Absorption and secretion in the stomach, intestines and pancreas
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What types of control manage GI actions and secretions ie hormonal, neuronal etc?
hormonal, paracrine, neurocrine
How much fluid is absorbed each day and through which organs?
over 9L, most in small intestine, rest in large intestine or lost in faeces
In a steady state, how does sodium intake by the GI tract relate to the sodium output by the renal system?
Na+ intake by GI tract = Na+ output by renal (and other) pathways
What are the 3 main functions of the stomach?
Secretion
Motor: regulates food intake/transit, mixing, ↓ food particle size = chyme
Humoral: gastrin, somatostatin (regulate 1)
What do the proximal secretions of the stomach consist of?
HCl
Pepsinogens
Intrinsic factor
Mucins/bicarbonate ions
What is the proximal part of the stomach made up of?
orad region + top half of the caudad region
What is the distal part of the stomach made up of?
bottom half of the caudad region
What do the distal secretions of the stomach consist of?
Gastrin
Somatostatin
Pepsinogens
What do the corpus enterochromaffin-like endocrine cells secrete? What does this secretion regulate?
histamine
gastric acid secretion
How many litres of secretions do stomach glands release a day?
over 2L
What 2 types of glands are present in the proximal mucosal layer of the stomach?
pyloric and oxyntic glands
What cells make up both the oxyntic and pyloric glands of the proximal part of the stomach ?
all cells apart from parietal and G cells ie:
epithelial
chief cells
mucous neck cells
enterochromaffin-like cells
D cells
enterochromaffin cells
Which stomach gland is specialised by its content of parietal cells? What do they secrete?
oxyntic, HCl, intrinsic factor (allows B12 absorption in ileum of SI)
Which stomach gland is specialised by its content of G cells? What do they secrete?
pyloric gland
gastrin hormone (H)
What are basal secretions rich in when the stomach is unstimulated and stimulated?
sodium
hydrogen bc of HCl secretions = acidic env.
In resting parietal cells, what 2 structures are found on the apical side of the cells?
Cytoplasmic pool of tubulovesicular membrane
Acid secreting H,K-ATPase
How does stimulation of parietal cells induce cytoskeletal changes?
Fusion of tubulovesicular and canalicular membranes
50-100x ↑SA
Microvilli appearance
Insertion of H,K-ATPase pump, K+ + Cl- channels
Does the invaginated membrane of parietal cells face the lumen when resting or active?
active
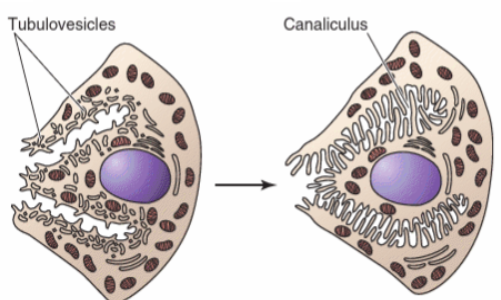
Does the right or the left diagram depict an active parietal cell? How can we tell? Which side is the apical side?
On the right bc fused tubulovesicular and canalicular membranes = microvilli facing the lumen
left
In parietal cells, which exchangers are in the basolateral membrane? How do they contribute to HCl secretion? Where is it secreted?
sodium potassium ATPase and bicarbonate chloride exchanger
HCO3/Cl exchanger = Cl - brought in to be secreted through the Cl- pump on the apical membrane + allows H2CO3 to be dissociated into bicarbonate and H = H secreted out through K/H exchanger on the apical membrane
into the lumen
How does the net secretion of HCl and absorption of HCO3 affect blood pH?
secretion of HCl = release of bicarbonate into the blood = alkaline tide after eating (raised pH)
How is potassium recycled in parietal cells?
K channels going into lumen
To sum up, what are the main steps of gastric acid secretion in parietal cells?
H2CO3 dissociates
H+ secreted across apical membrane via H+-K+ ATPase (Cl- follows via channel)
HCO3- absorbed into blood via a Cl--HCO3-- exchanger
Net secretion of HCl and absorption of HCO3
K is recycled into the lumen via K channels
What is a by-product of gastric acid secretion into the lumen by parietal cells? Which enzyme catalyses them to and from H2CO3?
CO2 and H2O
carbonic anhydrase
Which ligands lead to upregulation of HCl secretion? Which cells secrete each agonist?
histamine, ECL
ACh, vagus
gastrin, G cells
Which stimuli lead to downregulation of HCl secretion? Which cells secrete the ligands?
low pH
somatostatin by D cells
prostaglandins by parietal cells
Why does pH drop in the stomach and why does this lead to downregulation of HCl secretion?
food moves onto intestine = no more buffering against acid so pH drops low
no more secretion of HCl is needed bc no food left to break down
Which two pathways lead to the stimulation of the H/K ATPase on the apical membrane and which ligands led to the activation of each pathway?
