ch 14: cannabis
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
flowering hemp plant (Cannabis sativa) (2)
contains over 120 compounds called phytocannabinoids
psychoactive compound is ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
marijuana (4)
mix of dried leaves + flowering tops
smoked in pipes or bongs of rolled cigarettes (joints)
sometimes combined with tobacco
now available as edibles + vaping
how does marijuana potency (THC content) vary (4)
depending on genetic strain of the plant + growing conditions
can be increased by preventing pollination + seed production (sinsemilla)
hashish: concentrated form of cannabis → smoked or eaten
dabbing: cannabis is extracted w butane to form a waxy residue w high THC content → dap (one dose) is vaporized with a blowtorch or vape pen + inhaled
cannabis sativa vs indica (5)
sativa: tall, slender light green leaves
indica: shorter, bushier, darker
higher cannabidiol (CBD) to THC ratio
almost all strains are hybrids
growers cultivate different strains to adjust THC/CBD ratio for psychoactivity or therapeutic effects
phytocannabinoids
chemicals unique to cannabis
bind to cannabinoid receptors in the body
THC: most psychoactive → amount varies type of plant, growing conditions, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, neuro-protective effects
CBD: nonpsychoactive → anti-oxidant, anti-convulsant, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, neuro-protective effects
cannabis today vs 1960s/70s (3)
higher THC content
users can smoke less to obtain the same effect
higher THC increases risk of adverse reactions
synthetic cannabinoids (4)
dronabinol (marinol): has been replaced by the synthetic THC analogue nabione (cesamet) and nabiximols (sativex)
spice (K2): not legal → schedule II
binds more fully to brain cannabinoid receptors than THC → produces more intense effects
does not contain CBD → which reduces many of THC’s negative effects
routes of administration of cannabis + onset rate (5)
smoked → joints, bongs, pipes
easily absorbed by lungs + blood plasma lvls rise quickly
vaporizers
ingested → slower onset of effect + less predictability of action (user less in control)
liver metabolizes cannabis before it enters in brain → less THC gets to the brain
absorption, distribution + metabolism of THC (6)
rapidly absorbed in blood supply of the lungs
v. fat-soluble → easily cross BBB
gone from brain within a few hours as it accumulates in fatty tissue
metabolize din liver by CYP450 system → metabolites excreted in urine/feces
complete elimination is slow bc THC persists in fat tissue (20-30 hours half life_
THC-COOH can be detected in urine up to 2 weeks
How do CB1/CB2 receptor signals reduce neurotransmission, and where are CB1 receptors positioned to do this? (4)
Receptor type: Gi/o-coupled, metabotropic.
Signaling: ↓ cAMP, ↓ VG Ca²⁺ entry, ↑ K⁺ conductance → hyperpolarization & less vesicular release.
Localization: Presynaptic CB1 on terminals of ACh, DA, NE, 5-HT, GABA, Glu neurons → broad inhibition of transmitter release.
Longer-term: MAPK pathway & epigenetic changes → plasticity/learning/memory effects.
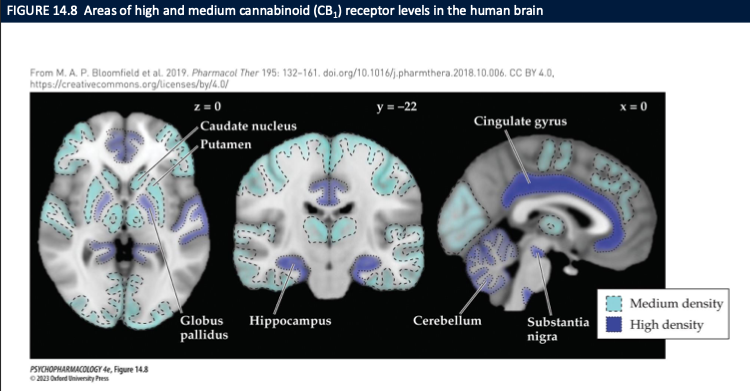
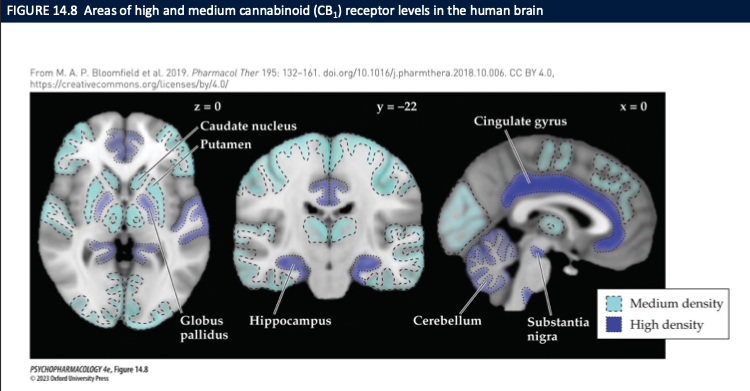
Where is CB1 receptor density highest in the brain (per the diagram), and what functions do these regions explain?
