Biochem-13-Structure of Tubulin and Microtubules- assembly/disassembly of microtubular structures
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what are the 3 main cytoskeletal filaments and their composition- what cellular structures made of these?
microfilaments- actin- mitotic spindle/cytoplasmic networks/cilia/axons
microtubulin- tubulin
intermediate filaments- 70+ protein types
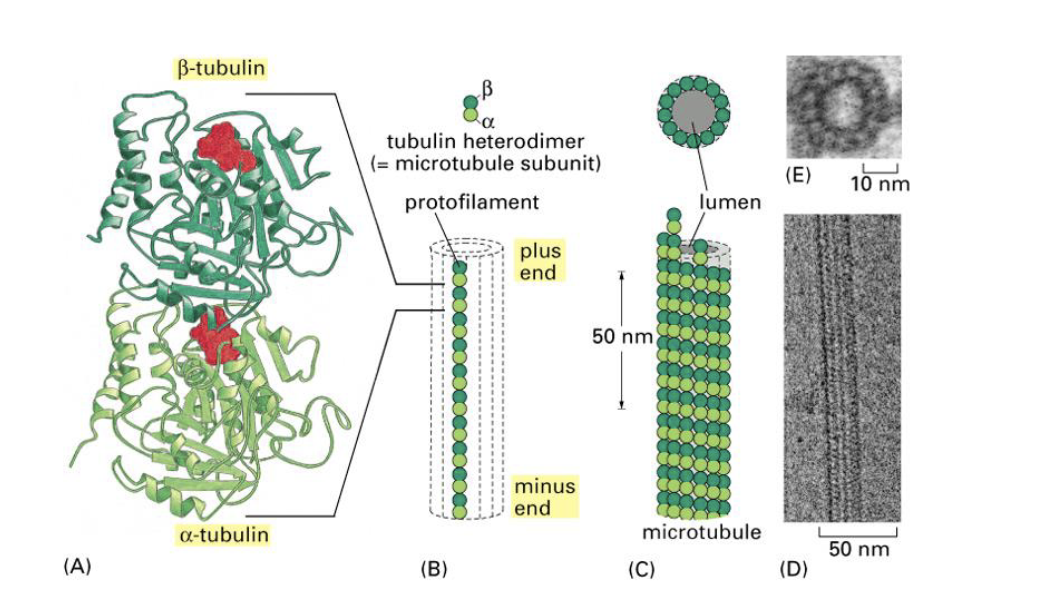
diameter of microtubules and who discovered them
George Palade- 24nm
composition and the structure of microtubules?
hollow like structure- 13 protofilaments
protofilaments- linear chain of polymerised alpha/beta tubular heterodimers
alpha(55kDA) tubulin at the minus end, beta(53kDA) tubulin at the plus end
both sides that GTP binding sites
how do microtubules assemble? what are the key interactions? what’s stronger?
adding alpha/beta/alpha/beta sequentially- helical fashion- these make longer protofilaments
protofilaments- linear chain of dimers. 13 of these make a hollow tube- microtubulin
this doesn’t happen sequentially!!! all protofilaments grow TOGETHER at the same time
top to bottom is stronger from + beta to - alpha end than side to side protofilament next to another protofilament
what conditions need to be met for experiments to look at microtubulin assembly?
GTP present for tubular polymerisation
low Ca2+- high calcium inhibits this
high tubulin conc.
normal 37. temperature
what assays can be done to measure assembly of microtubulin?
electron microscopy- time consuming and expensive
turbidity assay- the more polymers, its more turbid- measured at 340nm. shows the RATE of polymerisation. determine critical concentration of tubulin needed for growth
phases of assembly observed by turbidity assay? what is the critical concentration?
lag phase- where the 13 heterodimer protofilaments come together to form the hollow tube
exponential- where microtubules grow quickly
plateu- tubulin is limited
critical concentration is the concentration of tubulin needed for microtubulin growth
what is the microtubule organising centre? where is it located? key features
MTOC: centrosome near the nucleus
controls microtubule polymerisation throughout the cell
has gamma tubulin ring complexes y-TuRC- rapidly nucleate microtubule assembly. microtubules grow from the PLUS end(beta)
how do microtubules grow after nucleation?
grow rapidly after nucleation when alpha/beta heterodimers are available
alpha/beta have GTP binding sites
GTP on beta(+) is hydrolysed to GDP
GTP Cap is added to the new growing end to stabilise it
GTP role in assembly and disassembly?
+ end Beta tubulin E-GTP is hydrolysed to GDP and is less stable and has lower affinity
- end alpha tubulin N- GTP is still tightly bound and not hydrolysed
GTP cap- formed by the newly added beta tubulin and is GTP bound-slows the shrinkage and added to the new beta dimers to stabilise the growing end
when GTP cap is lost- protofilaments peel away and it shrinks

what are MAPs? what drugs are associated with this?
microtubule associated proteins
bind polymerised microtubules to keep the, stable and filaments organised
protects them from severing and crosslinks them to actin and membrane association
controls the filament numbers and bundling
Tau protein- when hyperphosphorylated the microtubules are disorganised and dissociate easier- neurodegeneration
Taxol- binds to Microtubule and blocks it from dissociation- a stabiliser.
colcemid/colchicine- blocks the assembly of microtubules to ctop cell division- in cancer
difference between a growing and shrinking microtubule?
growing: adding of alpha/beta GTP tubulin to the + end is faster than GTP hydrolysis. GTP cap on new beta tubulin stabilises longitudinal interactions. alpa tubulin - keeps GTP bound
shrinking- GTP hydrolysis on beta tubulin is faster than the addition of new dimers, GTP cap is lost and is less stable, begins to dissociated. released GDP can be recharged with GTP to grow again