UC Berkeley Chem 1A Midterm 1 Fall 2023 Flashcards
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is Chemistry?
The study of matter and the changes it undergoes
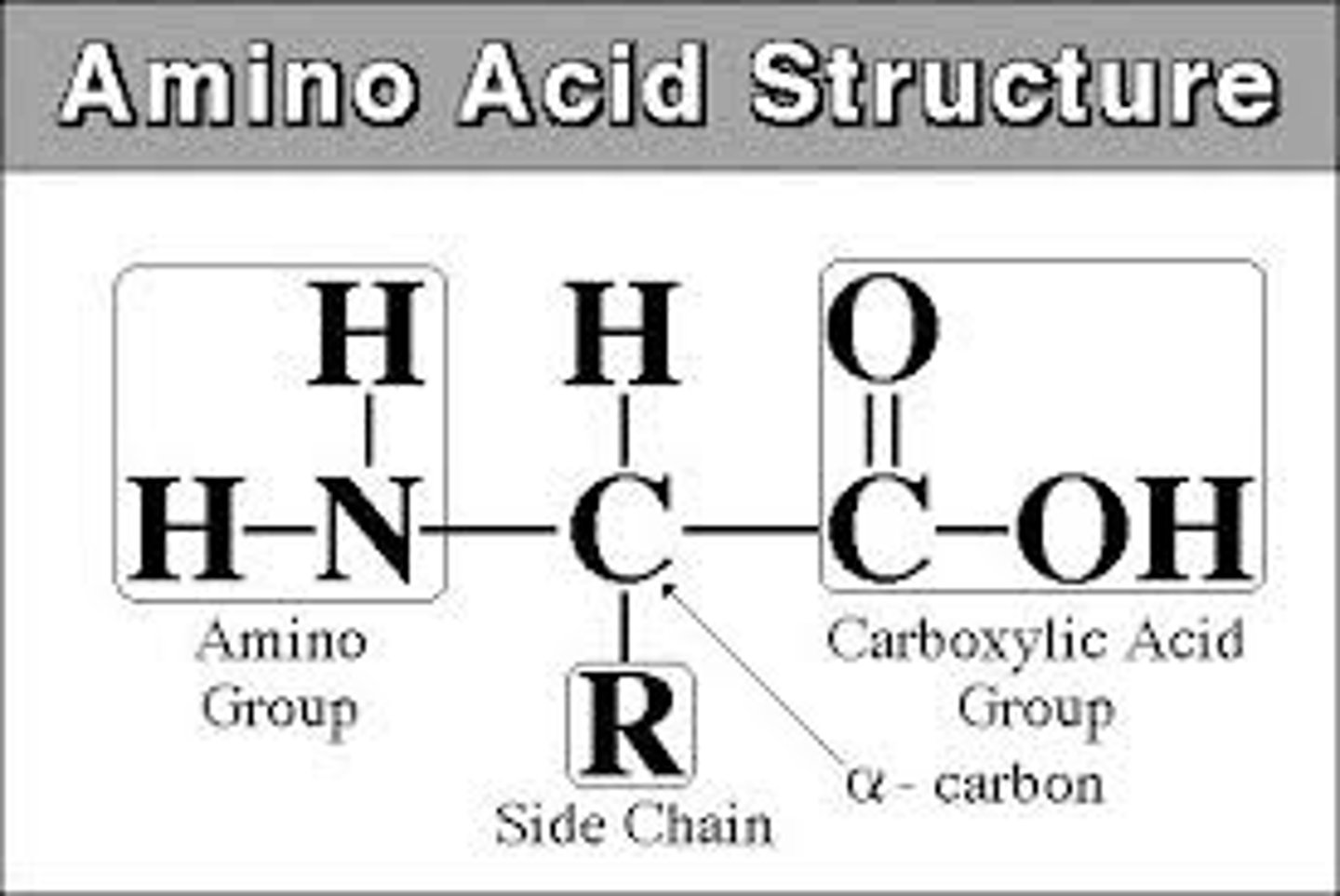
Amino Acids
Found in food, tastes somewhat bitter.
Pattern: C with C, C, N, H bond
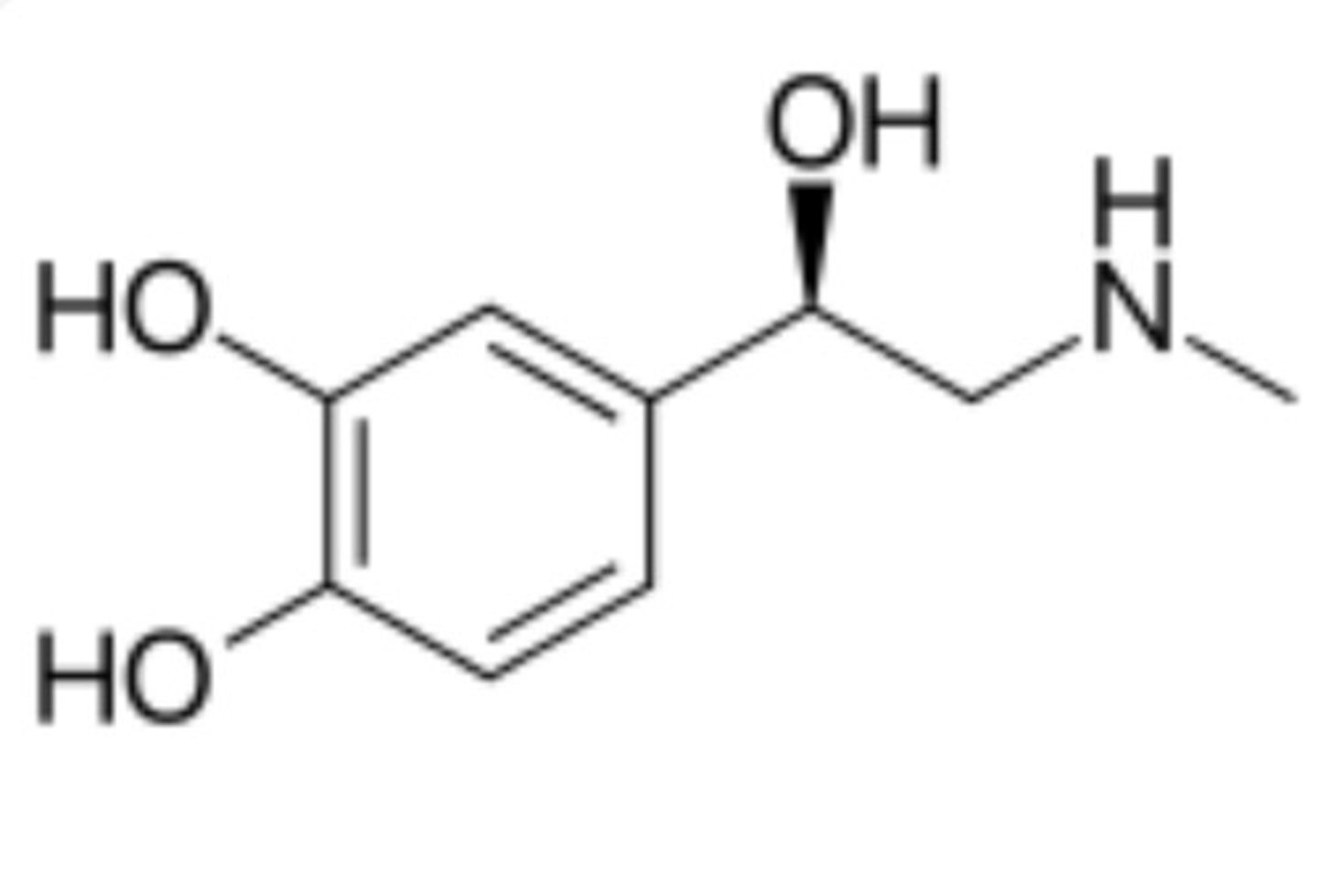
Neurotransmitters
Found in the body, tastes bitter
Pattern: 6 C bond with double bonds in every other C, has a tail
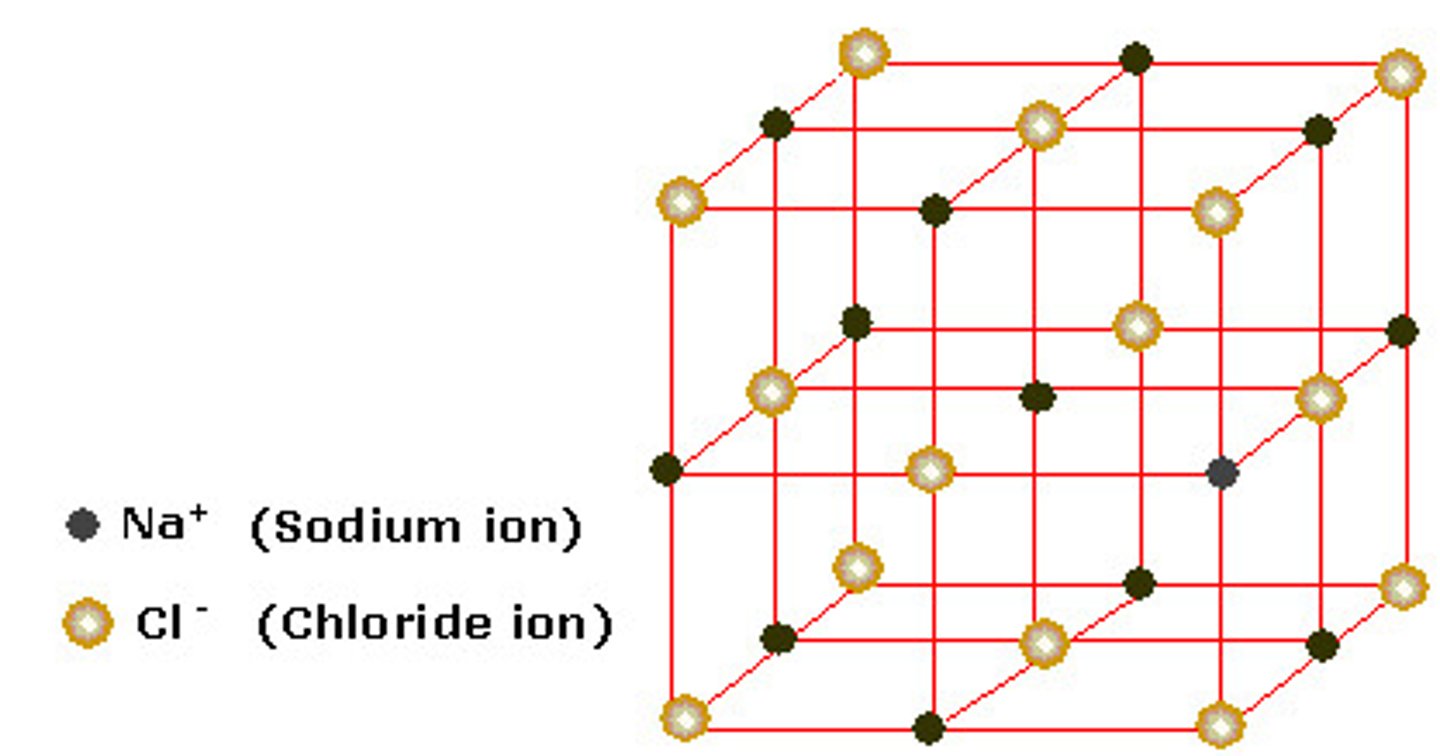
Metal Chlorides
Found in the ocean, tastes salty
Pattern: molecule is switched every other
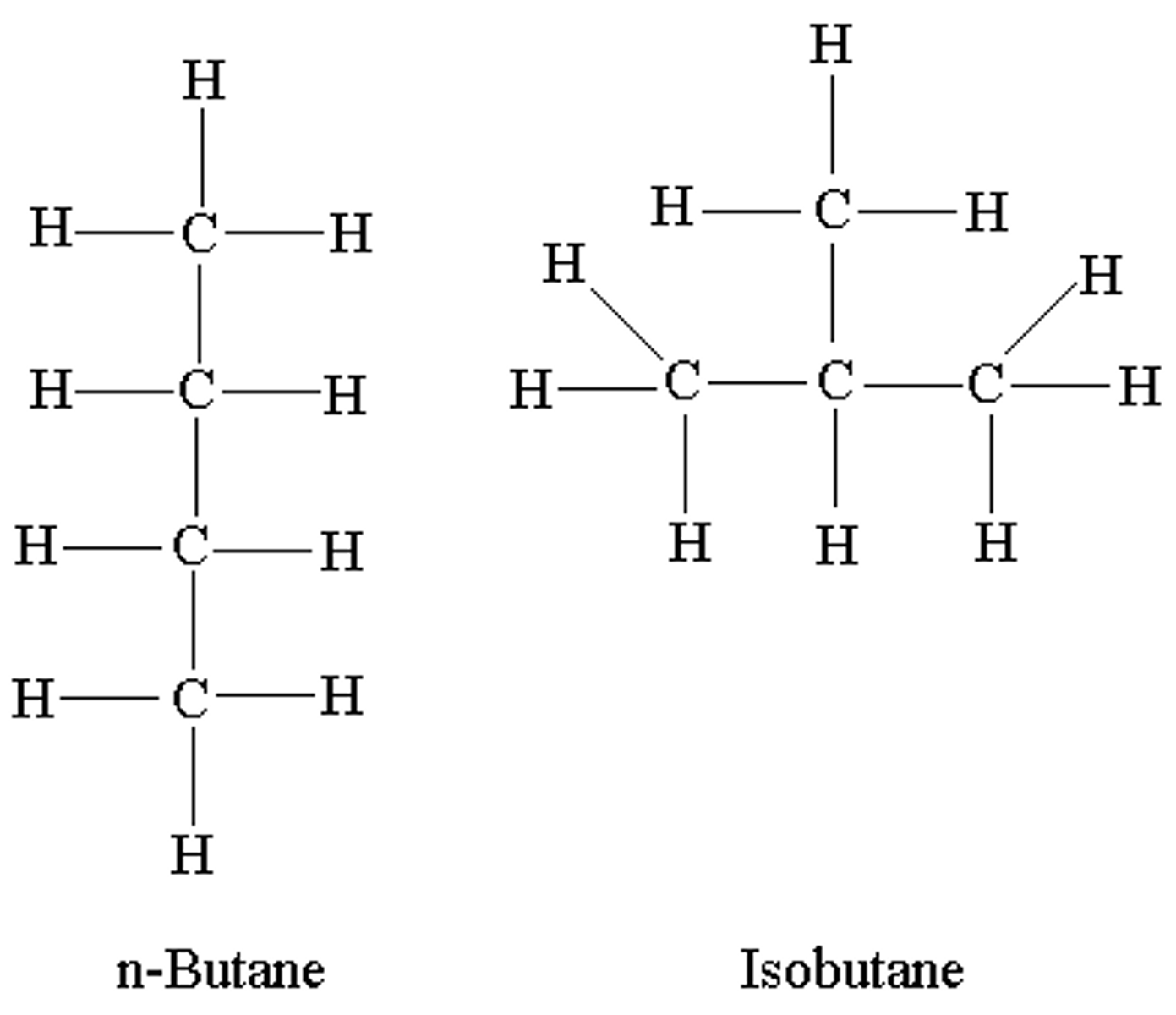
Isomers
Same molecular formula, different structural / atomic formula
Bonding ratio increases from
left to right (then center 1:4 , switched)
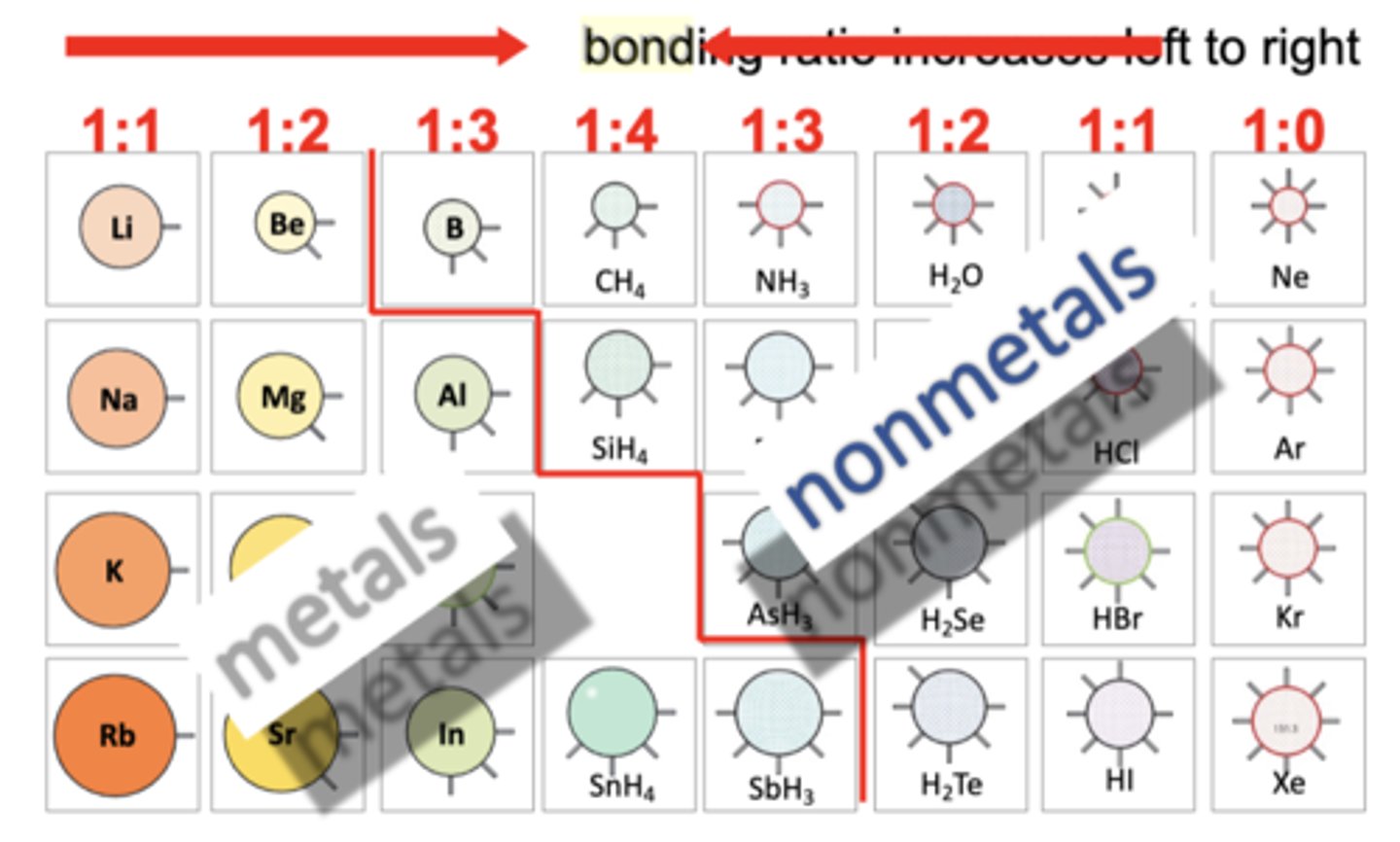
Reactivity increases from
Metals: top to bottom (due to increased radius, has less force, so easier to react!)
Non-metals: bottom to top
Mass increases from
top to bottom ⬇️ and left to right -->
Radius increases from
top to bottom⬇️ and right to left <--
