Niche Species Anatomy Online Practical
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
REPTILES
REPTILES
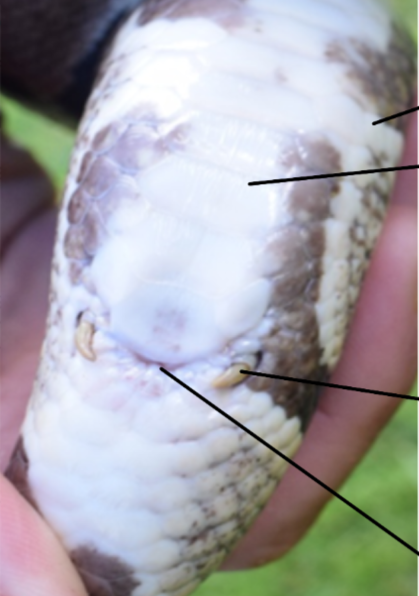
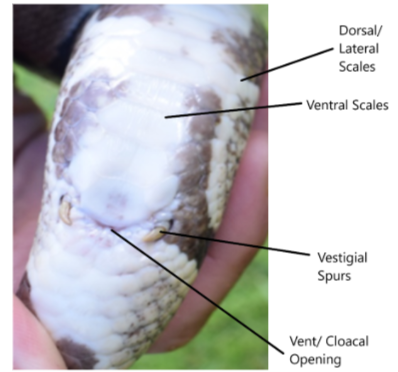
what is the purpose of the dorsal/later scales on a snake?
to display color variation for camouflage
what is the purpose of ventral scales on a snake?
- larger in size
- used for movement + to feel ground vibrations
where is the vent scale and what is it?
- ventral aspect near the tail
- opening for the cloaca
what are little spikes just below the vent called?
vestigial spurs (remnants of the pelvis/femur bones)
Identify the different features in this image
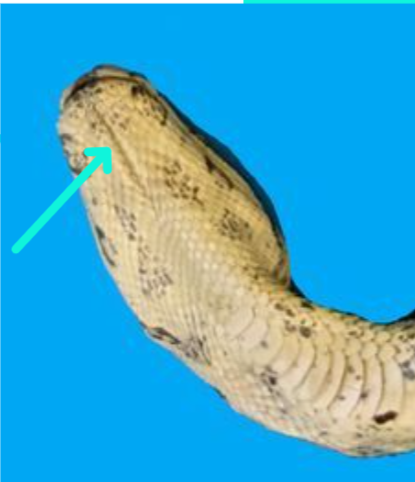
What is the function of infrared receptors/pits in some snake species (e.g. royal pythons)?
helps the snake to sense warm blooded prey and strike with accuracy even in the dark
what is the open slit-like structure on the upper inside of a snake’s mouth
Choanal Slit
what does the Choanal Slit house?
Jacobson’s organ
what is Jacobson’s organ?
a special sensory structure with paired openings in front of the snakes choanal slit
what is the name of the line that is visible externally beneath the lower jaw?
Mental Groove
where does the mental groove run on the body?
center of lower jaw bones to the throat

how many rows of teeth do snakes typically have
6 rows of teeth - 4 upper rows & 2 lower rows

what is the function of the Jacobson’s organ?
detects odors and pheromones
How do snakes smell things?
- flicking their tongues - allows tongue to pick up minute scent particles in the air
- tongue brought back into mouth and particles transferred into Jacobson’s organ
How are snakes able to open their mouths wide enough to swallow their prey?
interscale skin unfolding → mental groove folds in → epidermal cells less packed →
dermal skin stretches → stretching of elastin in deep dermis → mouth is able to open wider to ingest prey
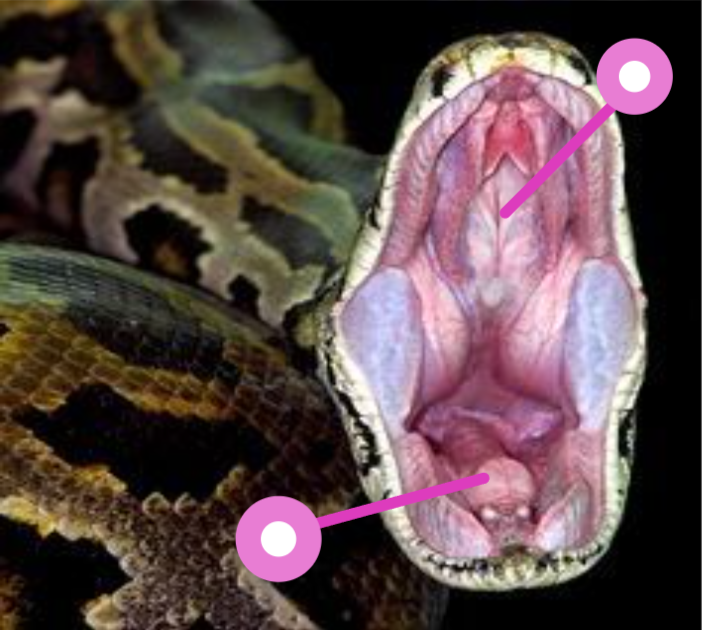
Identify these structures
Top = Choanal slit housing Jacobson’s organ
Bottom = glottis
what do you do when a snake latches onto you?
DO NOT PULL SNAKE
run them under cold water
where should incisions on a snake be made?
via paramedian incision (at the junction of the lateral and ventral scales)
(helps avoid hitting the large ventral abdominal vein)

what is the BCS of this snake?
Obesity - copious amounts of fat would be seen all the way up the body internally
Externally - cant see spine clearly, fat rolls, appearance of “hips”

what is the BCS of this snake?
Underweight
Internally - hardly any fat bodies
Externally - spine visible, neck thin + wrinkly, no thick point to body
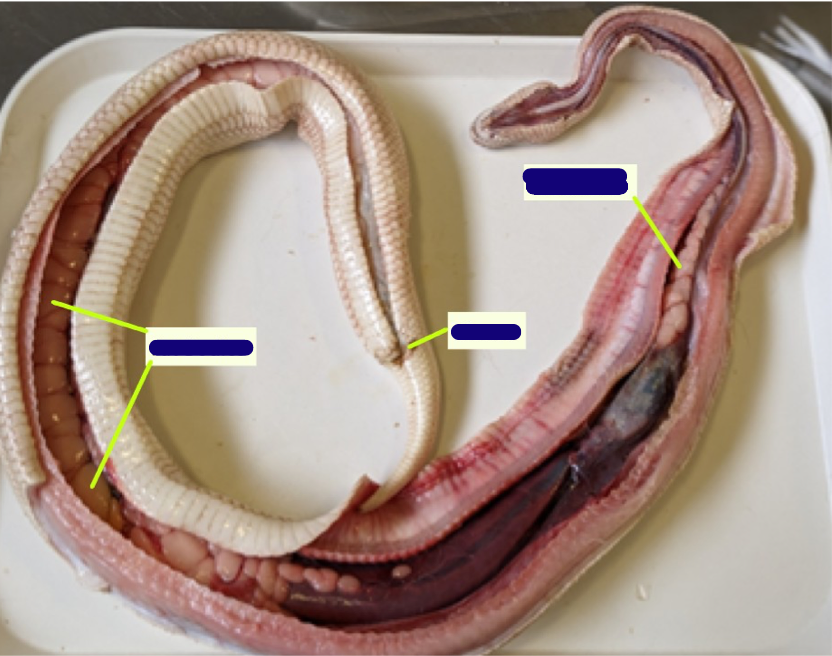
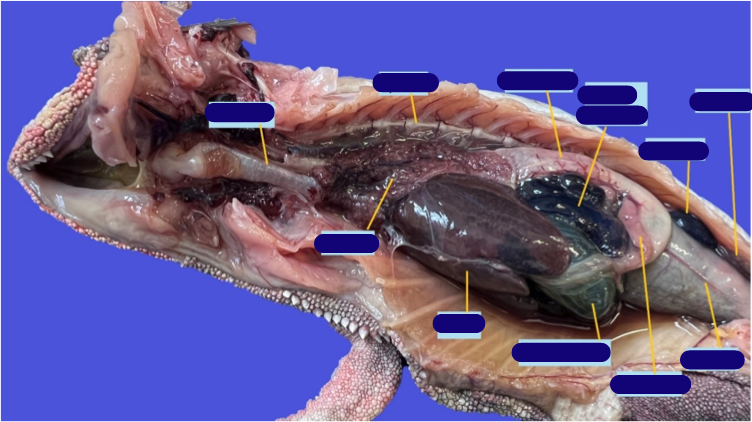
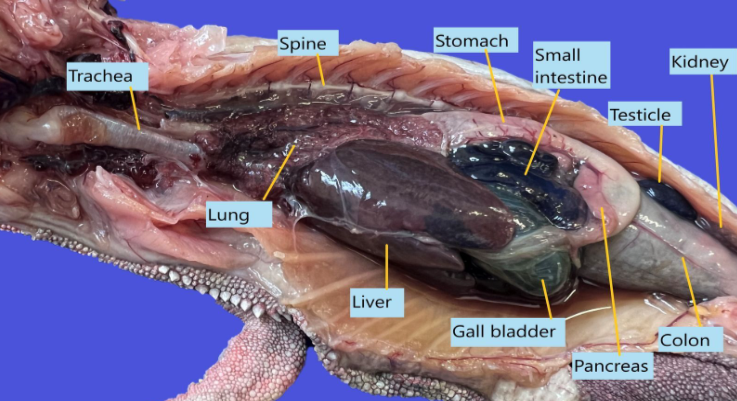
Identify these structures
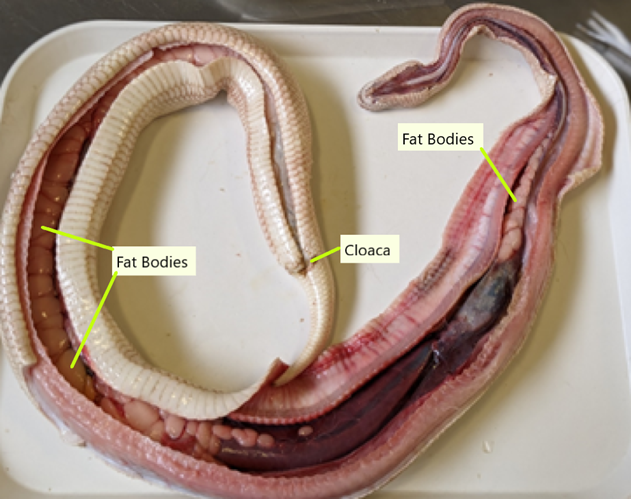
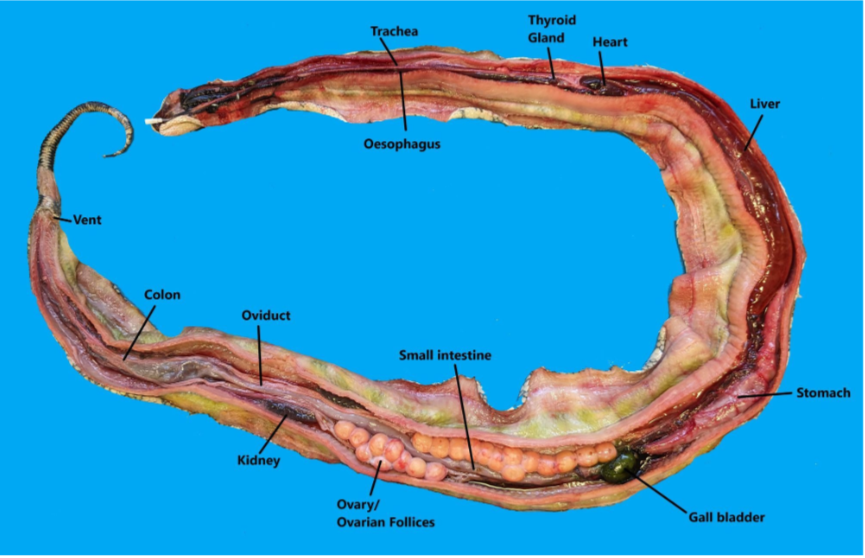
This is a fresh dissection of a snake. Identify the different internal organs in this snake
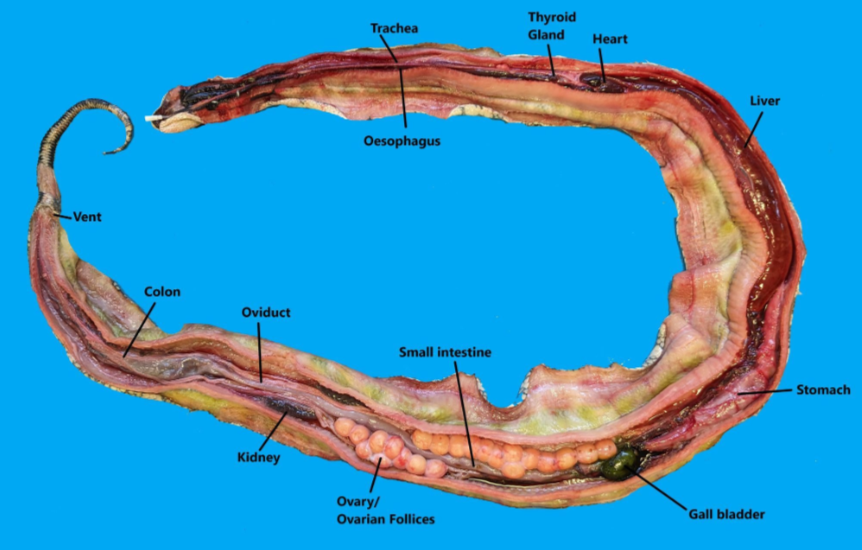
What is the function of the cranial region of the lung compared to the caudal region?
Cranial is vascularized and functions in gas exchange
Caudal mainly functions as air sac & non-respiratory
what important process is regulated by the thyroid gland in the snake?
Ecdysis (skin shedding)
Do snakes have a urinary bladder?
No - ureters feed into the urodeum of the cloaca
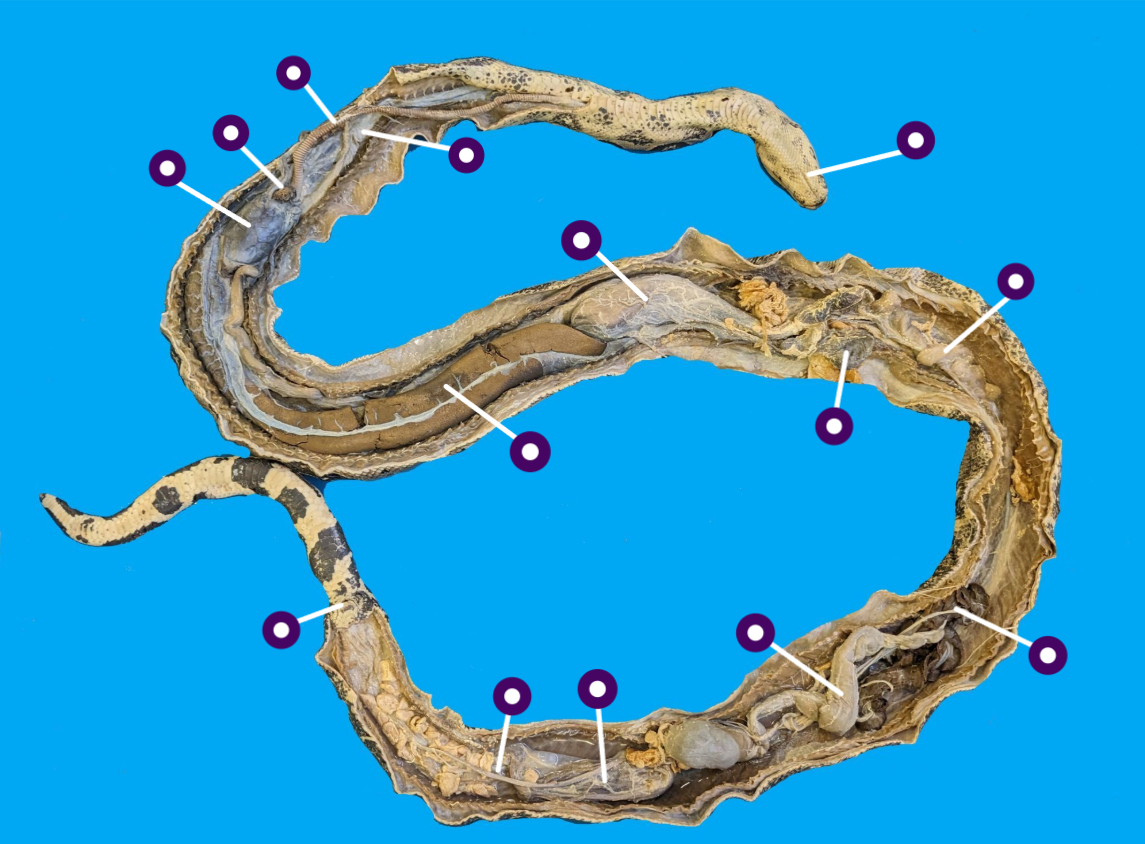
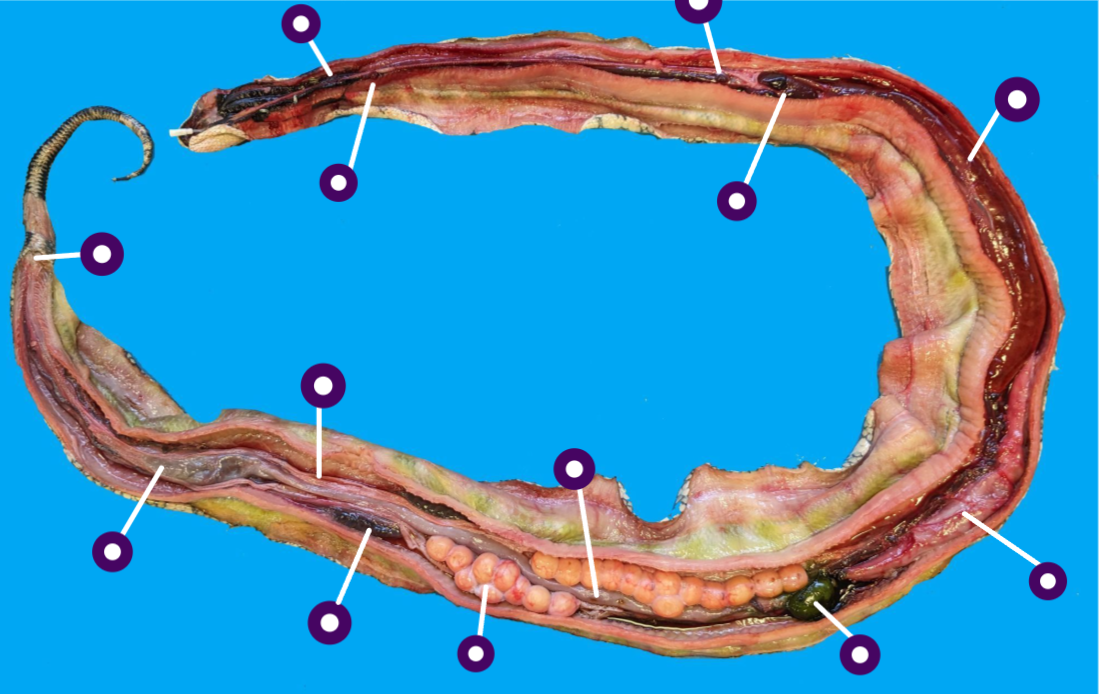
identify the structures of this embalmed species
describe the location and appearance of the thyroid gland in the snake
- cranial to the heart
- spherical + red/pink color
how many chambers does a snake heart have?
3 chambers - 2 atria, 1 ventricle
how many sections is the ventricle divided into?
3 sections
which veins carry deoxygenated blood to the sinus venosus?
left hepatic vein
left and right precaval veins and
post caval vein
what is the name of the 3 ventricular sections?
Cavum arteriosum
Cavum pulmonae
Cavum venosum
what is the function of the cavum arteriosum?
receives oxygenated blood from left atrium
what is the function of the cavum pulmonae
ventral to the other two, blood passes to pulmonary artery from here
what is the function of the cavum venosum
receives deoxygenated blood from right atrium
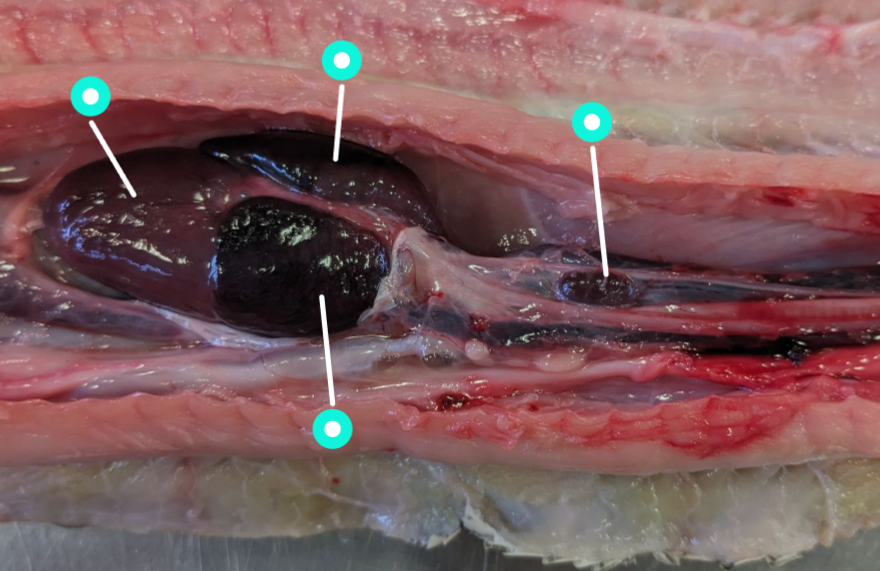
identify the structures in the image
ventricle, left atrium, right atrium, thyroid gland
what color are the intestines in chameleons?
pigmented black
which liver lobe is larger in lizards?
left liver lobe
where precisely are the kidneys located in reptiles?
caudal coelom within the pelvic canal
do all lizards have a urinary bladder?
no, some species of lizard do not have a urinary bladder
what is the function of the renal portal system in reptiles?
supplies blood to renal tubules - particularly when glomerular filtration is reduced
helps maintain kidney function and may protect against ischemic damage / necrosis
Why is UVB light important in reptiles?
enables natural synthesis of vitamin D3 in skin = essential for calcium absorption and metabolism
what are reptiles at risk of developing without adequate UVB exposure?
metabolic bone disease - weakens bones and overall health
What is the meaning of ectothermic?
rely on external sources of heat to regulate body temperature
define dysecdysis
abnormal shedding of skin
identify these structures
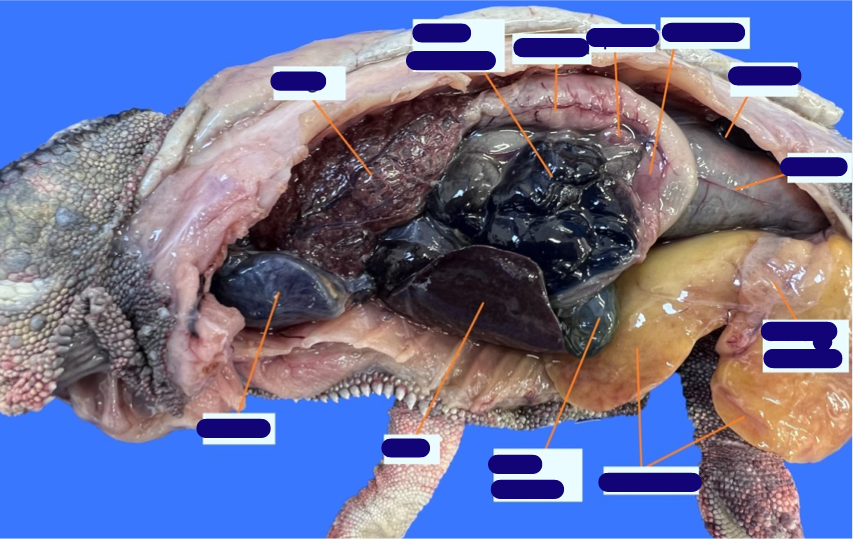
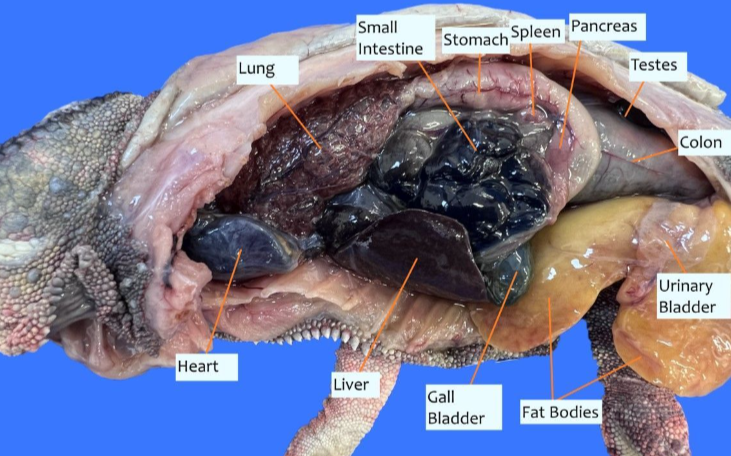
identify these structures