Pharmacodynamics
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
3-D structure of drug/receptor, chemical reactivity, and affinity for lipids/water
What influences drug-receptor interactions? (3)
Reversible (Drug-R Bonds)
Hydrogen, ionic, hydrophobic/VdWaals
(Reversible or irreversible?)
Irreversible (Drug-R Bonds)
Covalent bonds, rare
(Reversible or irreversible?)
Agonists (I)
Drug class binds to and alters activity of receptor, mimicking endogenous ligand
Full, partial, inverse
(3) subtypes of agonists
Full agonist
Agonist produces maximal effect similar to endogenous ligand
Partial agonist
Agonist produces submaximal effect similar to endogenous ligand
Reversibly, full agonist
Partial agonist
Bind __ (reversibly/irreversibly) to agonist site
ONLY do their function in absence of a __ __ (drug)
Inverse agonist
Agonist produces negative effects by inhibiting constitutive activity; Stabilize the inactive receptor conformation
Antagonists (I)
Drug class binds to and inactivates receptor “blockers/inhibitors”
(General class)
Competitive and non-competitive
(2) subtypes of antagonists
agonists, action
Antagonists prevents the action of __, but DO NOT have an __ on their own (like agonists)
Competitive antagonist
Antagonist binds to active site reversibly
Agonists, can, right, agonist potency, efficacy
Competitive Antagonist
Compete with __ for binding to receptor active site
Blockage __ (can/not) be overcome by increasing concentrations of agonist (E50)
Such increase in E50 shifts dose-response curve to the __
Reduces __ __
__ unchanged
right, no change
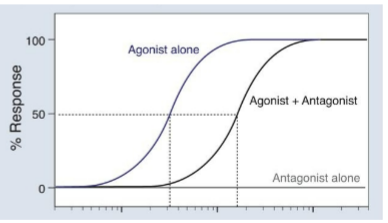
Competitive antagonist curve
Parallel shift in EC50 to the __
With __ __ in maximum response
Competitive Antagonists
Competitive/Non-C Antagonists
Non-competitive Antagonists
Competitive/Non-C Antagonists
Irreversibly, reversibly, irreversibly
Non-Competitive antagonists:
Either bind to active site __
bind at allosteric site __ or __
(Reversibly/irreversibly)
Pseudo-irreversible
Non-competitive antag. binding without a covalent bond may be reversible, however tight bind means dissociation is very slow
Not, efficacy
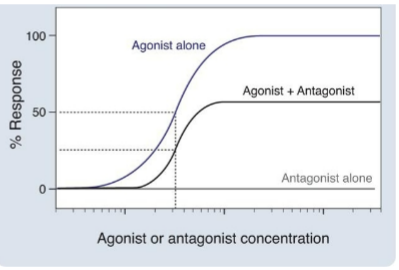
Non-Competitive Antagonists
Blockage __ (can/not) overcome from increasing concentrations of agonist
Decreases __
Downward, no change
Non-competitive antagonist curve
__ shift in maximal response /efficacy
__ __ in EC50
Neutral Antagonists
Most of this drug class have no intrinsic efficacy (cannot activate Rs)
Allosteric Modulators
Enhance/inhibit agonist action at different site than agonist binding site
Activator, inhibitor, not
Allosteric Modulators
Allosteric __ = facilitate agonist action, allosteric
Allosteric __ = Inhibit agonist action, allosteric
*Effects __ (can/not) be overcome by increasing concentration of agonist
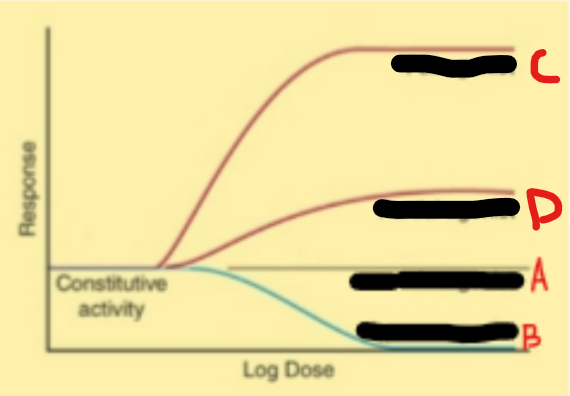
Constitutive Activity
Basal level of physiologic response in absence of agonist
Constitutive Activity drug curve
Effect of receptor alone, baseline activity
Intrinsic Activity
Ability of drug to stabilize active state and produce a response
Intrinsic Activity drug curve
Effect of drug + receptor
Neutral Antagonism
Indicates antagonists have 0 intrinsic efficacy
Intrinsic Activity drug curve
No response from antagonists alone
Concentration, maximal
Receptor Occupancy Theory
As drug __ increases:
Drug effect increases until some __ effect occurs
EC50
Drug concentration necessary for which half-maximal effect/response occurs
Kd
Drug concentration which half-maximal R binding occurs
Binding, low, binding
Receptor Occupancy Theory
__ of drug to Rs increases until all of Rs are occupied
Higher affinity = __ Kd
lower concentrations of drug needed to have drug __ to R
Graded Log Dose-Response Curves
Indicate maximal efficacy of drug in single person (curve)
Action/response, continuous
Graded Log Dose-Response Curves
Y-axis - __/__ as a __ variable
Efficacy
Magnitude of a response a drug causes when it interacts with receptor
Independent, complexes
Efficacy
__ (dependent/independent) of binding affinity
Dependent on number of drug-receptor __ formed and intrinsic efficacy of drug
Dependent, coupling, more
Potency
__ (dependent/independent) of binding affinity
Dependent on number of drug-receptor __ to physiologic response (intrinsic efficacy)
Lower EC50 = __ potent
Potency
Amount or concentration of drug necessary to produce particular effect
antagonist, inverse agonist, full agonist, partial agonist
Agonists vs antagonists
Quantal dose-response curves
Indicate the potential variability in responsiveness of individuals relative to populations
Binary, ED50, TD50, LD50
Quantal dose-response curves
Defined response is __ (does or does not occur pattern)
Used for determining __ (median effective dose), __ (median toxic dose), __ (median lethal dose)
% of individuals responding to drug
Y-axis of Quantal dose-response curves
Therapeutic Index (TI)
Indicates relative safety of drug
TD50/ED50
TI =
Safer drug
Higher TI means a….
Therapeutic Window
Dose range between minimal therapeutic response and minimal toxic response are observed
Tolerance
Gradual reduction in drug effects over days/weeks of drug exposure
Higher, clearance, endocytosis
Tolerance
__ dose required to produce given response
Mechanisms - Enhanced __, __
Tachyphylaxis
Rapid desensitization to drug effects in seconds to minutes
Not, molecular, phosphorylation, 3D, uncoupled, depletion
Tachyphylaxis
Higher dose may __ improve responsiveness, cells make __ adjustments
Mechanisms
Receptor __
endocytosis, __ modification
__ 2nd messenger
__ of vesicle
Down, desensitization, up, sensitization
Chronic agonist exposure results in receptor __-regulation or __
Chronic antagonist exposure results in receptor __-regulation or __
Receptor trafficking
Movement of receptors between plasma membrane and internal membrane-bound compartments
Lysosomes, plasma membrane
From receptor trafficking:
Internalized Rs may be degraded in __ or shuttled back to the __ __