Can make weaker attraction if ^ bigger radius
- reacts easier?
- cuts easier?
Hardness increases from
bottom to top (metals)
Coulomb's Law
F = kq1q2/r^2
Same sign (++, --) = REPEL
Opposite Sign (+-) = ATTRACT
Bigger q = stronger force
Bigger distance = weaker force
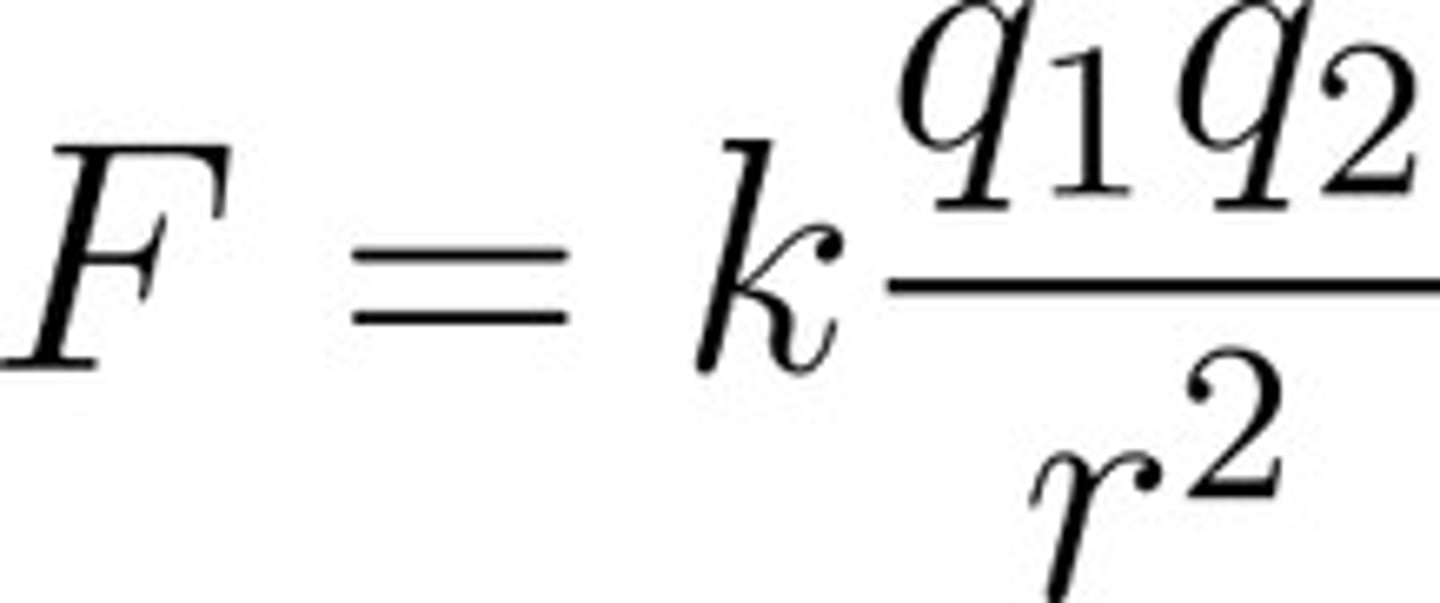
Z
Atomic # --> also # of protons (and electrons if neutral)

Average atomic mass
# of protons + average # of neutrons (atomic mass - atomic # or Z )

In Real Gas Law, what does the B stand for?
B = bigness coefficient. Depends on the radius / volume in PV = nRT
In Real Gas Law, what does the a stand for?
a = attraction coefficient
What is Zeff & how to find Zeff?
Zeff is the effective nuclear charge
# protons (Z) - # core electrons
Cation vs Anion behaviors
Cations (+) are positive charged ions that lost 1 or more e-
Anions (-) are negative charged ions that gained 1 or more e-
In electronegativity, is # of shells or # of protons more important? Why?
# of shells
This is due to radius. If the molecule have a tighter radius = ^ more force
How to find molecular geometry / electron domain ?