Gq protein = PLC stimulation = release of IP3 then Ca2, activating ATPase and H secretion by ACh (M3 receptor) and gastrin (CCKb receptor)
Gs = release of cAMP, activating ATPase and H secretion by histamine (H2 receptor)
Which two pathways lead to the inhibition of the H/K ATPase on the apical membrane and which ligands led to the activation of each pathway?
low pH
Gi protein = reduced cAMP = no activation of ATPase = no H secretion by somatostatin and prostaglandins
What are crypts of Lieberkühn, where are they found and what is their function?
tube-like glands
small and large intestines
secretion of enzymes, mucus + renew intestinal lining
Which electrolytes do the SI and LI absorb? Through which cells respectively?
sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate
villus cells (have microvilli) // surface absorptive epithelia
What is absorbed only by the SI? Through which enzymes?
nutrients from hydrolysed food after digestion (amino acids, monosaccharides, fatty acids, and vitamins)
luminal + brush border (microvilli) enzymes - break down nutrients into absorbable forms. like lactase, sucrase, maltase, and peptidases
Which cells in the intestines secrete fluid (and electrolytes)? What function does this have and which “symptom“ does it lead to? What is one issue of this?
crypt epithelial cells
protective against bacteria/toxins, flushes them out
diarrhea, can lead to dehydration
What separates the polar cells found in the intestines? What travels through these junctions?
tight junctions
fluids
What type of transport is found in the intestines, transcellular or paracellular? Which requires passive mechanisms and which requires active mechanisms?
both:
transcellular is active on at least one membrane
paracellular is passive, determined by tight junctions
Do the SI and LI absorb and secrete through active or passive mechanisms?
both
What is solute movement coupled to?
fluid movement (or reverse, “solvent drag“)
What regulates intestinal absorption/secretion?
hormones + neurotransmitters/neuroendocrines
What are the primary sites of absorption in the SI? Which electrolytes? What structures modulate this transport? How do they affect SA?
duodenum and jejunum
Na, Cl, K, HCO3
Folds of Kerckring (plica), Villi (+crypts), Microvilli
increased 600 fold (about 200m²)
What does the LI primarily absorb? and secrete?
water, Na, Cl
HCO3, K
Which structure within the GI tract is responsible for the largest absorption of fluids?
SI
Where do parietal cells secrete HCl from?
gastric mucosa
Define a brush border
cell surface domain made up of microvilli
What are the 3 main types of products absorbed during digestion?
carbohydrases, proteases and lipases
What does the pancreas primarily reabsorb?
nothing, secretory role
What explains the acidic nature of pancreatic venous blood?
Hydrogen transported into blood via sodium/hydrogen exchanger
What are the main pancreatic secretions?
enzymes activating CCK receptors (Amylase, lipase, trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, elastase)
isotonic aqueous portion
bicarbonate
What are the roles and secretory cells of pancreatic secretions, CCK-activating enzymes; bicarbonate; and isotonic aqueous portion?
acinar cells - key for digestion and satiety functions
through Cl-HCO3 exchanger - neutralises stomach acid in the duodenum, maintaining pH balance
Centro acinar cells (modified by ductal cells) - juice containing the bicarbonate and enzymes
What stimulates ductal cell activity? Where are these cells found?
receptors for CCK, ACh and secretin = production upregulation
pancreas
What does the large intestine primarily absorb?
Electrolytes like sodium and potassium
Which transporter proteins drive large intestine/colon absorption? On which membranes?
apical sodium channel (Na in)
basolateral sodium/potassium exchanger (Na out, K in)
apical and basolateral potassium channels (K out)
Which steroid hormone induces sodium channel synthesis in the apical membrane of the LI/colon?
aldosterone
What is primarily absorbed in the jejunum? Where is this located?
sodium, sugar/amino acids, bicarbonate, hydrogen, water
SI
What are the 2 primary driving forces for absorption in the jejunum of the SI?
low IC sodium = Na+-H+ ion exchanger + Na+-glucose cotransport
luminal bicarb = Na absorption by stimulating the apical Na-H ion exchanger (H+ source H2CO3)
What is primarily absorbed in the ileum? Where is this located?
sugar and amino acids, chloride, sodium, (NO BICARB)
SI
Which epithelial cells reabsorb bicarbonate in the small intestine?
epithelial cells making up the jejunum
Which transporters are the same in the ileum and jujenum of the SI?
