2.1 & 2.2 ap psych vocab
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Inattentional Blindness
Failing to see visible objects when attention is directed elsewhere.
Gestalt Psychology
Emphasizes the organization of stimuli into meaningful wholes.
Visual Cliff
Lab device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals.
Binocular Cues
Depth cues that depend on the use of two eyes.
Eg: Retinal Disparity
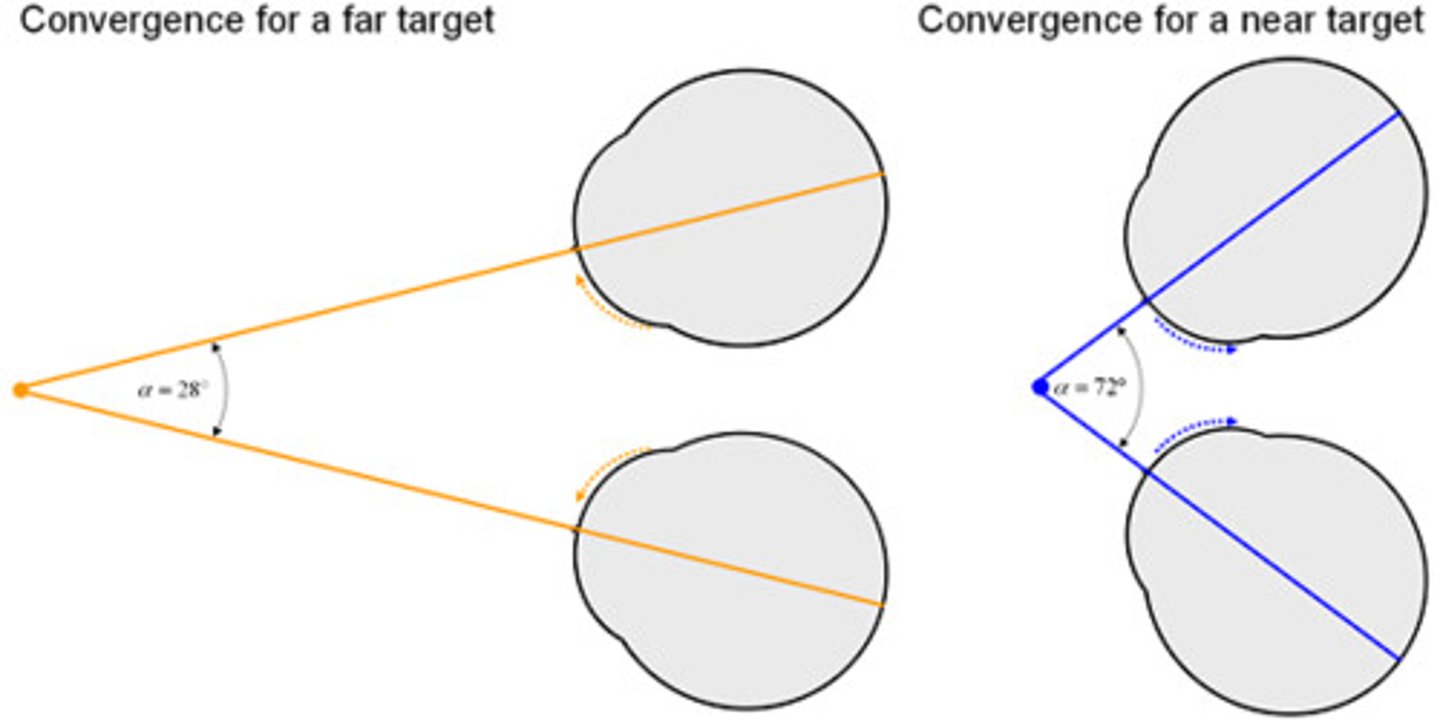
Convergence
the brain merges the images from both eyes to create a single perception (Binocular cue where eyes move inward to see near objects)
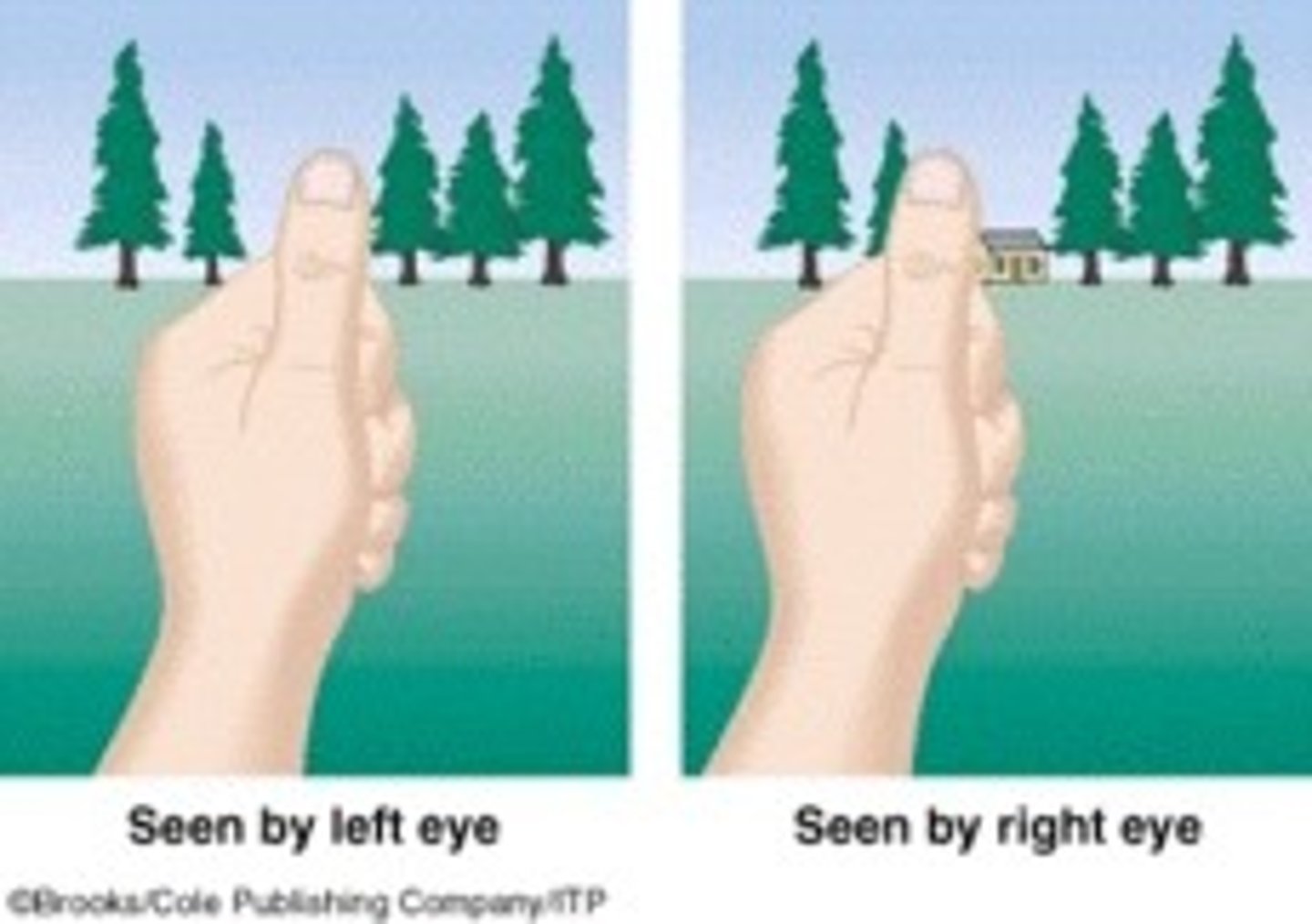
Retinal Disparity
Binocular cue from the different views each eye has of the world.
Relative Clarity
Hazy objects seen as more distant.
Relative Size
Assuming smaller objects are farther away.
Texture Gradient
Indistinct texture signals increasing distance.
Interposition
Objects that block the view of others are seen as closer.
Perceptual Constancies
Perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change.
Color Constancy
Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color.
Apparent Motion
Perceiving a stationary object as moving. (eg video doesnt move, its just a sequence of frames)
Stroboscopic Movement
Perception of continuous movement in a rapid series of slightly varying images.
Concept
the building blocks of thought, helping us to categorize and understand the world
Mental Set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
Priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response
Framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.