1. Count # of electron domains around central atom
- determines if linear, trigonal planar, or tetrahedral
2. Count # of lone pairs
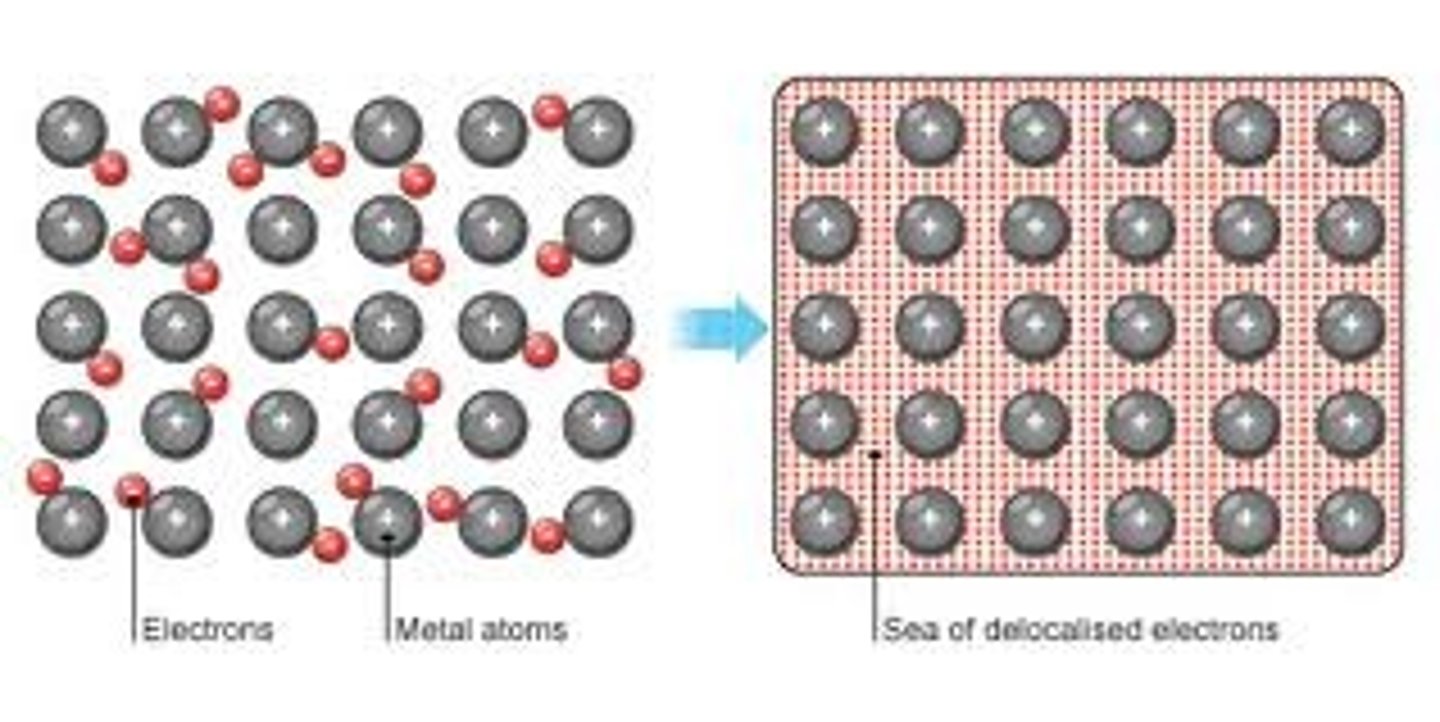
Metallic Bonding
Exists in substances consisting of only metallic elements
valence e- are free to move throughout the "electron sea"
- conducts
- 🚫 dissolve
- bendable / maleable
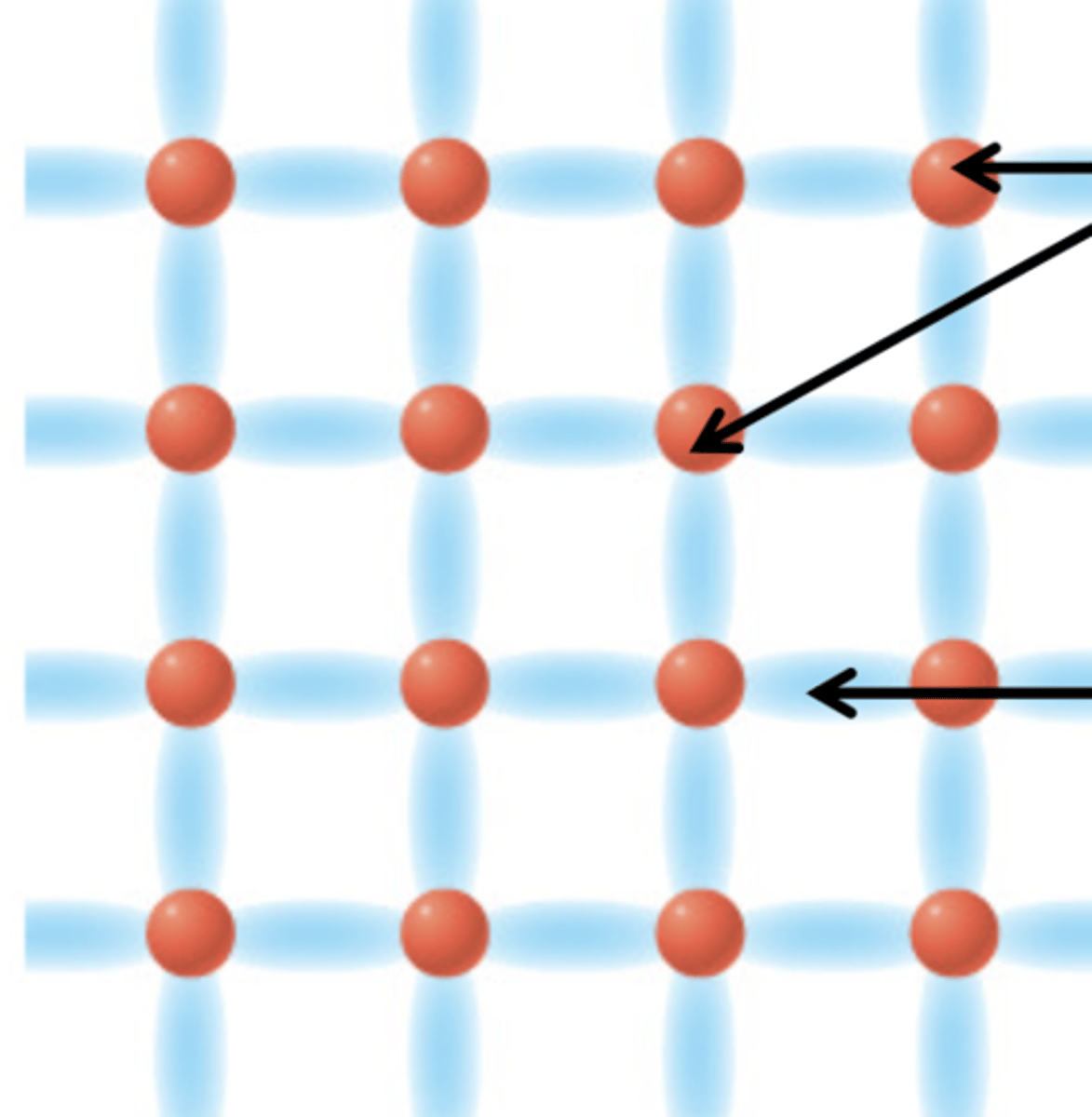
Extended / Network Covalent
Exists in substances consisting only of NONmetal elements
valence e- connect atoms w/ each other in 1, 2, or all 3 directions to create chains / networks
- 🚫 conduct
- 🚫 dissolve
- rigid / hard to break
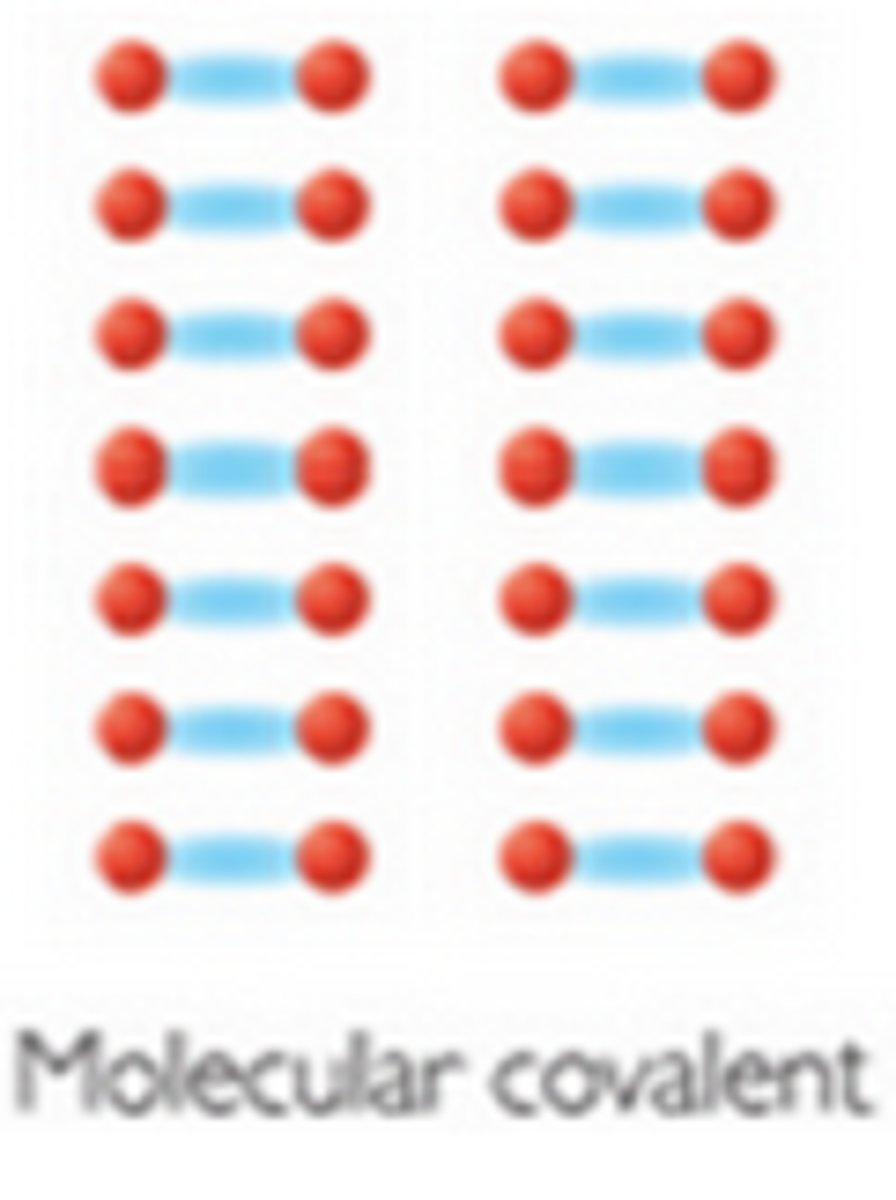
Molecular Covalent
Exists in substances consisting only of NONmetal elements
valence e- are shared between some atoms, creating small stable units
- 🚫 conduct
- most dissolve
- gases, liquids, or soft solids
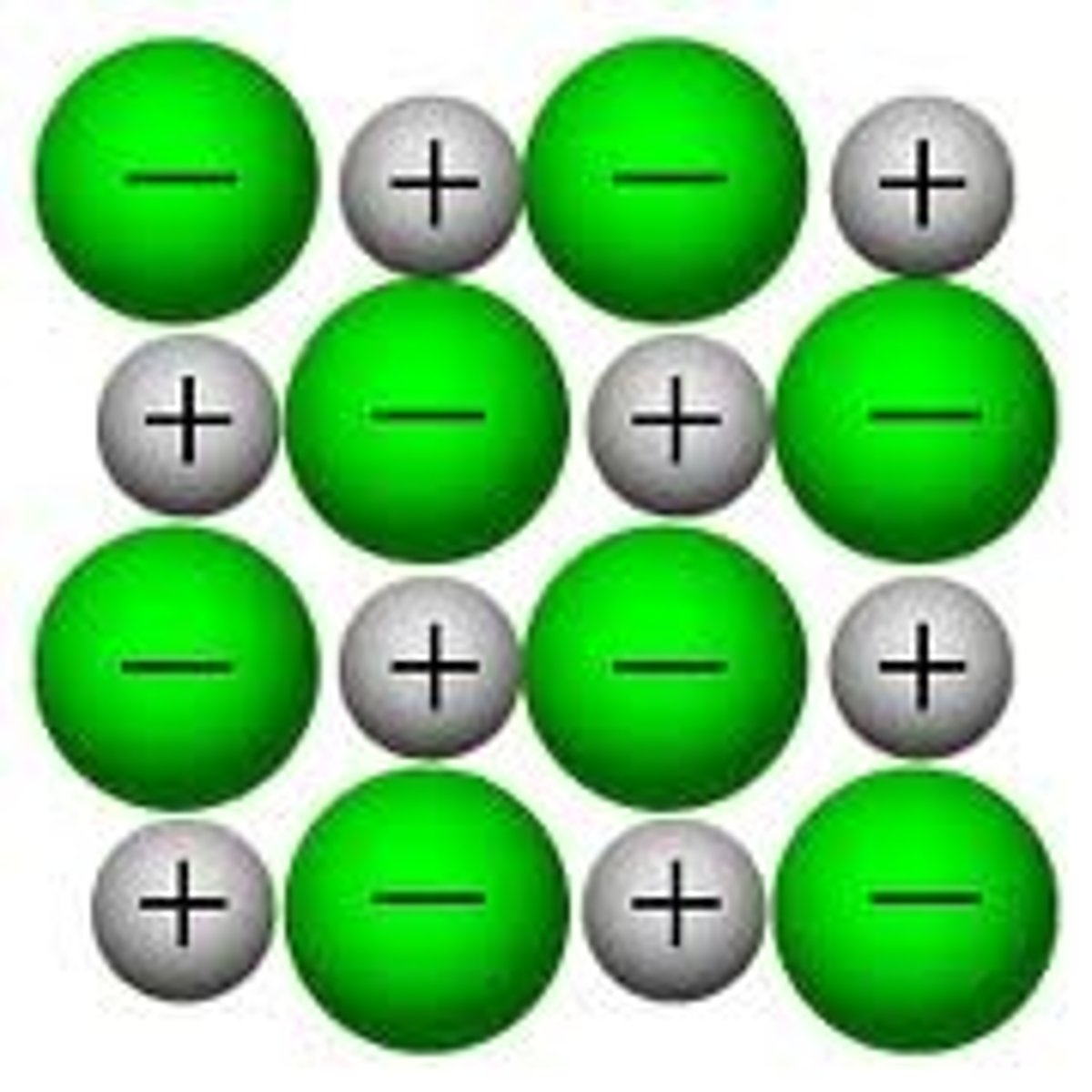
Ionic Bonding
Exists in substances consisting of metal AND nonmetal elements
metal atoms "give up" their ve- --> nonmetal atoms
- 🚫 conduct
- most dissolve
- hard, but brittle
When charges get too close, atoms fly apart !!! so can break/ snap/ crack
Noble Gas Envy
Atoms gain + and lose - electrons to fulfill their Noble Gas Envy!
Want to make an octet or 2 ve-!
3 and below --> rows of periodic table = can have more than 8 ve-

Metals tend to___ while nonmetals tend to ____
Metals tend to LOSE - ELECTRONS while nonmetals tend to GAIN + OR SHARE ELECTRONS.
How to draw lewis structure?
1. Count total # ve-
2. Arrange non-H atoms w/ 1 bond between each
3. Add H's to ends (HONC)
4. Add long pairs as needed to get octet
5. Re-count e- & make multiple bonds as needed
6. if have time, check FC!
How to check Formal Charge?
