VM 525 Final Exam
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Which of the following control(s) and coordinate(s) ruminant forestomach motility?
Vagus and ENS
What specific compartment of the forestomach initiates ruminal contractions?
Reticulum
What byproduct of microbial fermentation is the main source of energy for ruminants?
Volatile fatty acid
What happens to most proteins fed to ruminants?
Broken down by ruminal microbes
Which of the following classes of organisms is NOT considered part of the microbiome of the ruminant forestomach?
Viruses
What are the three principal motility patters of the ruminant forestomach?
Mixing, rumination and eructation
What are the major end products of microbial fermentation in the ruminant forestomach?
Volatile fatty acids
Microbial proteins
NH3
Gases (methane and CO2)
How does rumination contribute to the digestion process in ruminants?
Regurgitating and rechewing previously ingested food allows for further breakdown and increased surface area
List the 2 major intestinal structures located in the right flank of the ruminant
Cecum and duodenum
Which lymph nodes are palpable in normal cattle?
Parotid
Subiliac
Prescapular (superficial cervical)
Mammary (superficial inguinal)
Which of the following is true of adult ruminant saliva?
Contains urea, large volume per day, alkaline pH
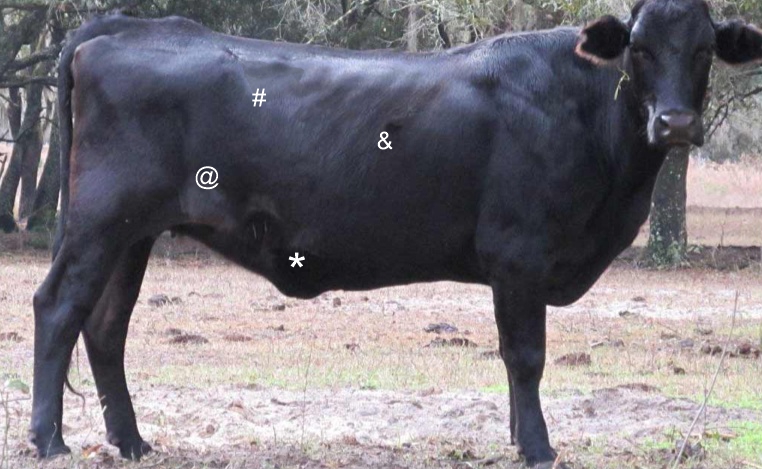

Which of the following symbols corresponds to the paralumbar fossa?
#
How much of the volume of blood entering the liver is provided by the hepatic artery?
~25%
The majority of nutrients arrive in the liver via the
Hepatic portal vein
The hepatic cells that synthesize albumin and clotting factors are the
hepatocytes
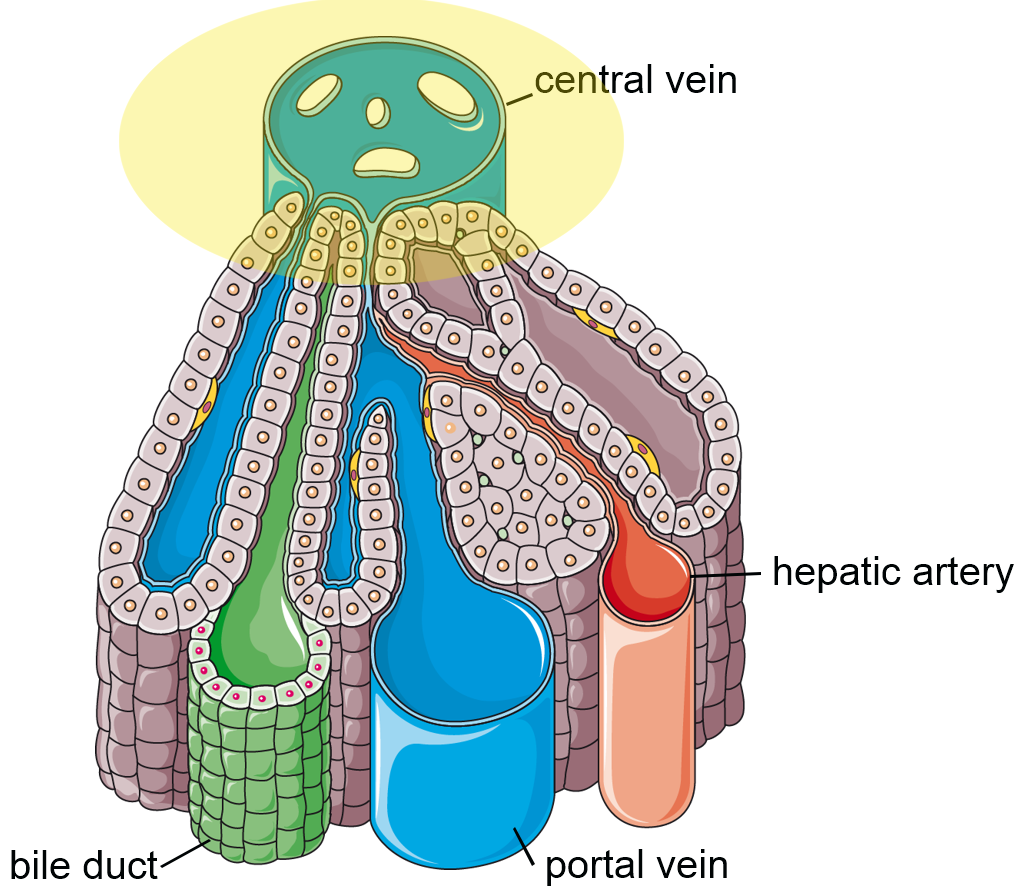
Diagram of a hepatic lobule. What is the relative oxygenation of the area highlighted in yellow?
Lowest of the hepatic lobule
Which of the following is NOT a zymogen (=proenzyme)?
A. Trypsin
B. Chymotrypsinogen
C. Proelastase
D. Trypsinogen
A. Trypsin
Cholecystokinin (CCK) does what?
Stimulates pancreatic secretion of proenzymes
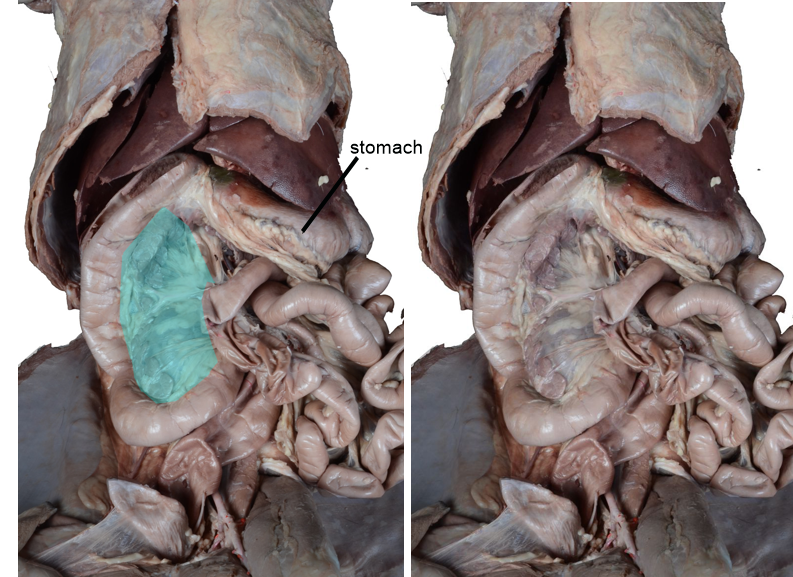
The peritoneal/mesenteric structure highlighted in blue in the left image is part of the
mesoduodenum
The ends of the greater omentum attach to the greater curvature of the stomach and the
Dorsal body wall
Which area is more likely to be affected by decreased oxygen (decreased blood flow)?
