Principles of Pediatric Care
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1/13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the three major pediatric milestones?
Putting things in mouth and crawling
Showing attachment to caregiver
Speech Patterns
Pediatric Milestons from 2 months to 2 yrs?
6-12 months:
Crawl independently + Put things in mouth = choking hazard
9-12 months:
Stand support, may begin to take steps
12-18 months:
Walk independtly, maybe run.
18 months - 2 yrs:
Climbs stairs w help

Newborn vs Infants
Newborn less than a month
Infant 1 month - 1 yr
Infant: increase RR and greater surface area-volume ratio (Greater heat loss)
Do pediatrics have difference in head size?
Yes, they have fontanelles: soft spots on newborn’s head where bones have not yet fused.
close at 7-18 months
*sunken fontanelles are a sign of possible dehydration
*large occipital region can block airway
Pediatric Anatomic differences in Head.
Nose and nares smaller/narrower
Tongue larger % of oropharynx
Cricoid ring narrowest point of airway, (glottis is narrowest point for adults)
Infant Tidal volume and blood volume
Tidal Volume: 6-8 mL vs 500 ml in adult
Blood Volume: 80 ml/kg, normally 70 mL/kg
Abnormal signs
Not Crying
Lethargy: Severely Ill Sign
Dehydrated
Bolus dosing
Newborn (0-28 days): 10 mL/kg can repeat twice, max out at 30/mL kg total
Over 1 month: 20 mL/kg, may repeat twice (max our at 60 mL/kg total)
IO sizing
Adult: Yellow
Over 6 months: Blue
Under 6 months: Pink
BGL site for infant
Sole of the foot
Sign of Pediatric Respiratory Distress
Nasal Flaring and Seesaw Breathing
Normal Pediatric Vital Signs
Elevated HR, RR,
Decreased SBP
Normal temp
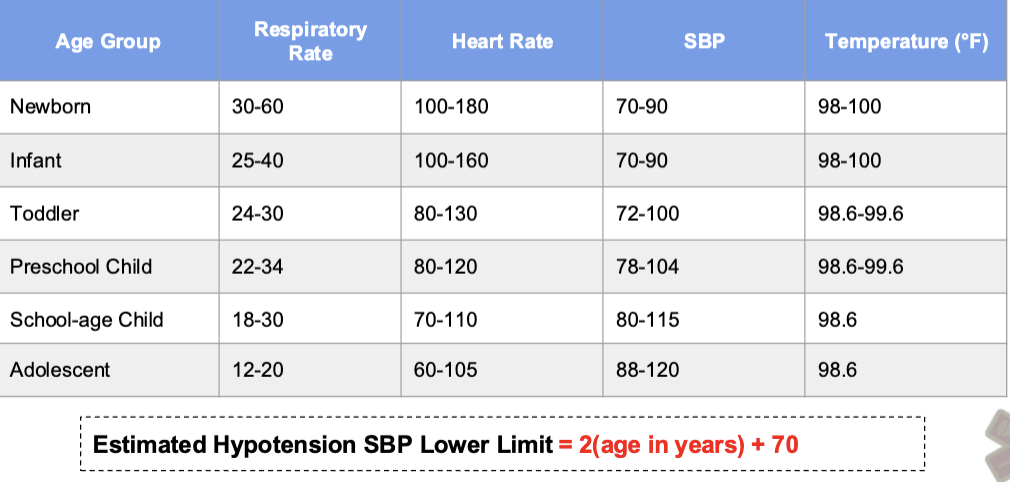
Under age of 3, BP generally not appropriate.
Capillary refill (<2 sec) a strong predictor of adequate perfusion
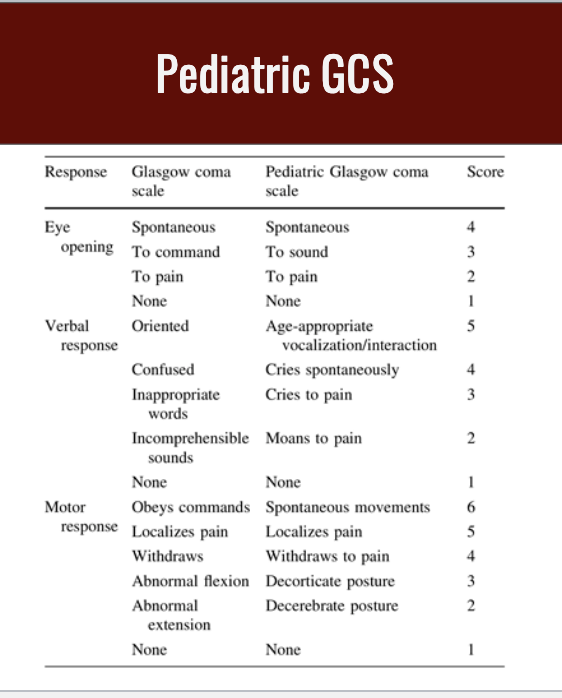
Pediatric GCS
Respiratory Distress
Less than 2y/o: nasal suction first
Over 2y/o: consider bronchodilators
Stridor: humidified O2
Bronchiolitis
Lower airway infection (viral) (2 month - 2 yr)
Most common: November-April
Increased mucous secretions, Increased lower airway edema
Signs: Fever, cough, dyspnea, expiratory wheezing, inspiratory rales
Treatment: SpO2 > 95, nebulized bronchodilators, and IV if dehydrated
Laryngotracheobronchitis (Croup)
Lower airway infection (viral) (6 month - 3 years)
Condition gets worse at night: inspiratory stridor, hoarseness, seal bark
Expiratory Stridor severe case
Treatment: Nebulized O2, Nebulzied epi