Nudge
a concept in behavioral economics that subtly alters the environment or context in which people make decisions with the aim of influencing their behavior
Gambler's Fallacy
Believing that past events affect the likelihood of future events
Example: Thinking that a coin is "due" to land heads after several tails
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
a framing effect in which people make decisions about a current situation based on what they have previously invested in the situation
Functional Fixedness
the tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions; an impediment to problem solving
Insight
a sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem
Confirmation Bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
Fixation
according to Freud, a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, in which conflicts were unresolved
Intuition
an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit, conscious reasoning
Belief Perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
Convergent Thinking
narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
Top-Down Processing
Using models, ideas, and prior expectations to interpret sensory information.
Schemas
Concepts or frameworks that organize and interpret information. (eg our schema for a dog is having 4 legs and a tail)
Cocktail Party Effect
Ability to focus on one voice among many. (eg hear own name said in noiisy room) (shows how we can selectively attend to certain stimuli in a noisy environment)
Change Blindness
Failing to notice changes in the environment due to innatention
Closure
Filling in gaps to create a complete, whole object.
we tend to see incomplete figures as whole
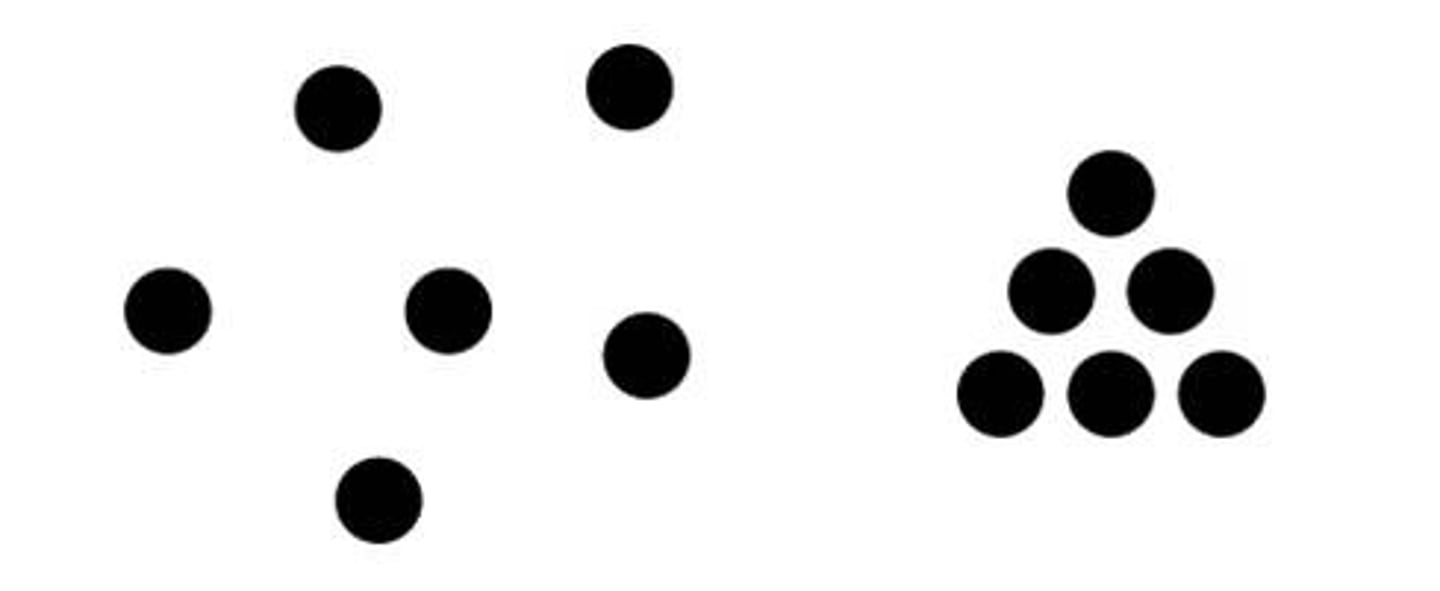
Proximity
Grouping nearby figures together.
