Heart and Cardiovascular System
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
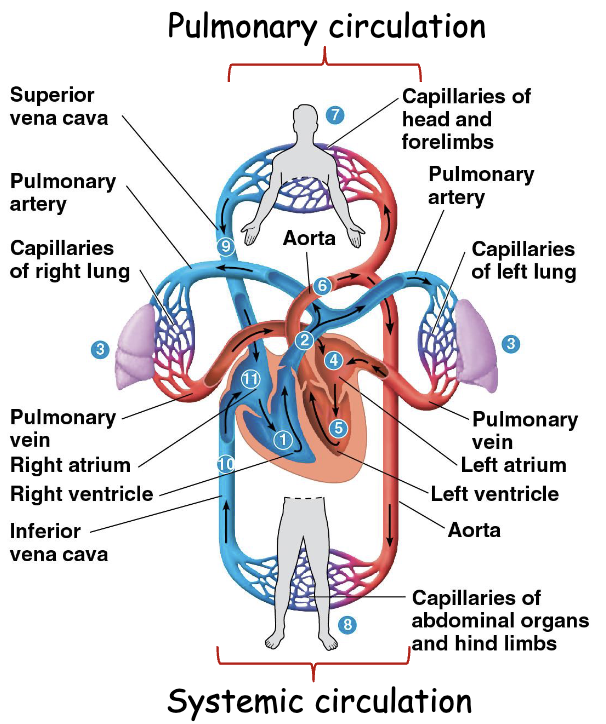
How does blood flow through the heart?
venous blood via the superior and inferior vena cava → right atrium → passes AV valve → moves to the right ventricle
right ventricle contracts → blood is is pumped to the lungs (systemic circulation)
in lungs, blood enters capillaries for oxygenation,
capillaries → left lung
left lung → pulmonary vein → returns to the left atrium,
left atrium → left ventricle
left ventricle contracts and blood → aorta
aorta → blood tissues,skeletal muscle etc. (systemic circulation)
systemic circulation → right atrium to start cycle again
Whats the function of the AV and SV nodse/valves?
PREVENT blood flow to LEFT ATRIUM when ventricle contracts by CLOSING mitral valve
What are the characteristics and functions of veins?
take blood → heart
How do action potentials travel down the heart?
Sinoatrial (SA) node generates electrical impulse using autorhythmic (pacemaker cells)
this is why its called the “pacemaker” of the heart
fires action potentials at a HIGHER frequency compared to AV node,
mechanical events happen AFTER electrical events
What happens after SA node generates action potential? Whats the mechanical and electrical event associated with this?
Action potential in SA node → atria
Electrical event: atrial depolarization (caused by action potential)
dePolarization for P WAVE on ECG
Mechanical event: atrial contraction
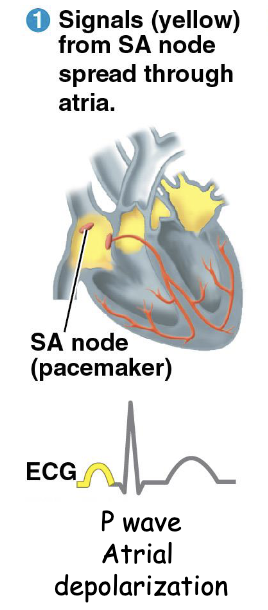
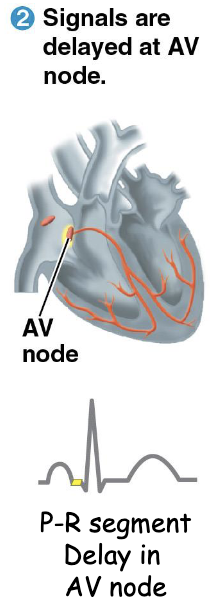
What happens after action potential travels to atria? Electrical and Mechanical events?
Action potential in atria → AP gets stuck at AV NODE (intyernodal pathway)
Electrical event: action potential DELAY
Para, Rest = P-R SEGMENT on ECG
Mechanical event: atria is contracting
Why does the action potential get stuck in the AV node?
the AV node delays the action potential in order to provide enough time for muscle cells in ATRIA to contract BEFORE muscle cells of VENTRICLE contract
What happens after action potential gets unstuck at the AV node?
Action potential in AV node → bundle of his
Electrical event: VENTRICULAR depolarization and ATRIAL REPOLARIZATION (masked by QRS complex in ECG)
ventriIQular contraction → Q
AtrRial Repolarization → R
= QRS on ECG
Mechanical event: atrial RELAXATION
ventricular depolarization
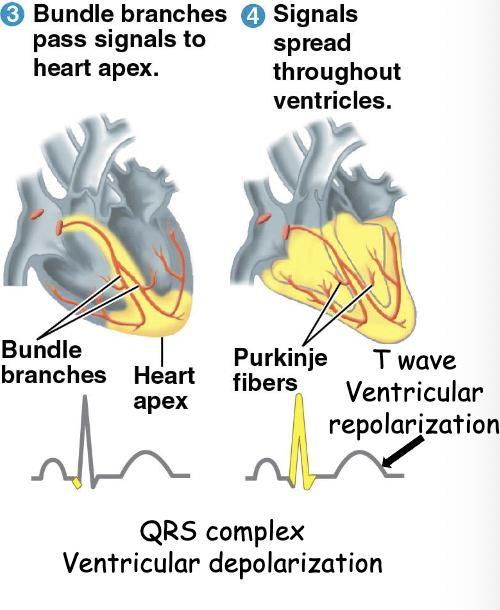
What happens after the QRS complex?
Action potential causes Ventricle to depolarize
Electrical: NONE
VenTricle conTraction= → S-T segment
Mechanical event: ventricular CONTRACTION
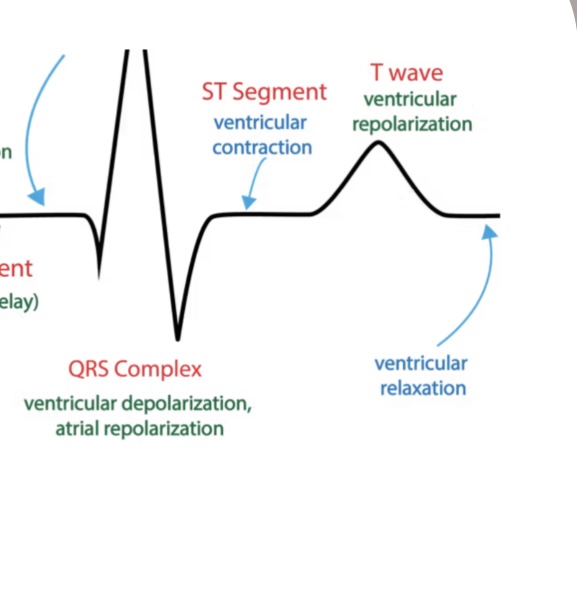
What happens after the S-T segment?
Electrical: NONE
VenTricle Repolarization = → T WAVE
Mechanical event: ventricular REPOLARIZATION
What are the roles of arteries and arterioles in the cardiovascular system? Describe their main characteristics.