Muscle Activation, Excitation, Contraction Coupling
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
what must happen for a skeletal muscle to contract?
activation at neuromuscular junction, excitation-contraction coupling
what is activation?
nervous system stimulation
what is generated during activation?
action potential in sarcolemma
what is increased during activation?
intracellular calcium levels
what happens during excitation-contraction coupling?
action potential spreads along sarcolemma, cross bridge cycling
what is the first phase of skeletal muscle contraction?
activation , motor neuron stimulates muscle fiber
what is the first step of activation?
action potential arrives at axon terminal
what happens once the action potential arrives at the axon terminal at a neuromuscular junction?
calcium channels open, calcium moves into axon terminal
what happens when calcium moves into the axon terminal during activation?
ACh releases into synaptic cleft
what happens once ACh is released into the synaptic cleft?
ACh binds to receptors on the sarcolemma
what does the binding of ACh to receptors on the sarcolemma result in?
sodium and potassium channels open
what happens after ACh binds to receptors and opens the Na+ and K+ channels?
ion movement causes depolarization; action potential in sarcolemma
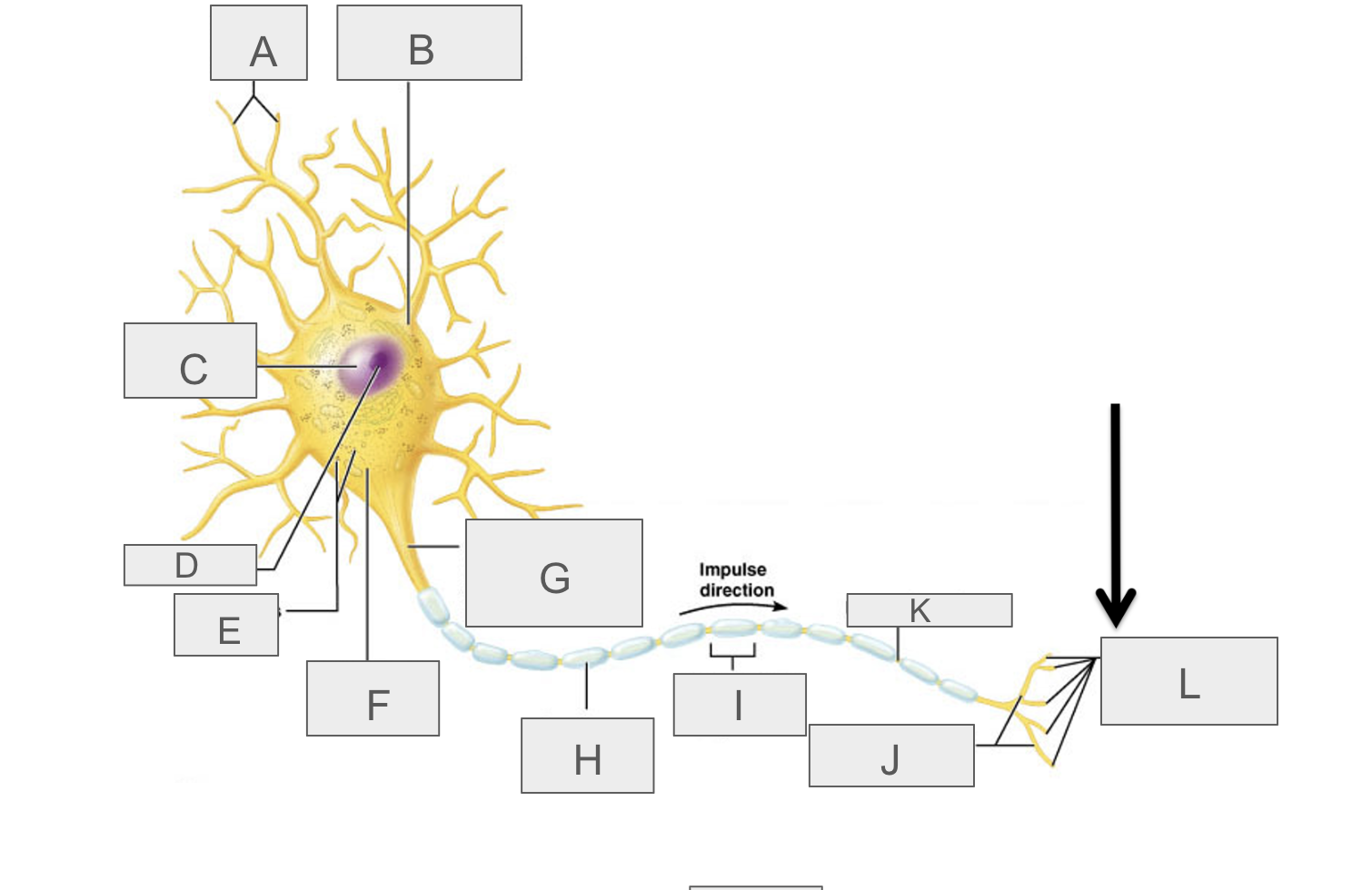
what is A?
