Current Electricity Grade 9 Science
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Amps
unit of current; A= C/s
Voltage
The potential difference measured in volts. The amount of work to be done to move a charge from one point to another along an electric circuit.
Volts
Unit for electric potential difference
Voltmeter
instrument that measures potential difference
ammeter
instrument used to measure current
series circuit
A circuit in which all parts are connected end to end to provide a single path of current.
parallel circuit
A closed circuit in which the current divides into two or more paths before recombining to complete the circuit
resistance
A material's opposition to the flow of electric current.
electrical energy
Energy made available by the flow of electric charge through a conductor; equal to power x time
high resistance due to large length and small Area
Resistance of long, thin wire
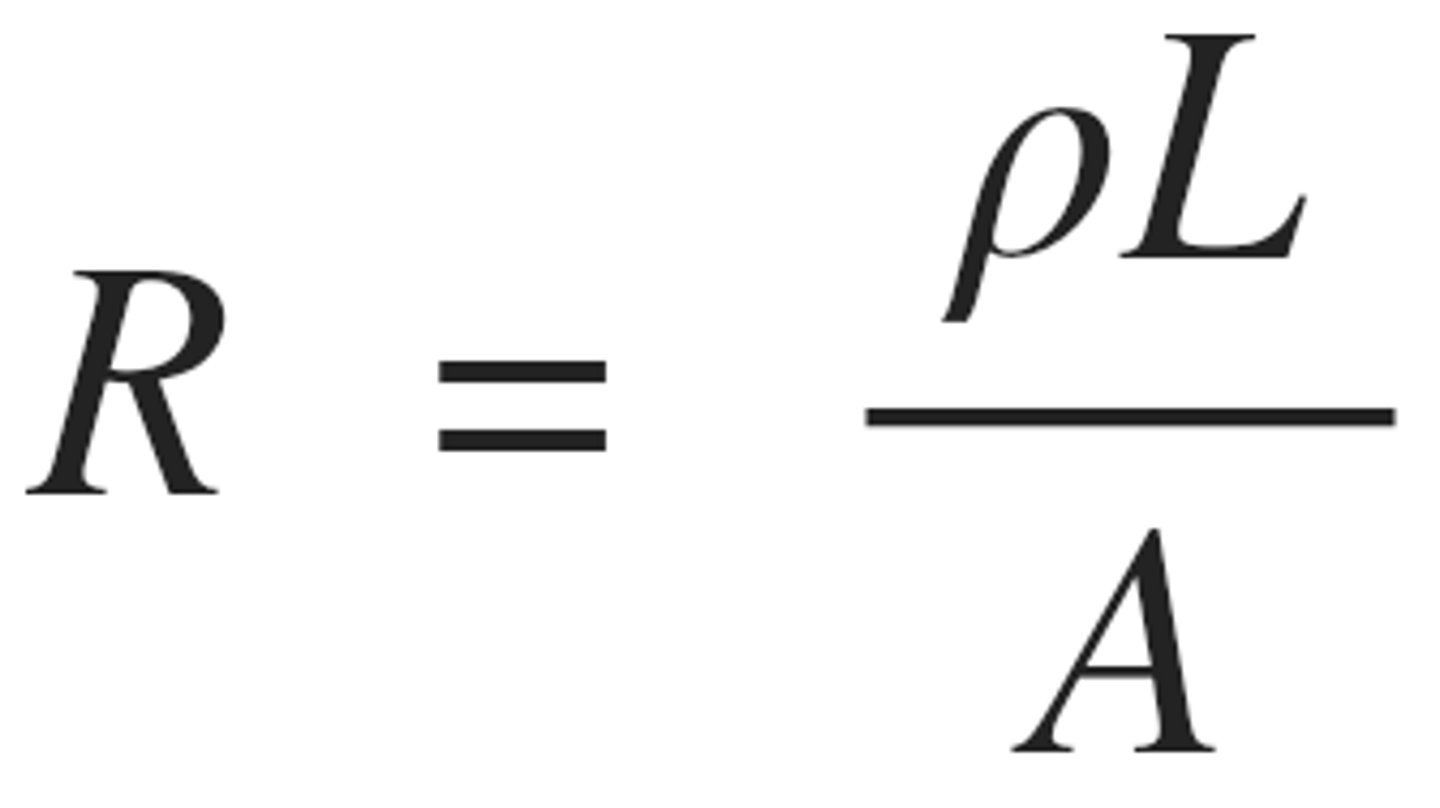
low resistance due to small length and large Area
Resistance of short, fat wire
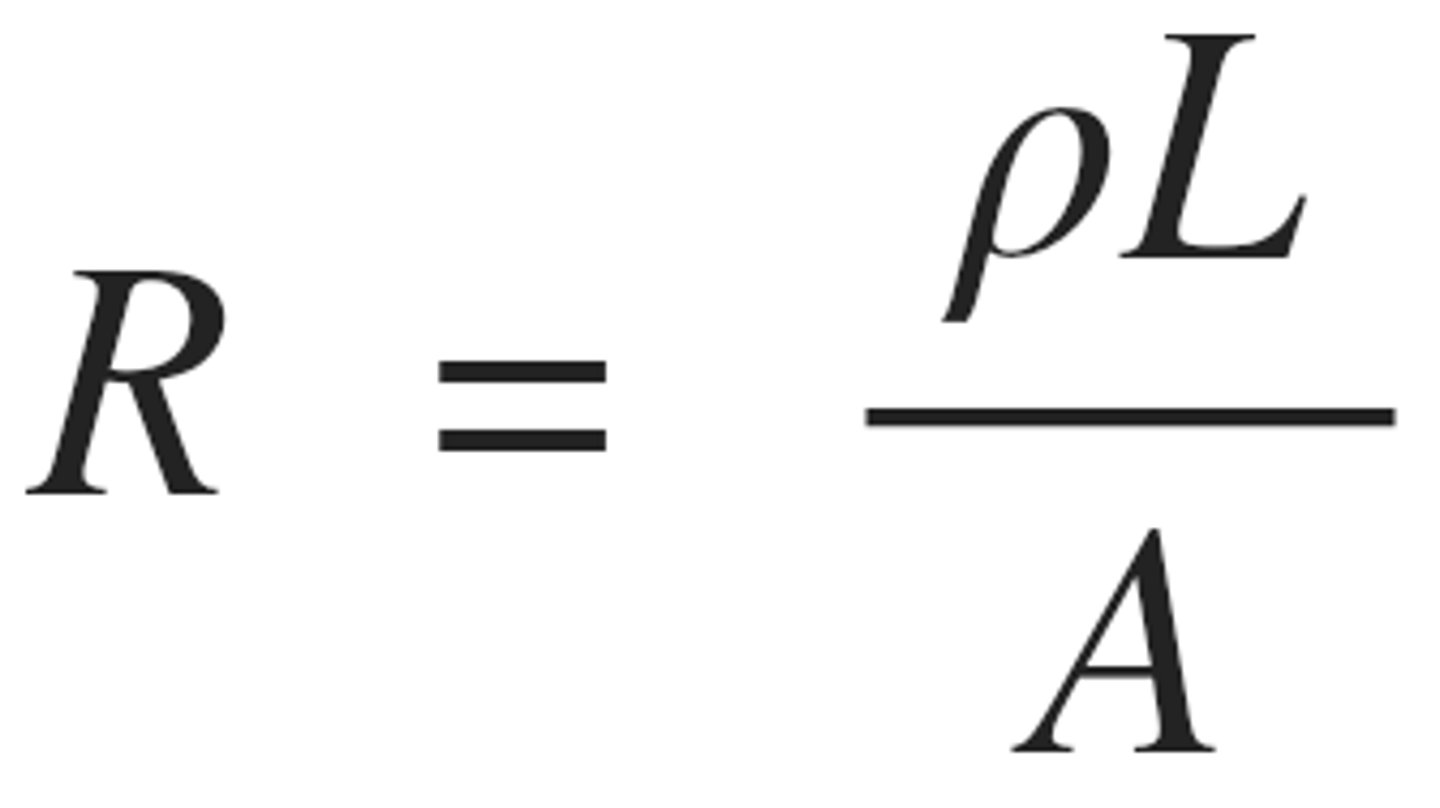
power source
Provides the voltage for the circuit.
load
the materials carried by a stream
lamp
light source
Conducting wire (conductor)
allows electrons to flow freely based on their loose hold of valence electrons
electric circuit
a complete, unbroken path through which electric charges can flow
mechanical energy
Kinetic or potential energy associated with the motion or position of an object
heat
the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures
schematic diagram
a way to represent a circuit on a piece of paper
series circuit
A circuit in which all parts are connected end to end to provide a single path of current.
parallel circuit
