Comprehensive Psychology: Classical & Operant Conditioning, Learning Theories
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is learning?
Any relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice.
What is observational learning?
Learning new behaviors by watching others.
Define associative learning.
Learning that certain events occur together.
What is classical conditioning?
Learning to make a reflex response to a stimulus other than the original, natural stimulus.
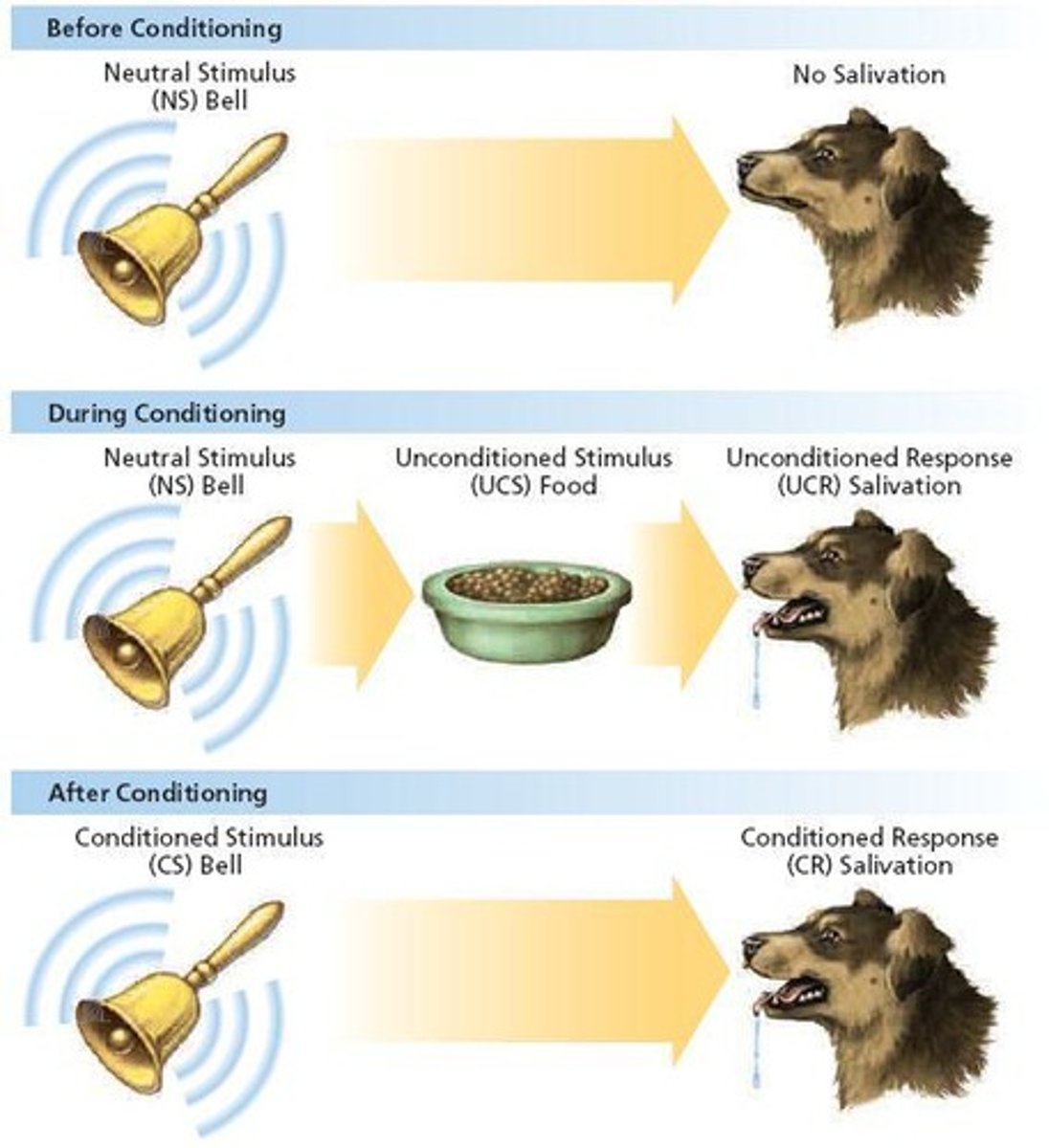
Who discovered classical conditioning?
Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist.

What is an unconditioned stimulus (UCS)?
A naturally occurring stimulus that leads to an involuntary response.
What is an unconditioned response (UCR)?
An involuntary response to a naturally occurring or unconditioned stimulus.
What is a conditioned stimulus (CS)?
A neutral stimulus that becomes able to produce a learned response by being paired with the UCS.
What is a conditioned response (CR)?
A learned reflex response to a conditioned stimulus.
What is acquisition in classical conditioning?
The repeated pairing of the neutral stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus.
What is stimulus generalization?
The tendency to respond to a stimulus that is similar to the original conditioned stimulus.
What is stimulus discrimination?
The tendency to stop responding to a stimulus similar to the original conditioned stimulus because it is not paired with the UCS.
What is extinction in classical conditioning?
The disappearance or weakening of a learned response following the removal of the unconditioned stimulus.
What is spontaneous recovery?
The reappearance of a learned response after extinction has occurred.
What is higher-order conditioning?
When a strong conditioned stimulus is paired with a neutral stimulus, causing the neutral stimulus to become a second conditioned stimulus.

What is conditioned emotional response (CER)?
An emotional response that has become classically conditioned to occur to learned stimuli.
What is conditioned taste aversion?
Development of a nausea response to a particular taste after it has been paired with nausea.
What is the cognitive perspective in classical conditioning?
The view that classical conditioning occurs because the CS provides information or expectancy about the UCS.
What is operant conditioning?
The learning of voluntary behavior through the effects of pleasant and unpleasant consequences.
What is Edward Thorndike's Law of Effect?
The law stating that responses followed by pleasurable consequences tend to be repeated.
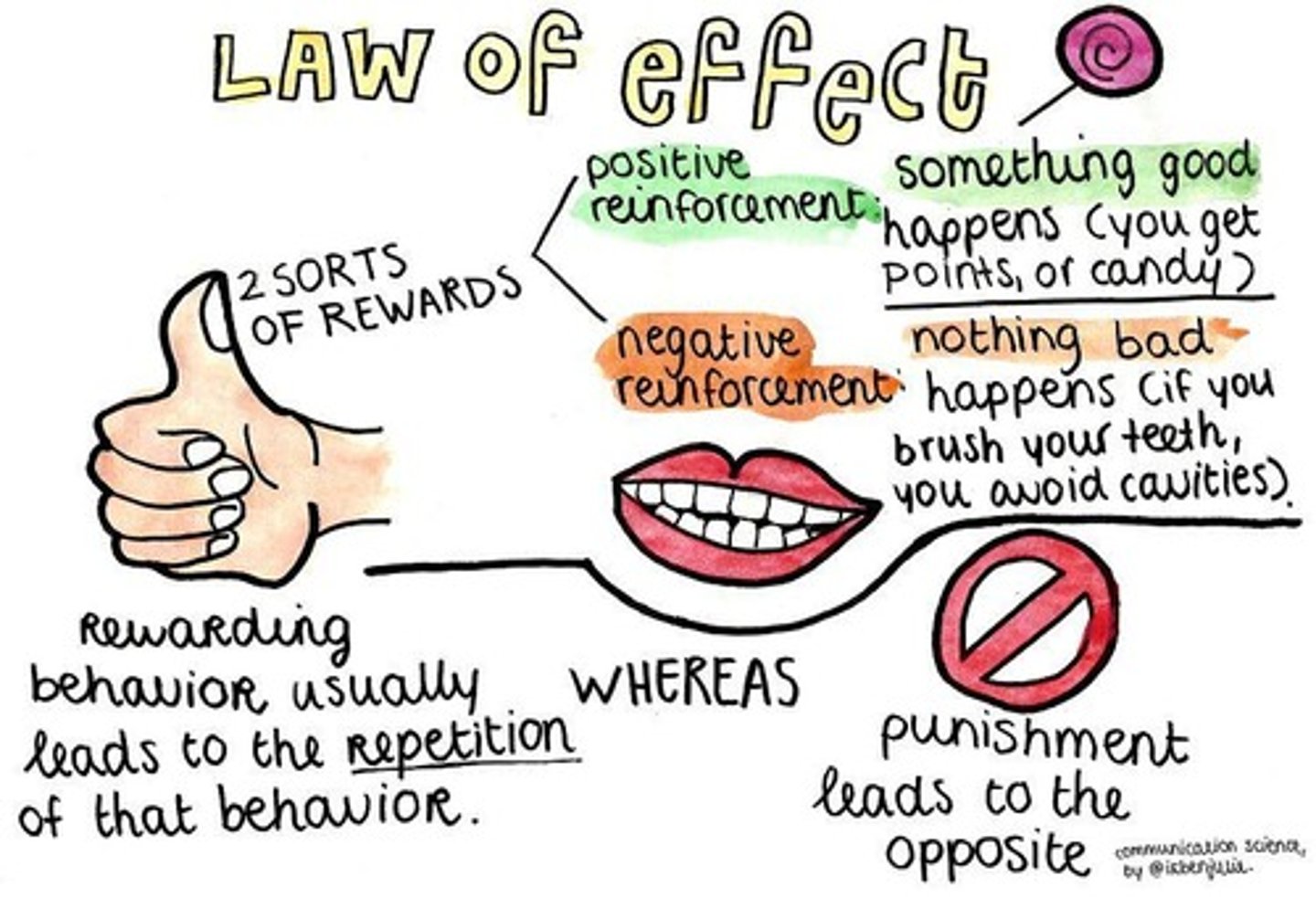
What is positive reinforcement?
The reinforcement of a response by the addition of a pleasurable stimulus.
What is negative reinforcement?
The reinforcement of a response by the removal of an unpleasant stimulus.
What is shaping in operant conditioning?
The reinforcement of successive approximations toward a desired behavior.
What is a primary reinforcer?
A reinforcer that is naturally reinforcing by meeting a basic biological need.
What is a secondary reinforcer?
A reinforcer that becomes reinforcing after being paired with a primary reinforcer.
What is continuous reinforcement?
The reinforcement of each and every correct response.
What is partial (intermittent) reinforcement?
A response that is reinforced after some, but not all, correct responses; it is very resistant to extinction.
