Lecture 5- quantity theory of money
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is the relationship between the money supply and the price level
Causal proportional relationship
What is the fundamental equation of exchange

What do you assume about V And what does this mean about the equation
Assume that V=V dash
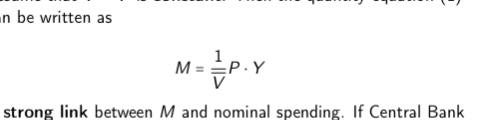
What does the strong link between ,M and nominal spending mean
In the long run and short run
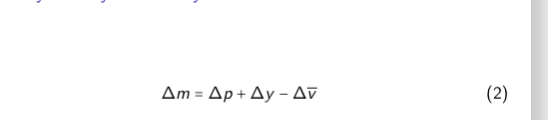
How would you interpret this equation
The growth rate of money stock consistent with a particular inflation target
What therefore does the central bank have to do

What are the implications from the Quantity theory of money
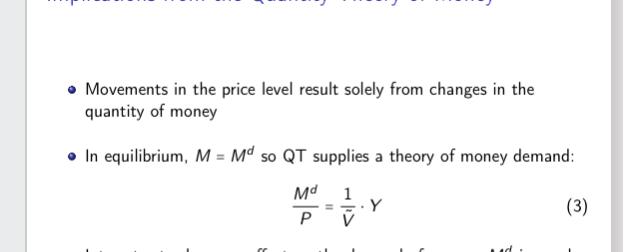
What is the effect of interest rates on the demand of money
No effect. Md is purely a function of income
What are the three motives for holding money
Transactions
Precautionary
Speculative motive
Explain transactions

Explain precautionary

Explain speculative motive

What is the equation you get when you put all three motives together

Why is veolcity not constant
The pro-cyclical movement of interest rates should induce pro-cyclical movements in velocity
What are other factors affecting the demand for money according to Portfolio Theory
Wealth
Risk
Liquidity and other assets
What is the theory of portfolio choice consistent with
The Keynesian liquidity references function, as demand for real money balances is
-positively related to income
And negatively related to the nominal intrest rate
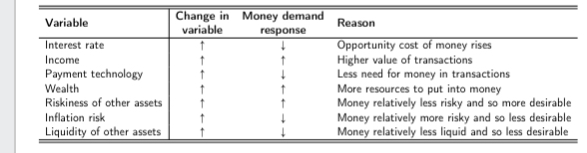
Overall table show in factors that determine the demand for money and why
What if Md is sensitive to Change in i
If not- velocity is more likley to be constant or at least predictable
This is consistent with Quantity theory view that aggregate spending is determined by the quantity theory of money
What does more sensitivity of Md to intrest rates molies
More unpredictable velocity
Less of a clear link between Money supply and aggregate spending
Support for liquidity theory
What if Md function is unstable and prone to big unpredictable shifts(KEYNES) then:
Velocity

Why does this matter

What does setting interest rate target provide
More information about stance of monetary policy than setting level for M(which becomes endogenous)
What is planned expenditure(E)
Total spending on domestically, produced goods and services that households, business, government, and foreigners want to make
Aggregate demand
C+I+G
Total output demanded in closed economy
What is the IS schedule

What is the consumption function equation

How is consumption expenditure positively related to disposable income
YD= Y-T
Positively related to disposable income
What is the investment function

What is fixed investment and what is inventory investment
Fixed is always planned
Inventory is unplanned
What does planned investment spending depend on
Interest rates and expectations
What is the equation for net exports
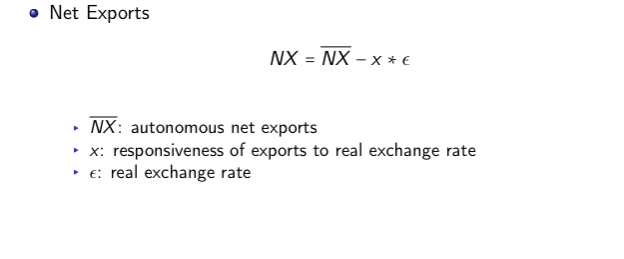
What are the signs for government purchases and tax

