Lactate Anaerobic Energy systems
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Steps in the Anaerobic Glycolytic System
Glycogen is converted to glucose by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase
Glucose is then broken down to pyruvic acid by enzyme phosphofructokinase → this is called anaerobic glycolysis
Pyruvic acid is then broken down by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase into lactic acid
Lactic acid denatures the enzymes involved in respiration meaning the muscle cells become slower are re-synthesising ATP
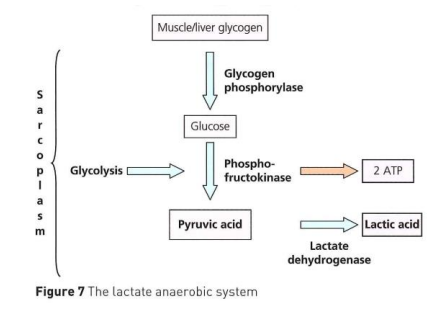
Summary of Anaerobic Glycolytic System
2 molecules of ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose breakdown
Takes place in sarcoplasm of muscle cell where there is no oxygen
Because its an anaerobic process, the pyruvic acid is broken down into lactic acid
The presence of oxygen is needed to break down lactic acid back into liver glycogen
What is OBLA?
Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation
Point at which lactate starts to accumulate in the muscle / blood / known as the lactate threshold
Starts at 4 mmol / litre
Occurs as body is unable to provide enough oxygen to break down lactic acid
Factors that affect OBLA
Intensity of exercise – higher intensity the faster OBLA occurs
VO2 max of a performer – higher the level the more delayed OBLA
Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) – closer the value to 1.00 quicker OBLA occurs
Muscle fibre type – if slow twitch fibres used, delays OBLA
What are the advantages of the Anaerobic Glycolytic system?
ATP can be re-synthesised very quickly
Lasts longer than ATP-PC systems
In the presence of oxygen, lactic acid can be converted back into liver glycogen
Can be used for a sprint finish
What are the disadvantages of the Anaerobic Glycolytic system?
Lactic acid is the by-product, the acid denatures enzymes involved in respiration meaning the muscle cells become slower at resynthesizing ATP
Can cause a lot of fatigue
Only a small amount of energy can be released from glycogen (5%)