dendrites
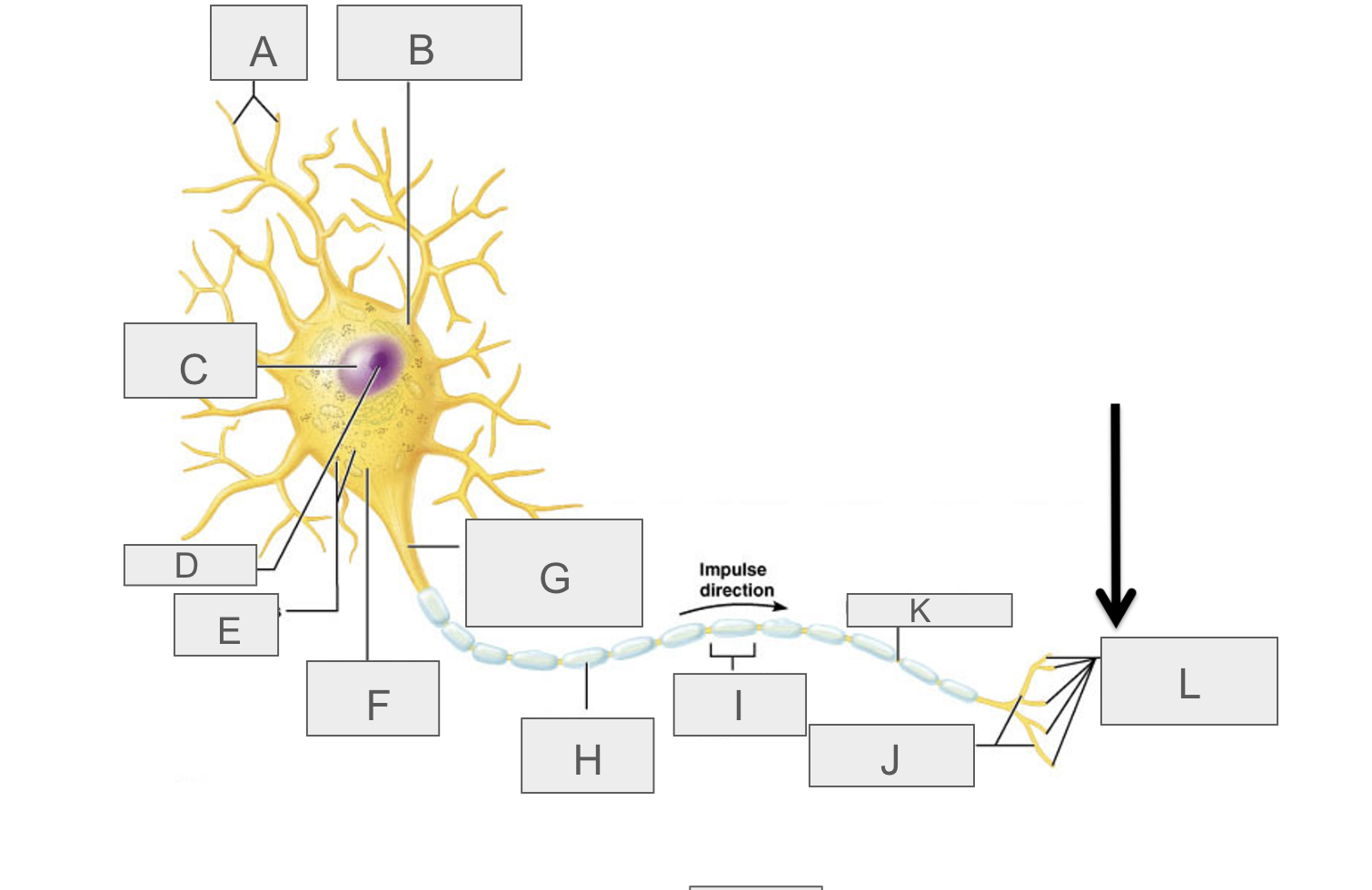
what is B?