What is the goods market equilibrium

How would you solve for the goods market equilibrium
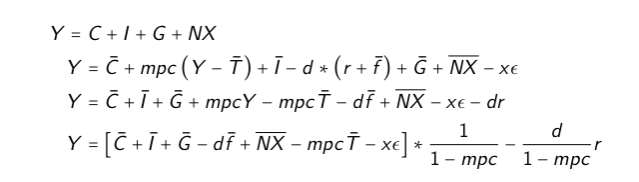
What factors shift the IS curve and what factors change the slope of the IS curve

What does the IS curve tell us and examine

What does the IS curve assume

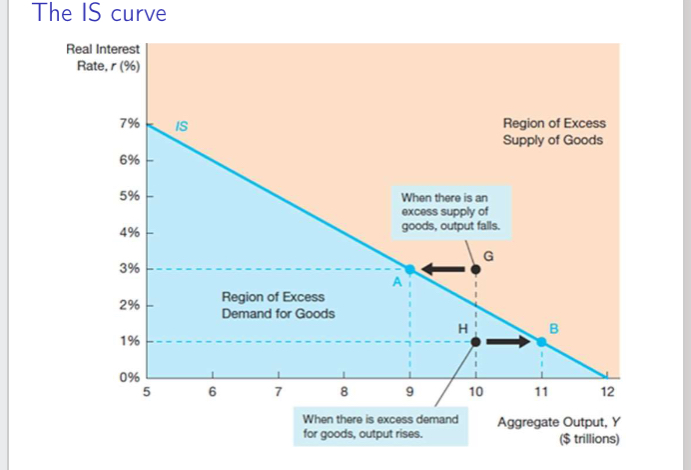
What relationship is the is curve and show graph
Relationship between equilibrium aggregate output and the interest rate e
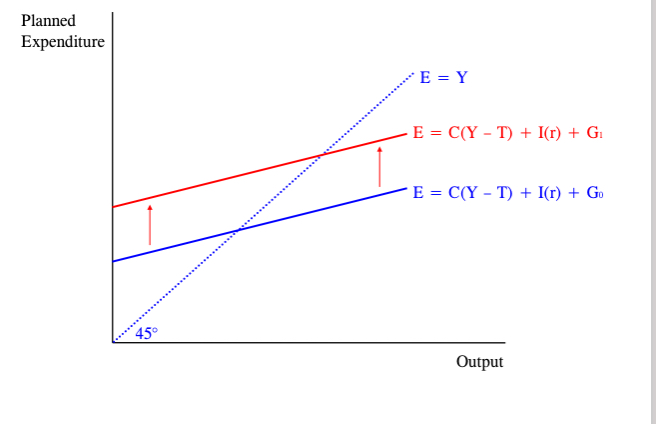
Effect of an increase in G at a given interest rate
Shifts in the IS curve from autonomous changes

What is the Taylor rule

What is the equation for the central bank conducting monetary policy as a response to changes in output and inflation
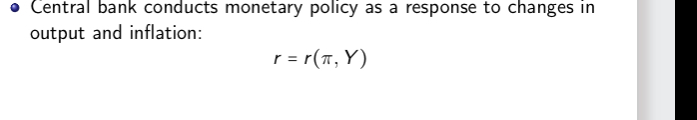
What happens when output rises and when there is an increase in inflation

