ap test 4
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
endocrine system
communicates through the release of chemical messengers like hormones in the blood
nervous system
commuicates through electrical and chemical to send messages cell to cell
Three steps of the nervous system
sense organs get stimulated by changes in both the body and environment then send messages back to the CNS
CNS, which is the brain and spinal cord, process the information and responds in the correct manor
CNS issues commands to the muscles and glands to carry given response
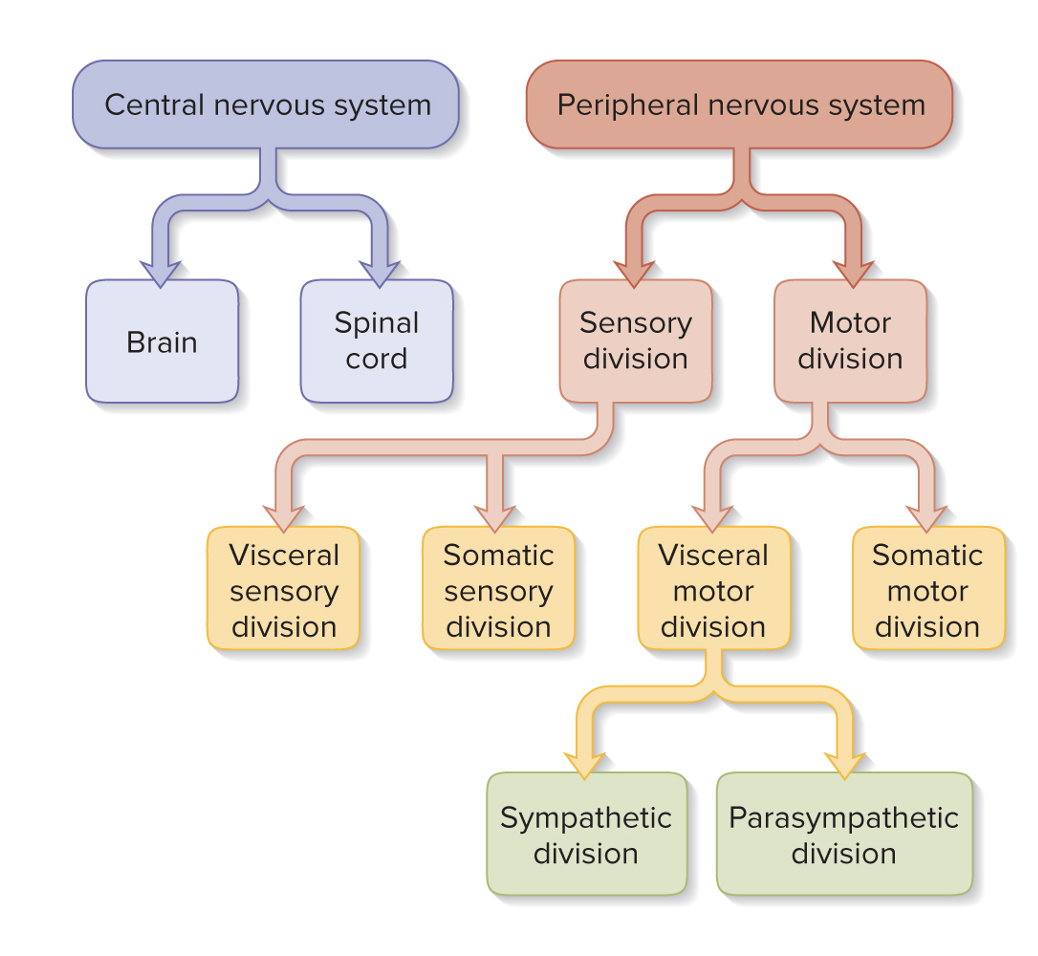
Two subdivisions of nervous system
CNS (spinal cord and brain) and PNS (everything else)
PNS is made up of two things
Nerves and ganglion. Nerves are a bundles of axons (nerve fibers) wrapped in fibrous ct that carry electrical impulses and ganglion are clusters of neuron cells (somas) that acts as processing centers.