A. Centrilobular
B. Periportal
A.
Where would direct acting toxins absorbed from the intestine damage the liver?
A. Centrilobular
B. Periportal
B.
T/F: Increased blood levels of hepatocellular enzymes such as ALT, AST and SDH are indicators of liver failure (severe dysfunction)
False - indicators of liver damage
Which factors stimulate bile and pancreatic secretion? Select all that apply
A. Increased pH of duodenal contents
B. The arrival of peptides in the lumen of the duodenum
C. Arrival of starches in the duodenal lumen
D. Decreased pH of duodenal contents
E. The arrival of fats in the lumen of the duodenum
B. D. And E.
Drug metabolism by hepatocytes is maximal in the
Centrilobular zone
Unconjugated (=free) bilirubin is derived from
Heme, in turn derived from hemoglobin released from dead RBCs
Ammonia derived from degraded amino acids is: select all that apply
A. Converted to urea in the liver and secreted mostly in the saliva of ruminants
B. Converted to urea in the liver and mostly excreted by the kidneys in cats and dogs
C. In horses, converted to urea in the liver and mostly secreted into the colon
D. Filtered from the blood in the liver and secreted into the bile and then into the feces
A B and C
Which of the following structures provides a large surface area for absorption in the small intestine?
A. crypts of lieberkun
B. lacteals
C. villi
D. rugae
C.
Where do the enterocytes at the tips of intestinal villi originate?
Undifferentiated columnar cells in the crypts
In the villus, relative oxygenation
Is greatest at the base of the villus and decreases towards the tip
What region of the abdomen is the liver in? the pancreas?
Cranial abdomen; the liver is specifically in the hypochondriac region (“below the [costal] cartilages”)
What structure(s) are usually the first to be seen on abdominal exploratory via the linea alba?
Fat in falciform ligament; greater omentum
Why is the duodenum more difficult to exteriorize in surgery than the jejunum?
Short mesoduodenum keeps it close to the dorsal body wall; the duodenocolic ligament anchors it to the descending colon
What do the vessels that supply and drain the spleen run in? Where do they enter the spleen?
Vessels run in the gastrosplenic ligament, a part of the greater omentum. They enter the spleen at the hilus
Where is the head of the spleen? The tail?
Head of spleen is very dorsal, on left side of abdomen caudal to stomach. Tail is more variable: depending on the state of the spleen, it can extend to the ventral body wall on the left side and even curl over the right side of the ventral abdomen.
Where is the body of the spleen?
Generally follows the outline of the greater curvature of the stomach
Where does the greater mesentery attach to the body wall?
Roof of abdomen
What are the borders of the epiploic foramen?
Caudal vena cava and portal vein viewed from the right side of the abdomen
What does the epiploic foramen lead to?
Omental bursa
Where do the diaphragmatic crura attach?
Ventral to the first 3-4 lumbar vertebrae
What are the three ways the small intestine provides this surface?
Mucosal folds
Villi
Microvilli
What parts of the intestine provide a barrier?
Gut microbiota
Mucus layer
Epithelial cells and tight junctions
Immune cells in lamina propria
Peyer’s patches
Secretory epithelial cells have been discussed, but what other cells reside in the crypts?
Stem cells and paneth cells
What are lacteals?
Fenestrated lymphatic vessels important for transport of absorbed triglycerides
Where does unconjugated bilirubin originate?
