1.2.6 - price determination
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
key term - Market equilibrium
a situation that occurs in a market when the price is the quantity that consumers wish to buy is exactly balanced by the quantity that firms wish to supply
where does market equilibrium exist
Pe and qe
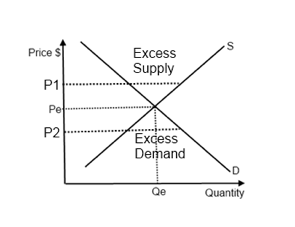
what happens when price is higher then Pe
excess supply
decrease price
what happens when price is lower then Pe
excess demand
increase price
key term - comparative static analyis
examines the effect on equilibrium of a change in the external condition affecting the market.
price determination
the process through which the interaction of supply and demand to determine prices
price mechanism (3 factors)
price signalling
incentivising
rationing
describe how changes in consumer preferences affects the market equillibrium
the initial equilibrium shows p0 and quantity traded of Q0
the likely change is an increase in demand as peoples preference changes shift the demand curve to the right
new equillibrium is Q1 and P1, there will be excess demand
market forces will cause price to shift from p0 to p1, which will lead to an extention in supply as more producers are willing to supply at a higher price
explain the rationing effect
allocate and ration scarce resources
if many consumers demand a good, but supply is scare = high price
limited supply will be rationed
to those willing to pay the highest price. This mechanism ensures that resources are distributed efficiently among consumers based on their willingness to pay.
define incentive function
motivates producers or consumers to follow a course of action to change behaviour.
It encourages production or consumption through financial benefits or penalties.
signalling - funtion of a price mechanis,
rising prices signals to consumers to reduce demand - signals producers to adjust output levels to reduce excess supply and restore market equilibrium.