sensory or afferent division of PNS
Somatic: carries signals from muscles or bones or skin to cns
Visceral: carries singals from the visera like heart, lungs, kidney, stomach
Motor efferent division of PNS
Somatic: Carries the CNS signals to muscles or skin aka voluntary
Visceral: Carries CNS signals to the heart or lung or bladder aka involuntary
PNS motor or efferent division of visceral has two divisions
sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest)
Helpful Picture
Excitability
responds to environment changes (stimuli)
Conductivity
Can produce electrical signal that travels down nerve fibers (axon) to other cells
Secretion
Nerve fiber ends called axon terminals can release chemical neurotransmitters that affect other cells
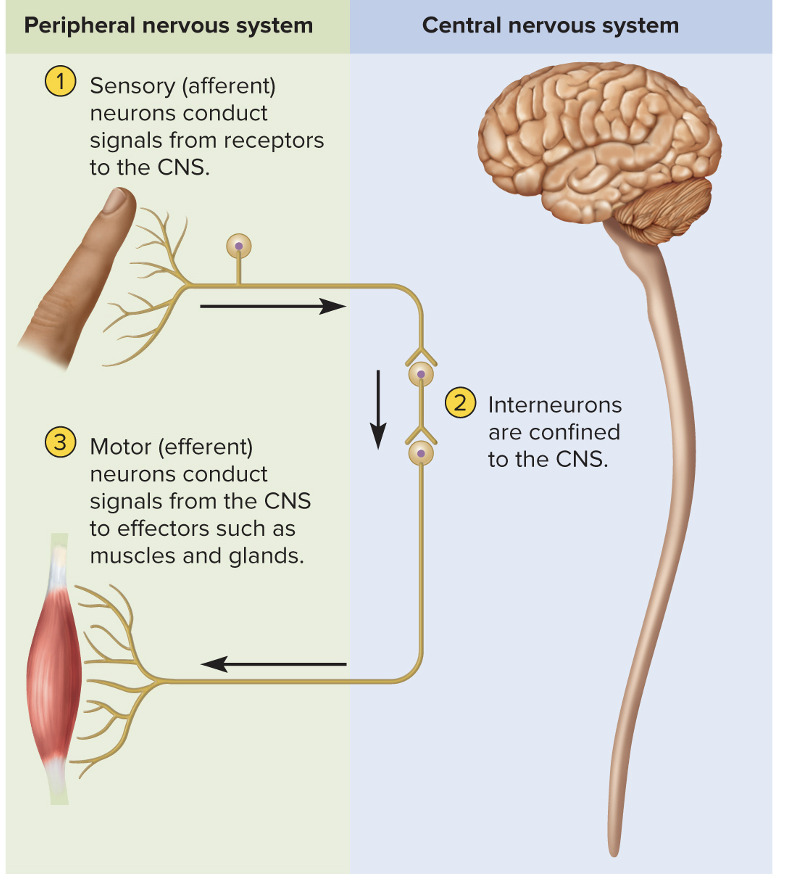
Sensory or Afferent
Detect then report to CNS
Interneurons
90% of all neurons and lies in the CNS. It is the bridge between the motor and sensory and gets the signals then makes the decisions
Motor or efferent neurons
Sends out the signals to the muscles or glands from CNS
Helpful Pic
Parts of Neuron
Soma, Nucleus, cytoplasm, dendrites, axon, axon terminals, and myelin sheath
Multipolar neuron
One axon with many dendrites (mostly in CNS and interneurons)
Bipolar neuron
one axon and one dendrite (Nose, retina, inner ear) = sensory
Unipolar neuron
singe process away from soma (Sensory cells from skin to spinal cord)
Anaxonic neuron
No axon (Retina, brain, adernal gland)
anterograde transport
Down the axon to the terminal away from soma (use Kinesin)
Retrograde transport
up the axon returning to soma (use Dynein)
Fast anterograde transport
Organelles, enzymes, synaptic vesicles, and small molecules
Fast retrograde transport
Recycled materials and hijacked by pathogens like rabies, herpes and tetanus.
Slow axonal transport
Stop-and-go movement and always anterograde
Glia
binds neurons, makes framework, cover mature neurons, gives precision
Oligodendrocytes
form myelin sheets in CNS that increase the speed
Ependymal cells
line internal cavities like brain and secrete cerebrospinal fluid
micro gila
phagocytes that develop white blood cells and concentrate in damaged areas
Astrocytes
most abundant gila and covers brain. They…
Create supportive framework
Form the blood–brain barrier
Monitor activity;
Regulate blood flow to match metabolic need
Convert glucose to lactate
Secrete nerve growth factors
Communicate electrically with neurons.