High/medium CB1 density:
Basal ganglia: caudate/putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra → motor effects (slowed movement, altered initiation).
Hippocampus → memory/learning deficits (short-term memory).
Cerebellum → coordination/ataxia.
Cingulate cortex → attention/affect modulation.
Implication: Cannabis alters movement, memory, coordination, and emotion via dense CB1 expression in these circuits; CB2 adds immune/microglial modulation.
What are the CB1-mediated behavioral “tetrad” effects of THC in rodents (4), and which drugs are used to prove CB1 involvement? (2)
Tetrad (CB1): ↓ locomotion,
hypothermia,
catalepsy,
hypophagia
CB1 antagonists: SR141716A (rimonabant), AM251 → block THC/CB agonist effects
How do CB agonists affect anxiety, and why is the effect dose-dependent? (3)
Low dose: anxiolytic (network modulation; reduced Glu drive in fear circuits)
High dose: anxiogenic (broader inhibition incl. GABA, network dysregulation)
Net result = biphasic dose–response
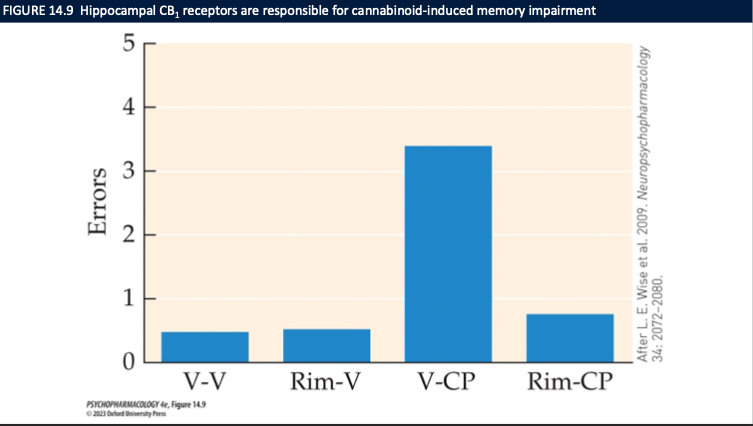
What is the role of CB1 in cannabis-induced memory impairment, and what does Fig. 14.9 show? (3)
CB1 activation in hippocampus (CA1) → ↓ LTP → memory impairment
Fig. 14.9: Vehicle→CP group = high errors; Rimonabant→CP = errors normalized
Conclusion: CB1 is required for the memory deficit (rimonabant blocks it)
What are key immune effects of CB2 activation? (3)
↓ cytokine release (anti-inflammatory)
Alters immune cell migration to inflammatory sites
Expressed in immune system, plus microglia & some neurons
cannabidiol (CBD) has a similar structure to ____ but is not ___ or _____ and can act as a ____ of CB1 receptors which inhibits the _____ → enhancing activity of the _____
THC
intoxicating
dependence-producing
negative allosteric modulator
breakdown of endogenous cannabinoids
endocannabinoid system
