australopithecus afarensis shows sexual dimorphism
Selam
Australopithecus afarenis, is almost complete and also a child
Taung Child
Australopithecus africanus, first and best example of early hominin brain evolution
Laetoli footprint trail
stralopithecus afarensis, made by some of the first upright-walking hominids
Ardi (the Ar. ramidus partial skeleton)
Ardipithecus ramidus, reflects a human-African ape common ancestor that was not chimpanzee-like.
Core
body of the tool
Hammerstone
stone tool used to chip away core
Toumai
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, possibly very close to the time of the chimpanzee-human divergence
Twiggy
Homo habilis, evidence for the validity of the Homo habilis species
Flake
flakes of stone that fall off core when hit with hammerstone
Oldowan Stone Tool Industry
Oldest recognized stone tool culture, including very simple tools
The Killer Ape Hypothesis
Proposed that hunting was what drove human evolution (the Osteodontokeratic tool culture was created by A. Africanus)
Who did Dart think was the killer ape?
A. Africanus
What are cutmarks on bones?
Scrapes in the bones
What evidence is there that marrow was extracted from bones using stone tools
Cutmarks
Osteodontokeratic Tool Culture What is it?
The use of bone (osteo), tooth (donto), horn (keratic) tools
If A. africanus didn't collect the bones in the caves, then who/what did?
Other agents such as the prey of the predators (example: hyenas are bone collectors)
What is the evidence that Oldowan stone tools were used to acquire meat?
There really aren't different types of tools in the Oldowan, the point is sharp edges to cut stuff
Which plants follow a C3 photosynthetic pathway?
Trees and fruit
Which plants follow a C4 photosynthetic pathway?
Grasses
Which hominin is the likely stone tool maker at Olduvai?
Homo because Paranthropus didn't have the brain size and was not a carnivore
Which hominin is associated with the 3.4 mya "cut-marked" bones from Dikika, Ethiopia?
Paranthropus
What kind of "tools" are hypothesized to have made the cut marks?
stone
What is the general trend for hominin diets in terms of the use of the C3 and C4 vegetation
Have different carbon isotope signatures
Which hominin has a nearly pure C4 signal?
Paranthropus boisei
What is the savannah hypothesis for the origins of bipedalism?
An idea that we shifted to bipedalism as a response to living in an open habitat like the savannah
What environments were occupied by the earliest bipeds (e.g., Ardipithecus and Australopithecus)?
wood and grass lands
In addition to H. ergaster/erectus, what other hominin lineage adapted to life on the savannah?
p. bosei
Why is the savannah hypothesis wrong when it comes to explaining the origins of bipedalism?
Savannah's didn't exist in early Pliocene and Miocene, early hominins lived in woodland habitats,
What evidence do we have that this lineage exploited savannah habitats
c4 rich diet
Why might adaptations to savannah life explain the anatomy and behavior of Homo erectus/ergaster?
A bipedal posture reduces exposure to the sun, they weren't pure carnivores, capable of running which permitted persistence hunting
Where are fossils of Homo erectus/ergaster found?
Turkan area
What is the age of the oldest fossils attributed to H. erectus/ergaster that are found outside of Africa?
1.8 MYA
Where are these fossils found?
Dmanisi, Georgia
When does H. erectus/ergaster appear in the fossil record?
1.8 MYA - 250 KYA