# valence electrons when alone - # of bonds - # non bonding e-
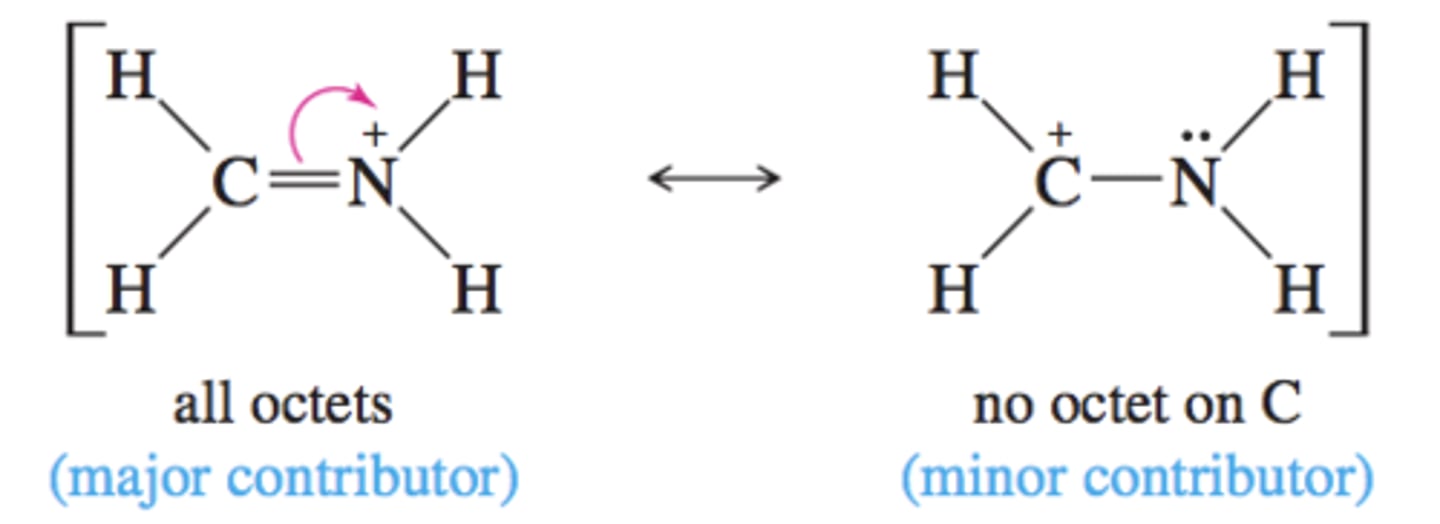
Resonance Contributors
Using multiple drawings to represent a structure -
same molecular formula, different electron placement
Kinetic Molecular Theory
1. Constant random motions --> straight lines
2. Elastic collisions between particles (no loss of energy)
3. Particles are infinitely small (no volume)

KE formula
KE = 1/2 * mv^2
m = mass
v = velocity (🚫 volume!)
KE = 1/2 mv^2 = 3/2 RT
High T = KE wins (gas)
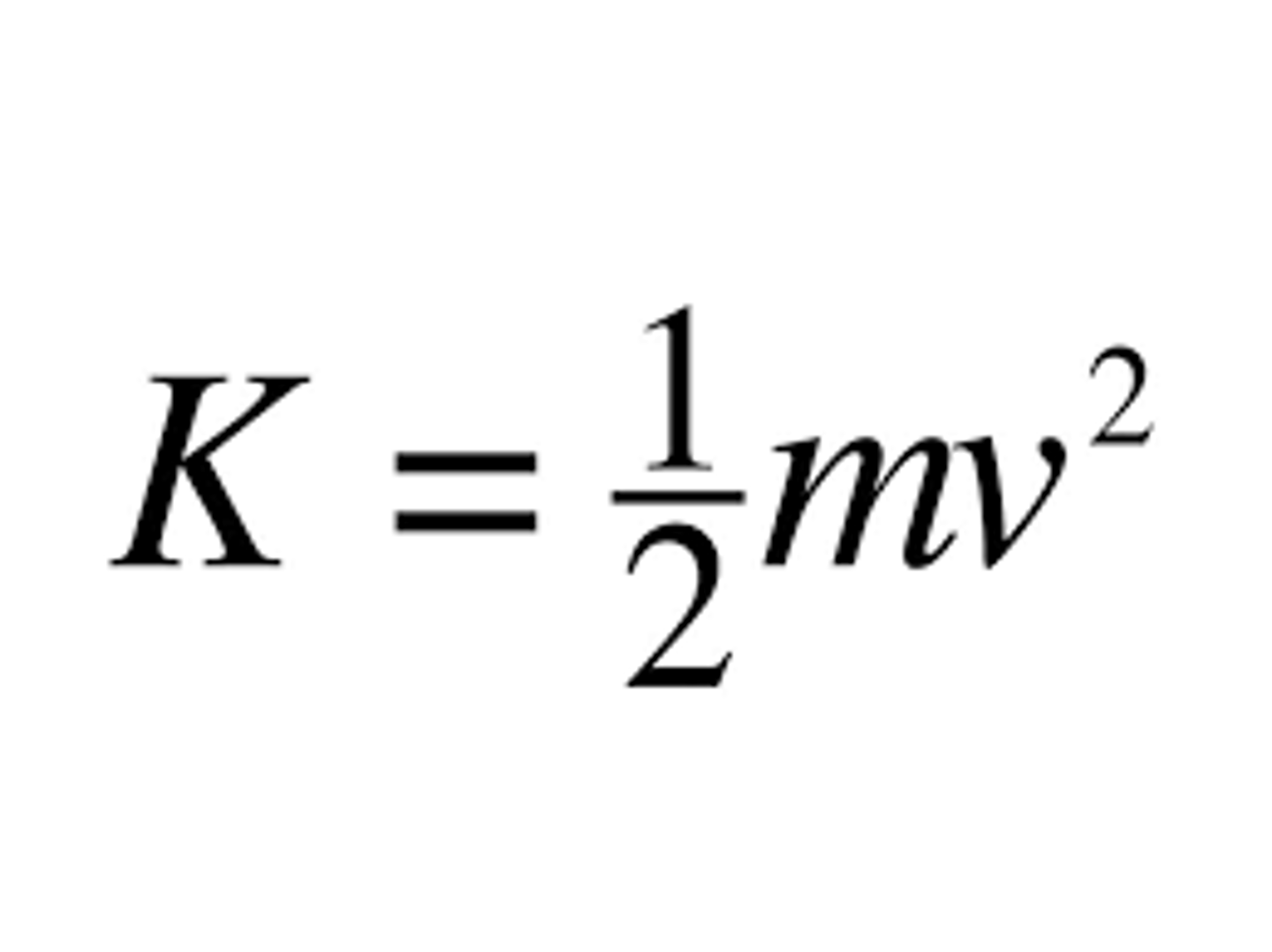
Charles's Law
Volume + Temp proportional WHEN pressure held constant
V = kT
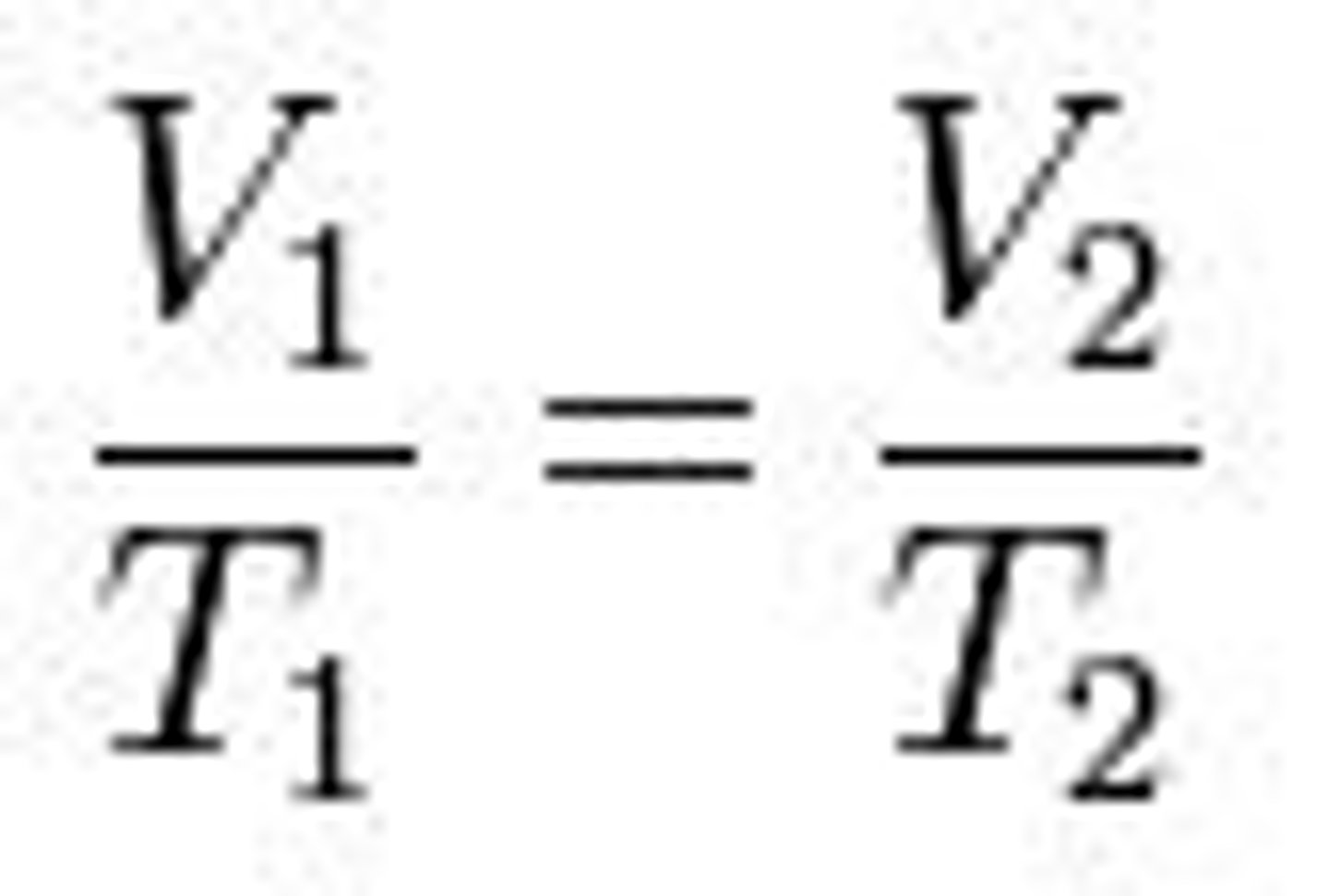
Gay-Lussac's
Pressure + Temp proportional WHEN Volume + Moles of gas held constant
P = kT
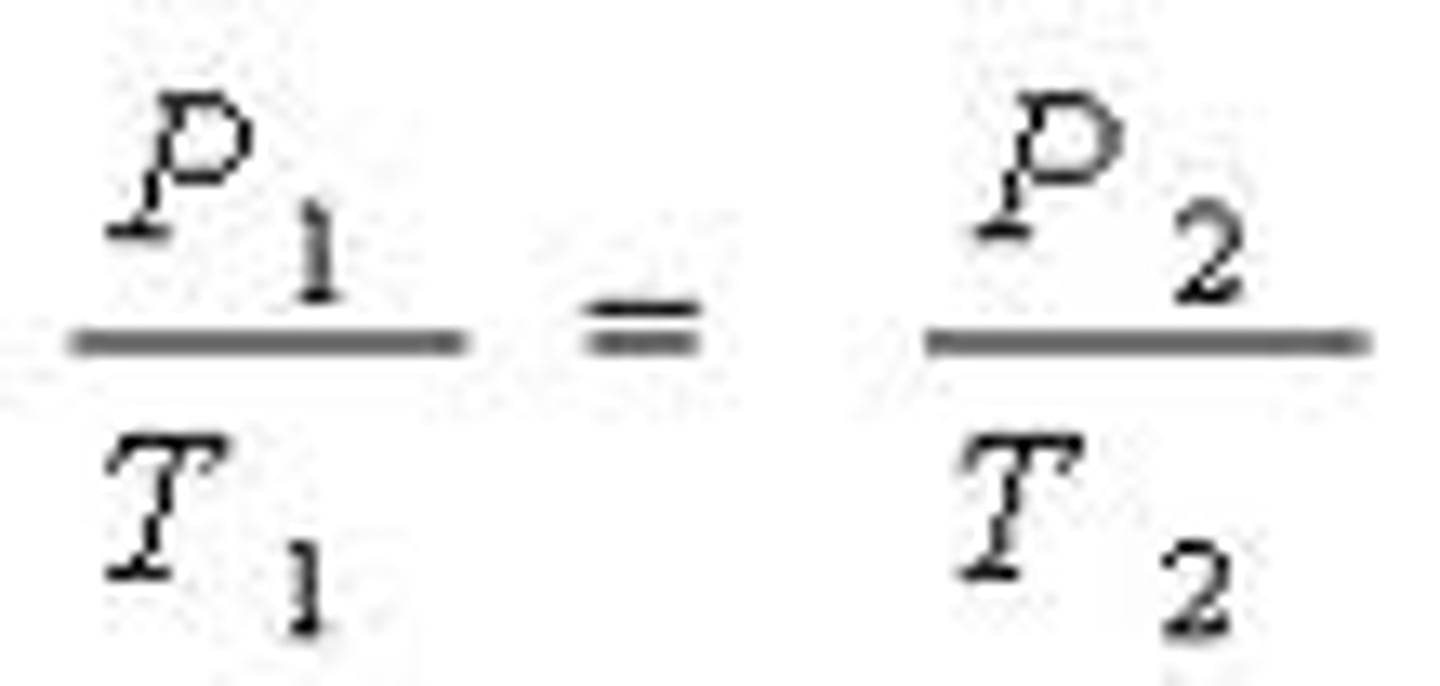
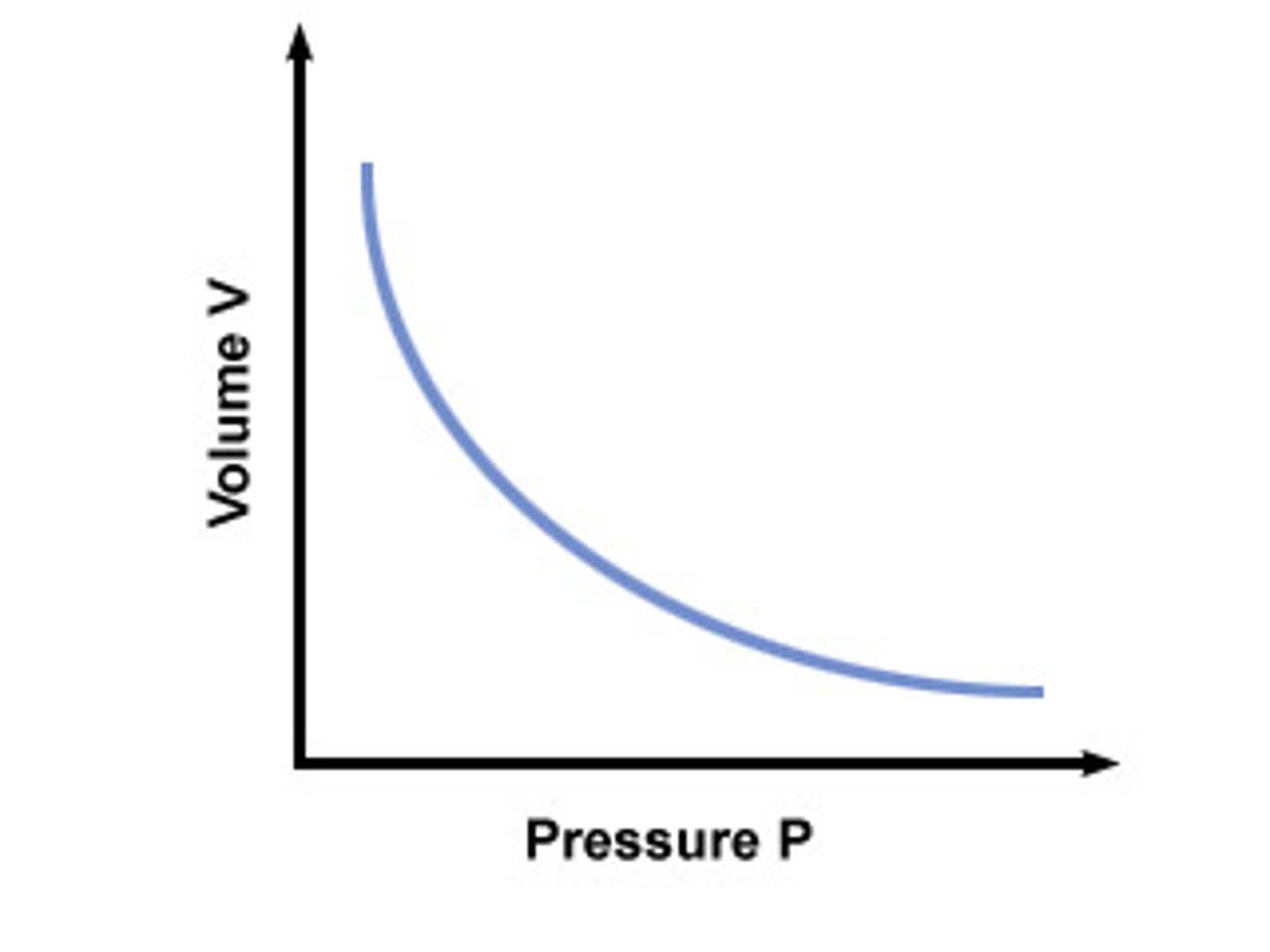
Bolye's Law
Volume + Pressure inversely proportional (^ P = ⬇️V)