Regulate chemical composition of tissue fluid
form hard scar tissue
Two PNS gila
schwann cells, which form myelin sheets and satellite cells, which surround the somas
Myelin sheath (Oligodendrocytes in CNS & Schwann cells in PNS)
Insulation around the axon and increases action potential conduction velocity, produce myelin
Myelination
Completed in late adolescence and is why dietary fat is important when growing up
Neurilemma
thick outermost coil of myelin sheath (PNS), which contains Schwann cell nucleus
____ Schwann cells (PNS) or oligodendrocytes (CNS) are needed to myelinate one axon
Many
Nodes of ranvier
gaps between the segments of wrapped axon (internodes)
internodes
myelin covered axon
Initial segment
bare section of axon between the axon hillock and the first glial cell
What has large amount of voltage sodium passages that trigger APs
axon hillock, initial segment, trigger zone (most sodium passgae), help initiate the signals for AP
the larger, more surface area, or more myelin of a axon allows it to
conduct signals faster
PNS can be regenerated if there is
soma and some neurilemma
Steps of PNS regeneration
Axon distal to the injury degenerates
Macrophages clean up tissue debris
Neurosoma swells
nucleus moves off center
Axon stump sprouts multiple growth processes
Schwann cells, basal lamina, neurilemma form regeneration tube
Regeneration tube guides regrowth to original destination
the neuroma shrink down
could take 2 years or more
four major chemical categories of neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine, Amino acids, Monoamines, Neuropeptides
Acetylcholine
Acetyl acid and choline
amino acids
glycine, glutamate, aspartate, and g-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Monoamines which are synthesized from amino acids
catecholamines—epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopaminee
Neuropeptides which are chains of 2 to 40 amino acids that get stored in secretory granules
cholecystokinin and substance P
Gases
Nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide
Purines
adenosine and ATP
Excitatory Cholinergic Synapse
Use acetylcholine (ACh), which ACh diffuses and binds to postsynaptic receptors then the receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that open and allow Na+ and K+ across the membrane leading to depolarization and action potential
Inhibitory GABA-ergic Synapse
Action potential leads to release of GABA, which binds to Cl, then hyperpolarizes and less likely to fire.
Excitatory Adrenergic Synapse
Monoamines and neuropeptide bind to g protein that then activate seconder messager system
Clearance of the neurotransmitter to stop can occur in three ways
Degradation(Enzyme), reuptake(recycled), and diffusion(go away)
Neuromodulators are chemicals that
get secreted by neurons that have long term modulatory effects on groups of neurons such as altering the rate of neurotransmitter synthesis, release, reuptake, or breakdown
Enkephalins and endorphins
neuropeptides or chains of amino acids that act as neuromodulators to inhibit pain signals in the CNS
Chemical synapses
allow for decision making, but they travel slower
Glutamate and aspartate produce
EPSPs (depolarize)
Glycine and GABA produce
IPSPs (hyperpolarize)
Acetylcholine (ACh) and norepinephrin
ACh inhibits heart
Norepinephrine stimulates heart
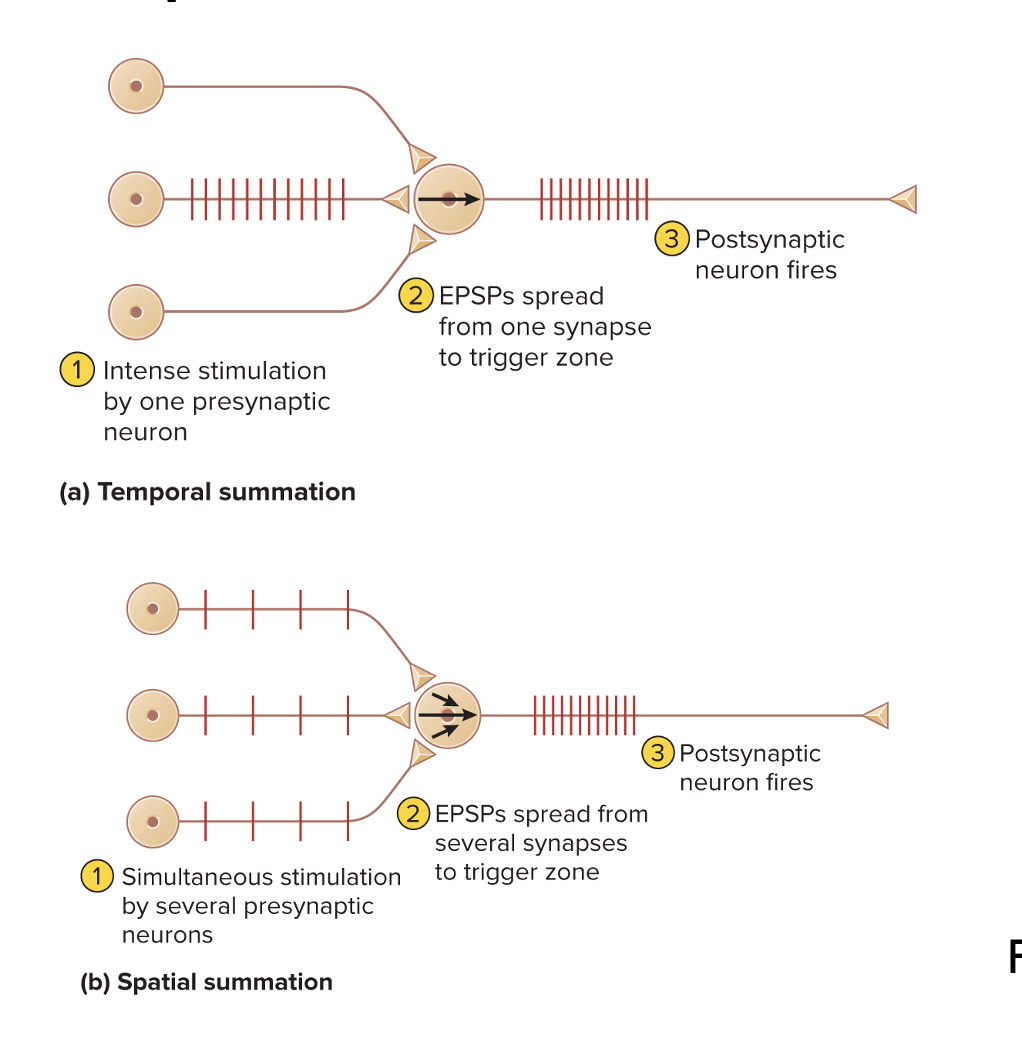
Summation
is the process of adding up postsynaptic potentials and responding to their net effect
Temporal summation
Occurs when a single synapse generates EPSPs so quickly that each is generated before the previous one fades