brain imaging shows ___ promotes regional brain activation + _____ → ___ tends to decrease these processes
THC
enhanced local blood flow
CBD
what are endocannabinoids + types(6)
cannabinoid receptor agonists synthesized by the body
anandamide: partial agonist
2-AG: full agonist at CB1 and CH2
lipid soluble → can’t be stored in vesicles
synthesized + released when needed
triggered by a rise in intracellular Ca2+ lvls
what do endocannabinoids help regulate and what does the endocannabinoid system mediate? (2)
help regulate mood states, anxiety and fear, reactions to stress → confirmed by rodent studies
hippocampal endocannabinoid system is an important mediator of anxiety responses
how are endocannabinoids removed + metabolized
removed from extracellular by an endocannabinoid membrane transporter
anandamide metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH)
2-AG by monoacyl-glycerol lipase (MAGL)
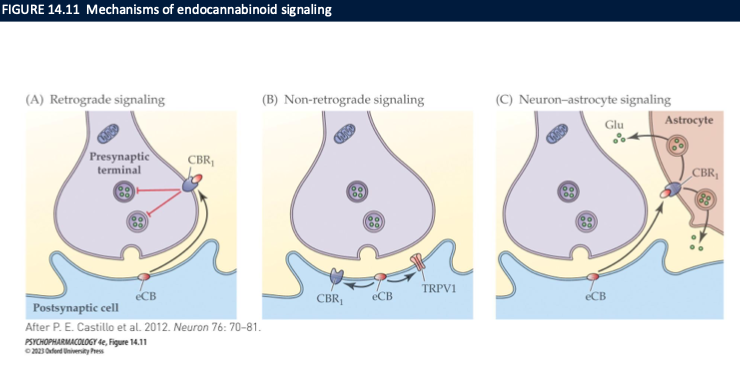
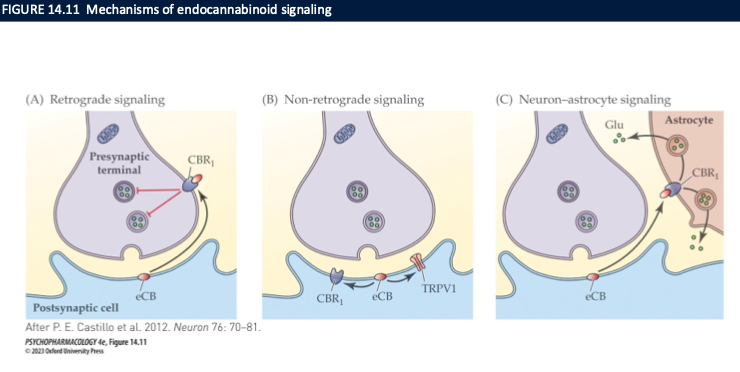
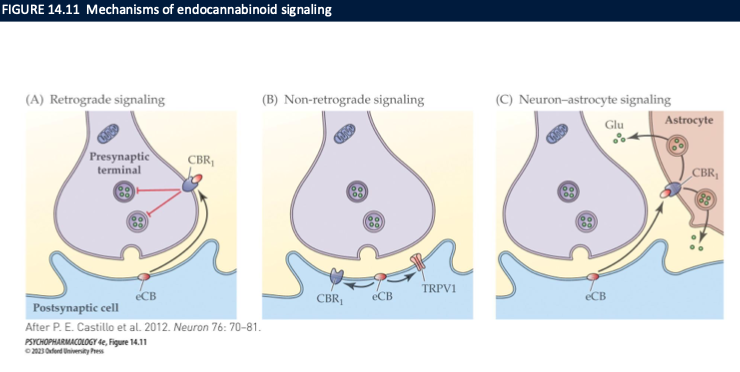
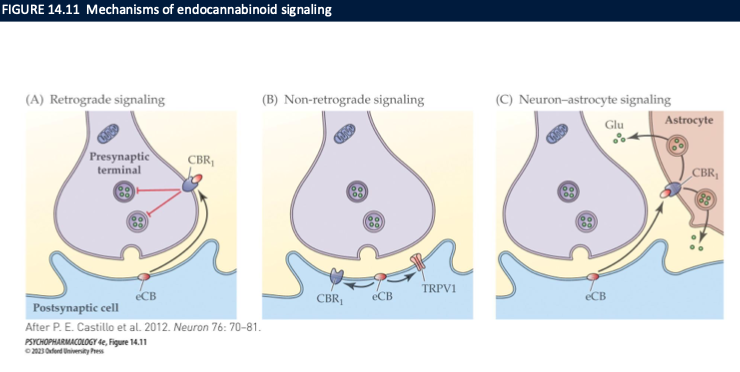
mechanism of endocannabinoid signalling
retrograde signalling (2-AG)
DSE: depolarization-induced suppression of excitation
DSI: depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition
non-retrograde signalling → anandamide
neuron-astrocyte signalling
What are 3 major functions of the endocannabinoid system highlighted in class? (3)
Extinction of learned fear → deficits may ↑ PTSD risk
Regulation of eating/hunger/energy via CB₁ in hypothalamus & reward circuits
Pain regulation → sensory + affective, esp. neuropathic pain
How do CB₁ receptors promote feeding? (4)
CB₁ in hypothalamus → ↑ orexigenic peptides (NPY/AgRP, ↓ POMC tone)
CB₁ in stomach/brain → interacts with ghrelin → hunger signaling
CB₁ in reward/cortex/OFC → ↑ palatability & food reward
CB₁ antagonists (rimonabant) → reliably ↓ food intake