cell body
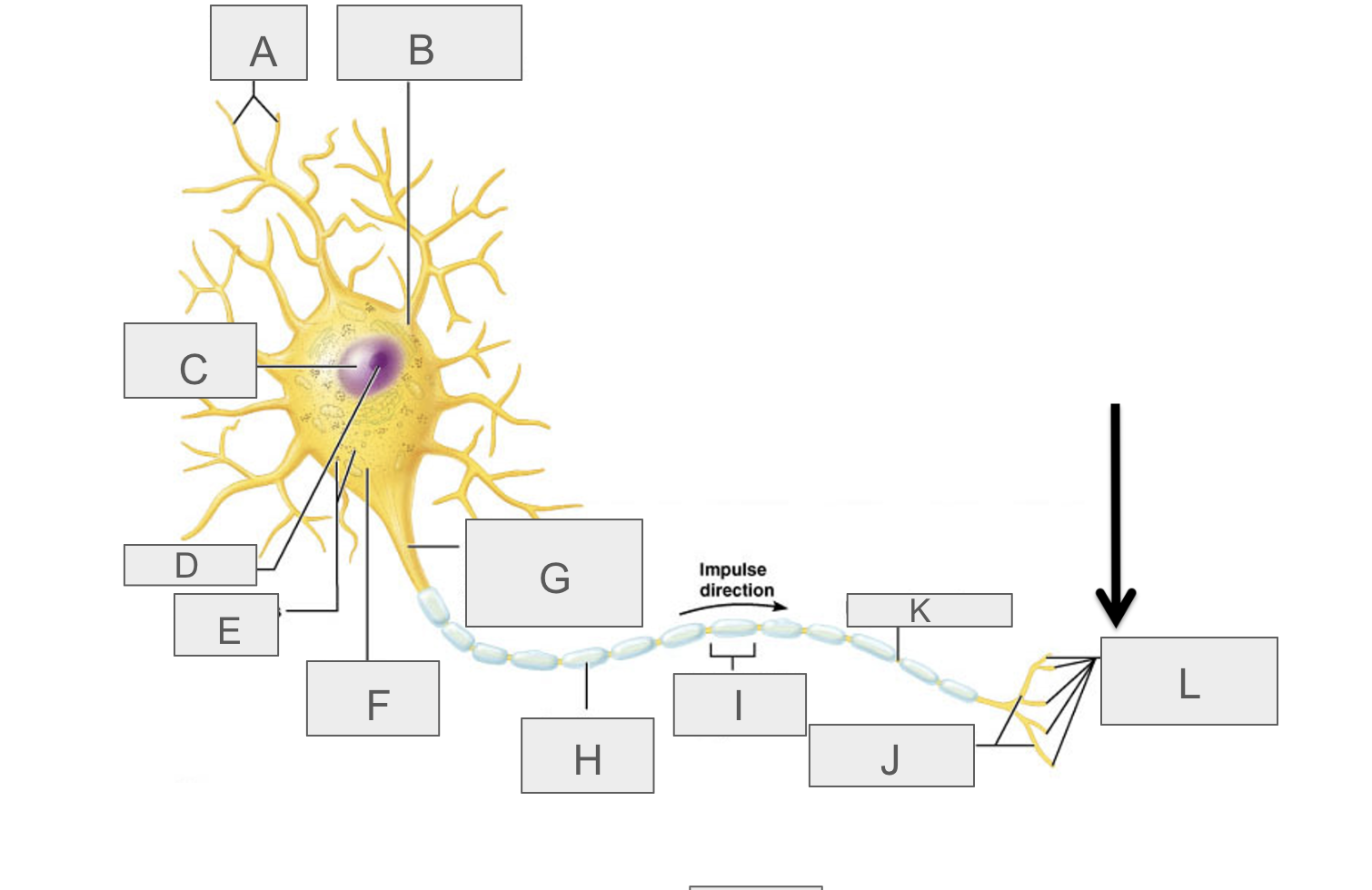
what is C?