Heme released from dead or dying RBC
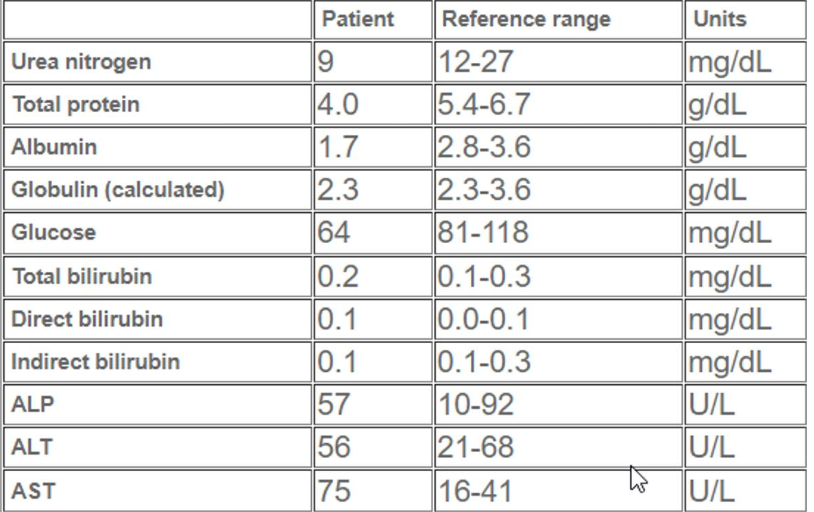
A dog presents with depression and anorexia. What can you conclude about it’s liver based on this lab data?
Loss of function
Which of these substances directly stimulate pancreatic secretion?
A. Ach, gastrin and histamine
B. Dopamine, norepinephrine and VIP
C. Ach, CCK and secretin
D. Gastrin, histamine and norepinephrine
C.
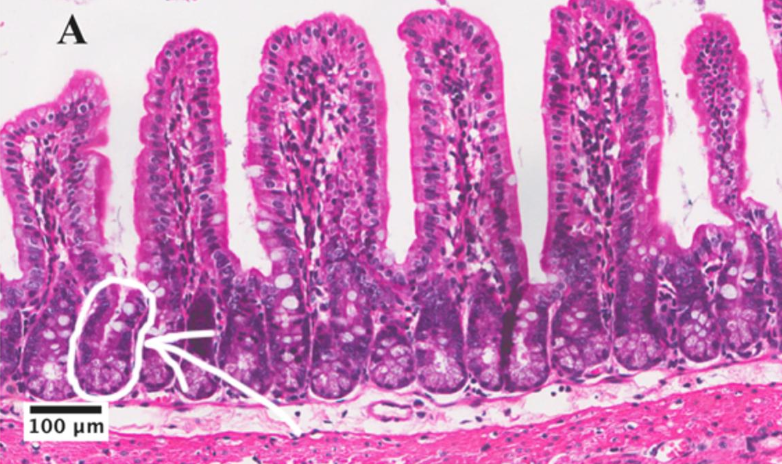
What is the structure surrounded by a while line and indicated by the arrow?
Crypt of lieberkuhn
What is the first step in lipid digestion and absorption?
Emulsification by bile
Where is the intestine are most bile salts reabsorbed from?
Ileum
What cell type does pancreatic lipase come from?
Pancreatic acinar cells
Why are micelles needed?
For water solubility
Where do chylomicrons form within the enterocyte?
Golgi apparatus
What enzyme initiates luminal digestion of proteins?
Pepsin
In what anatomic location are most polypeptide chains broken down into amino acids?
Intestinal brush border
Which of the following is NOT absorbed by sodium-dependent co-transport?
A. Glucose
B. Galactose
C. Fructose
Fructose
In what form can carbohydrates be absorbed from the enterocyte?
Monosaccharides
What vitamin is calcium absorption dependent on in the SI?
Vitamin D
What organs are supplied by the celiac artery?
Liver, stomach, pancreas, spleen, orad part of descending duodenum
Name the 3 main branches of the celiac artery and list the organs each of them goes to.
1. Left gastric: stomach (and a bit of the caudal esophagus)
2. Hepatic: liver, cranial/orad descending duodenum, cranial part of right lobe of pancreas
3. Splenic: spleen, stomach, left lobe of pancreas
What organs are supplied by the cranial mesenteric artery?