Avogadro's Law
volume of gases = number of molecules WHEN Pressure + Temp stay constant
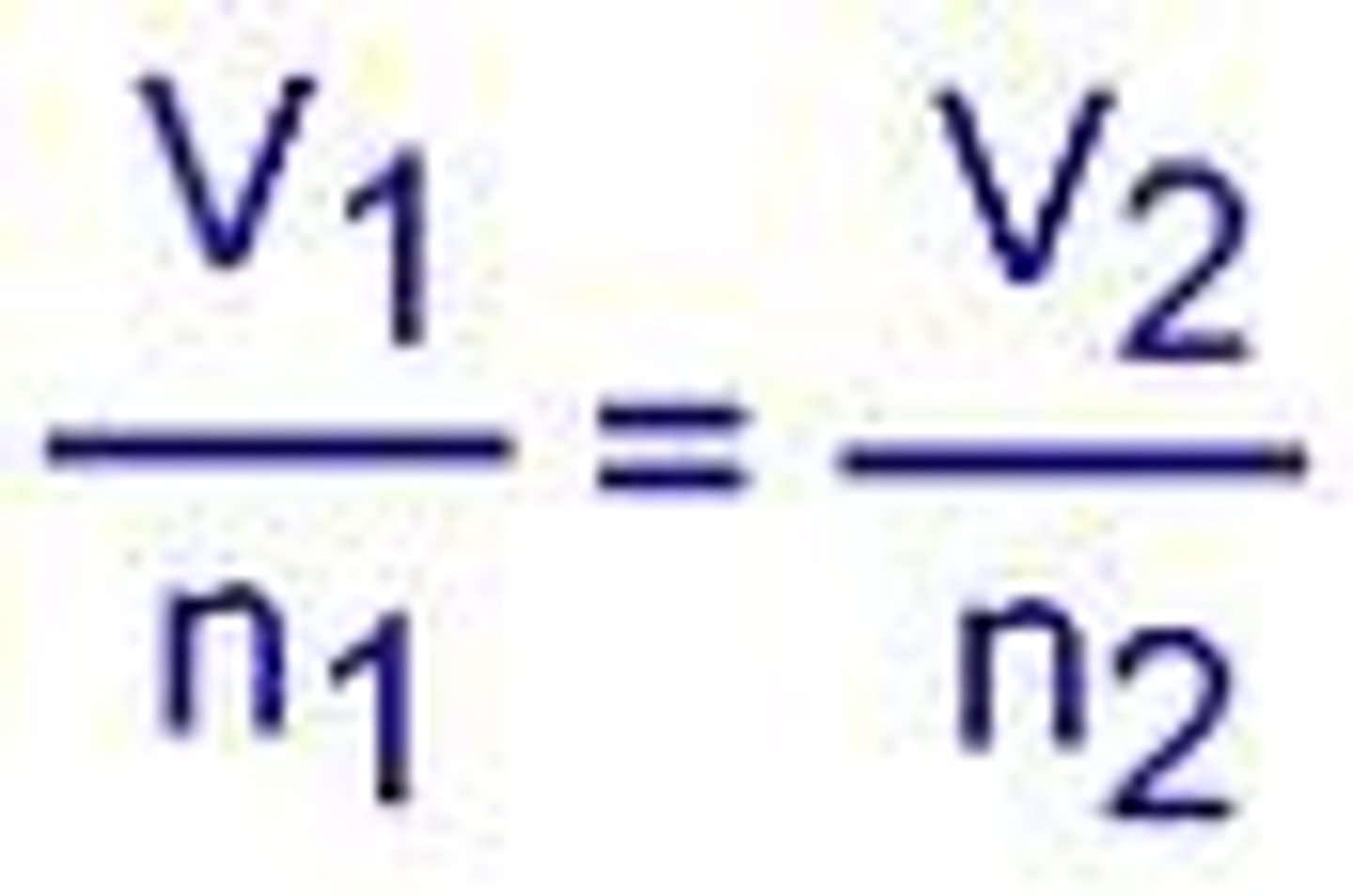
V
Volume
v
velocity
2 Types of container:
1. Flexible (variable V)
2. Rigid (fixed V)
V Bar
average / most popular velocity
K
kelvin --> Celcius + 273.15
n
Number of moles --> PV = nRT
r
Gas constant --> PV = nRT, typically 0.0821 L atm/molK
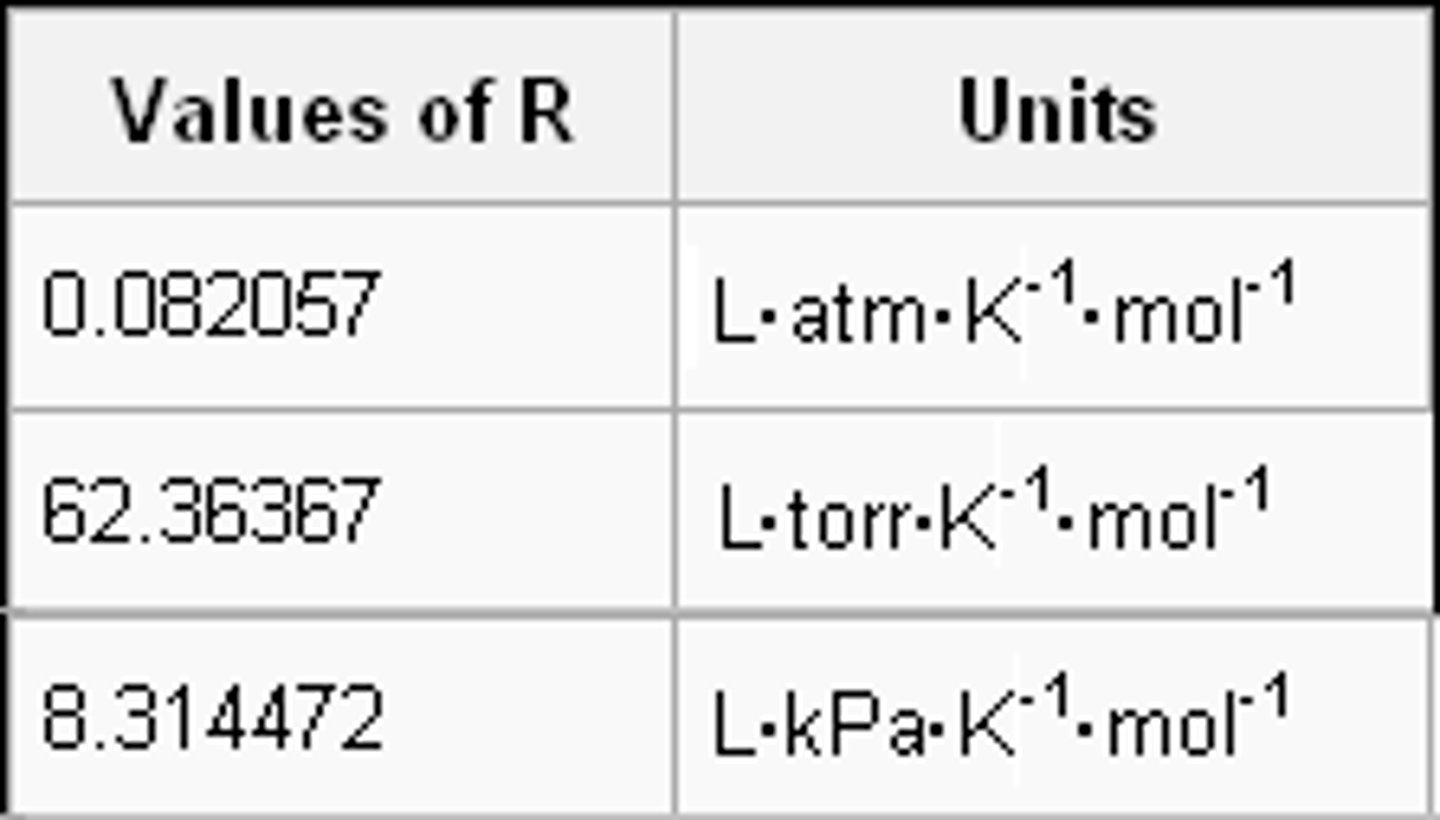
Pa, Torr, Bar
Pa = Pascal
Units of measure for pressure
Boiling Point
STRONGER attractions = HIGHER temp (more KE required)
Temp @ which its equilibrium vapor pressure = to pressure exerted on the liquid by its gaseous surroundings
i.e. if an open container, pressure = Earth's atmosphere
- presence of an Oxygen can raise boiling point by a lot
Real Gas Law
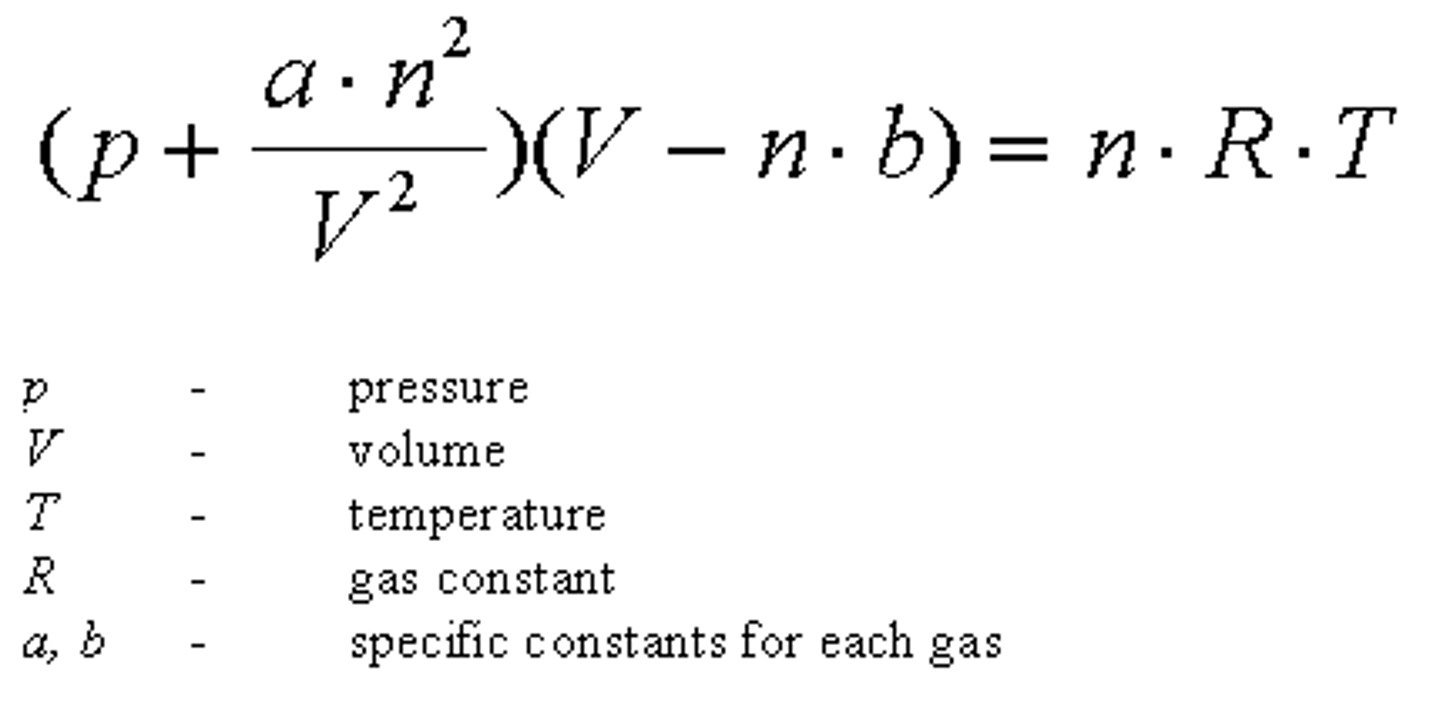
High T favors _______, Low T favors ______
High T favors motion of gases, Low T favors attraction of liquids