What is a fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement?
A schedule where the number of responses required for reinforcement is always the same, e.g., FR-5 indicates reinforcement after every 5th response.

What is a variable ratio schedule of reinforcement?
A schedule where the number of responses required for reinforcement varies; e.g., VR-5 indicates an average of every 5th response.
What is a fixed interval schedule of reinforcement?
A schedule where the interval of time that must pass before reinforcement is always the same, e.g., FI-5 indicates reinforcement every five minutes.
What is a variable interval schedule of reinforcement?
A schedule where the interval of time that must pass before reinforcement varies; e.g., VI-5 indicates reinforcement on average every 5 minutes.
What is punishment in the context of behavior?
Any event or object that, when following a response, makes that response less likely to happen again.
What is positive punishment?
Punishment of a response by the addition or experiencing of an unpleasant stimulus.
What is negative punishment?
Punishment of a response by the removal of a pleasurable stimulus.
What are the three ways to make punishment more effective?
1. Punishment should immediately follow the behavior. 2. Punishment should be consistent. 3. Pair punishment of the wrong behavior with reinforcement of the right behavior.
What is a discriminative stimulus?
A stimulus that provides a cue for making a certain response in order to obtain reinforcement.
What is instinctive drift?
The tendency for an animal's behavior to revert to genetically controlled patterns.
What is behavior modification?
The use of operant conditioning techniques to bring about desired changes in behavior.
What is a token economy?
A type of behavior modification in which desired behavior is rewarded with tokens.
What is applied behavior analysis (ABA)?
A modern term for a form of behavior modification that uses shaping to mold a desired behavior.
What is latent learning?
Learning that remains hidden until its application becomes useful.
Who conducted significant research on latent learning?
Edward Tolman, who studied rats in mazes.
What are mirror neurons?
Neurons that fire when performing and observing others doing an activity, related to imitation and empathy.
What is intrinsic motivation?
The desire to perform a behavior for its own sake, driven by self-fulfillment or enjoyment.
What is extrinsic motivation?
The desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid punishment.
What is overjustification?
When excessive rewards discourage a learner from performing a task they already enjoy.
What is insight learning?
The sudden perception of relationships among various parts of a problem, leading to a quick solution.
What is learned helplessness?
A condition where an individual continues to fail and eventually quits due to repeated failures.