nucleus
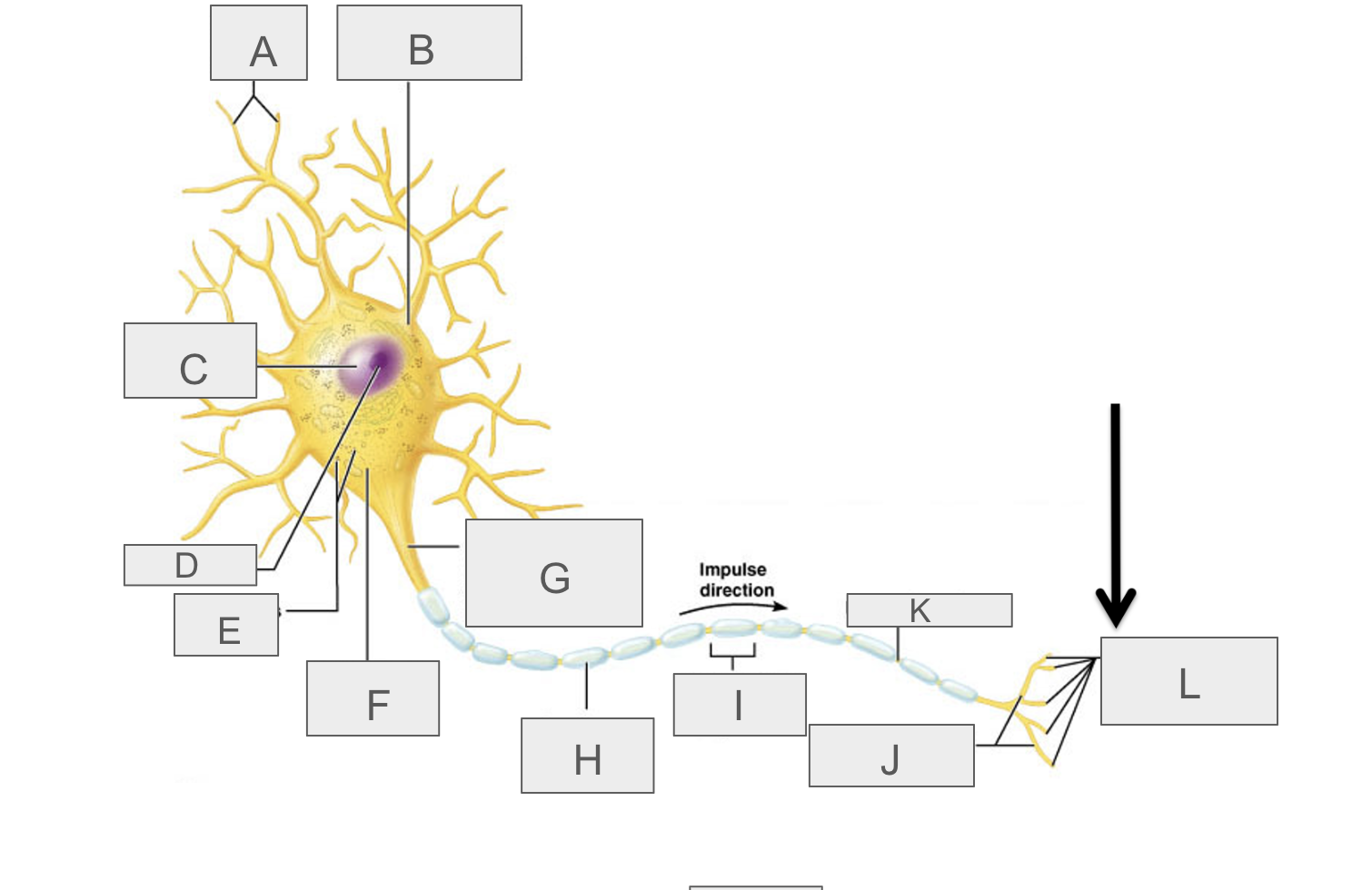
what is D?