2 apical - sodium, sugar amino acid cotransporter and sodium hydrogen exchanger
2 basolateral - sodium potassium exchanger, sugar amino acid channel
Which transporters are different in the ileum and jujenum of the SI?
bicarbonate absent in the ileum + ileum has a basolateral chloride channel and an apical bicarbonate chloride exchanger
Overall, what are the main driving forces in the SI absorption mechanism?
sodium (low IC level and basolateral )
What is the net movement of NaCl in the ileum of the SI? How does this affect water movement?
into the cell and absorbed into blood plasma
increased water mvt into plasma
What is responsible for the net absorption of NaHCO3?
jejunum of the SI
What cellular structures allow the absorption of products of hydrolysis ie of digestive products?
microvilli making up the jejunum + ileum brush border
Name examples of carbohydrases. Which type of blood are they absorbed into?
alpha amylase, alpha dextrinase, maltase, sucrase, trehelase, lactase
villus blood ie lymphatic system
What is the structure of a villus? What is it responsible for?
contains veins, arteries and capillaries as well as a central lacteal (specialised lymph capillary)
transports nutrients into the blood
Name examples of products of proteins after proteases
pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, carboxypeptidases
Which 3 transporters are responsible for glucose, galactose and fructose to enter epithelial cells of the SI?
SGLT1 for sodium/glucose or sodium/galactose
GLUT5 for fructose (facilitated diffusion)
Which basolateral transporters provide the driving force and the ability to reabsorb glucose, galactose, fructose and sodium into the blood?
sodium/potassium ATPase
GLUT2 channels that allow passage of glucose/galactose/fructose
Which enzyme catalyses dipeptides and tripeptide into amino acids?
peptidase
Which apical transporters are responsible for protein absorption?
2 cotransporters: na+/amino acid and H+/di.tripeptides
1 exchanger: sodium for hydrogen
Which basolateral transporters are responsible for driving force and protein absorption?
Na+/K+ exchanger = driving force
amino acid channel ie facilitated diffusion
Where do all digestive products end up? Except which one, and where does it go?
blood
micelles (lipids), lacteal
Where does pancreatic lipid and lipase/esterase hydrolysis occur? What allows this mechanism?
duodenum + jejunum
bile salts
What are the products of lipid digestion? What are they solubilised into?
cholesterol, lysophospolipids, monoglycerides + free fatty acid
mixed micelles, glycerol is soluble
What is the exterior of micelles lined with?
amphipathic bile salts
What happens to fatty acids/lipids once in the mucous layer lining the epithelial layer of the intestine? Through which 3 methods?
surface is protonated + they cross luminal surface of enterocytes (intestinal cells)
Diffusion
Incorporated into enterocyte membrane
Carrier mediated transport
What happens to lipid products once in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in enterocytes?
re-esterified with free fatty acids ie formation of triglycerides or phospholipids
What are newly formed phospholipids/triglycerides within enterocytes packaged into? What happens to this package?
chylomicrons
exocytosis into lacteals (part of lymphatic system)
What happens to bile salts in enterocytes? How?
recycling through enterohepatic (intestine-liver) circulation
Give a brief overview of lipid absorption
lipids are:
emulsified + hydrolysed into small droplets called micelles thanks to bile salts - duodenum + jejunum
protonated and cross enterocyte membrane
fatty acids re-esterified with glycerol into triglycerides/phospholipids
packaged into chylomicrons and reabsorbed into lymphatic system into bloodstream, glycerol straight into bloodstream
bile salts recycled
How do phospholipids/triglycerides enter blood circulation vs glycerol?
packaged into chylomicrons that enter lymphatic system through lacteals then into bloodstream vs straight into bloodstream
Briefly describe the similarities between lipid, protein and carbohydrate absorption?
all require a first step of enzyme break down/digestion form macronutrients into fatty acids/glycerol; amino acids; monosaccharides
all are absorbed in SI
all are transported into bloodstream eventually
Briefly describe the differences between lipid, protein and carbohydrate absorption?
proteins and carbohydrates mainly absorbed through active transport and facilitated diffusion then diffuse into bloodstream
lipids breakdown products absorbed into enterocytes, undergo many packaging mechanisms until sent into lymphatic system then bloodstream
How are lipids digested?
emulsified by bile salts in the small intestine and broken down by pancreatic lipase into monoglycerides and free fatty acids
How are proteins digested?
broken down by stomach acid (HCl) and enzymes like pepsin, followed by pancreatic proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin) in the small intestine, which break proteins into amino acids and smaller peptides
How are carbohydrates digested?
broken down by amylase in the mouth and pancreas into disaccharides, which are further digested by enzymes like sucrase and lactase on the intestinal brush border into monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose).