CP - Carbon Compounds
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
macromolecule
a molecule containing a very large number of atoms, such as a protein, nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer
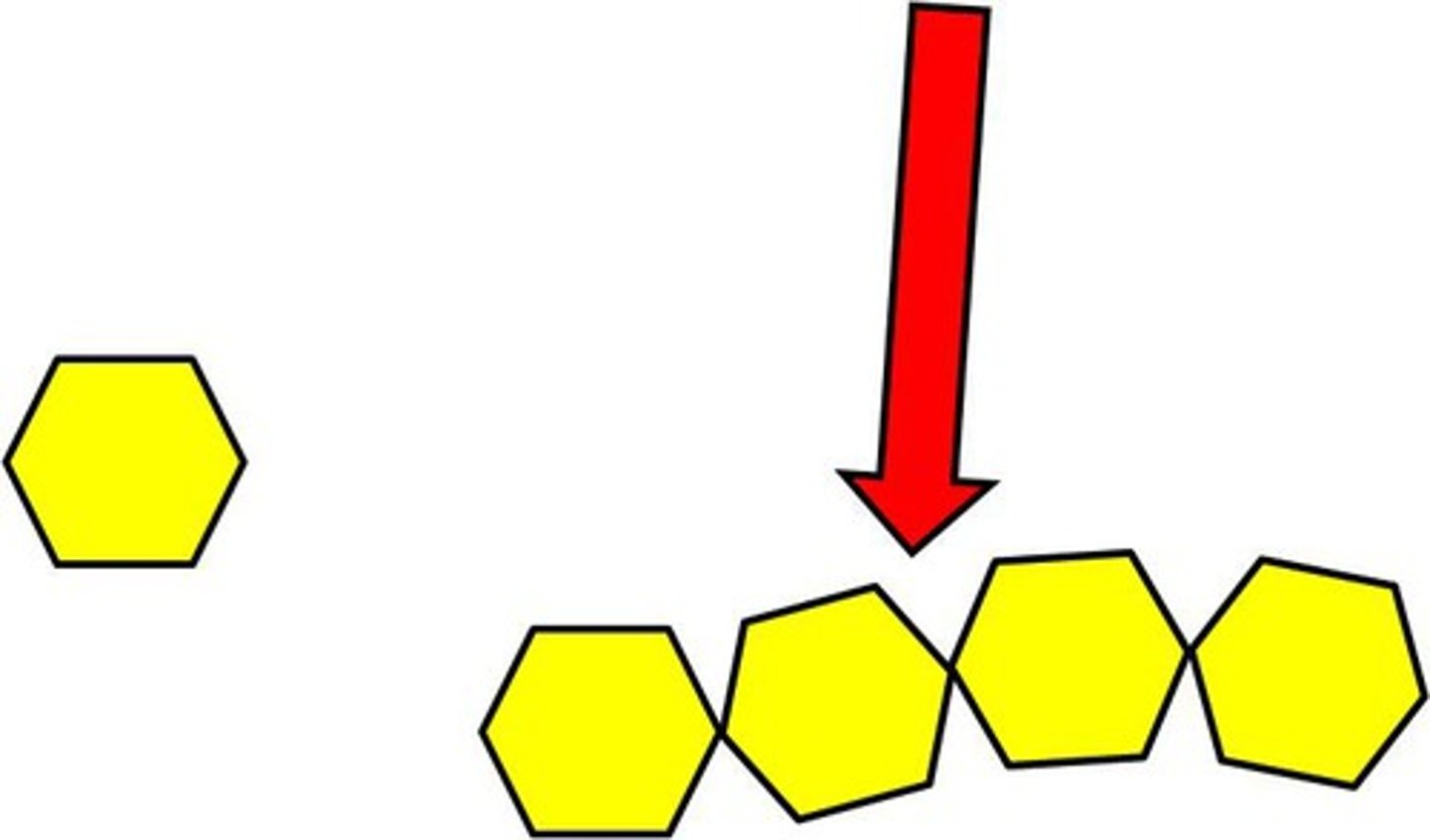
monomer
a simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
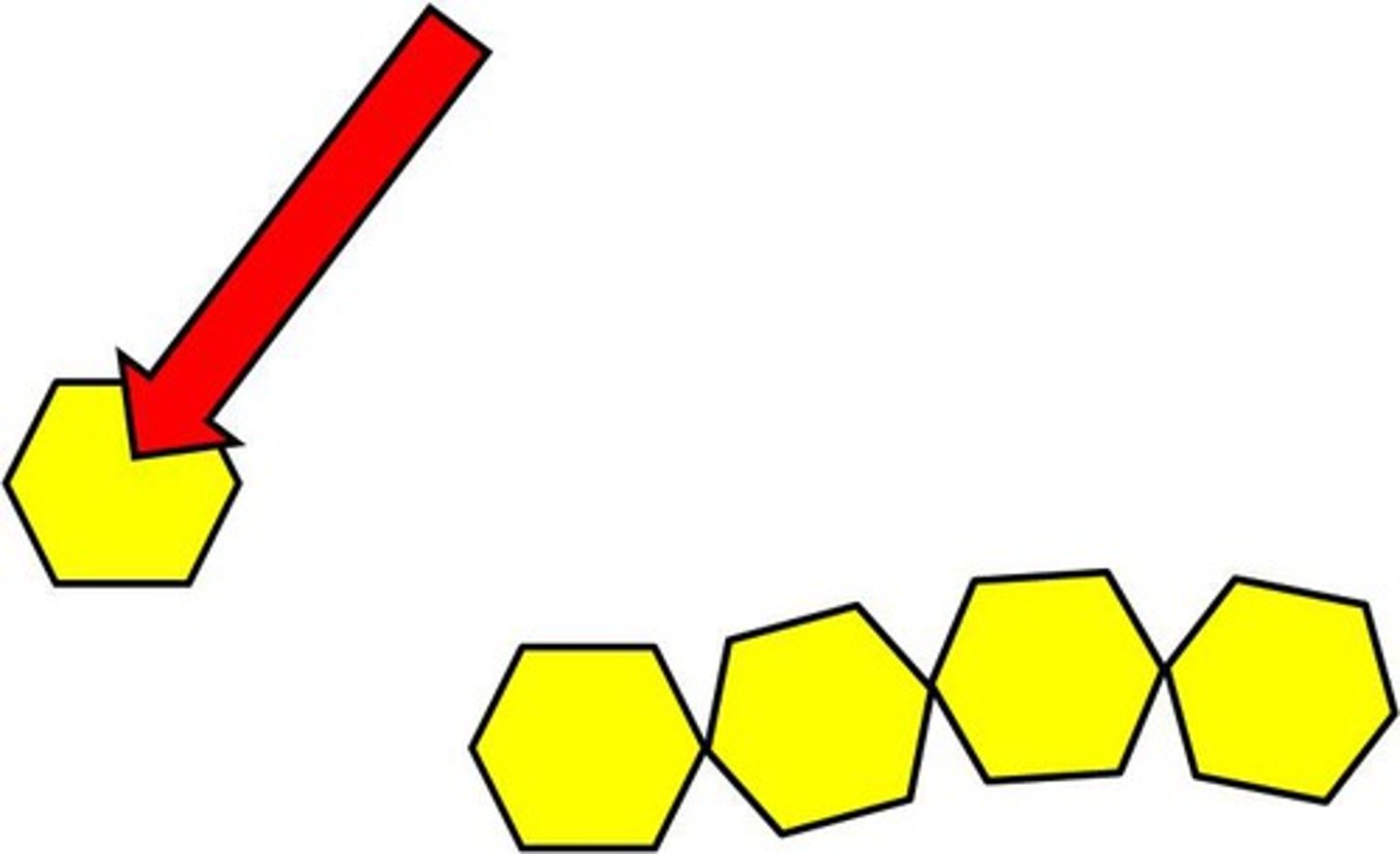
polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
carbohydrate
compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; type of nutrient that is the major source of energy for the body; commonly referred to as sugars
lipid
macromolecule made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms; includes fats, oils, and waxes
nucleic acid
a complex organic substance present in living cells, especially DNA or RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain
protein
an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
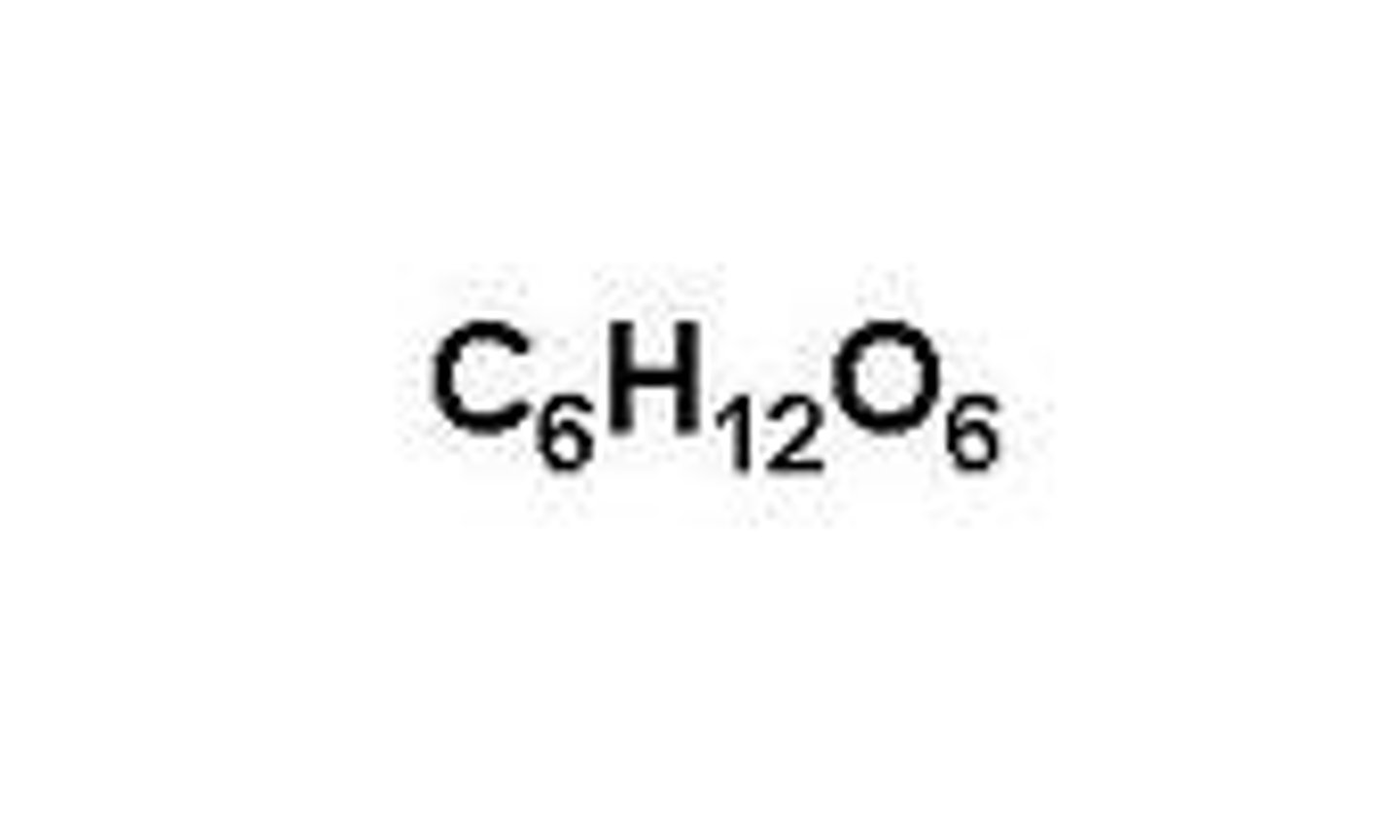
glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues
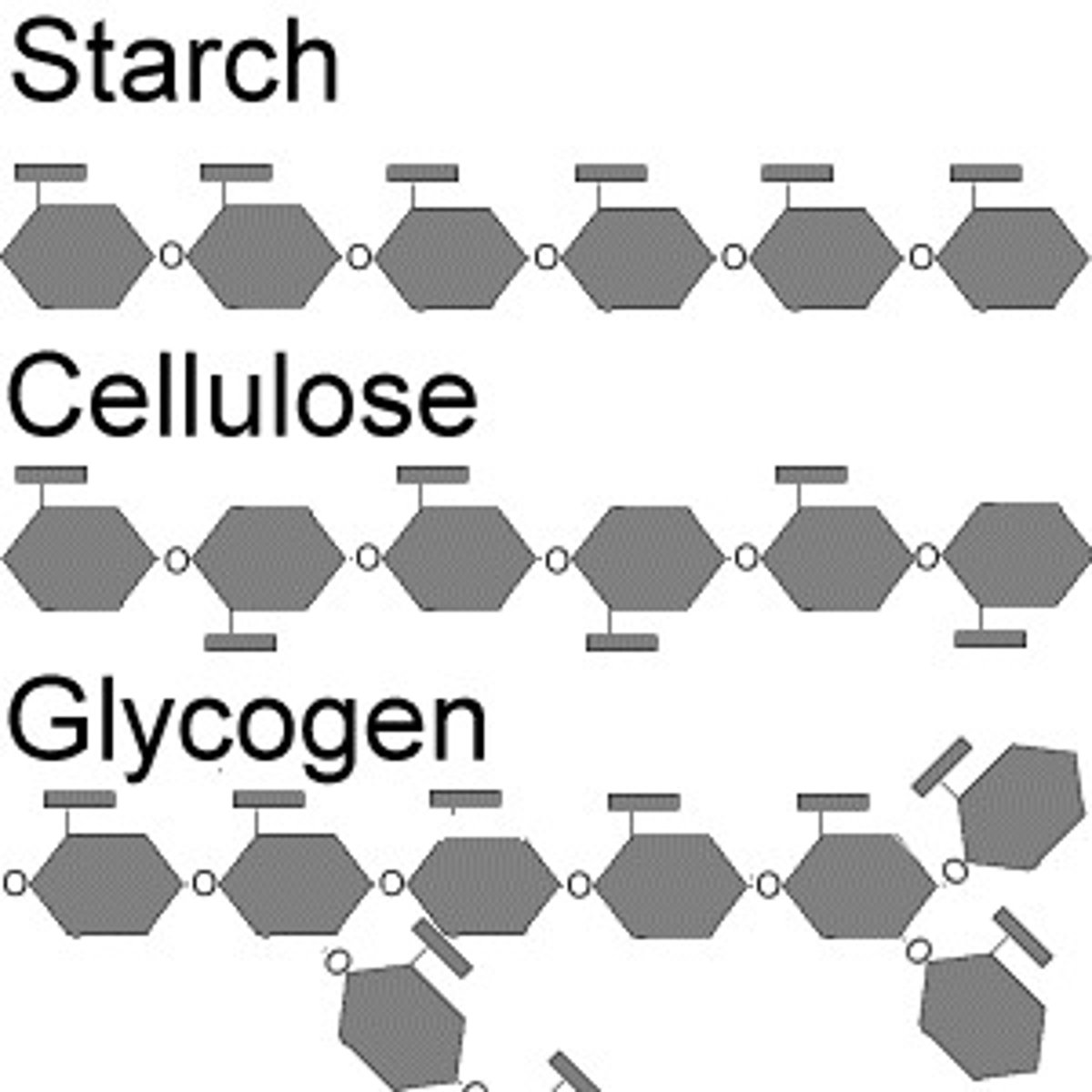
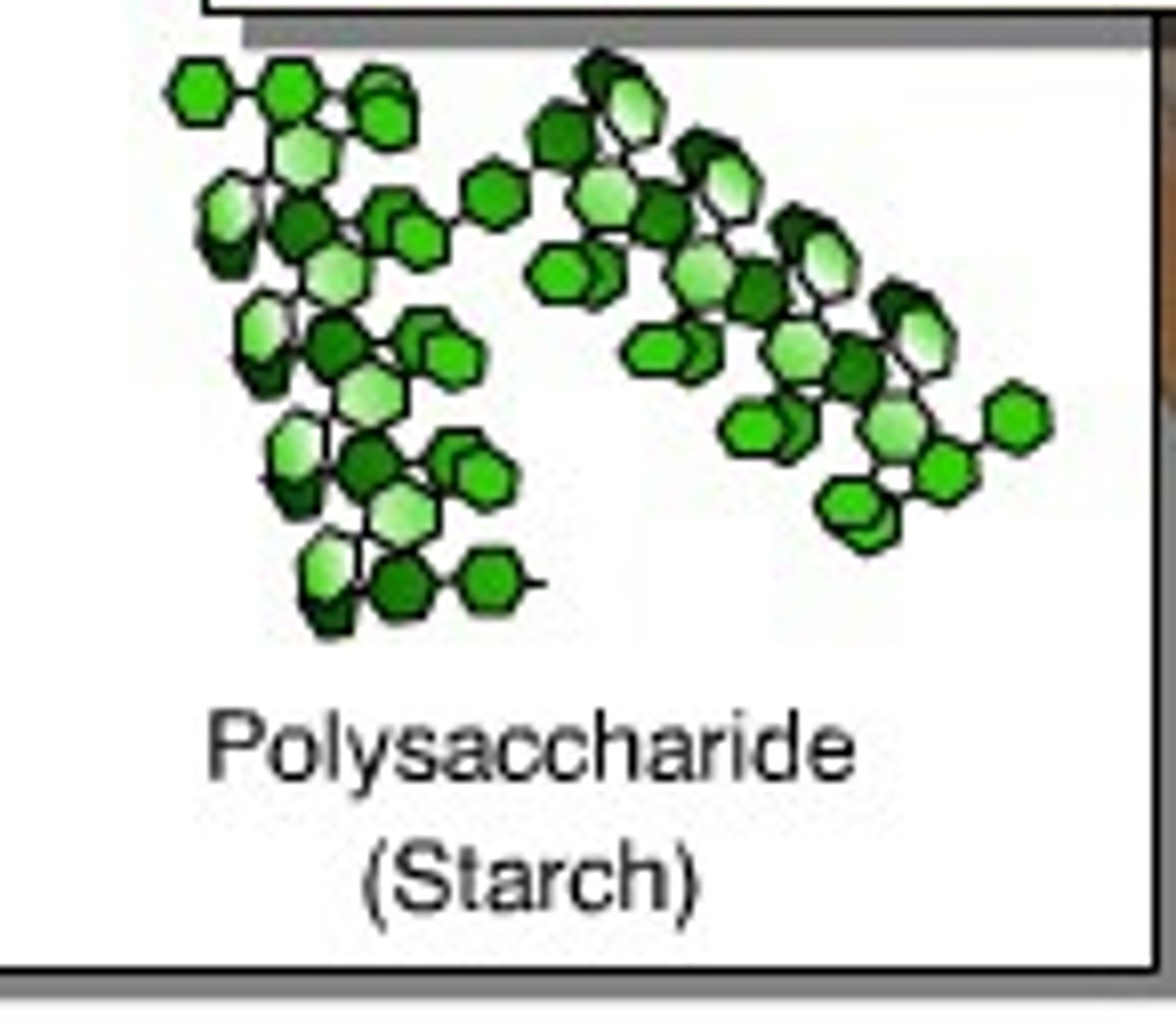
starch
a storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose
cellulose
polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls
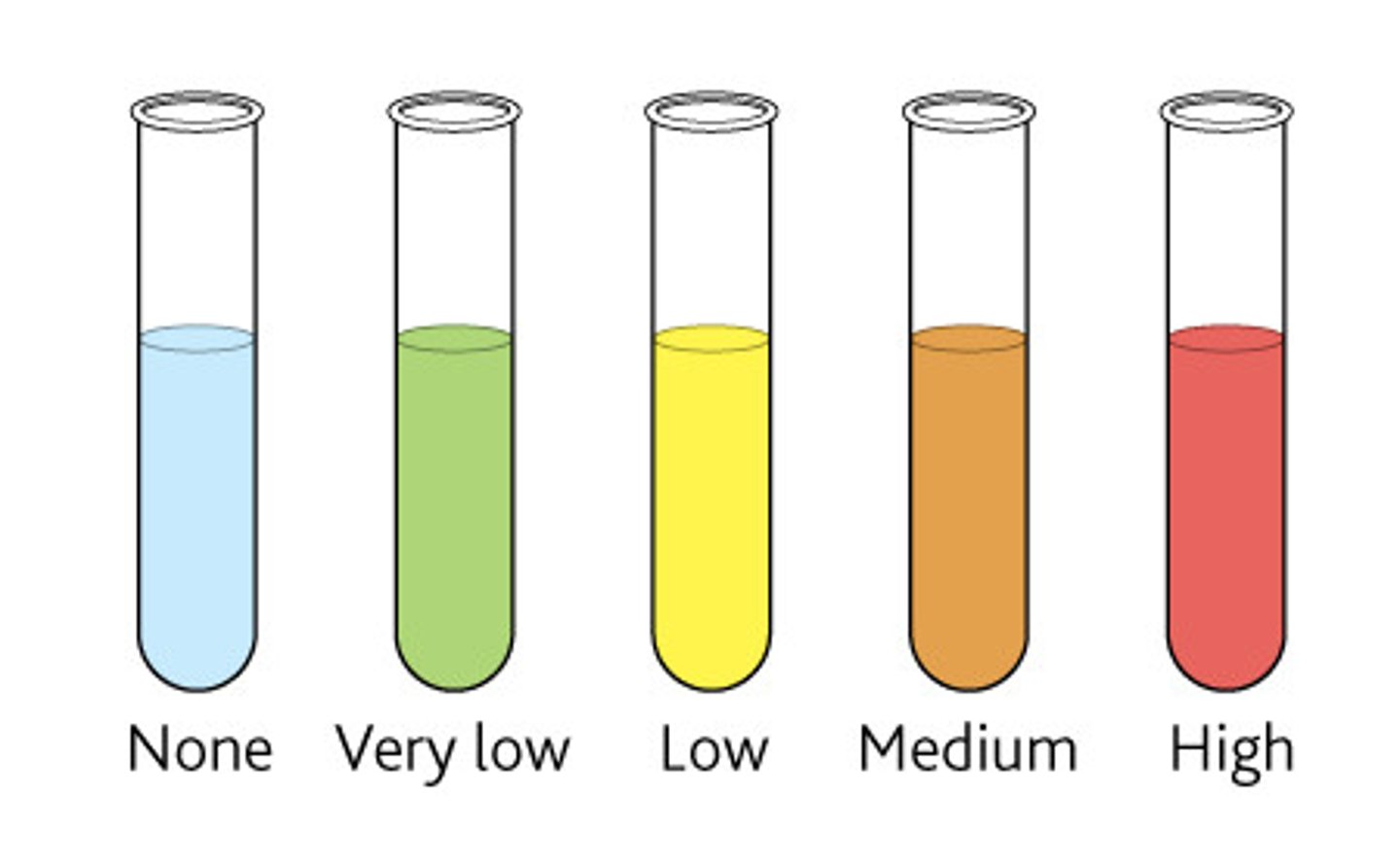
Benedict's Solution
a chemical indicator that, when added to a solution and heated, changes from blue to yellow-orange to orange in the presence of increasing concentrations of sugar

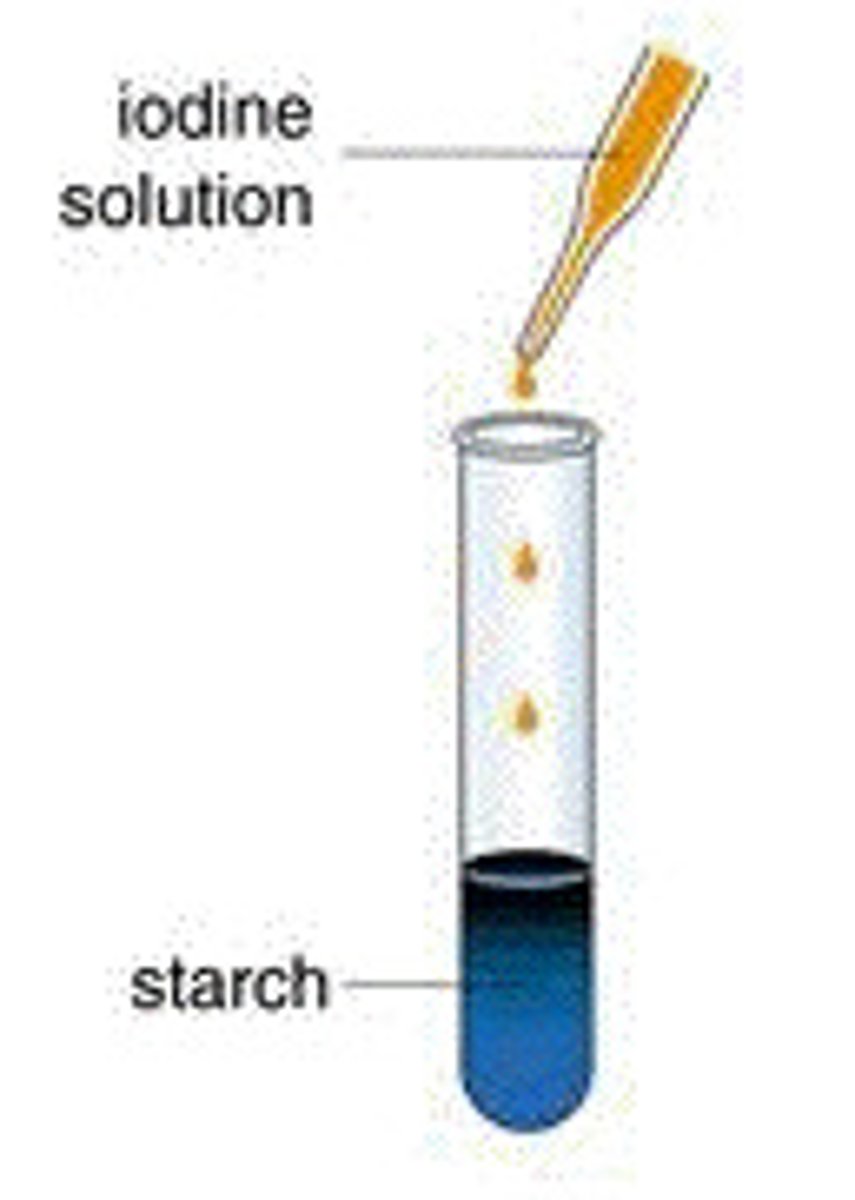
Iodine Solution
used to test for starch and changes color from yellow-brown to purple-black if starch is present
glycogen
an extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain often bonded to glycerol in a lipid
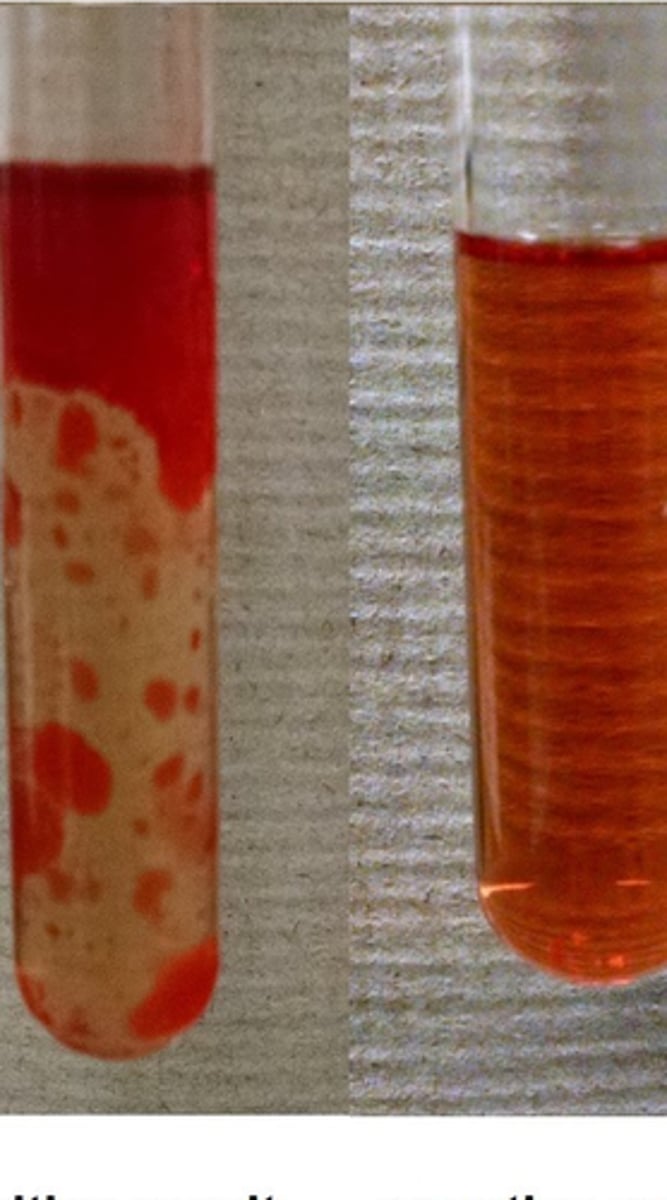
Sudan IV Solution
a solution that tests for lipids; the solution will change from a pale red if negative to a solution with dark red blobs if positive

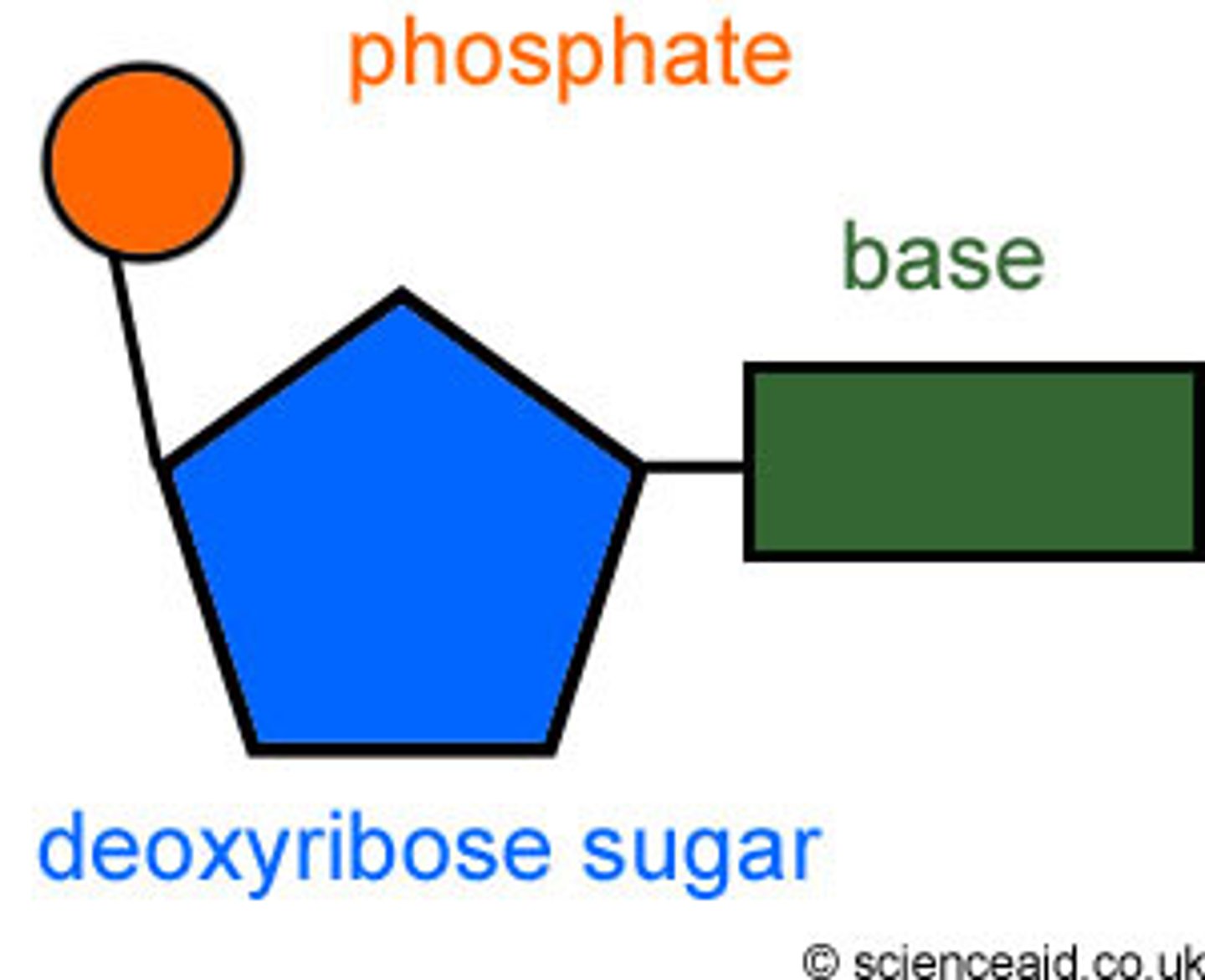
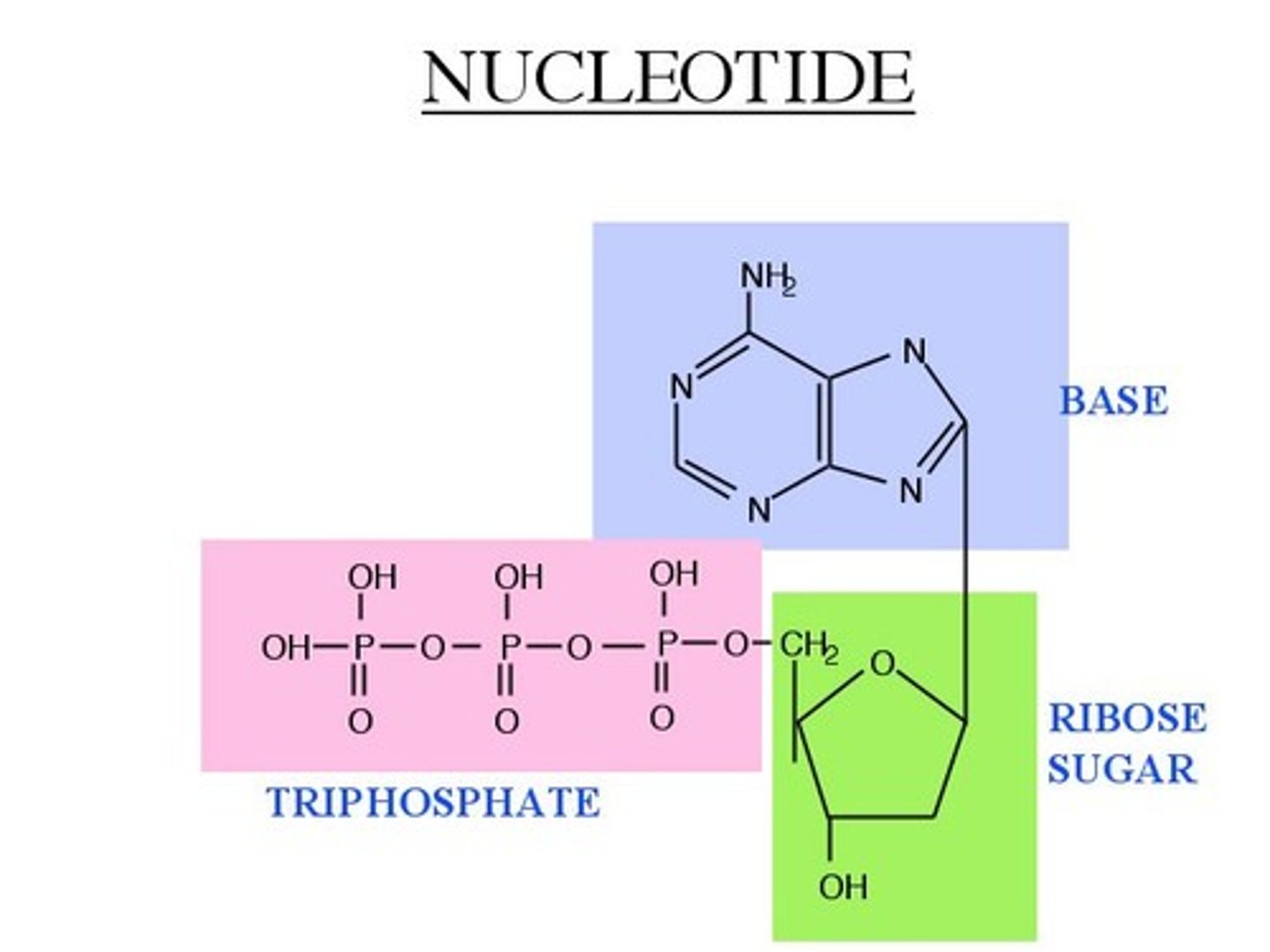
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
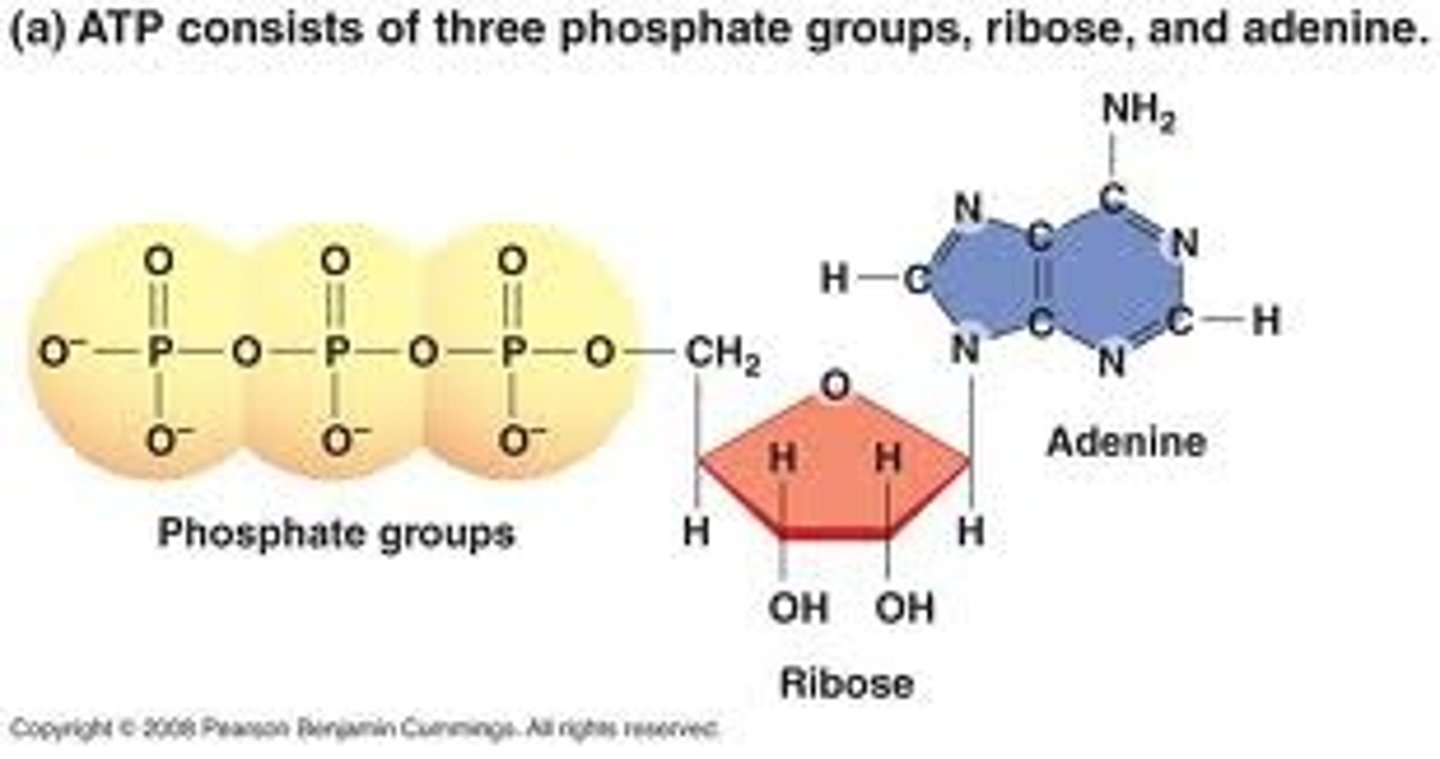
adenosine triphosphate