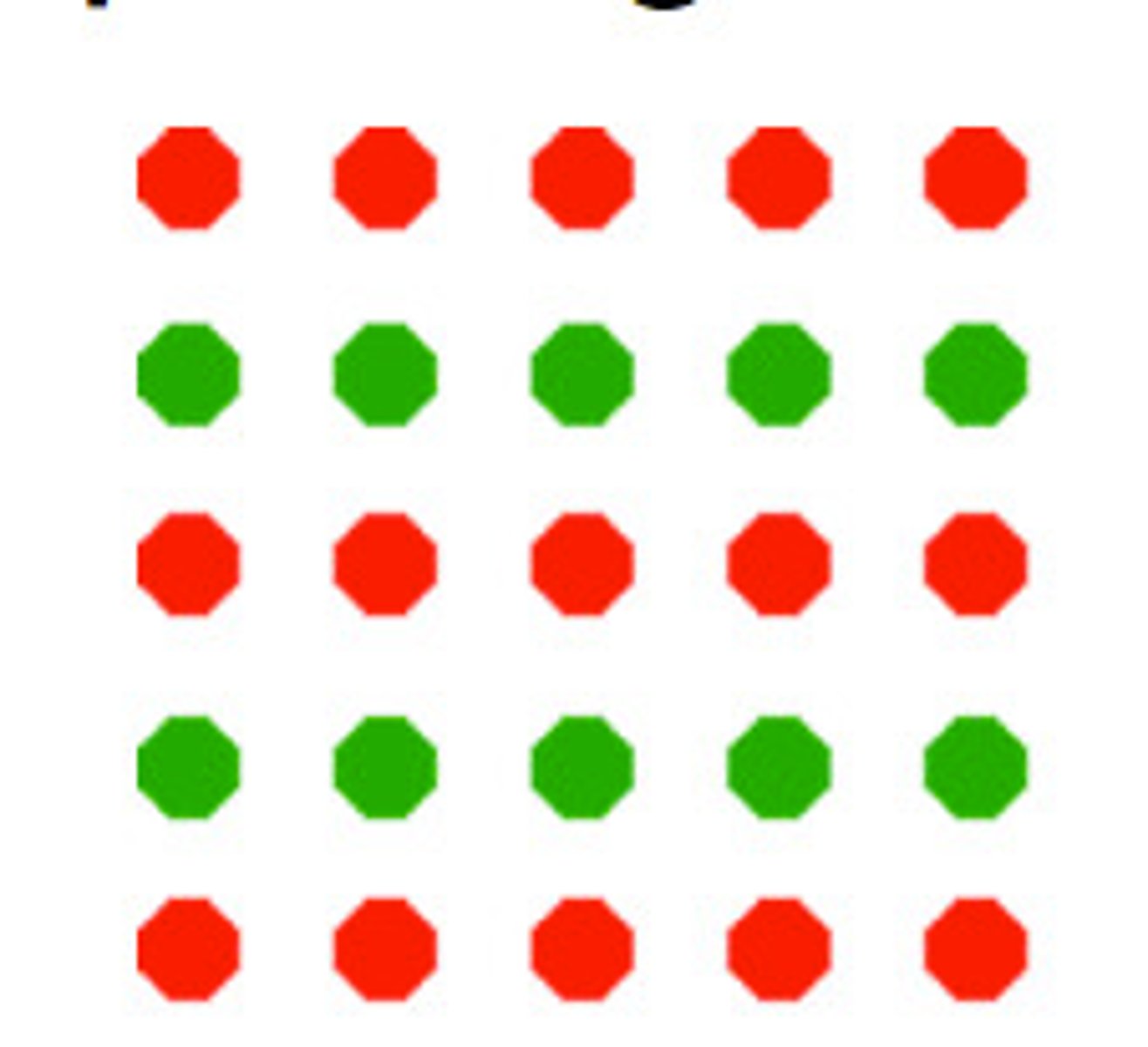
Similarity
Grouping similar figures together. (eg group objects of same color together)
Prototype
The most typical example of a concept. For instance, when
you think of the concept "bird," a robin might be the _____ that comes
to mind because it has all the common characteristics of birds.
Accommodation
Changing schemas to incorporate new information.
Example: Learning that some birds can't fly and updating
your bird schema to include flightless birds like penguins.
Algorithm
A methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem.
Creativity
the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas
Divergent Thinking
expands the number of possible problem solutions (creative thinking that diverges in different directions)
Bottom-Up Processing
relies on external sensory info, process as sensing
Perceptual Set
Mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another. (eg expect to see a certain shape in the clouds bc someone mentioned it)
Attention
Focusing awareness on a particular stimulus.
Selective Attention
Focusing on a specific aspect while ignoring others.
