titrations
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Explain the titration practical
1) use pipette to transfer 25 cm³ of sodium hydroxide solution into a conical flask. (Conical flask reduce the risk of splashing).
2) Add five drops of indicator E.G.methyl orange to the alkali in the conical flask
3)place a conical flask on a white tile so we can see the colour change more clearly
4)fill burette with sulphuric acid
5)Add acid to the alkaline until the solution is neutral once we start to see A colour change we now add the acid drop by drop until the solution is neutral. It’s important to swirl solution to make sure the acid and alkali mix
6)read volume of acid added from burette
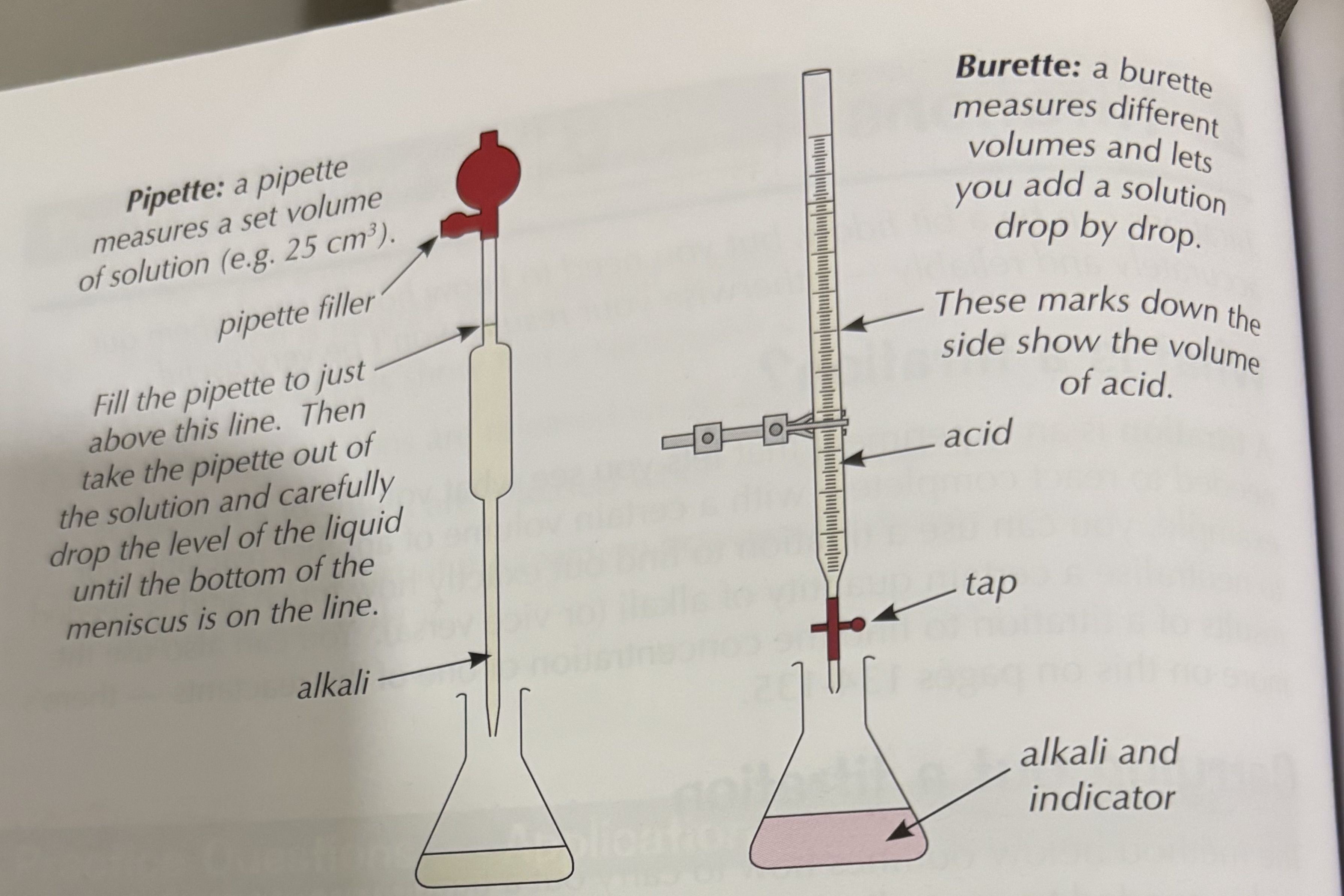
How should you read the volume of acid
When reading make sure eyes are level with surface of liquid . The surface of liquid naturally curves (meniscus is the curve ) always read burette at button of meniscus
What are universal indicators used for
Universal indicators is used to estimate the pH of a solution because it can turn a variety of colours. Each colour indicates a narrow range of pH values. It’s made from a mixture of different indicators. The colour gradually changes from red in acidic solutions to violet and alkaline solutions.
Why can’t you use universal indicators in an acid-alkali titration
Because the colour change is too gradual / doesn’t provide a sudden colour change so it will be hard to see the end point
What are good indicators and why?
Phenolphthalein, methyl orange and litmus are good indicators to use for titrations they are known as single indicators bc they only contain one colour changing compound, so have one distinct colour change at particular pH
What are titrations used for?
Titrations allow you to find unknown concentrations of acids or alkalis.
What is the 'end point' of a titration?
The end point is the point at which all of the acid or alkali is neutralised, and the indicator changes colour.
During a titration, why should the flask be placed on a white tile?
So that you can more easily see the colour change of the indicator, as the alkali or acid is neutralised.
During a titration, why should you continuously stir the flask?
So that the acid/alkali is evenly mixed and the colour all changes at once.
What colour is phenolphthalein in alkaline solution
Pink
What colour is phenolphthalein in acidic solution
Colourless
What colour is phenolphthalein in neutral solution
Colourless
What colour is methyl orange in an alkaline solution?
Yellow
What colour is methyl orange in an acidic solution?
Red
What colour is litmus in alkalis
Blue
What colour is litmus in acids
Red