Intestines, from aborad part of descending duodenum all the way to the cranial/orad part of the left colon
What organs does the portal vein drain?
All intestines, stomach, spleen, pancreas
What organs or structures does the abdominal caudal vena cava drain?
Hind limbs, all pelvic structures, kidneys, adrenals
What lymphocenter drains most of the intestines?
Cranial mesenteric
What lymph nodes drain the hind limbs and the pelvis?
Medial iliac
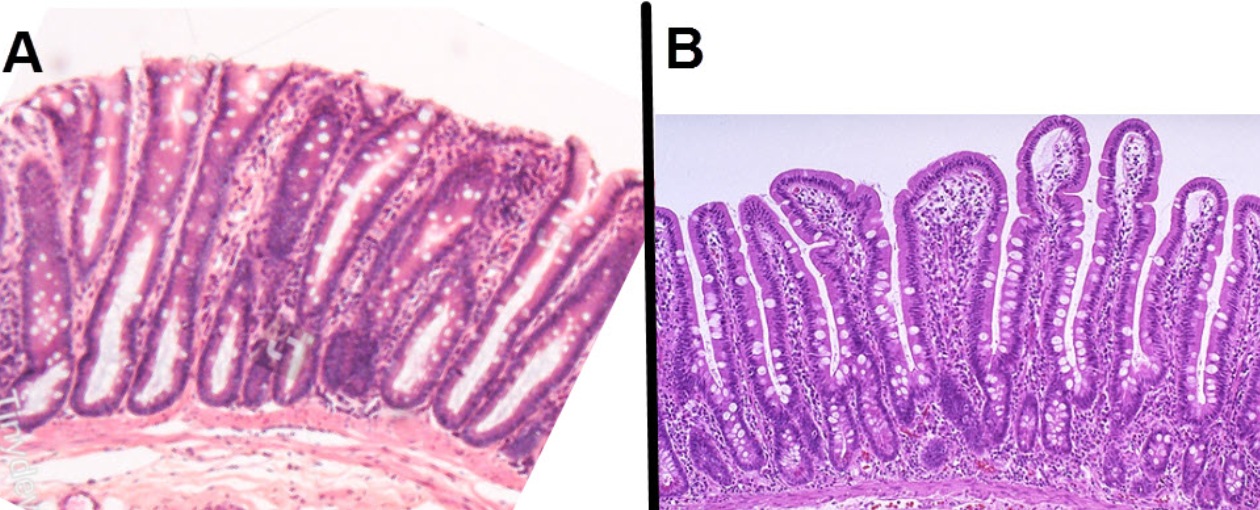
These 2 images have similar magnifications. Which of the 2 micrographs represents the colonic mucosa?
A
Which of the following branches of the aorta supply the stomach, spleen and liver?
Celiac
An artery supplying the caudal duodenum and pancreas would be called
Caudal pancreaticoduodenal
Which of the following (if present in that species) opens into the lumen of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla? Select all that apply
A. Pancreatic duct
B. Cystic duct
C. Accessory pancreatic duct
D. Common bile duct
A and D
What happens during the membranous phase of digestion?
Di and tri-saccharides are broken down into monosaccharides
How does glucose cross the apical cell membrane of enterocytes in the villi?
Na+ co-transport
How are bile acids absorbed in the small intestine?
Na+ co-transport
How and where do chylomicrons enter the systemic circulation?
Interstitial fluid of villi > lacteals > lymphatics > cysterna chyli > thoracic duct > large veins at or near thoracic inlet
The taeniae (plural of taenia) of the equine large intestine (FYIO also present in the pig) are
Thick bands of longitudinal muscle in the intestinal wall
Which of the following electrolytes are actively secreted by crypt cells?