Epiglottitis
Lower airway infection (2 yr - 6 yr)
Almost completely occluded airway

Pertussis
Bacterial infection
S/S Whoop coughing

Febrile Seizures
A seizure triggered by rapid rate of fever increasing

Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Brief Resolved Unexplained Event (BRUE)
Sudden onset always transport, start CPR in absence of death
Common cause of SIDS
Preventable Sleep-Related (suffocation) death
Pediatric MVC
Birth - 2: rear facing car seat
2 - 4: forward facing car seat
4 - 8: booster seat
8+ seat belt
*Improper restrained child usually activates trauma
*pediatrics often sustain blunt force trauma
Children compensation?
compensate very well due to cardiovascular mechanisms until they cant decompensate very quickly
What causes cardiac arrests in pediatric populations
Hypoxia is the most common cause of arrests in pediatrics
When do you start compressions in infant?
HR below 60
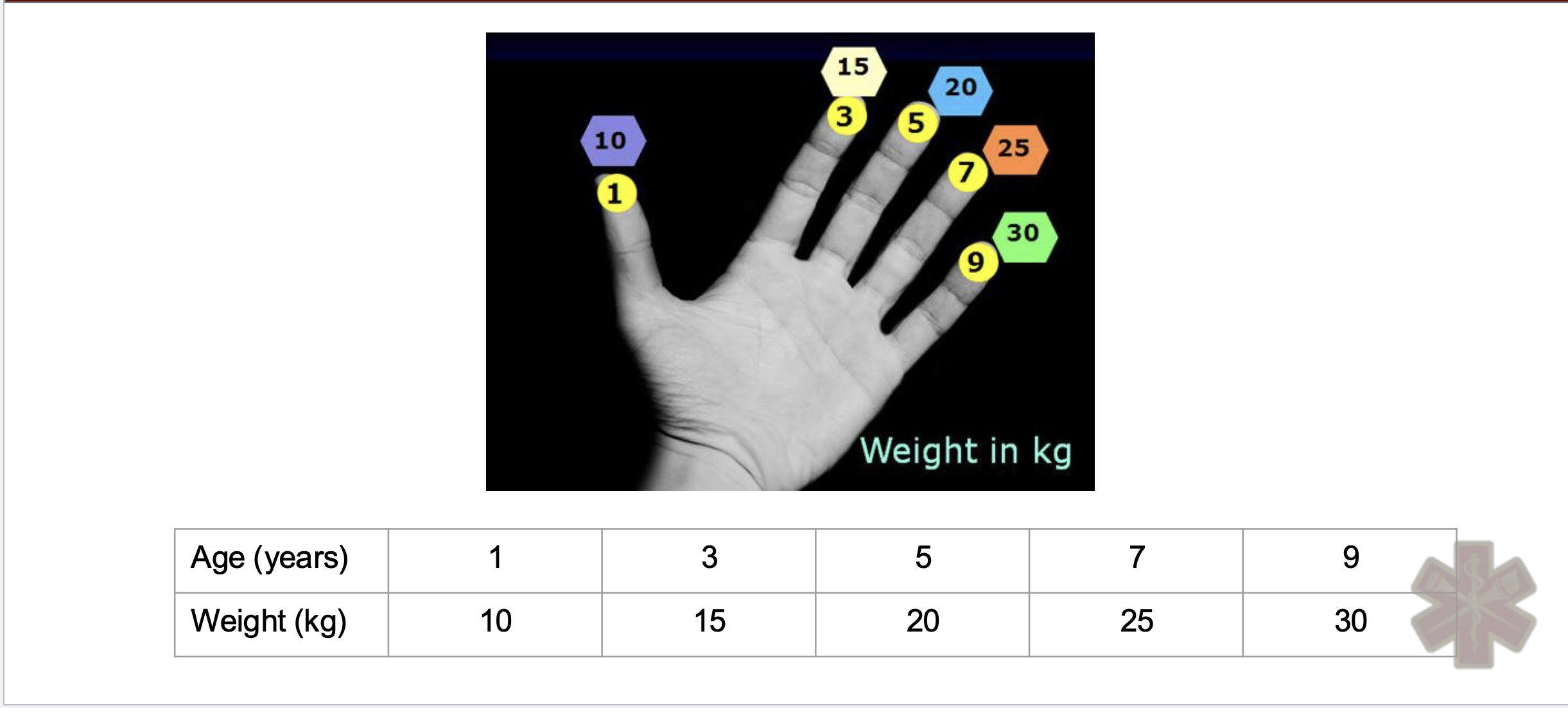
Estimating pediatric body weight