nucleolus
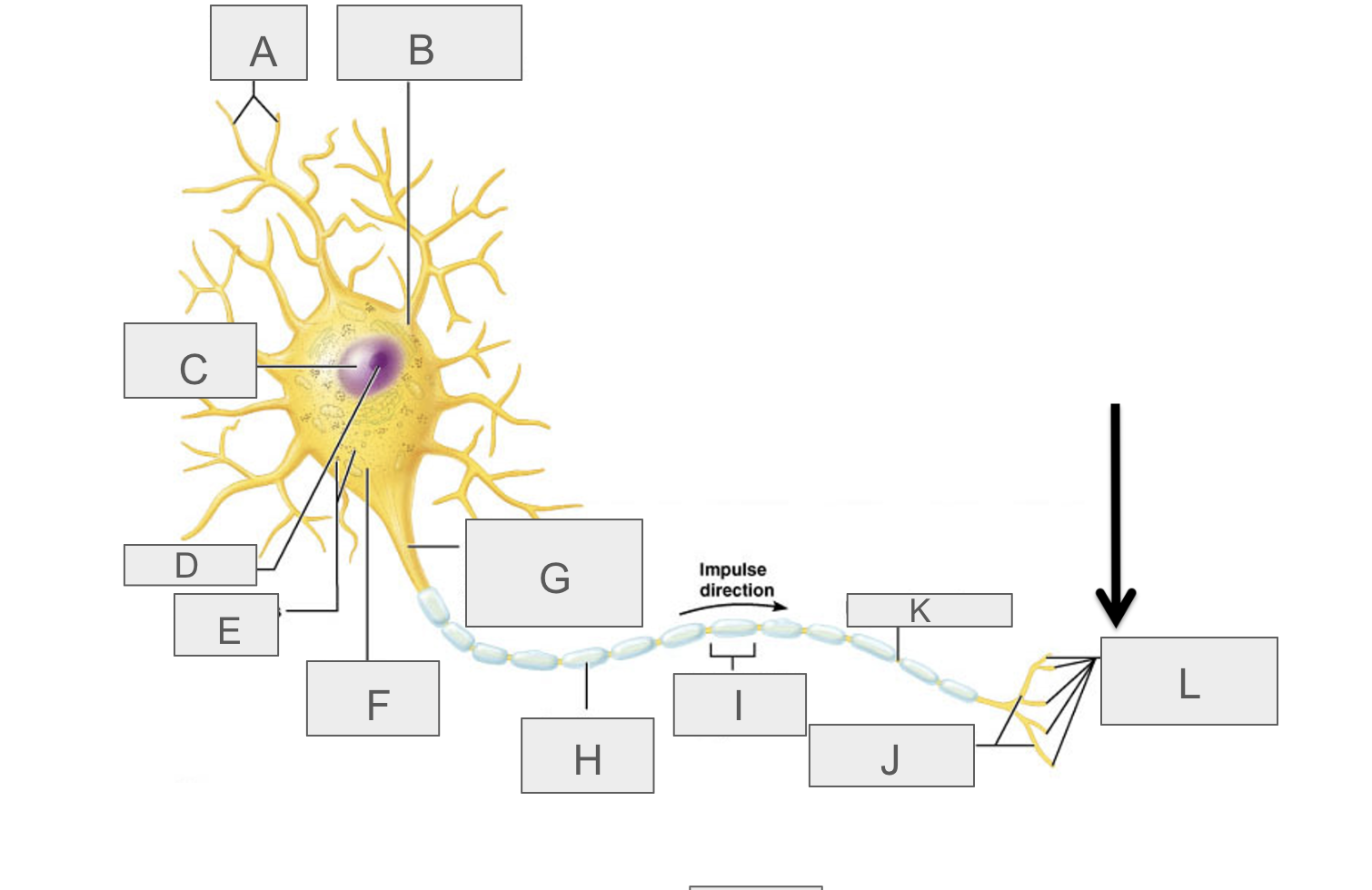
what is E?