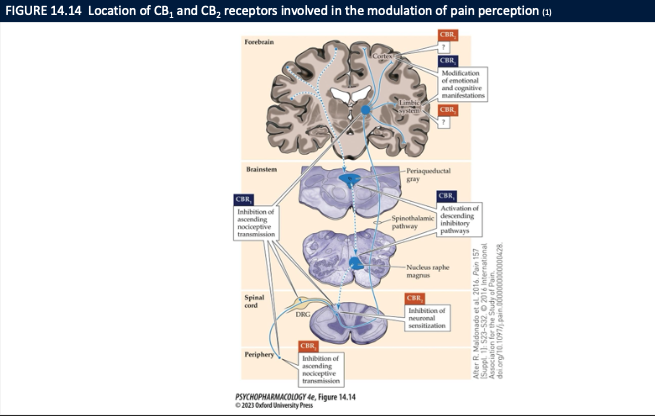
Where are CB₁/CB₂ receptors that mediate cannabinoid analgesia? (4)
PAG / RVM / brainstem pain modulatory regions
Spinal dorsal horn (primary sensory input)
Thalamus & limbic areas (amygdala) → ↓ emotional reaction to pain
Effect: ↓ pain perception and ↓ pain unpleasantness
Why is endocannabinoid signaling a target for PTSD, obesity, and chronic pain? (3)
PTSD → eCBs facilitate extinction
Obesity → eCBs drive feeding/reward → block CB₁ to reduce intake
Chronic/neuropathic pain → eCBs dampen nociceptive transmission at multiple levels
What major processes do endocannabinoids normally regulate? (5)
Neuroplasticity, learning/memory, neurogenesis, homeostasis
Stress & emotional regulation, reward signaling
Pain & appetite
Anti-inflammatory / antioxidant effects
⚠ Cannabis during brain development can disrupt these
What are the main medical/therapeutic cannabinoid options and what are they for? (4)
Pure THC: dronabinol (Marinol), nabilone (Cesamet) → ↑appetite, anti-nausea
THC + CBD extract: nabiximols (Sativex) → neuropathic pain, MS spasticity
CBD only: Epidiolex → pediatric epilepsy
Medical marijuana: mixed indications (pain, nausea, spasticity)
What are the 4 stages and main acute effects of cannabis? (3)
4 stages: buzz → high → stoned → come-down
Physiologic: ↑HR, ↑BP, ↑appetite
Magnitude depends on dose, frequency, user characteristics, setting, expectations
How do we know cannabis effects are CB₁-mediated, and what can go wrong at high doses? (4)
intoxication reduced by CB₁ antagonist rimonabant → CB₁-dependent
High doses: anxiety, transient psychotic symptoms, paranoia, violent behavior
Acute toxic reaction = CNS excitation or depression + tachycardia + GI upset
Rarely life-threatening
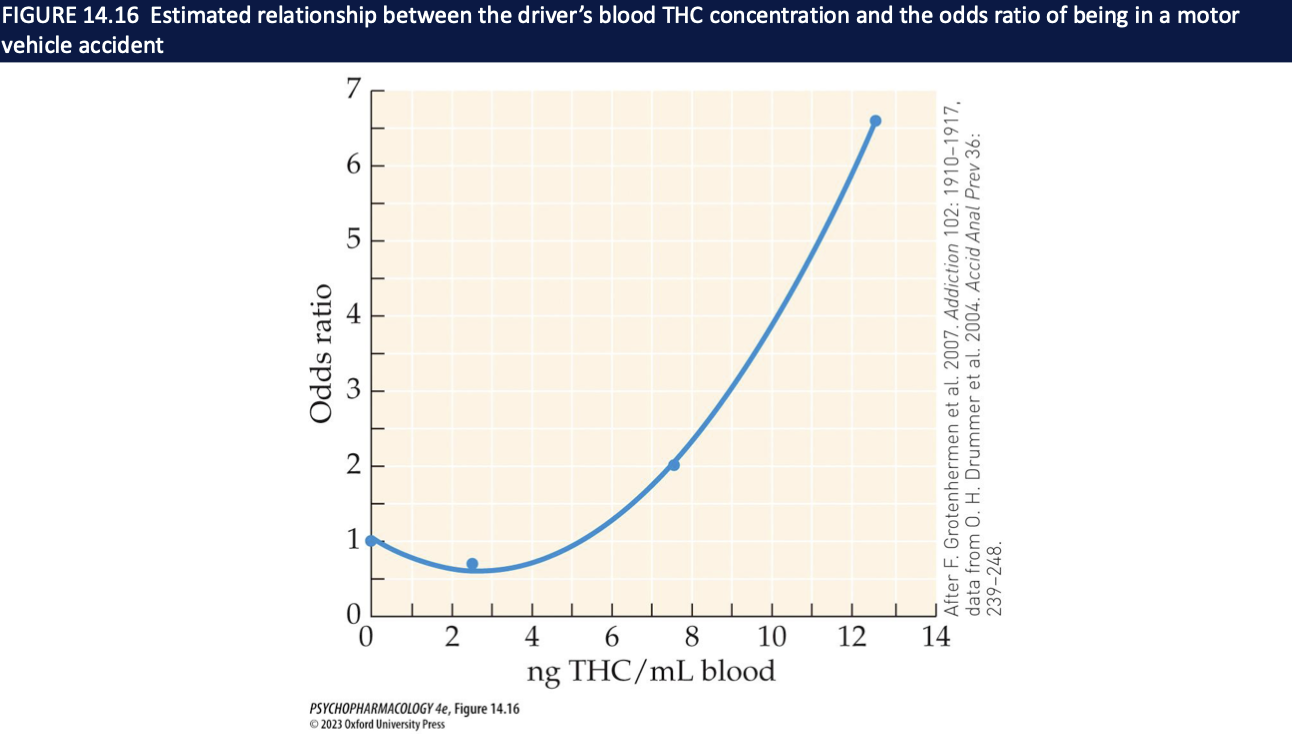
How does cannabis affect cognition and driving? What does the THC–crash graph show?
