First law of thermodynamics
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
temperature
average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample
why is temperature average
substances are made of constantly moving particles
can bounce off of each other erratically
kinetic energy formula
KE=1/2mv2
0K
absolute zero temp
no kinetic energy
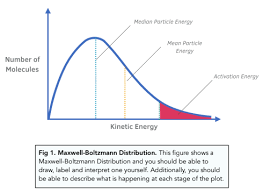
Maxwell boltzmann distributino diagram
higher average kinetic energy → higher temperature …?
energy
ability of matter to do stuff/cause a change
joule
SI unit for energy
thermochemistry
study of energy changes esp heat that accomapny chem rxns and physical processes
2 types of energy
kinetic energy
potential energy
calorie (Cal)
common unit of energy
how man cal in a Cal
1000 cals
cal → J
1 cal=4.18J
kinetic energy
energy due to motionw
what does kinetic energy depend on
depends on speed and mass
potential energy
energy due to position and size
stored energy
first law of thermodynamics
energy can be converted from 1 form to another, but cannot be created nor destroyed
other name for first law of thermodynamics
law of conservation of energy
system
particular part of the universe on which we focus attention
surroundings
everything else besides the systme
system and surroundings equivalence equatin
qsystem = -q surroundings, or vice versa
what is q
heat
internal energy (E)
sum of all possible forms of energy in teh system
internal energy equation
E=PE+KEj
exothermic rxn
process in which eat flows from system to surroundings
endothermic process
heat flows to system from surroundings
types of systems
open
closed
isolated
open system
free exchange across system boundaries
closed system
energy can be exchanged but matter cannot
isolated system
no matter or energy crosses system boundaries
how is energy exchanged
heat exchange
heat
energy transferred between systems from temp diff
what is heat measured in
joules
zero law of thermodynamics
heat spontaneously flows from high temp to lower until equilibrium
room temp
25C
body temp
37
is there heat flow at equilibrium
there is no heat flow at equilibrium
chemical potential energy
energy of a substance due to temperature
potential energy diagram
shows change in potential energy in a system as reacting to products
heat of rxn (q)
heat released or absorbed during a chem rxn
ΔH
qmolrxn
enthalpy
ΔH
activation energy
energy inputed to start rxn
thermochemical equations
include value for heat absorbed or released when a rxn occurs
specific heat capacity
energy needed to raise temp of 1g of substance by 1C or 1K
units of specific heat capacity
J/gC or J/gK
what does a lower heat cap mean
easier to heat up
calorie
amount of energy needed to raise 1g of water by 1c or 1k
specific heat of h20
4.18
heat capacity
amount of heat needed to raise or lower the temp of a whole substance by 1C
state functions
independent of how the changes take place
volume, temp, ΔH, pressure, etc
bond energy/enthalpy
energy absorbed when bodns are broken
when is bond energy endothermic
breaking
when is bond energy exothermic
for forming
relationship between bond energy and stability
the higher the bond eneryg, the more stable the bond
how is bond energy tabulated
positive values
rules for calculating ΔH from bond enthalpy
draw lewis structures for both reactants and products
calculate total amount of energy absorbed to break bonds (psoitive)
calculate amount of energy released when bonds of products form (negative)
ΔH is the difference between these.values
what kind of bond does N2 have
triple
what kindo f bond does 02 have
double
hess’s law of heat summation
if a rxn is carried out in a series of steps, ΔH for the net rxn will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy charges for the individual steps
rules for manipulating paths with hess’s law
if a rxn is reversed, the sign of ΔH is too
if coefficients in a balanced eqn are multiplied or divided by an integer, so are the ΔH values
Formulas cancelled from both sides of eq must be substances in identical physical states
standard state
set of criteria that allows us to study rxns under same conditions
standard heat of rxn (ΔHrxn)
1 atm, 25C
standard formation rxns
rxn that forms exactly 1 mol of a compound from its elements in standard state
standard state of an element
most stable form of an element at standard state
what is carbon anturally found as
graphite
standard enthalpy of formation
amount of energy absorbed or released qhen forming 1 mole of a compound from elements in their most stable form at standard state
baseline for comp
methods for calculating enthalpy
calorimetry
ΔHf
hess’s law
why do elements form bons
to become more stable
lower energy means more stability
in nature, things go towards lower energy
energy is loewr bc released when bond is formed
total energy of universe
0…?
methods for calculating enthalpy
calorimetry - mcΔT → kJ/mol rxn
Δ°Hf
Hess’s law