Spatial summation
Occurs when EPSPs from several different synapses add up to threshold at an axon hilloc
Helpful image
Presynaptic facilitation
when one presynaptic neuron enhances another one
Presynaptic inhibition
when one presynaptic neuron suppresses another one or halts unwanted transmission
Conduction
nerve fibers conduct sensory and motor info up and down the spinal cord
neural integration
spinal neurons receive information from sources and use it for a output
locomotion
This involves central pattern generators, which are groups of neurons that coordinate repetitive sequences of contractions for walking
reflexes
involuntary response to stimuli
Cauda equina
bundle of nerve roots that occupy the vertebral canal from L2 to S5
Meninges
three fibrous membranes that enclose the brain and spinal cord
Dura mater
Forms loose-fitting sleeve (dural sheath) around spinal cord that is thick
Arachnoid mater
arachnoid membrane adhering to dura (middle layer under dura)
Pia mater
transparent membrane that follows contours of spinal cord and fuses dura (deepest layer)
Gray matter
dull in color (no myelin) that contains neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and proximal portions of axons
White matter
white color due to myelin and has axon bundles
Two posterior (dorsal) horns of grey matter
receive sensory nerve fibers
Two anterior (ventral) horns of grey matter
contain cell bodies of somatic motor neurons
Left and right sides connected by
gray commissure
Know this
Poliomyelitis
Destroys motor neurons in brainstem and anterior horn of spinal cord leads to muscle pain, weakness, and loss of some reflexes, then followed by paralysis, muscular atrophy, and respiratory arrest
ALS or Lou Gehrig disease
Destruction of motor neurons and muscular atrophy that leads to sclerosis (scarring) of lateral regions of the spinal cord
Astrocytes fail to reabsorb the neurotransmitter glutamate from the tissue fluid which accumulates to toxic levels
Early signs: muscular weakness; difficulty speaking, swallowing, and using hands
Sensory and intellectual functions remain unaffected
Endoneurium
loose connective tissue external to neurilemma - covers whole axon (nerve fiber)
Perineurium
layers of overlapping squamous cells that wrap fascicles - bundles of nerve fibers
Epineurium
dense irregular connective tissue that wraps each nerve
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves
8 cervical (C1 to C8)
12 thoracic (T1 to T12)
5 lumbar (L1 to L5)
5 sacral (S1 to S5)
1 coccygeal (Co1)
Posterior (dorsal) root
Has cells sensory bodies sending input to spinal cord (PNS) located at Dorsal root ganglion
Anterior (ventral) root
motor output out of spinal cord
Reflexes
quick, involuntary, stereotyped(same every time) reactions of glands or muscle to stimulation
proprioceptors
muscle spindles that sense organs to monitor position and movement of body parts (very abundant in hands)
Stretch (myotatic) reflex
when a muscle is stretched, it “fights back” and contracts
Reciprocal inhibition
reflex phenomenon that prevents muscles from working against each other by inhibiting antagonist when agonist is excited
Intersegmental reflex
one in which the input and output occur at different levels (segments) of the spinal cord like Pain in foot causes contraction of abdominal muscles
Paraplegia
paralysis of both lower limbs
Quadriplegia
paralysis of all four limbs
Hemiplegia
paralysis on one side of the body
Paresis
partial paralysis or weakness of the limbs
ionotropic
direct and fast and short acting (ligand gate)
metabotropic
indirect and slow but long lasting (G protein)