Impairs learning, memory, attention, decision making (hippocampal-dependent)
Impairs complex psychomotor tasks → driving gets worse (↑ with alcohol)
Graph: as blood THC ↑, odds of motor vehicle accident ↑ (rising curve)
Takeaway: acute THC = cognitive + motor risk
Are cannabinoids rewarding/reinforcing in animals? (4)
Yes, but weaker than opioids/psychostimulants
THC = partial CB₁ agonist; some synthetics (WIN55,212-2) = full CB₁ → stronger reinforcement
CB₁ part of brain reward system and interacts with endogenous opioids
Still enough for self-administration in animal models
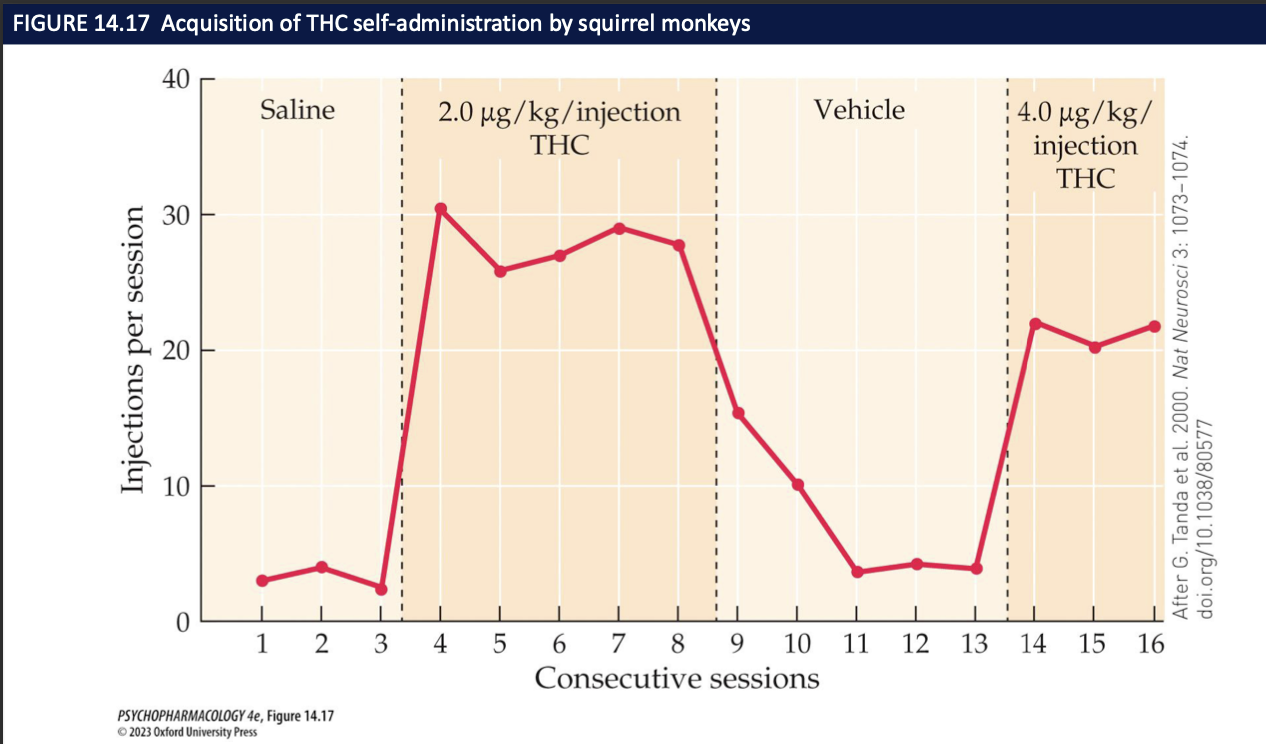
What is the mechanism for cannabinoid reinforcement, and what does the monkey graph show? (3)
Presynaptic CB₁ on GABAergic terminals in VTA → ↓ GABA on DA neurons → disinhibition → ↑ DA firing → ↑ DA in NAcc
That DA increase = reinforcing signal
Monkey self-administration graph: THC injections → responding ↑; vehicle → responding ↓ → THC functions as a reinforcer
