object localization
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is object localization
approaches for deriving 3D information from 2D images
what are the two different techniques of object localization
right angle technique
tube shift technique
what is the right angle technique
ID position of object relative to surrounding anatomic landmarks on both projections
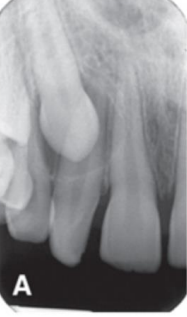
in the right angle technique, the periapical localizes in the
MD and SI dimensions
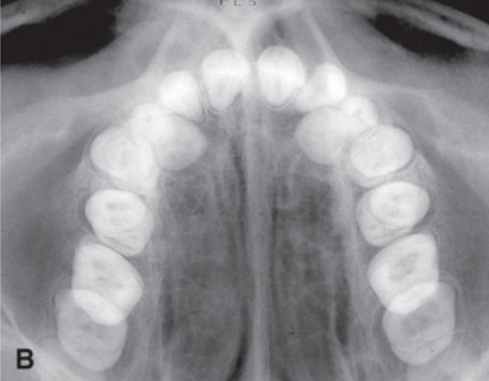
in the right angle technique, the occlusal localizes in the
MD and BL dimensions
what is the tube shift technique
uses the change in relative positions of two seperate objects that occurs when the image projection angle is changed- beam angulation changes opposite to the direction of the tube movement
what is the SLOB rule