PE
Potential Energy - Attractions between atoms
Low T = PE wins (Liquid)
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory
Assumes the e- pairs --> valence shell of central adom will adopt an arrangement that MINIMIZES repulsions by MAXIMIZING distance
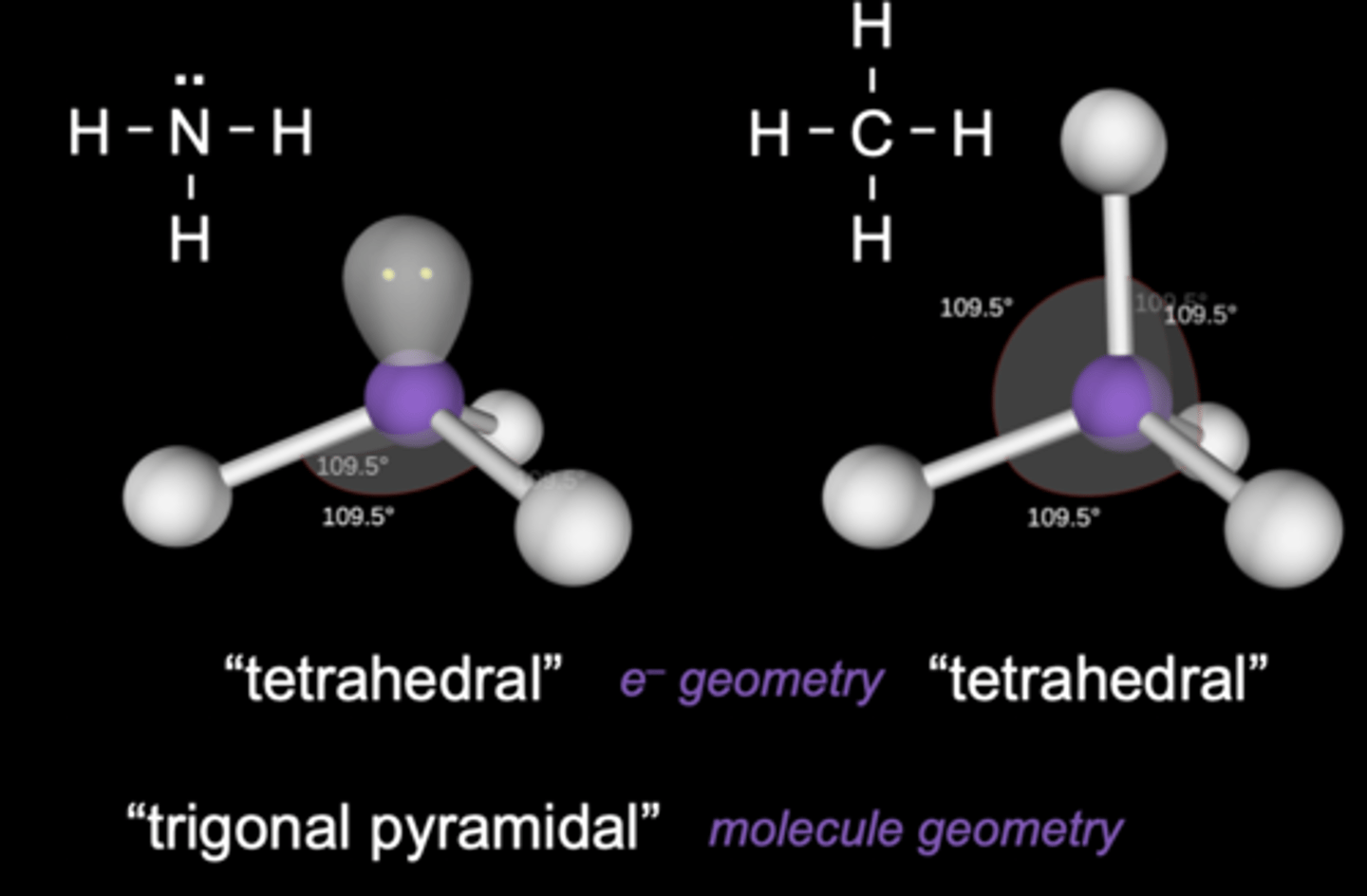
VSEPR Theory for 4 e- domains
109.5 degrees
e- geometry = tetrahedral
molecular geometry =
- if 1 lone pair: trigonal pyramidal
- if 2 lone pairs: bent
VSEPR Theory for 3 e- domains
120 degrees
e- geometry = trigonal planar
molecular geometry = bent
VSEPR Theory for 2 e- domains
Linear, 180 degrees
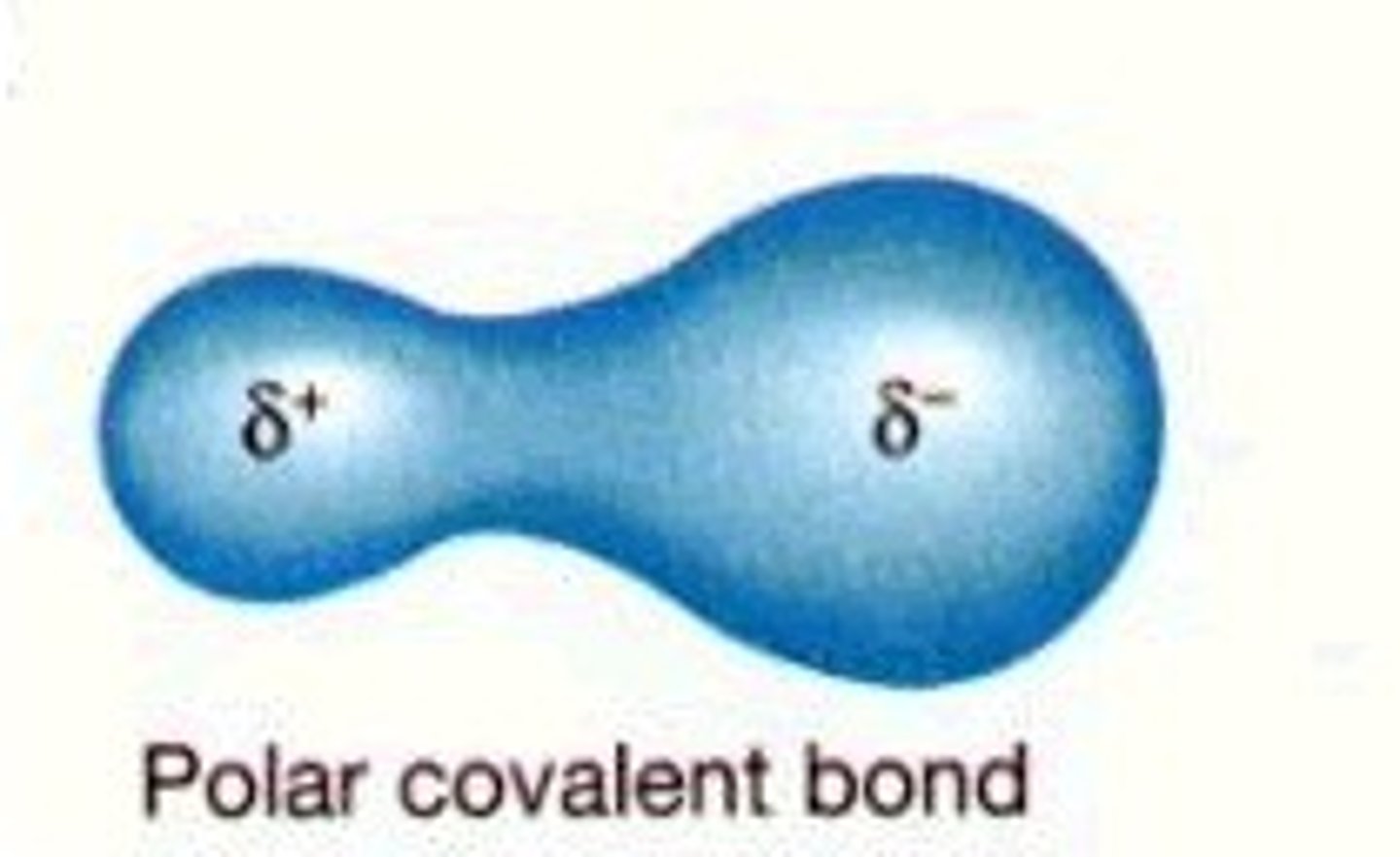
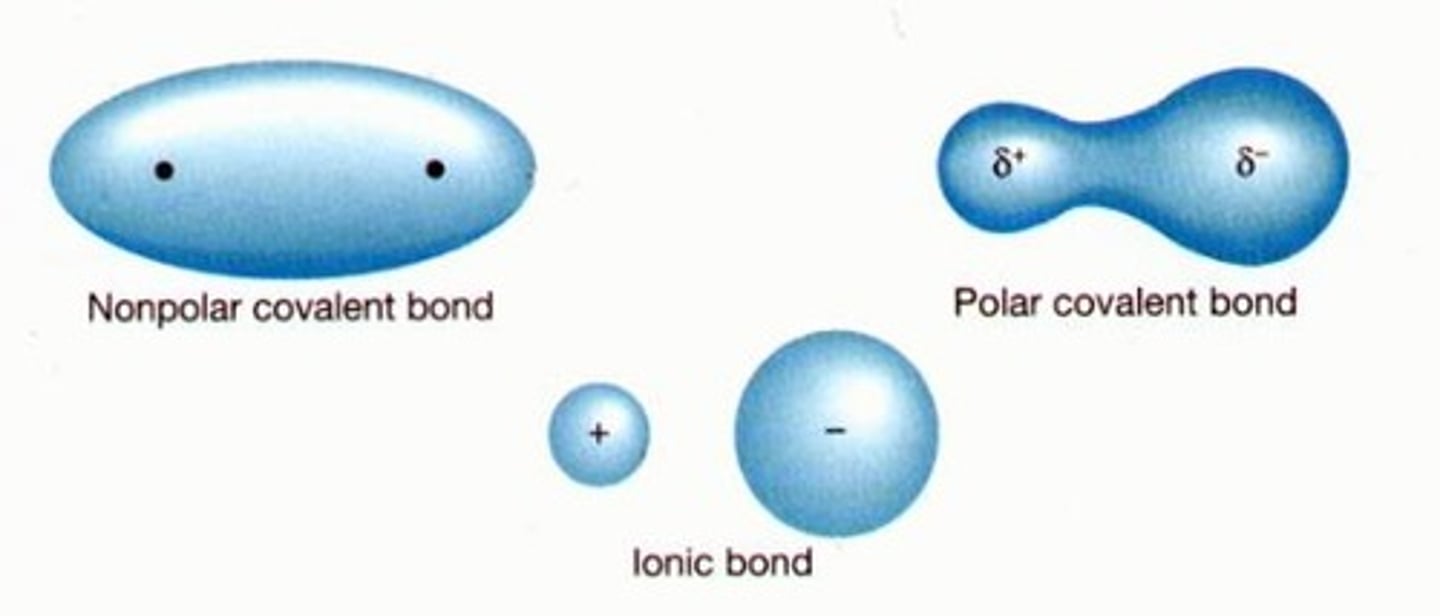
Polar Covalent Bond
unequal sharing of electrons
Non-polar Covalent Bond
equal sharing of electrons
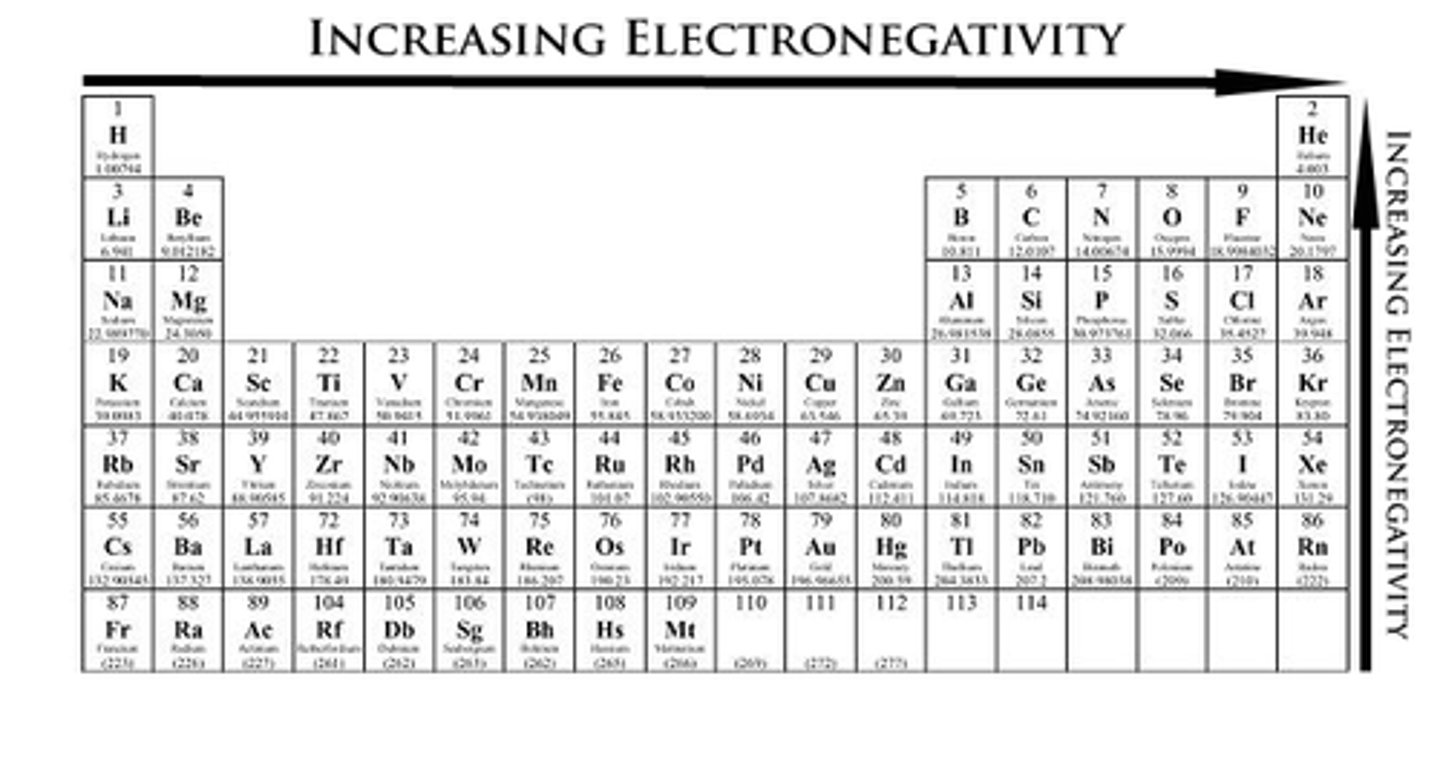
Electronegativity increases from...
left to right -->, bottom to top^