How can chronic cannabis use lead to cannabis use disorder (CUD)? (4)
DSM-5: criteria for intoxication, withdrawal, CUD
Early start, frequent/heavy use, tobacco co-use, male sex → ↑ risk
Biological + psychosocial variables (mood/anxiety/personality disorders, availability) also push risk up
Even though most users don’t develop CUD, a meaningful minority does
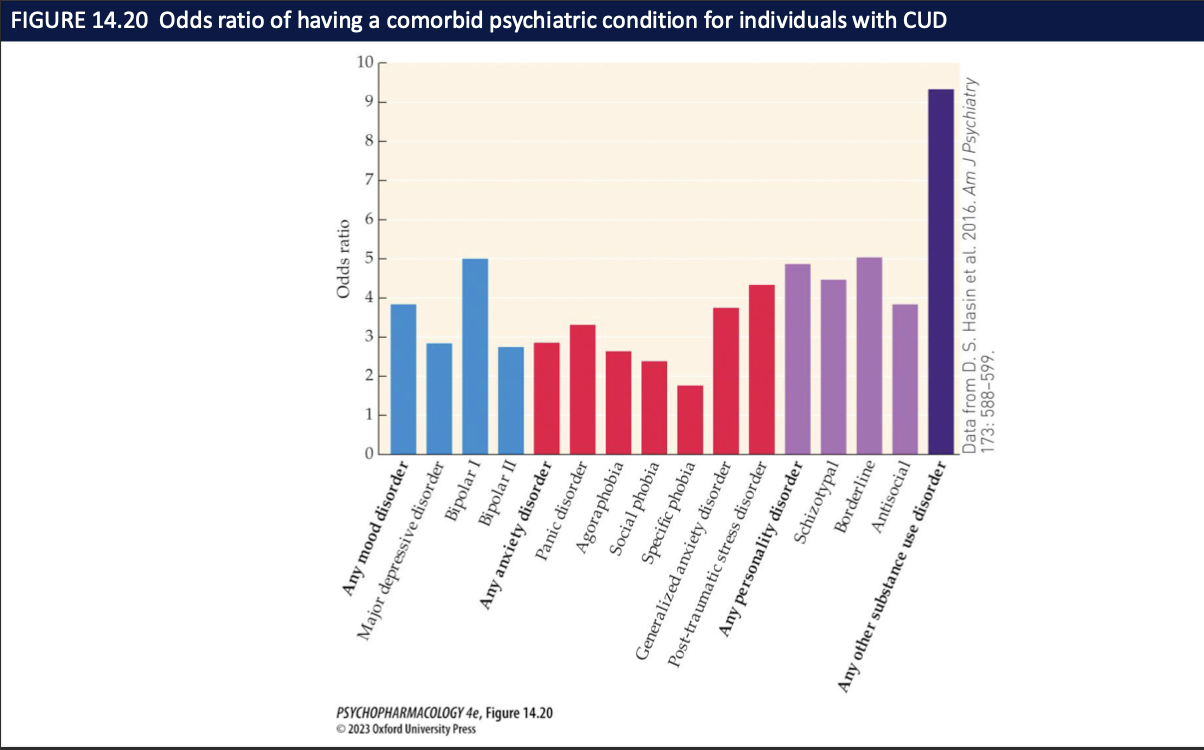
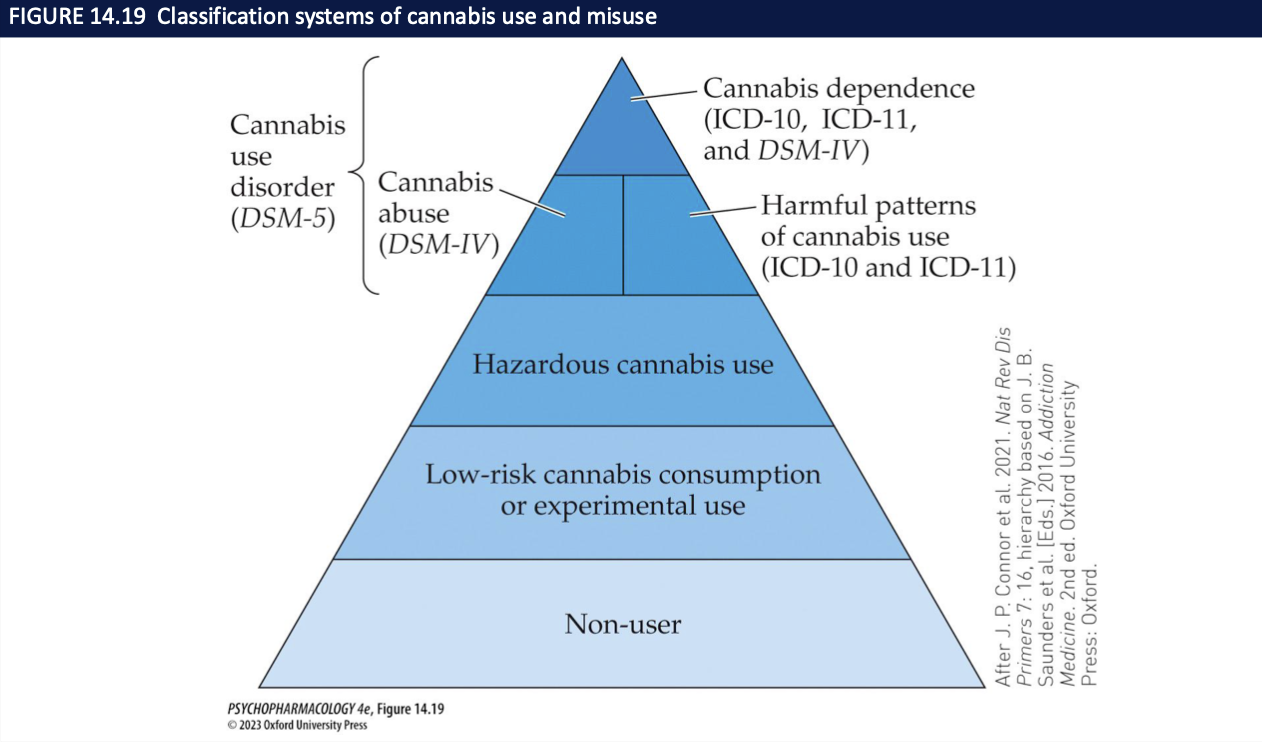
What do the cannabis-use pyramid and odds-ratio graph tell us? (4)
Pyramid: largest layer = low-risk/occasional; smaller layers = hazardous → CUD → dependence
Shows progression is possible but not inevitable
Odds-ratio graph: people with CUD have higher odds of other psychiatric conditions (esp. mood/anxiety)
Takeaway: severity ↑ → comorbidity ↑
What long-term effects can regular cannabis use produce? (3)
Tolerance: CB₁ receptor desensitization/down-regulation with repeated use
Dependence: can develop; generally milder than other drugs