SL: same lingual- lingual objects shift is the same direction as the tubehead
OB: opposite buccal- buccal objects shift opposite direction from the tubehead
if the object does not move w respect to reference object, it lies at the same depth (same vertical plane) as the reference object
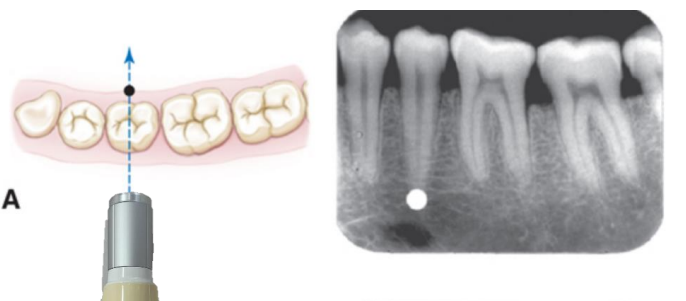
where do we expect this object to shift when the tube is moved mesially
mesial
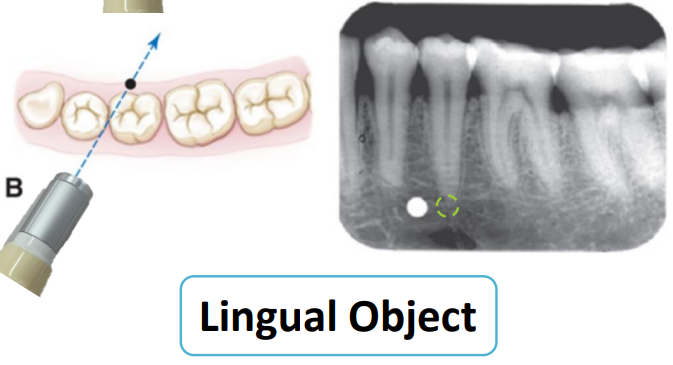
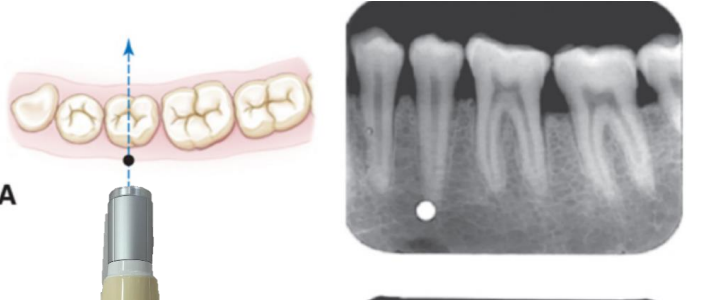
where do we expect this object to shift when the tube is moved mesially
distally
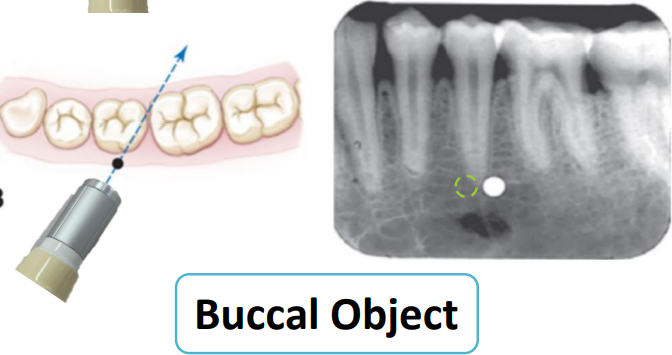
what should you use as a reference to determine the direction of the tube head shift
anatomy
how does distance play a role in the tube shift technique
the farther the object from the reference, the more the object moves
what are steps to take to identify where an object of interest is relative to a reference point
