AQA A-Level Chemistry - Alkenes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
describe the structure of a C=C double bond
made up of a single sigma bond (planar)
and a Pi bond (above and below plane)
Pi bond weaker than sigma bond so bond enthalpy of double bond is not double of single bond
bond is an area of high electron density do is attractive to electrophiles
describe the test for alkenes
add to bromine water
goes from orange-brown to colourless
what are the properties of alkenes?
low mp/bp - similar to matching alkane (only VDW)
insoluble in water
soluble in organic solvents
what form of polymerisation involves only alkenes?
addition
how do you name an addition polymer?
poly (alkene monomer)
draw the formation of poly (ethene) from ethene
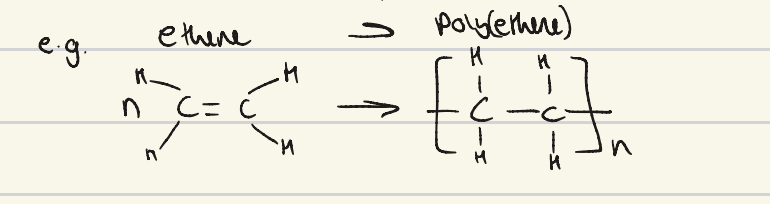
what are the properties of addition polymers?
unreactive - saturated, long alkane molecules
good for packaging and electrical insulation
non biodegradable - end up in landfill, litter, harm small animals
have to be recycled - if burnt they release toxic gases - HCl
what are the two types of poly (ethene)?
LDPE
HDPE
describe LDPE
properties : more flexible, used for plastic bags and bottles
structure : molecules are loosely packed due to being highly branched - less VDW, meaning low BP and more flexible
polymerisation : 200C, 2000 atm, O2 - radical polymerisation
describe HDPE