nasal bodies
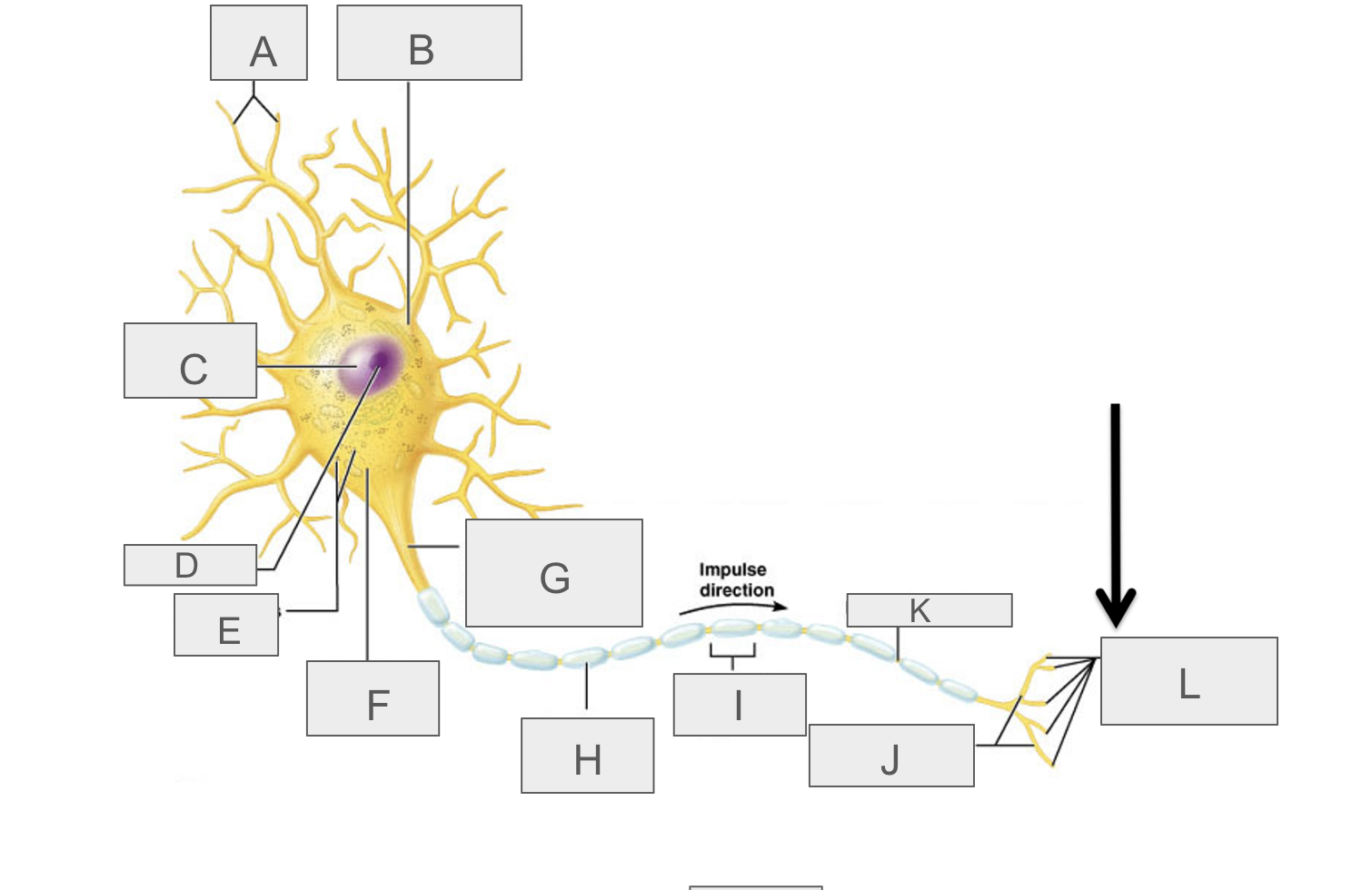
what is F?