identify reference structure
identify tube shift
identify how object shifted
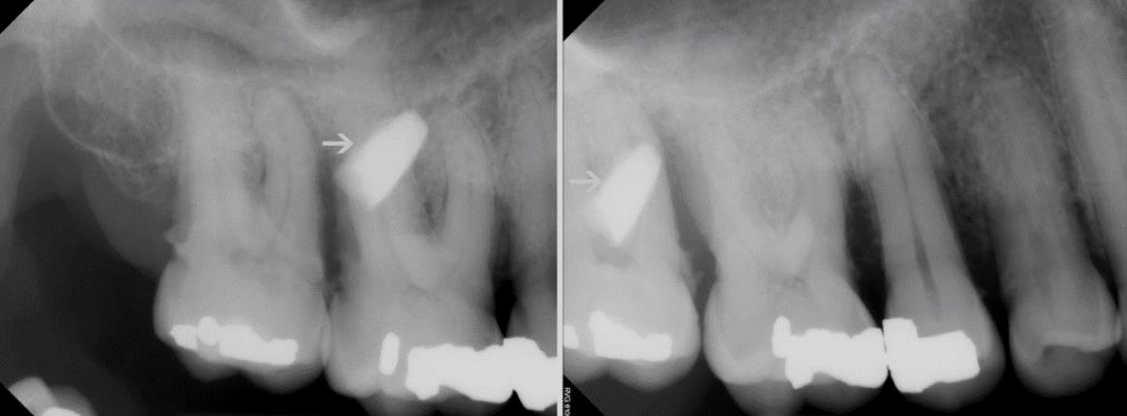
where is the opaque foreign object relative to #3
object is B to #3
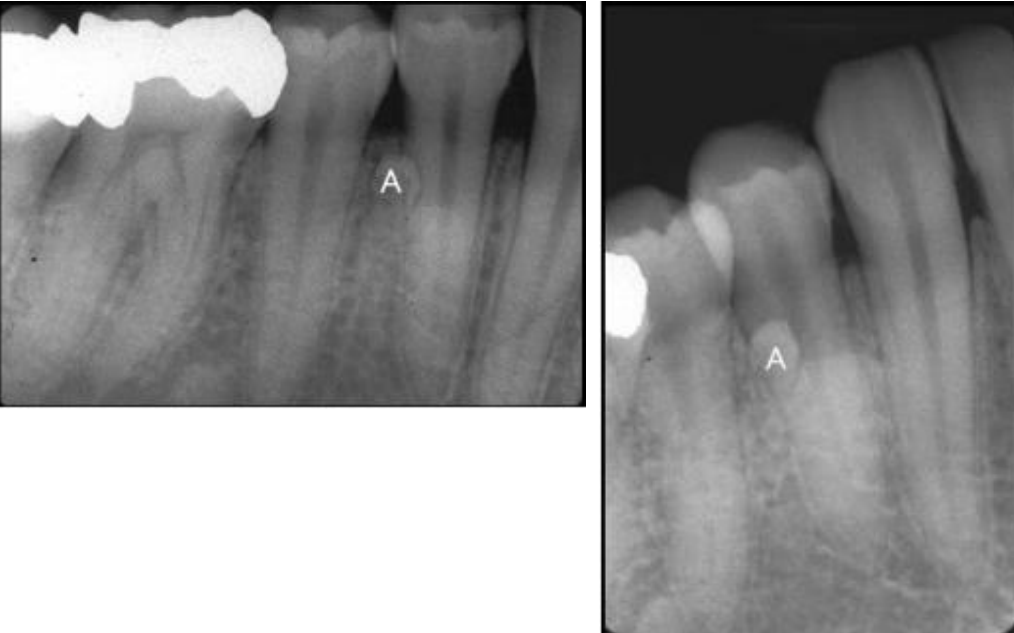
where is the supernumerary tooth A relative to #28
lingual
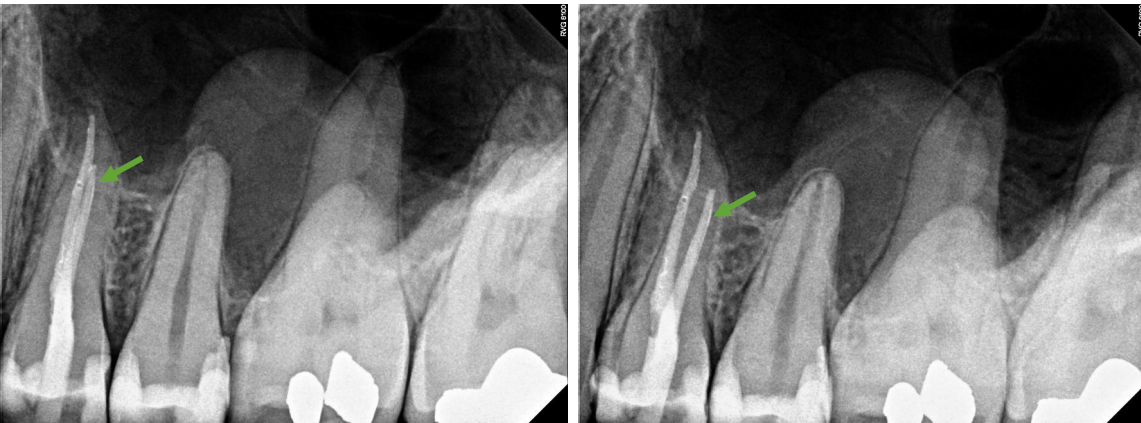
which RCT of #12 is indicated by the green arrow
buccal
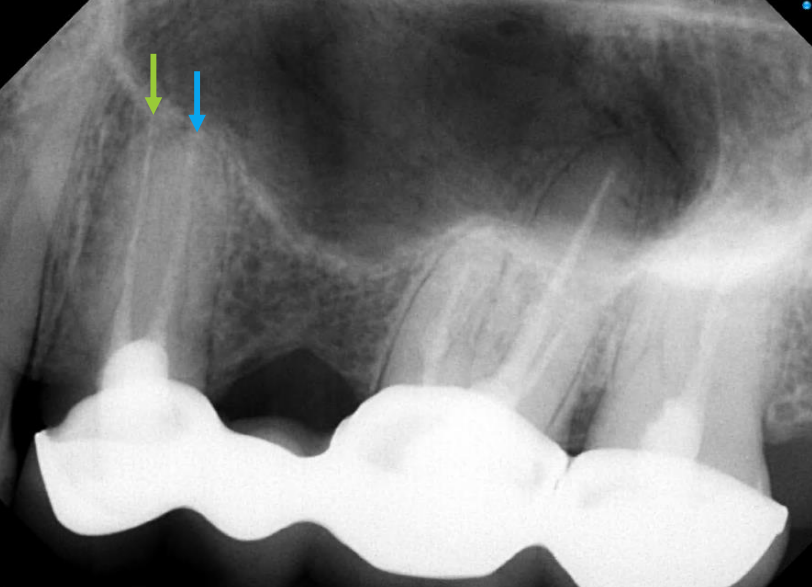
which root of #12 is indicated by the blue arrow
palatal/lingual (L root of #14 is projected closer to the DB root so this means the tube head is also coming from distal→ #13 distal root is the palatal root)
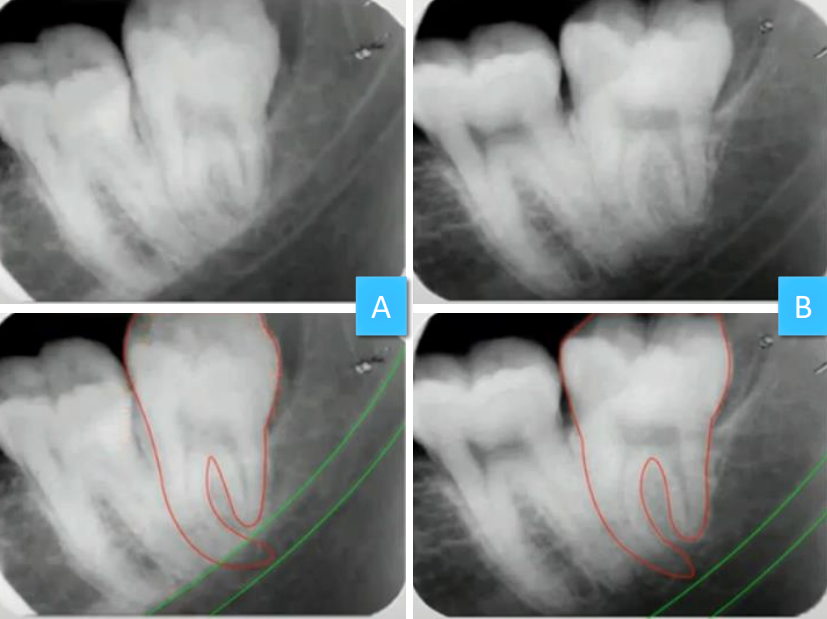
where is the mandibular canal relative to the apices of #17
lingual
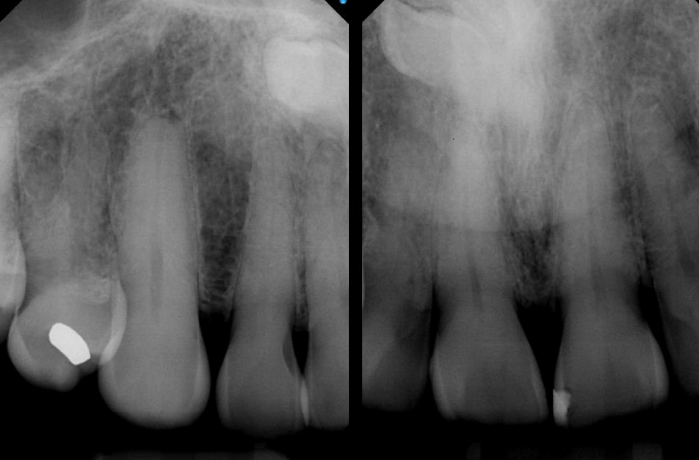
is the crown of the supernumerary tooth facial or palatal to the apex
facial