Chapter 5 Biology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is taxonomy?
The science of naming and classifying organisms
What is binomial nomenclature?
Two word naming system
How did Linnaeus group species?
He grouped them according to their major physical characteristics (ex. number of legs or leaf shape).
Today we group organisms based on _______ __________
evolutionary relationships
3 Domains
Bacteria - common bacteria, Archaea - bacteria that live in extreme environments, Eukarya - all eukaryotic organisms
4 Kingdoms of Classification
Plant, Animal, Protist, Fungi
What was Charles Darwin’s contribution to science
An English naturalist. He traveled the world for years studying and collecting specimens.
2 important ideas darwin proposed
Evolution occurs - he proposed that species change over time instead of being created, and then remaining unchanging
Evolution occurs because of Natural selection - individuals with beneficial traits produce more offspring. Over time this changes the traits in the population.
Did Charles Darwin discover evolution?
HOW it happened
Where did Darwin travel?
Galapagos Islands and South America
Darwin’s observations on his voyage
1.He found fossil seashells on the top of mountains.
2. Found fossils that should be a low elevations
3.. Experienced an earthquake and saw a sea floor rise up
4.. He found fossils of extinct animals that were both similar and different from modern day animals. He wondered if they could be related.
What organisms Darwin study on the Galapagos Islands
Finches and Tortoises
4 conclusions, what are they of theory of Evolution
Variation exists in every population.
Populations produce more offspring than can survive.
Resources are always limited so some individuals will be more successful than others.
Individuals that are more “fit” will have more surviving offspring. Their traits will become more common in the population.
What are fossils?
the preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past
What does extinction mean?
permanent loss of a species from the ecosystem
What are homologous structures
same structure, different function
What are analogous structures
Body parts that share a common function, but not structure
What did Darwin conclude about comparing embryology
more similar developmental stages indicated more recent common ancestry.
What is a vestigial structure
is one that is reduced in size and function
Example of Vestigial structure
Hind legs on a whale, cave fish eyes
Example of homologous structure
The humerus bone in humans, cats, whales, and bats
Example of Analogous Structures
Wings or the ability to move through the air
What is a cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
Know that organisms with similar DNA/ amino acid sequences share a more ____________
recent common ancestor
What is biogeography
the study of the distribution of organisms around the world, and why organisms live where they do.
How does biogeography relate to adaptations in organisms
The environmental conditions in each country were different so different traits were more advantageous in each.
Adaptations are traits that best suit a given environment.
_______ are organisms that can and do reproduce to make live, viable, and fertile offspring
Species
What is adaptive radiation
the process of a single species evolving into new species as they adapt to different environmental conditions.
Ex. Galapagos finch
What are the 5 causes of change in allele frequencies in a population? Know each one’s meaning
Mutation
Gene flow
Genetic drift
Natural selection
Sexual selection
Mutation
the random change in DNA of an individual
In order for speciation to occur, what needs to happen?
For speciation to occur, some members of the population must become ISOLATED from the rest.
Gene Flow
the movement of individuals into or out of a population
Genetic Drift
the random change in allele frequencies due to loss of population
Two types of genetic drift
bottleneck effect and founder effect
What is the bottleneck effect?
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population that more than likely was from a natural disaster
What is the founder effect?
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
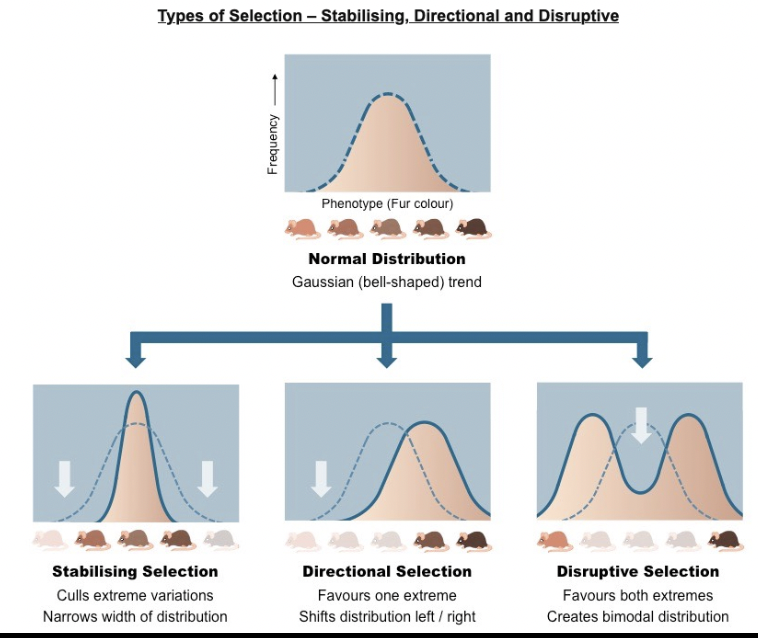
What is disruptive selection?