Withdrawal (if present): irritability, sleep disturbance, ↓ appetite, anxiety; usually not severe
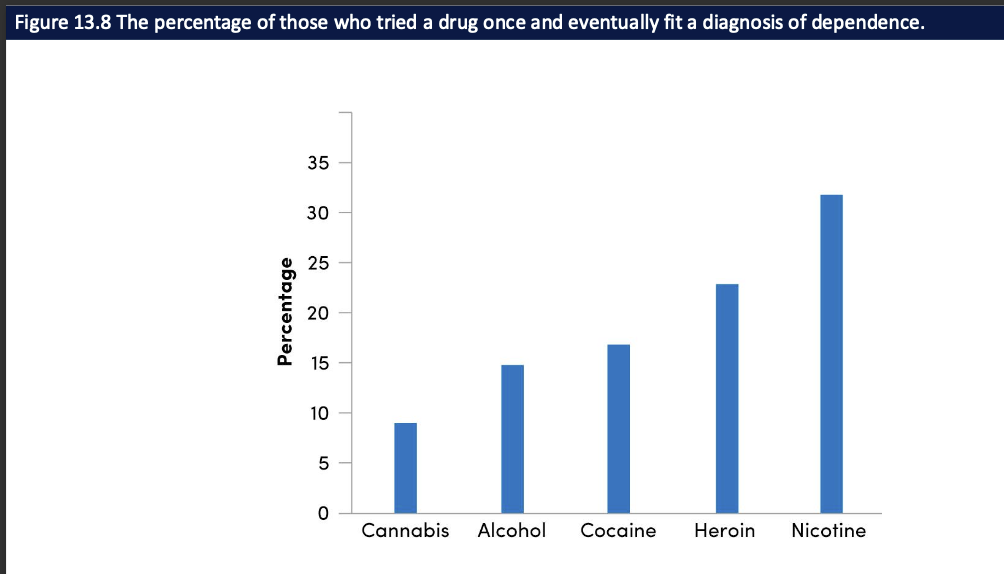
What does the “% who progress to dependence” graph show? (4)
Some who try cannabis eventually develop CUD/dependence
% is lower than cocaine, heroin, nicotine
But not zero → cannabis still has real addiction potential
Takeaway: “less addictive” ≠ “non-addictive”
How is cannabis use disorder (CUD) treated? (4)
Long-term heavy use → CUD (craving, loss of control, continued use despite problems)
Best evidence: CBT, relapse-prevention, contingency management
Meds (dronabinol, nabiximols) haven’t reliably improved long-term abstinence
Goal: reduce use + prevent relapse
What cognitive/functional problems are linked to chronic cannabis use? (4)
Impaired attention, working memory, learning (especially with frequent/recent use)
Heaviest effects when onset is in adolescence and use is sustained
Linked to lower educational attainment and poorer occupational outcomes
