Biol 208: Lecture 26 - Primary Production (Terrestrial + Aquatic)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Define ecosystem + What ecosystem ecology focuses on + What the Key processes are
Ecosystem = Biological community together with its associated physical and chemical environment
Ecosystem Ecology = Understanding how organisms interact with their environment and how this influences the flow of energy + the cycling of nutrients
Key processes = Primary production, decomposition + Nutrient cycling
What is the unit of measurement for Primary production
kgC/m² or KgC/m³
weight of carbon per unit area
Define Primary productivity
Fixation of Energy
And the unit of measurement
= The amount of Energy fixed by autotrophs over an Interval of time
Fixation of energy = use solar E to convert CO2 into sugar + other forms of biomass → Photosynthesis
Units = KgC/m³/year
2 Measures of Primary production
GPP
NPP
Why do we need to know the difference
GPP = gross primary production
TOTAL amount of E fixed by ALL autotrophs in the ecosystem
= Photosynthesis
NPP = Net primary production
Total amount of E fixed by all autotrophs MINUS the cost associated with its fixation
= Photosynthesis - Respiration
Why we need to know the difference?
Because ONLY NPP refers to the amount of energy available to consumers in an ecosystem
What is Remote sensing?
How does it work?
A method of measuring ecosystem level primary production
Remote sensing = science of acquiring info about the earth’s surface without contact
How it works = Senses + records the amount of Reflected or emitted energy
uses camera sensors on satellites (Landsat 1 = first)
What is TERRESTRIAL Primary productivity Mainly limited by?
Moisture + Temperature
NPP = low in the arctic zone (Temp limits)
NPP = low in southern prairies (Moisture limits)
NPP increases with increasing precipitation (point do not fall perfectly on the line indicating there are other factors that are also important for NPP)
What is AET?
Units?
How does it change with precipitation + Temperature
Actual Evapotranspiration = The amount of water that evaporates + transpires off a landscape during a given time
Units = mm water/time
Measure that accounts for BOTH TEMP + PRECIPITATION
AET increases with increased precipitation + temp
Soil Fertility
Liebig’s Law of the Minimum
Soil fertility limits NPP (adding nutrients = increases NPP)
Liebig’s law of the minimum: Plant growth is not limited by the Total amount of all soil nutrients but by the single MOST LIMITED nutrient that is present in the lowest quantity
Do all plants respond the same to nutrient addition?
Why or Why not?
NO
Some species have high nutrient efficiency = Grow best under low nutrient (competition avoidance). When nutrients are added theses species are outcompeted
How does DIVERSITY affect NPP?
Which 3 plant functional groups had the highest NPP?
Greater Primary producer diversity = Greater NPP
C4, grasses + legumes had the highest NPP
What is NPP mainly limited by in AQUATIC SYSTEMS?
Nutrient availability
Where is MARINE NPP usually the greatest
3 reasons why
Near the shores
why:
Nutrients runoff from terrestrial
Nutrient UPWELLING (@ equator as well)
Nutrient availability from breakdown of organic matter
Info Dump on the Nutrient Enrichment experiment done on samples from the Baltic sea
Methods
What is the limiting nutrient in marine ecosystems?
Water samples in flasks with nutrient enrichment treatment: Nitrogen, Phosphorus + Control
Measured Chlorophyll concentration
NITROGEN = most limiting nutrient
amount of chlorophyll increased with addition of Nitrogen
What is the limiting nutrient in FRESHWATER ecosystems?
Algal NPP is correlated with PHSOPHORUS
Info Dump on the Whole lake experiments at ELA
What is ELA
Manipulation of Lake 266: Methods + Results
ELA = Experimental lake area in Ontario (58 lakes)
Area for international research for long term fresh-water experiments
Eutrophication experiments
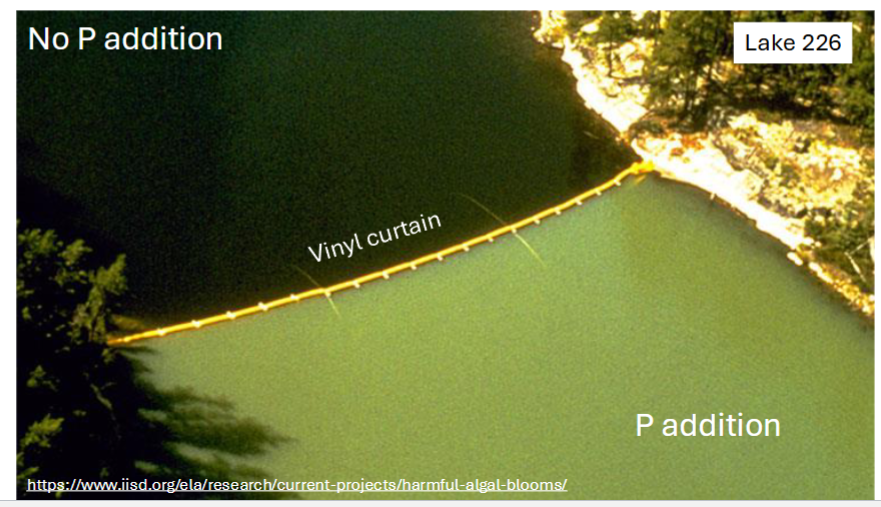
Lake 266:
Vinyl curtain to divide the lake
Fertilize from 1973-1980 with C, N + P
Results: Phytoplankton biomass increased 4-8x’s with the addition of Phosphorus
Phosphorus was banned in detergents + other cleaning products

Eutrophication Define
what things can it cause
= Nutrient enrichment of a water body through natural processes or pollution
causes:
Rapid Algal growth
Hypoxia
Dead zones
Define Hypoxia + Dead zones
Hypoxia = Low water O2 levels less than 2mg O2/L
Dead zones = Areas of Hypoxias → DEVOID OF LIFE
typically the consequence of pollution, eutrophication and high rates of decomposition
Where are Global Hypoxia hotspots located?