compound used by cells to store and release energy; typically referred to as ATP
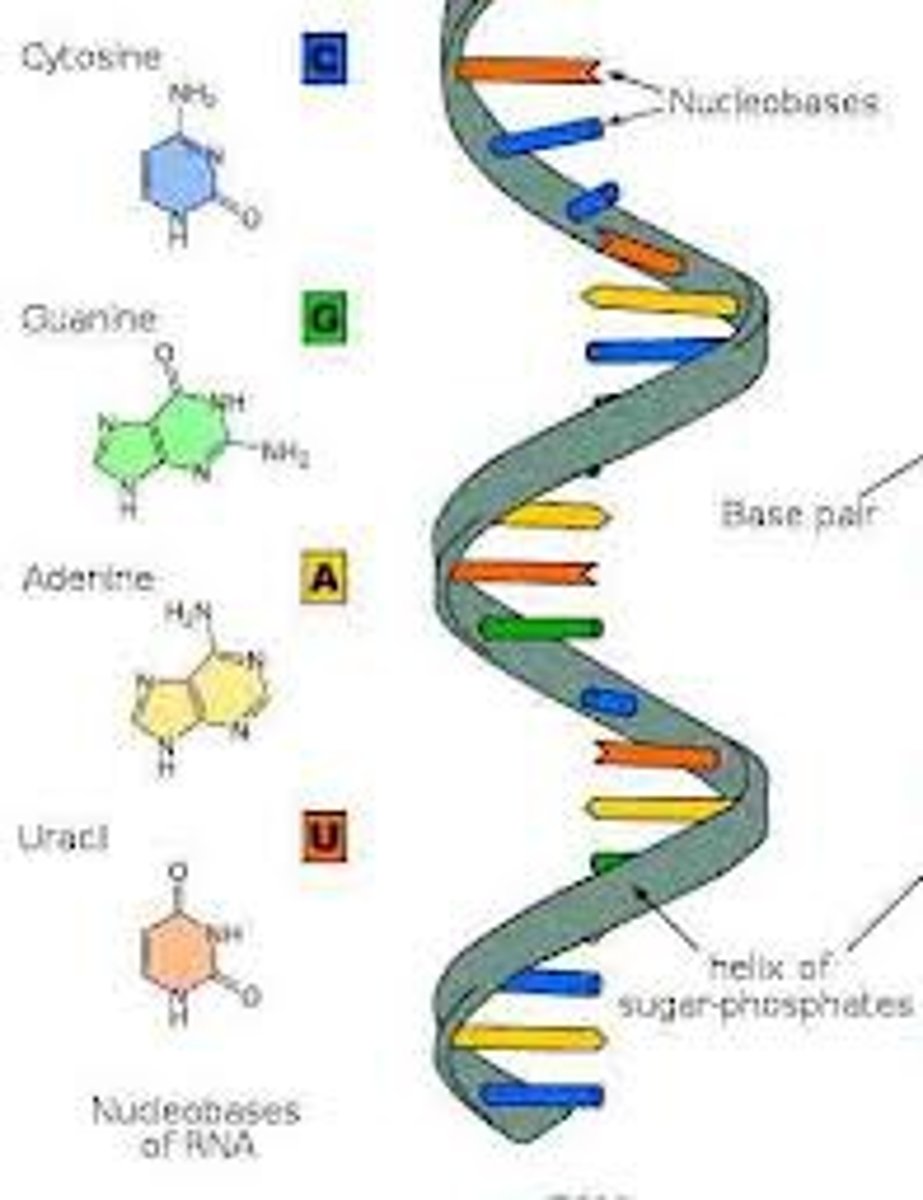
ribonucleic acid
a single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose; typically referred to as RNA
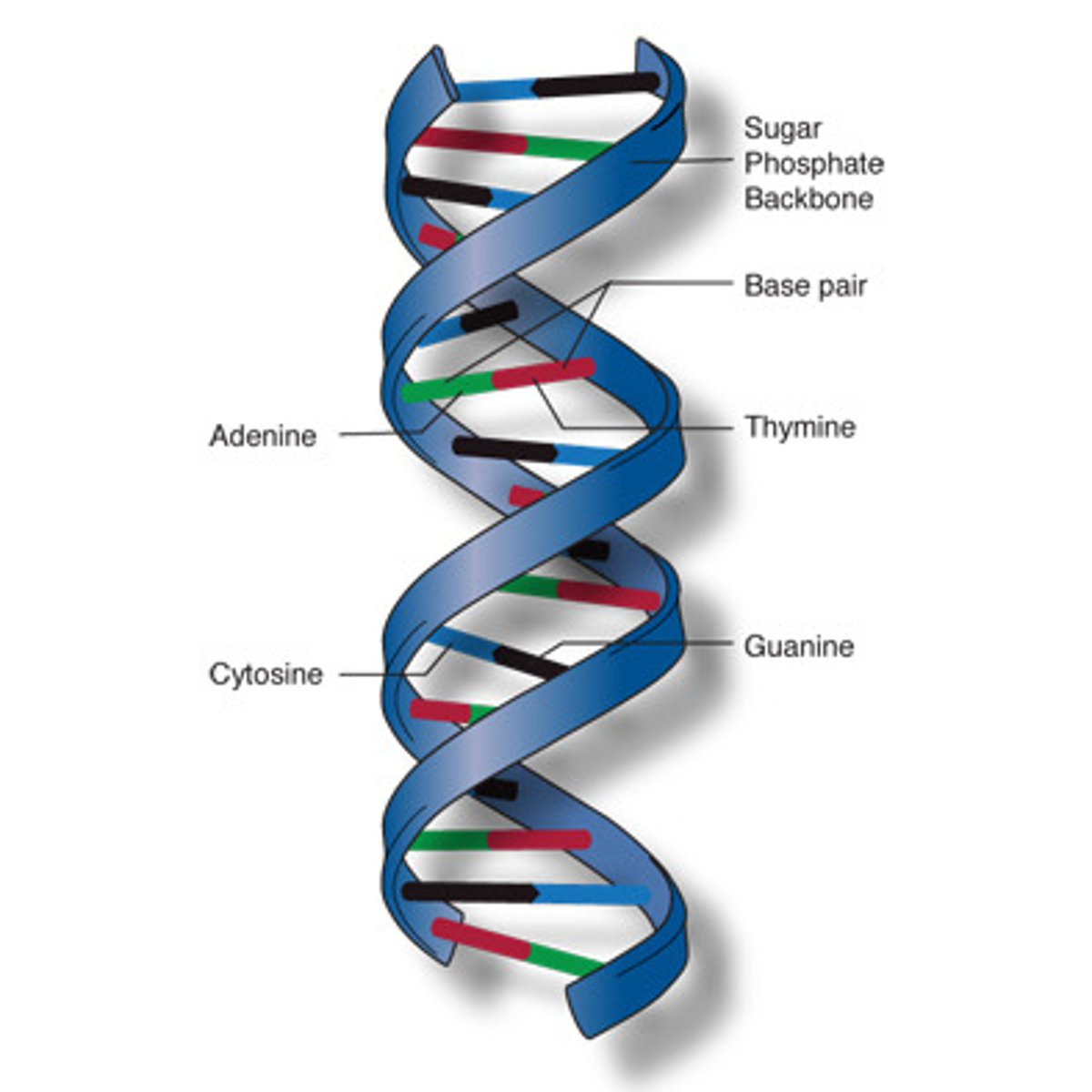
deoxyribonucleic acid
double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins; typically referred to as DNA