properties: harder, used for kitchenware, buckets
structure: very little branching so molecules are tightly packed
polymerisation: 60C, 2 atm, Ziegler-Natta process (uses TiCl3 catalyst)
what is the IUPAC name of PVC (poly vinyl chloride)?
poly (chloroethene)
describe PVC
without plasticiser → rigid plastic, used for doors+window frames (uPVC)
with plasticiser → more flexible, used for clothing or electrical insulation
describe the boiling points of addition polymers
in general, high mp/bp → long molecules → high Mr → lots of VDW forces
more branching → lower BP as molecules can’t pack together as well so VDW forces are weaker
less branching → higher BP as molecules can pack very close together so lots of VDW
what is an electrophile?
electron pair acceptor
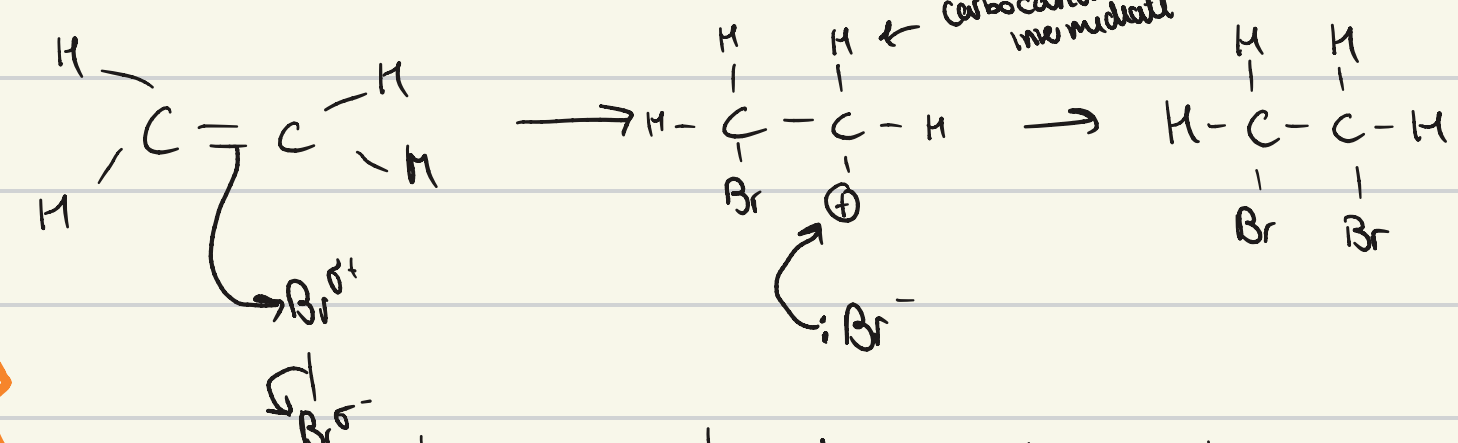
give the general equation for reaction of an alkene and a halogen
alkene + halogen molecule → dihaloalkane
give the mechanism for the reaction to form a dihaloalkane
give the general equation for the reaction of an alkene and a hydrogen halide
alkene + hydrogen halide → haloalkane
give the mechanism for the formation of a haloalkane by electrophilic addition
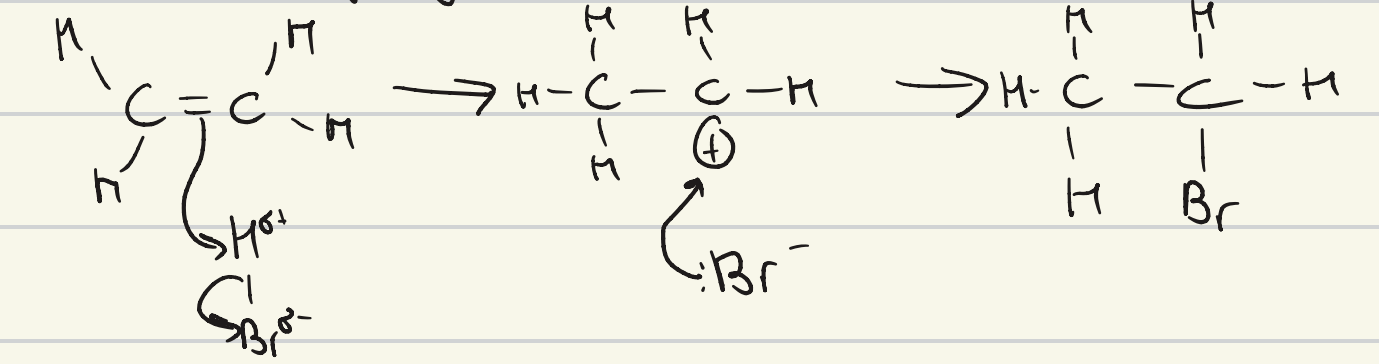
what can occur if the alkene reacting in electrophilic addition is unsymmetrical?
a major and minor product can be formed
due to markovnikov rule
what is markovnikov rule?