Some effects may improve with abstinence, but not always fully
What do imaging and animal studies suggest about long-term cannabis exposure? (3)
Imaging: some users show reduced gray matter / altered activation in PFC and related regions
Animal/adolescent models: chronic THC → changes in glutamatergic, GABAergic, DA systems and PFC impairments
Suggests: developing brain is more vulnerable → supports caution with early, heavy use
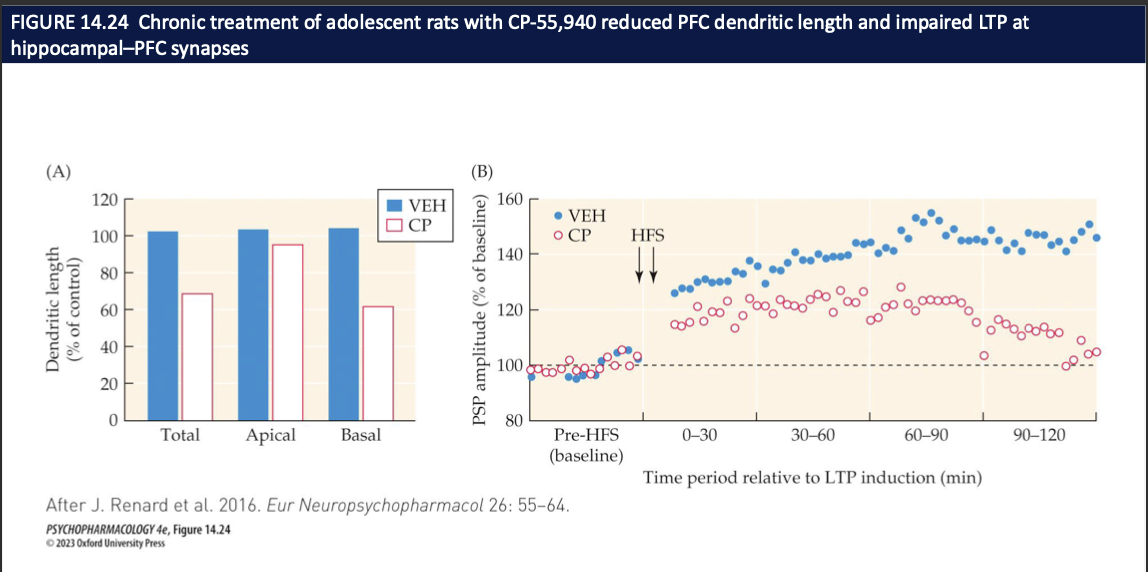
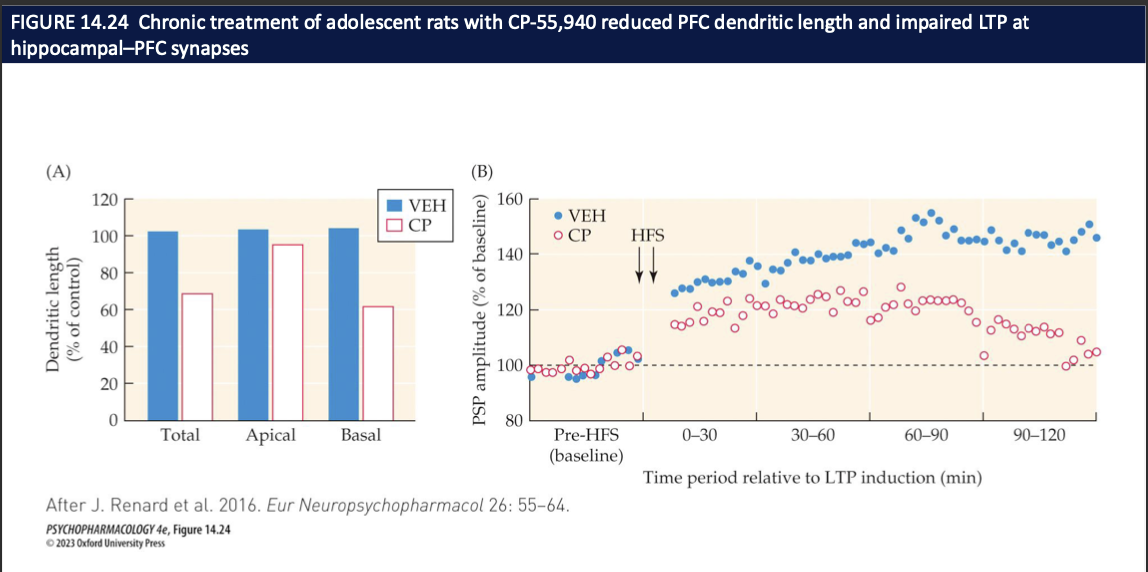
How does repeated adolescent exposure to a strong CB₁ agonist (CP-55,940) affect PFC structure and plasticity? (4)
CP = THC-like CB₁ receptor agonist
Chronic CP in adolescence → PFC dendritic length ↓ (total, apical, basal) vs vehicle
Same animals → LTP at hippocampus→PFC synapses is blunted after HFS
Interpretation: early, heavy cannabinoid signaling can weaken PFC wiring + learning-related plasticity → possible basis for cognitive effects of early cannabis use