Near where there is High HUMAN activity
Primary Production + Consumer Influence
Define:
Trophic cascade
Bottom up vs. Top-down control
Trophic cascade = Effects of Predators on prey that alter abundance, biomass or productivity of community
Bottom up = Abiotic factors that limit primary prod (eg. Temp + nutrients) = control primary prod.
Top down = Consumers in an ecosystem = control primary productivity
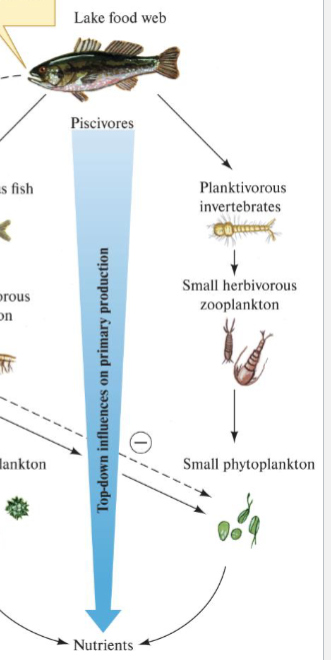
How does increasing Predators affect Planktivore, Herbivore + Phytoplankton (NPP)
Decrease Planktivore
Increase Herbivore
Decrease phytoplankton = Decrease NPP
How did Grazing by large animals affect primary production?
Intermediate grazing = OVERCOMPENSATION of plants = INCREASE NPP
Secondary production Define
Production of biomass by heterotrophic consumer organisms
Ecosystem with greater primary prod generally support high levels of secondary prod
Define: Trophic dynamics + Ecological Efficiency
Trophic Dynamics = Transfer of E from one part of the ecosystem to another
Ecological Efficiency = Percent biomass produced at lower trophic levels that is transferred to biomass produced at next higher level
Top-down vs. Bottom up control on SECONDARY PRODUCTION
Which is more important?
Top down = higher influence on Herbivore population
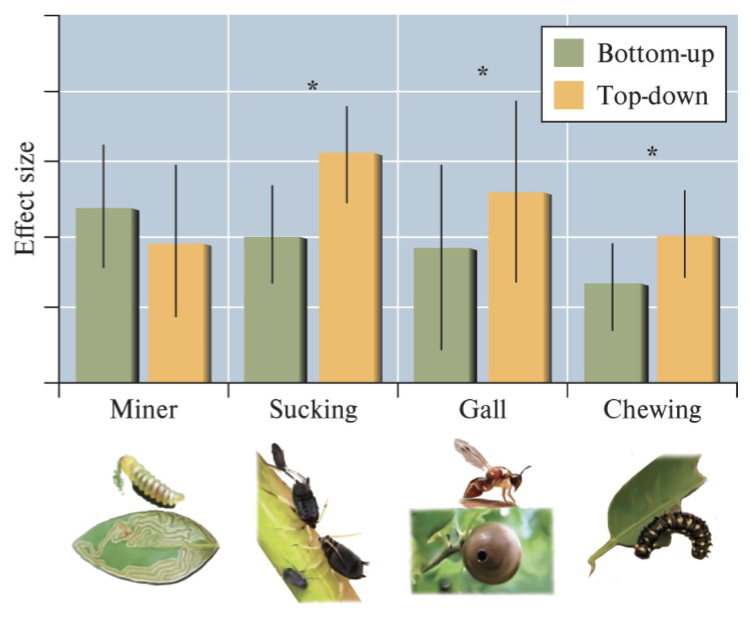
Why does Top-down control have Less effect on MINER in this graph when top down is the most important control of herbivore populations?
Miner larvae = in the middle of the leaf + protected from predators
What is the WORLD IS GREEN hypothesis?
Dominance of plants on our planet is evidence that herbivore populations are being kept in check by the predators
Evidence of Top-Down control on herbivores/ secondary producers