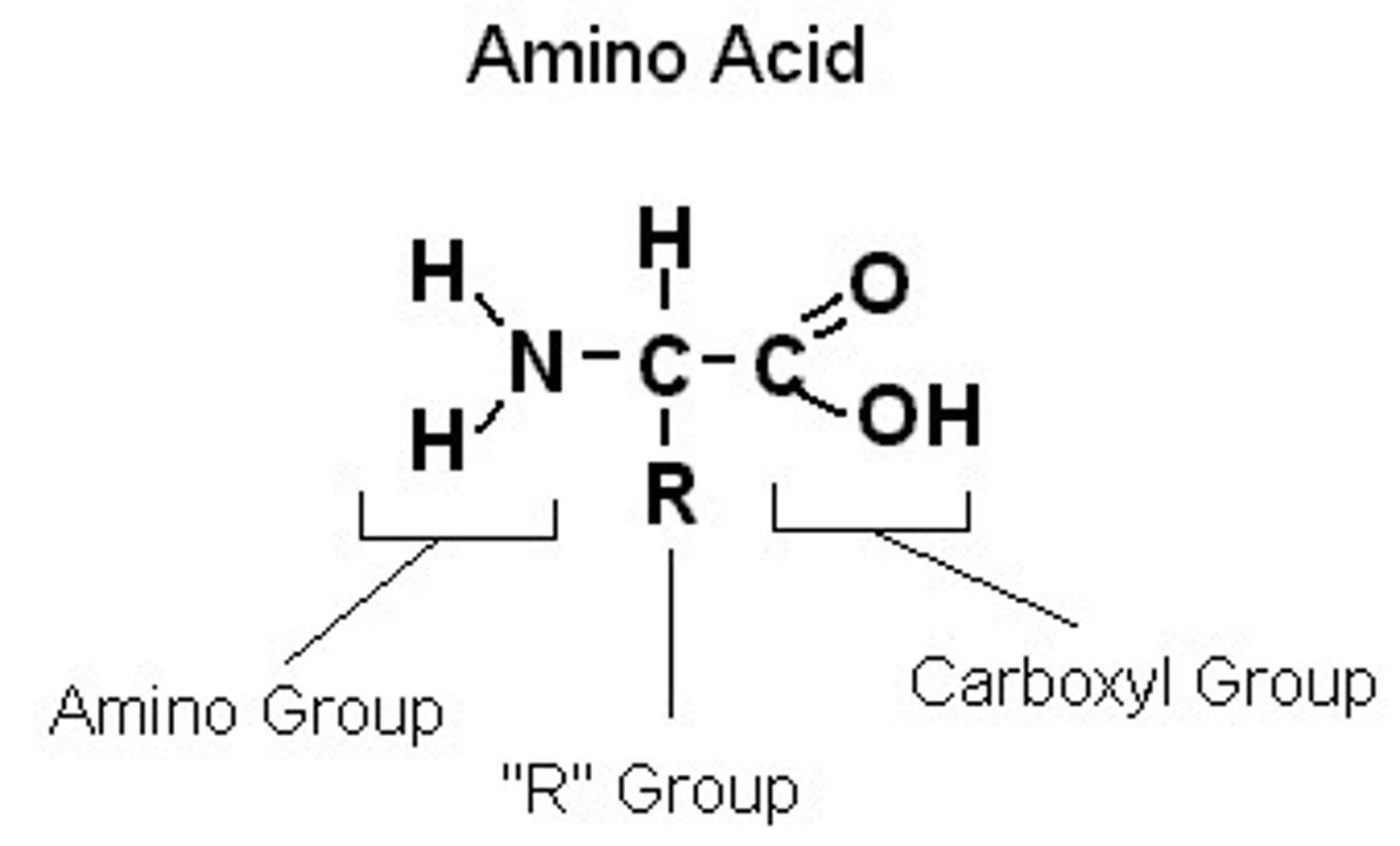
amino acid
compound with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end; monomers of proteins
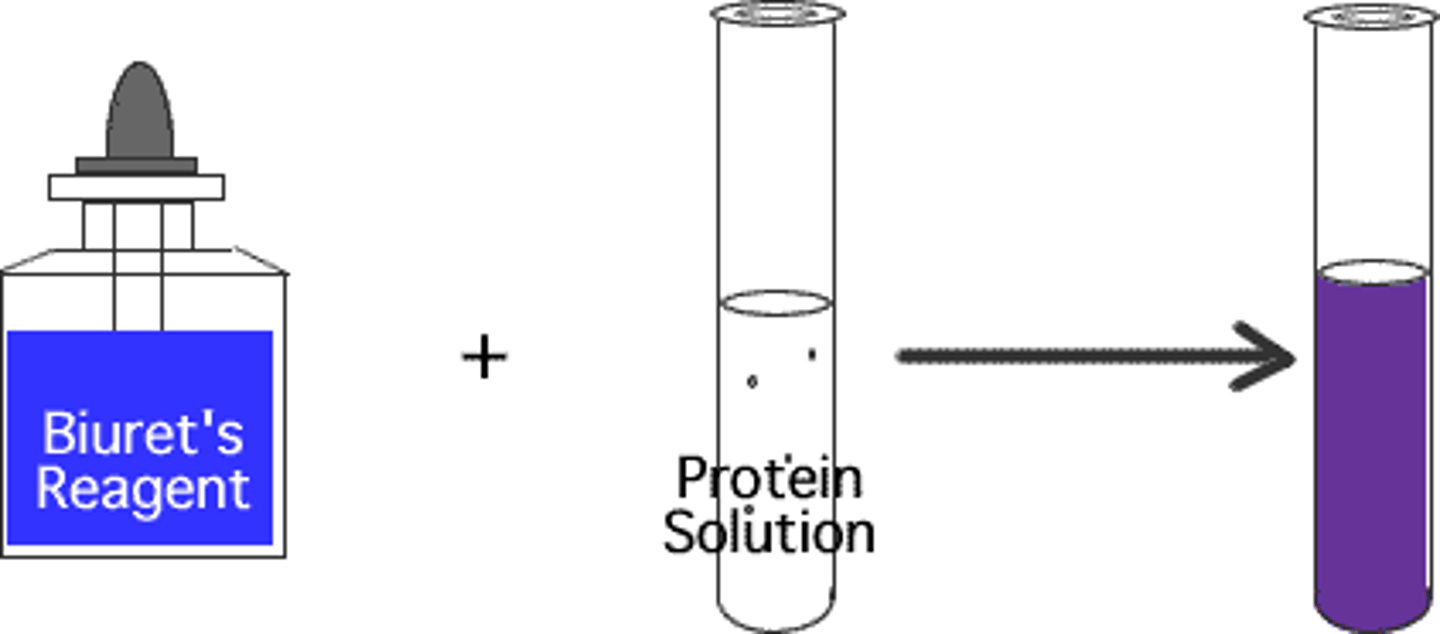
Biuret Solution
the indicator solution for protein; light blue in color if negative and changes to violet or purple if positive