A circuit that contains more than one path for current flow.
current
A flow of electric charge.
DC
discharge
Amps (A)
The unit of measurement for current (amount of charge/sec)
Charge
A measure of the extra positive or negative particles that an object has.
current x time
Coulombs (C)
unit of charge
electrons
negatively charged particles
ammeter
A device used to measure current in a circuit
Voltmeter
A device used to measure voltage, or electrical potential energy difference
potential difference (voltage)
the difference between the electric potential energy per unit of charge at two points in a circuit
Resistance
the characteristic of a material that slows electron flow
units are measured in ohms
resistor
An electrical device that resists the flow of electrical current
Ohms law
V=IR
open and closed circuit
circuit open = device off
circuit closed = device on
how to measure voltage
charge in energy divided by coulombs
Current symbol
I (A)
Charge symbol
Q
Time symbol
T
how to caculate current ( I )
Q divided by T
colombs divided by time
caculate time ( T )
Q divided by I
coulombs divided by current
caculate charge ( Q )
current x time
caculate resistance
Voltage divided by Current
V divided by I
A load had 2 A of current flowing through it. The voltage across the load is 6.0 V. Calculate the resistance
R = V divided by I
R = 6.0 divided by 2 = 3
A 12 ohm resistor is connected to a power supply set at 6 V. Calculate the current going though the resistor
I = R divided by V
I= 6 divided by 12 = 2
Resistance formula
R= V divided by
I = R divided by V
Voltage formula
V=IR
How much time does it take for 80 C to pass through a light that draws on 40 A?
80 divided by 40 = 2mins
1 minute
60 seconds (turn it into seconds)