Cl- and bicarbonate
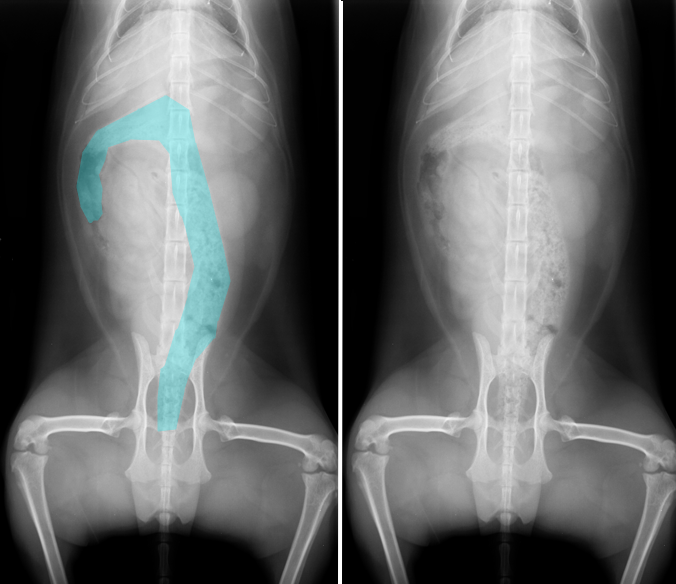
What structure is highlighted in blue in the left image below?
Colon
What path does a food particle in the equine ileum follow to reach the anus?
Ileocecal sphincter > cecum > Cecocolic orifice > ventral colon (right then left) > pelvic flexure > dorsal colon (left then right) > transverse colon > descending colon > rectum > anus
Rank the different parts of the digestive tract of a generic mammal based on microbial population (largest concentration of microbes = 1, smallest concentration of microbes = 4 ).
Cecum and colon > ileum > duodenum and jejunum > oral cavity > stomach
Which domestic mammal(s) have a spiral colon?
pigs and ruminants
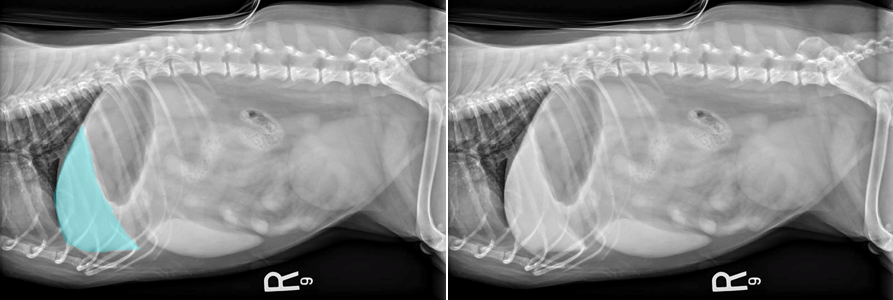
What structure is highlighted in blue in the left image below?
Liver
Which of the following statements is true of colonic function in all adult mammals?
A. Very little H+CO3 is secreted in the colon
B. AA are absorbed via co-transport with Na+
C. Glucose is absorbed via co-transport with Na+
D. Na+ and Cl- are the principal electrolytes absorbed in the colon
D.
Which of the following statements about fermentation in the cecum and large intestine (=hindgut) of horses is correct?
A. VFA are absorbed from both the equine hindgut and the ruminant forestomach
B. Urea is secreted in the equine large intestine neutralizes the acids produced during fermentation
C. The process of fermentation in the equine hindgut is essentially the same as in the ruminant forestomach
All of the above
T/F: Bicarbonate secretion is an important function of the colon
True
Similar to foregut fermentation, microbial fermentation in the hind gut of the horse leads to the absorption of
VFAs, water and Na+
Which of the following organs/structures is located on the right side of the abdomen in a normal dog or cat?