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range as a response to natural selection
What is stabilizing selection?
favors intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes when in response to natural selection
What is directional selection?
favors individuals at one end of the phenotypic range when in response to natural selection
Natural Selection
the change in a population’s allele frequencies due to environmental pressures
Sexual Selection
the change in a population’s allele frequencies due to reproductive pressures
What does “fitness” mean in evolution
refers to how well suited an organism is for the current environmental conditions.
What are the 3 types of selections in natural selection based on environmental changing
Stabilising Selection
Directional selection
Disruptive selection
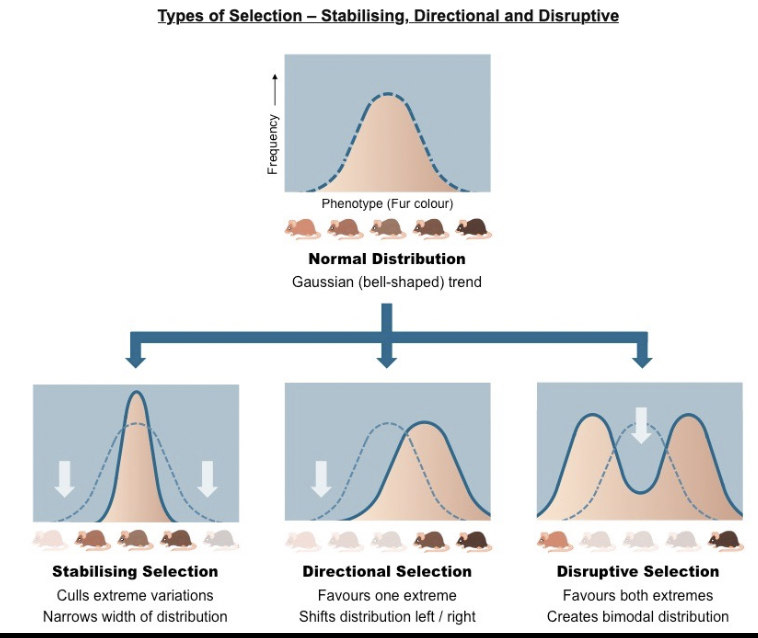
What do the 3 graphs represent and what's happening
The top image is of our initial population. Most of the mice are medium brown. A few are lighter and a few are darker.
The three images below show how the phenotype changes based on the selective pressure on the population.
The white arrow represents which color of mice are being selected against or are removed from the population.
The solid blue line is the final distribution of of mice after a few generations of that pressure.
What needs to happen in order for speciation to occur
some members of the population must become isolated from the rest.
What are the ways in which it can occur
Temporarily Isolated, Reproductive Isolation
What is temporal isolation?
A type of isolation that occurs when two or more species reproduce at different times
What is behavioral isolation?
A type of Isolation caused by differences in courtship or mating behaviors
What is geographic isolation?
A type of isolation in which populations are physically separated and therefore never mate
Isolation, how does isolation happen
Geographical isolation, Allopatric speciation, Sympatric speciation
What is coevolution
process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time
Example of coevolution
Flowers and pollinators
What does punctuated equilibrium mean
Evolution occurs in rapid bursts of speciation, followed by long periods of no change.
What happens when the environment changes slowly instead of quickly
We see gradual speciation events. This is what Darwin predicted would be found in the fossil record.