What does the mp curve show

Increase in government spending

Shift to tighter monetary policy
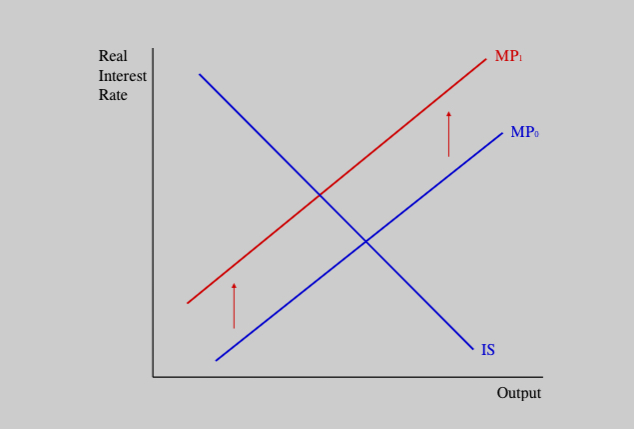
Simultaneous changes in fiscal(-) and monetary policy
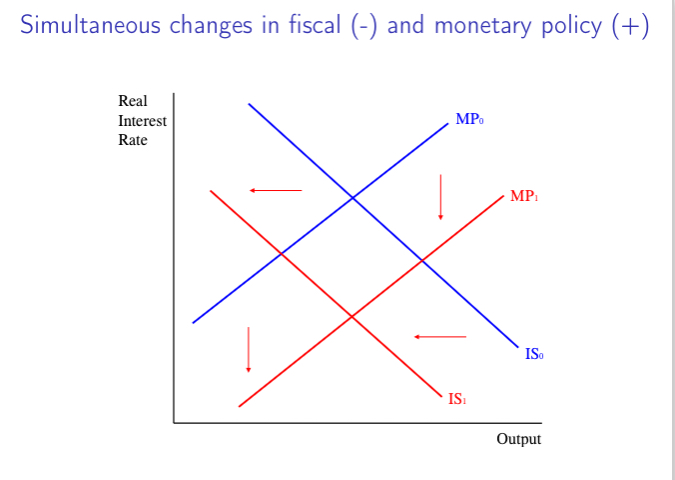
What is the equation in the money market equilibrium and rewrite in terms of real interest rate
How the central bank controls intrest rates
What may changes in M also effect
Directly controlled by the bank
May also affect P
Also expected inflation
M.V=P.V

What may change in nominal money supply also affect
Supply of real money balances(M/P) in the money market

What is key to understanding how CBs control the real intrest rate and what are the two scenarios
Price adjustments dynamics

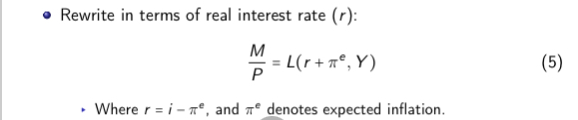
Rewrite this equation assuming prices are fixed
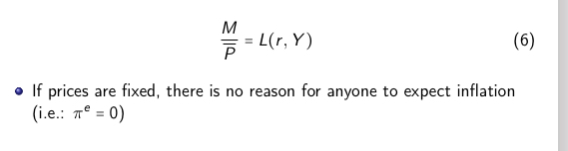

Hope to bring back the equilibrium

The effects of an increase in the money supply with sticky rices graph
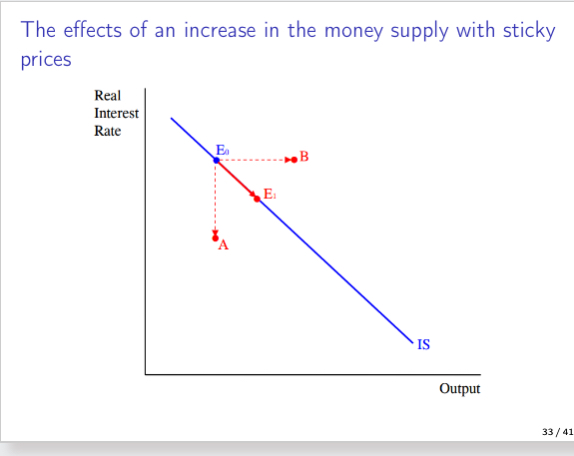
The effects of an increase in the money supply with sticky rices Explanation

How do prices adjust in practise - flexible
Assuming full sticky prices Changes in nominal supply(M) cause changes in real intrest rate
If prices are flexible they jump up at time of money supply increase Lessing rise in real money supply
How do prices adjust in practice - sluggish
rise slowly to their new long-run equilibrium level after money supply increase

Equations showing the effect of an increase in the money supply with flexible prices and what appends to expected inflation

Effect of an increase in the money supply with flexible prices
imbalance between supply and demand of real balances

Effects of an increase in the money supply if all prices are completely and instantaneously flexible