Electronegativity
Ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself BASED ON Zeff!
- nonmetal vs nonmetal EN = similar (covalent bonds)
- metal vs nonmental EN = diff (ionic bonds)
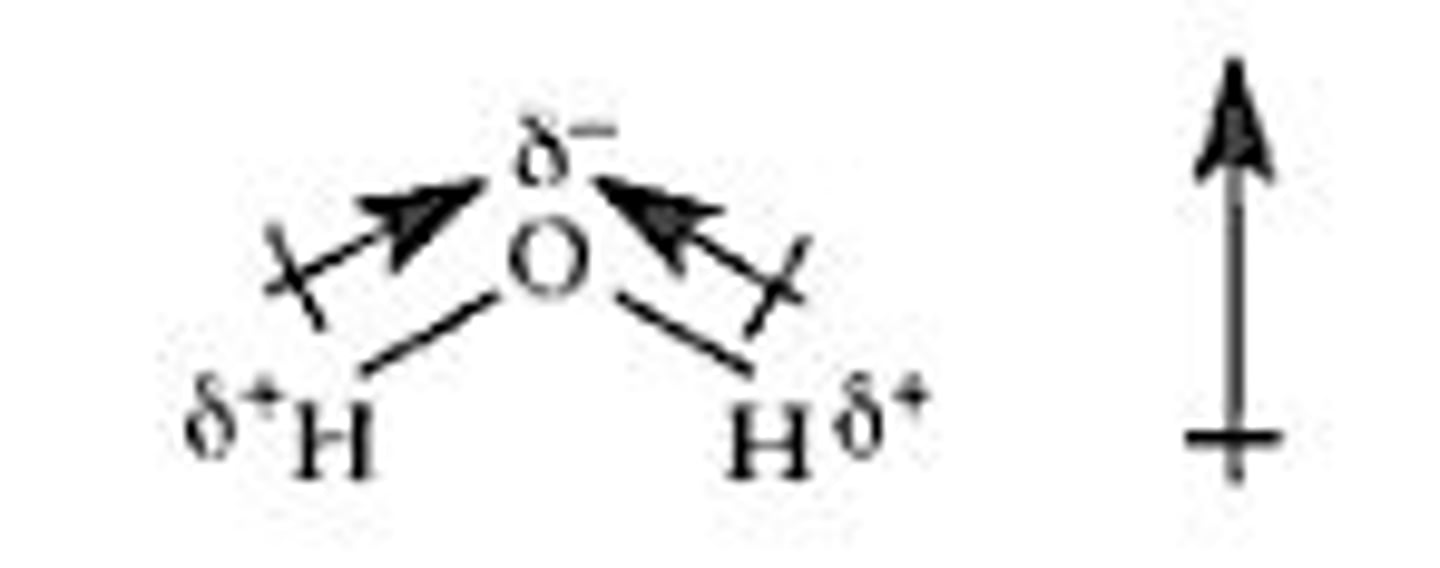
Nonzero net molecular dipole
Will cause the molecule to be dipole-dipole, when the EN do not cancel out (x, y directions)
Dipole-Dipole interaction
an attraction between regions of PERMANENT POLAR molecules (x, y of EN doesn't cancel) that have partial charges of opposite sign
H-Bond counts as D-D when also interacting w/ lone pair
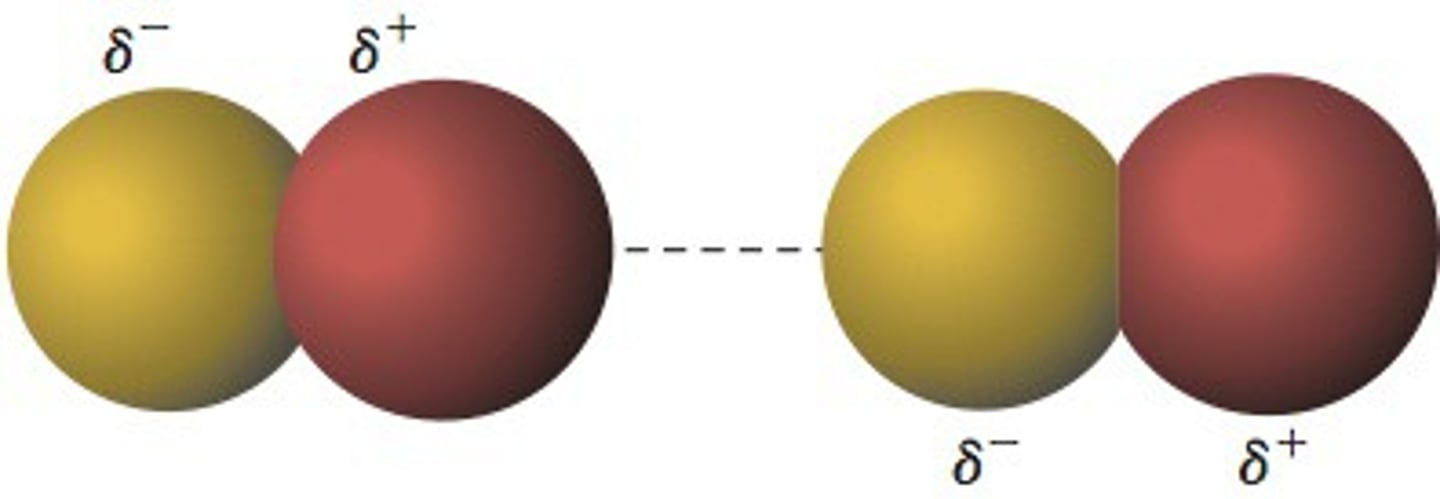
Induced Dipole - Induced Dipole interaction
ALL (even nonpolar) have ID-ID
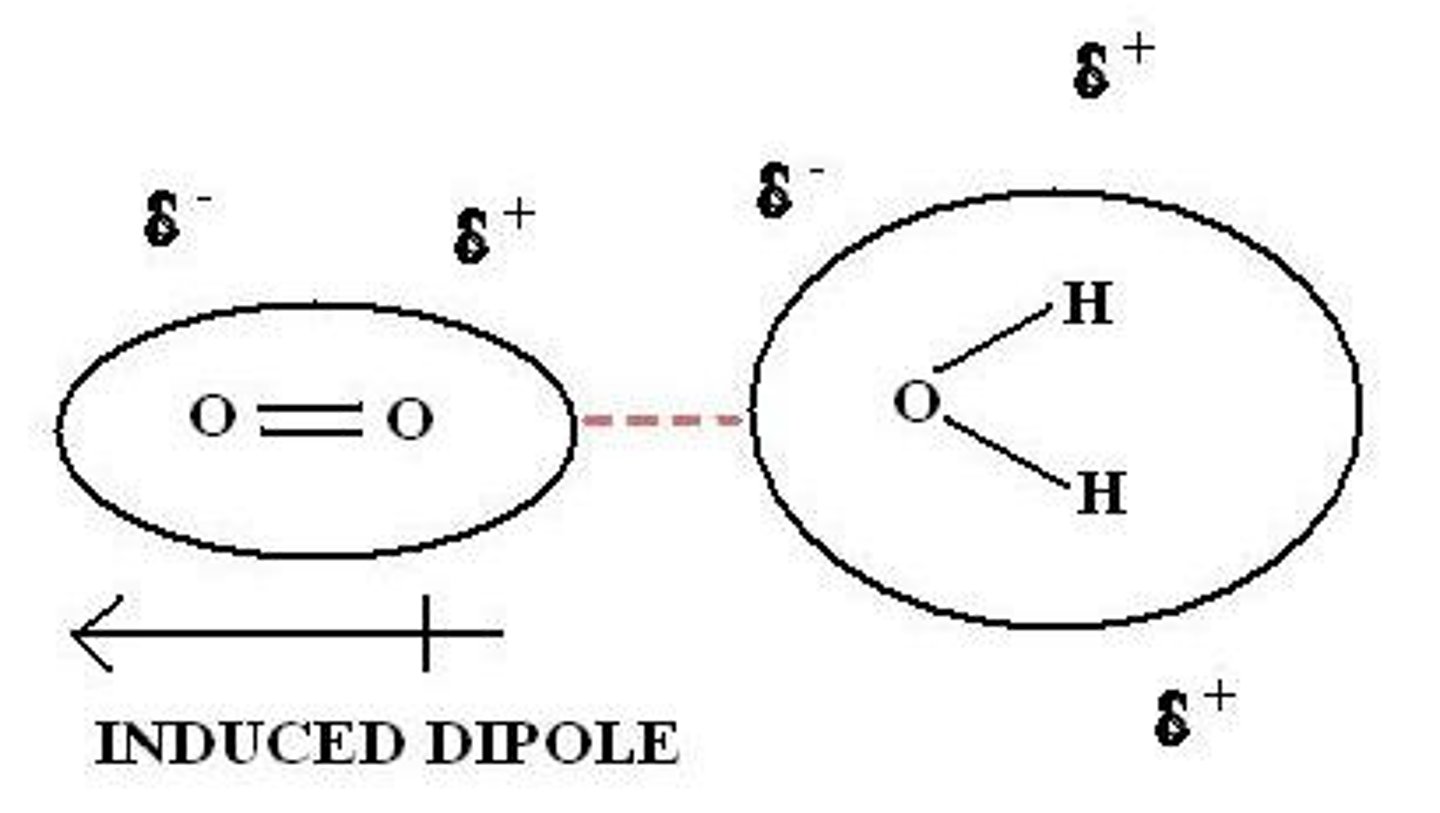
Dipole - Induced Dipole
A weak attraction that results when a polar molecule induces a dipole in an atom or in a nonpolar molecule by disturbing the arrangement of electrons in the nonpolar species.