if an unsymmetrical alkene reacts in electrophilic addition, a major and minor product will be formed
the major product will be the one with the more stable carbocation intermediate (tertiary > secondary > primary)
why are tertiary carbocations more stable and why do they form the major product?
they are more stable because of the inductive effect of 3 alkyl groups (better than 2)
this means they remain in the reaction mixture for longer so are more likely to form a product
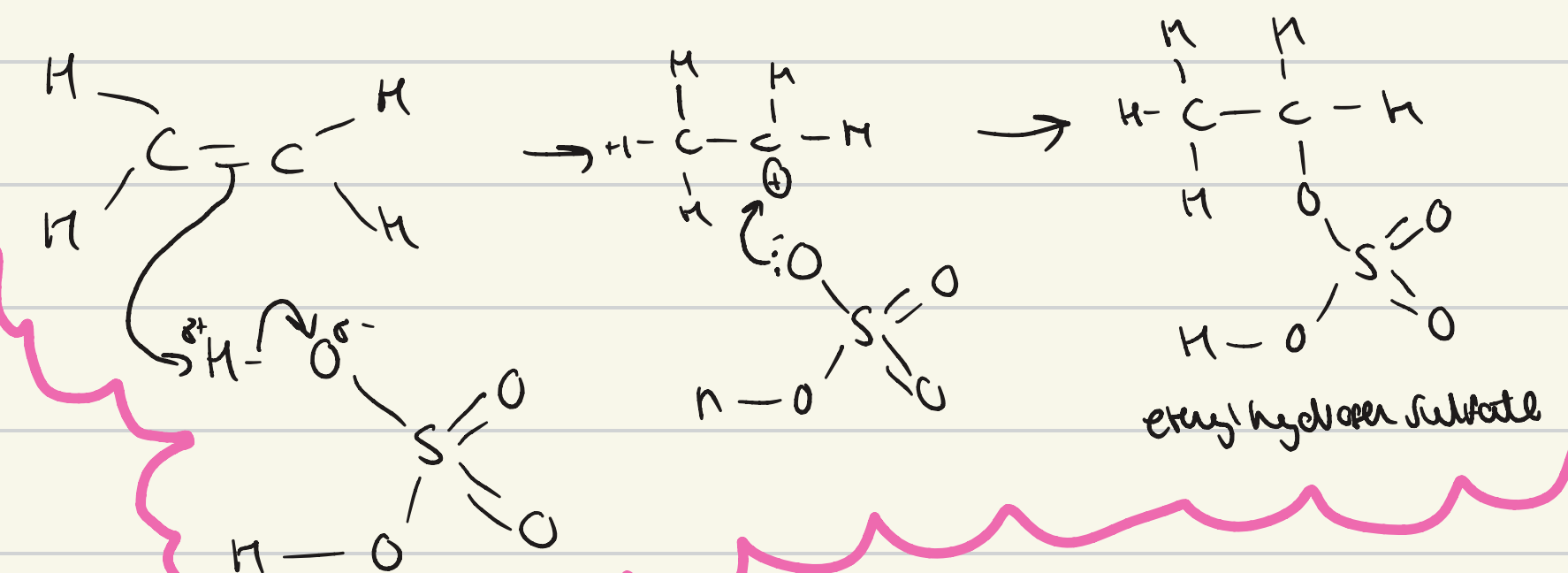
what is the general equation for the electrophilic addition to an alkene of concentrated sulfuric acid at RTP?
alkene + conc H2SO4 → alkyl hydrogen sulfate
give the mechanism for the electrophilic addition of sulfuric acid to an alkene?
give the equation for hydration of ethene?
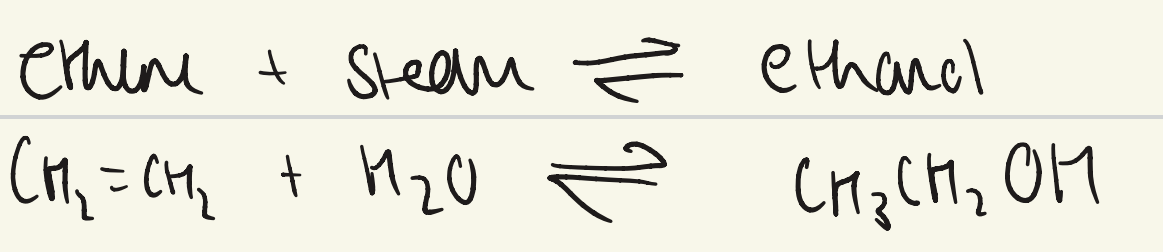
what are the conditions for industrial manufacture of ethanol (hydration of ethene)?
concentrated phosphoric acid
catalyst
60 atm
600 K
what are the advantages of industrial manufacture of ethanol?
100% atom economy
continuous process
fast
high yield
what are the disadvantages of industrial manufacture of ethanol?
uses fossil fuels
uses medium amount of energy
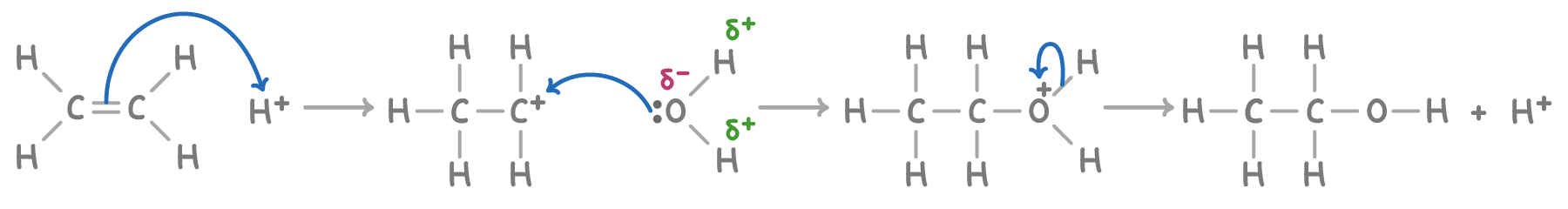
what is the mechanism for hydration of ethene?
what are the equations for combustion of an alkene?
alkene + O2 → CO2 + H2O
alkene + O2 → C + H2O
alkene + O2 → CO + H2O