Descending duodenum
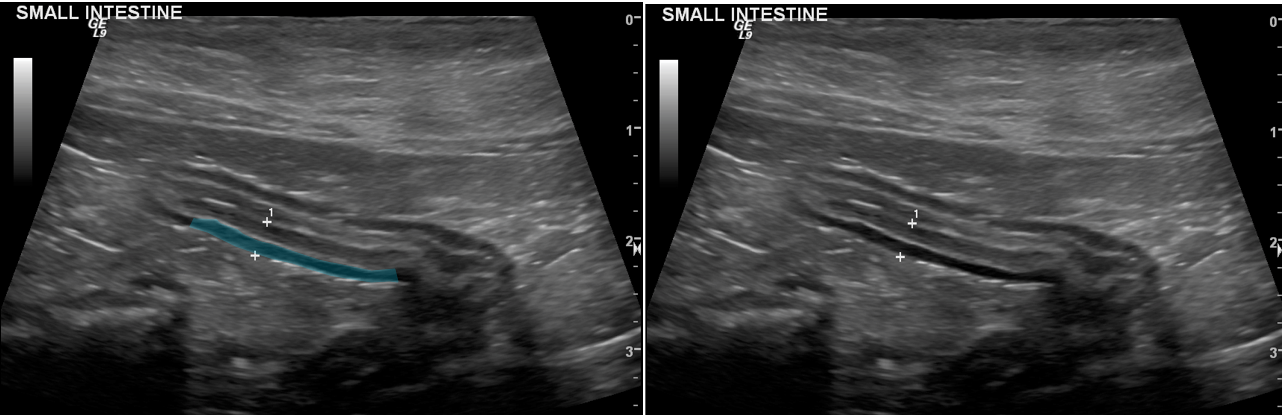
Longitudinal section through a loop of small intestine viewed with ultrasonography. The + sign labeled 1 is in the lumen of the loop. The unlabeled image on the right is for reference.
The hypoechoic area highlighted in blue in the left image below is the
Tunica muscularis
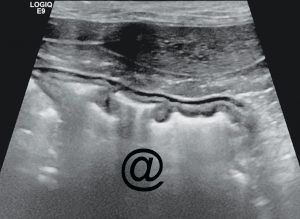
US of a normal feline abdomen (below), probe placed on the ventral abdomen, just caudal to the rib cage and to the right of midline. What is the structure/region labeled @?
Stomach
Where should you place your US probe to visualize the head of the spleen in a normal, healthy dog or cat?
Cranial left flank
In a normal ruminant, what part of the digestive tract should be located just deep to the abdominal wall in the right paralumbar fossa?
Descending duodenum
What is the SI adapted for?
Absorption and digestion
Which of the following can be absorbed intact by enterocytes in the SI?
A. Polypeptides
B. Sucrose
C. Lactose
D. Dipeptides
D
What first activates pancreatic zymogens after they are secreted into the lumen of the duodenum?
Chymotrypsin
Where are the enterocytes responsible for ion and water secretion located?
Crypts of lieberkuhn
What is the main channel responsible for secretion in the intestine?
CFTR
Cryptosporidiosis damages the tips of villi, leading to blunting and shortening of villi and loss of the brush border. Loss of the brush border results in loss of brush border enzymes and thus an inability to digest which substances?
A. Sucrose
B. Amino acids
C. Glucose
D. Lactose
A and D
What will happen if the intestinal lumen contains a lot of nutrients that cannot be digested and absorbed?
Water will be drawn into the lumen
Which of the following nutrients are absorbed intact by enterocytes?
A. sucrose
B. Amino acids
C. Ions such as Na, Cl
D. lactose
E. Glucose
B, C and E
Absorption of glucose and amino acids is dependent on
Na+ co-transport
Oral administration of a solution containing Na+, glucose, and amino acids will lead to
passive absorption of water following Na+, glucose and amino acids absorption
Absorption of nutrients via Na+ co-transport
Which of the following hormones or neurotransmitters stimulates gastric motility?
A. Gastrin
B. Secretin
C. Gastric inhibitor peptide
D. CCK
A.