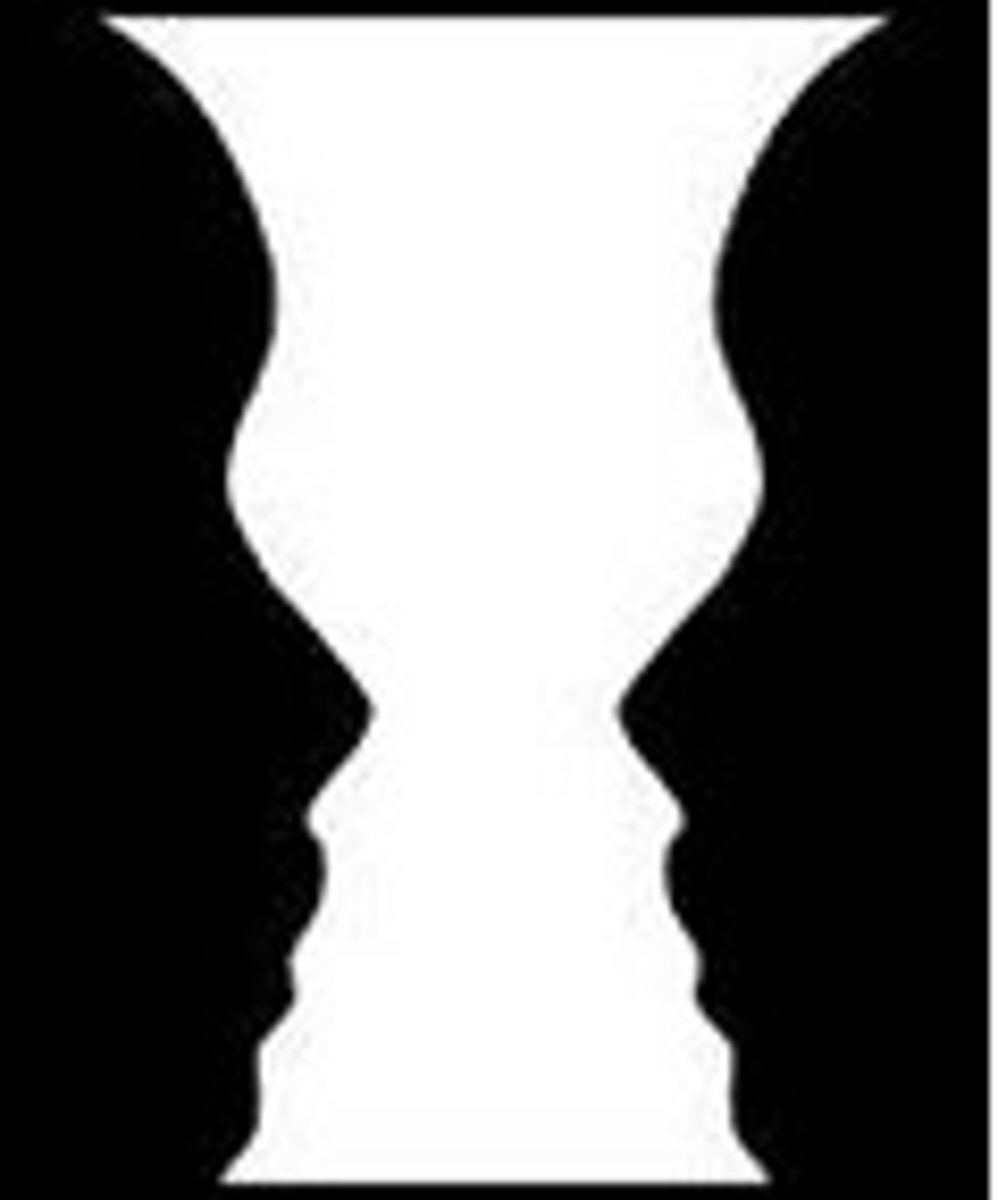
Figure and Ground (figure-ground)
we differentiate diff objects from their background

Grouping
Perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups.
Depth Perception
Ability to see objects in three dimensions.
Monocular Cues
allow us to percieve depth even with one eye
Linear Perspective
Parallel lines appear to converge with distance.
Perceptual Adaptation
Ability to adjust to an artificially displaced visual field.
Phi Phenomenon
Illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession.
Autokinetic Effect
Perceived movement of a stationary point of light in a dark room.
Schema
frameworks for thinking that help us organize and interpret information.
Assimilation
ncorporating new information into existing schemas without changing them. Example: Seeing a new breed of dog and adding it to your existing schema of what dogs are.
Executive Functions
higher order thinking processes that include planning, organizing, inhibition, and decision-making
Heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms
Representativeness Heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
Availability Heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.