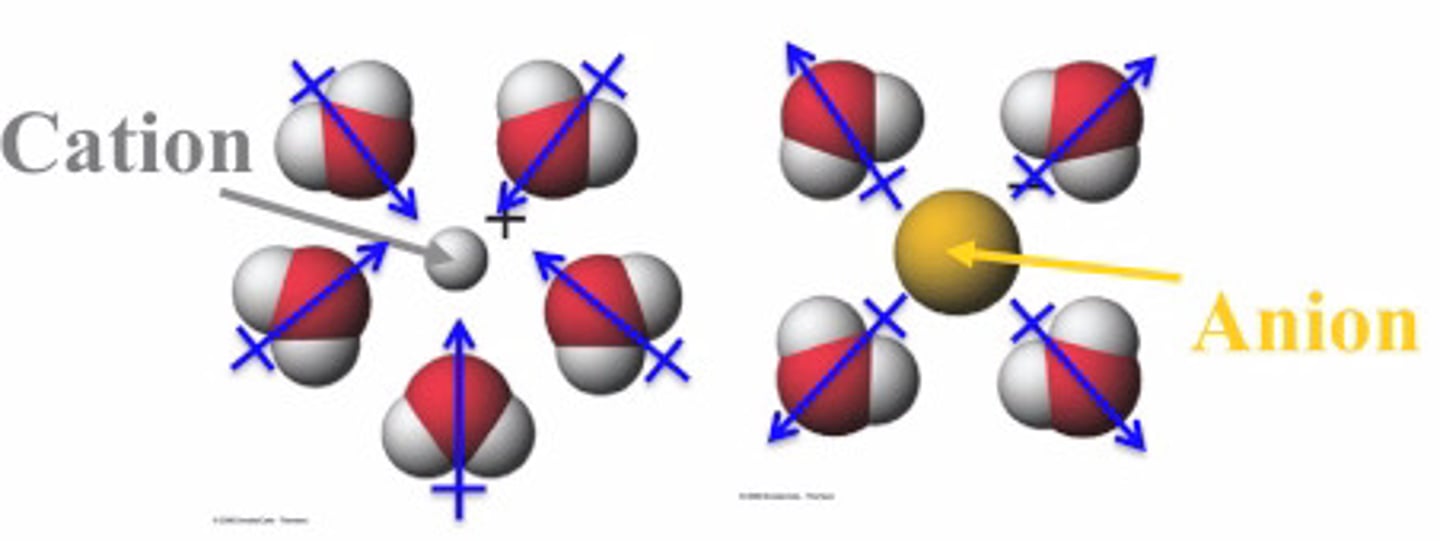
Ion-Ion interaction
interactive force between ions of opposite charge. Ions will often be indicated w/ a charge around the species, showing FC that do not cancel out
requires nonzero FORMAL CHARGE
DIFFERENT from Ionic bonding *that is between a metal and a nonmetal.*
ion-dipole = ion attracted to polar dipole
Order from weakest - strongest IMF moments
ID-ID < D-ID < D-D < H Bond (NOT BOND) < I-D < ion-ion
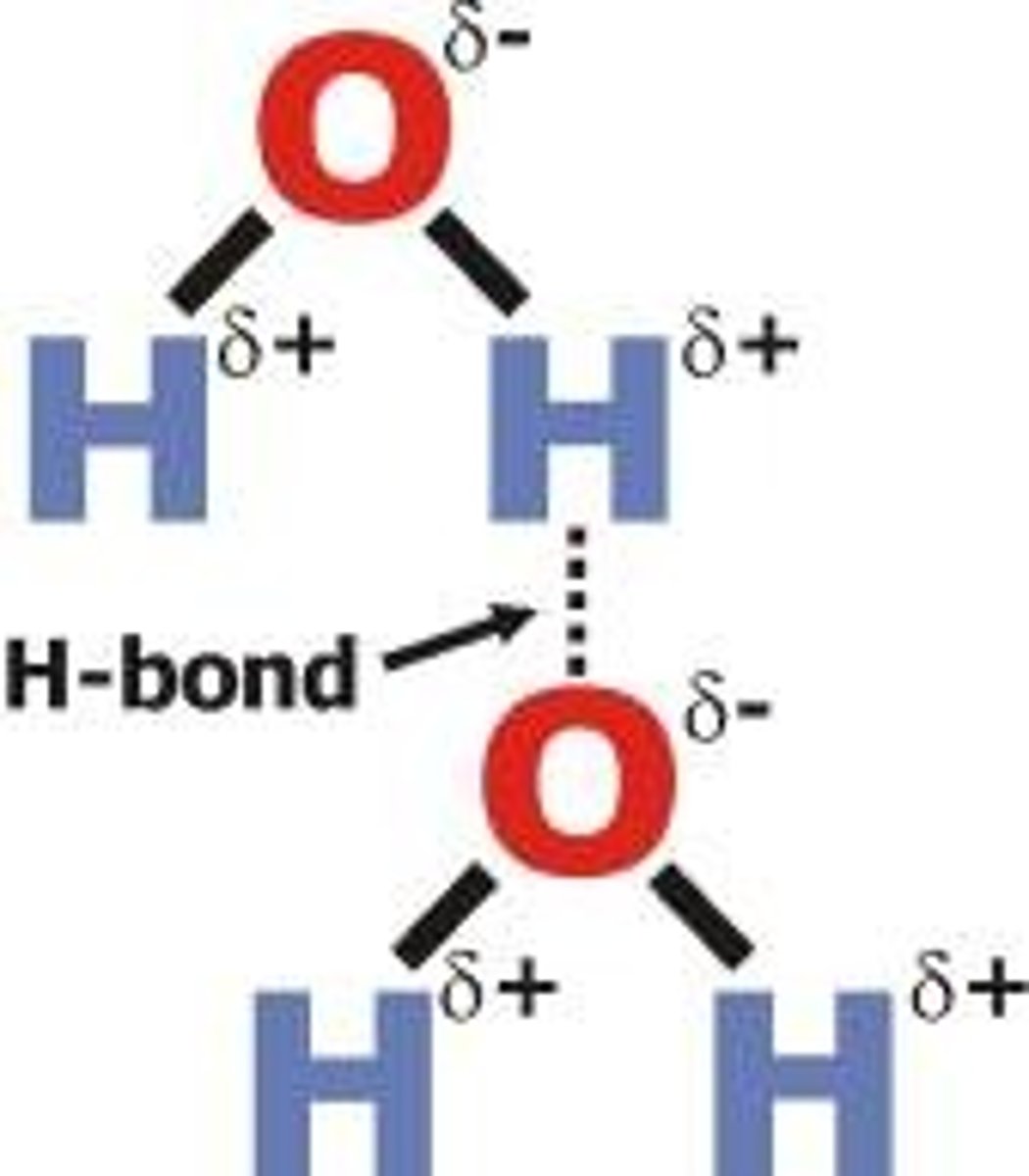
Hydrogen Bond
Unusually strong Dipole-Dipole moment, between Hydrogen atom + N, O, or F
Needs a Negative acceptor (delta - N, O, F) and H-Positive bond donor (delta + H attached to a N, O, F)
What causes higher boiling point?
stronger intermolecular forces
Net Molecular Dipole
When add up all the bond dipoles, what it adds up to (nonzero, zero net molecular dipole)
Strength in ID-ID interactions depends on ____
Surface Area. So, longer, straight chains = stronger interaction (^ more opportunities to induce dipoles)
like dissolves like rule
Dissolution occurs only if pure substances' interactions are similar --> strength
i.e. ID-ID does not dissolve into or with D-ID
Solvent
Component of a Solution @ a significantly ^ larger concentration
Solute
Component of a colution @ significantly ⬇️ lesser concentration
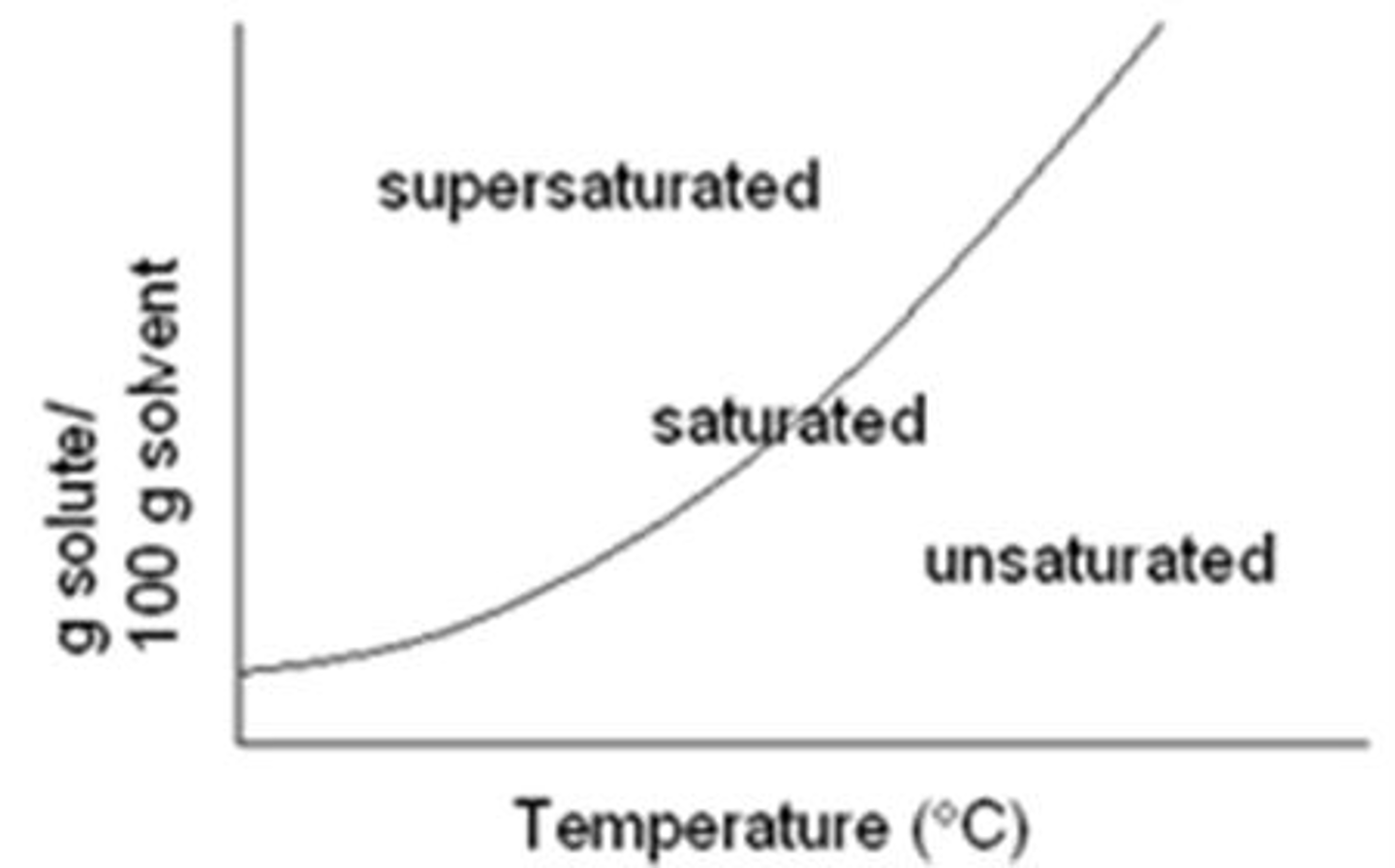
Saturated
Max amount of solute dissolved
Unsaturated
Even ^ more solute could be dissolved
Precipitate
Extra / over saturated --> extra solute sits @ bottom & doesn't fully dissolve
Solubility & Temperature
solubility increases ^ = temperature increases ^, in general
Non-polar bonds --> periodic table
1. When an atom is bonded to the same atom
2. C-H bond
Dipoles and Polarity differences occur with what type of bond?
Covalent bonds!
Covalent bonds describe the sharing of electrons between two atoms. Polarity describes how evenly this is shared. So a nonpolar bond means the electrons are being shared pretty evenly.