axon hillock
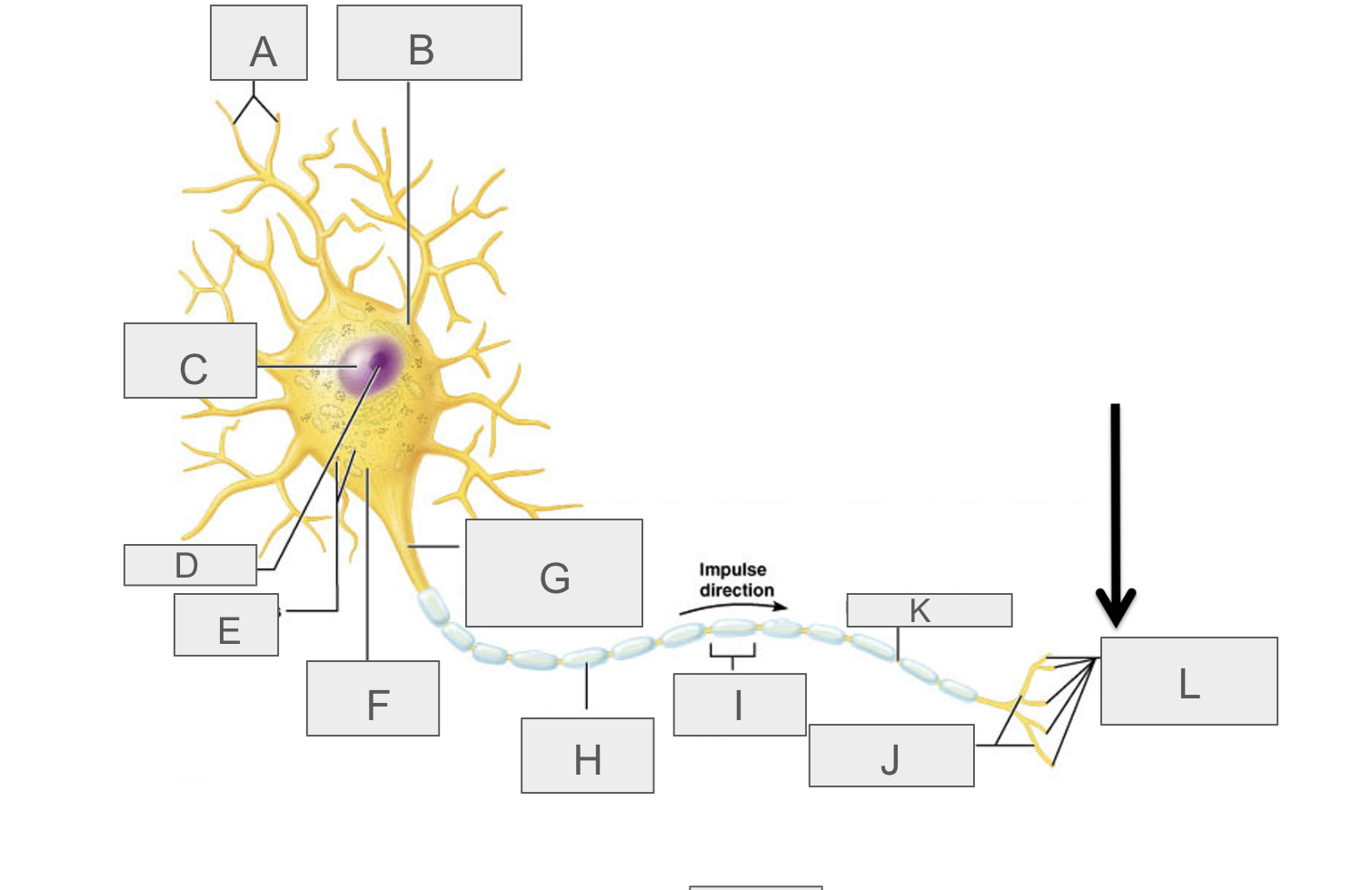
what is G?
axon
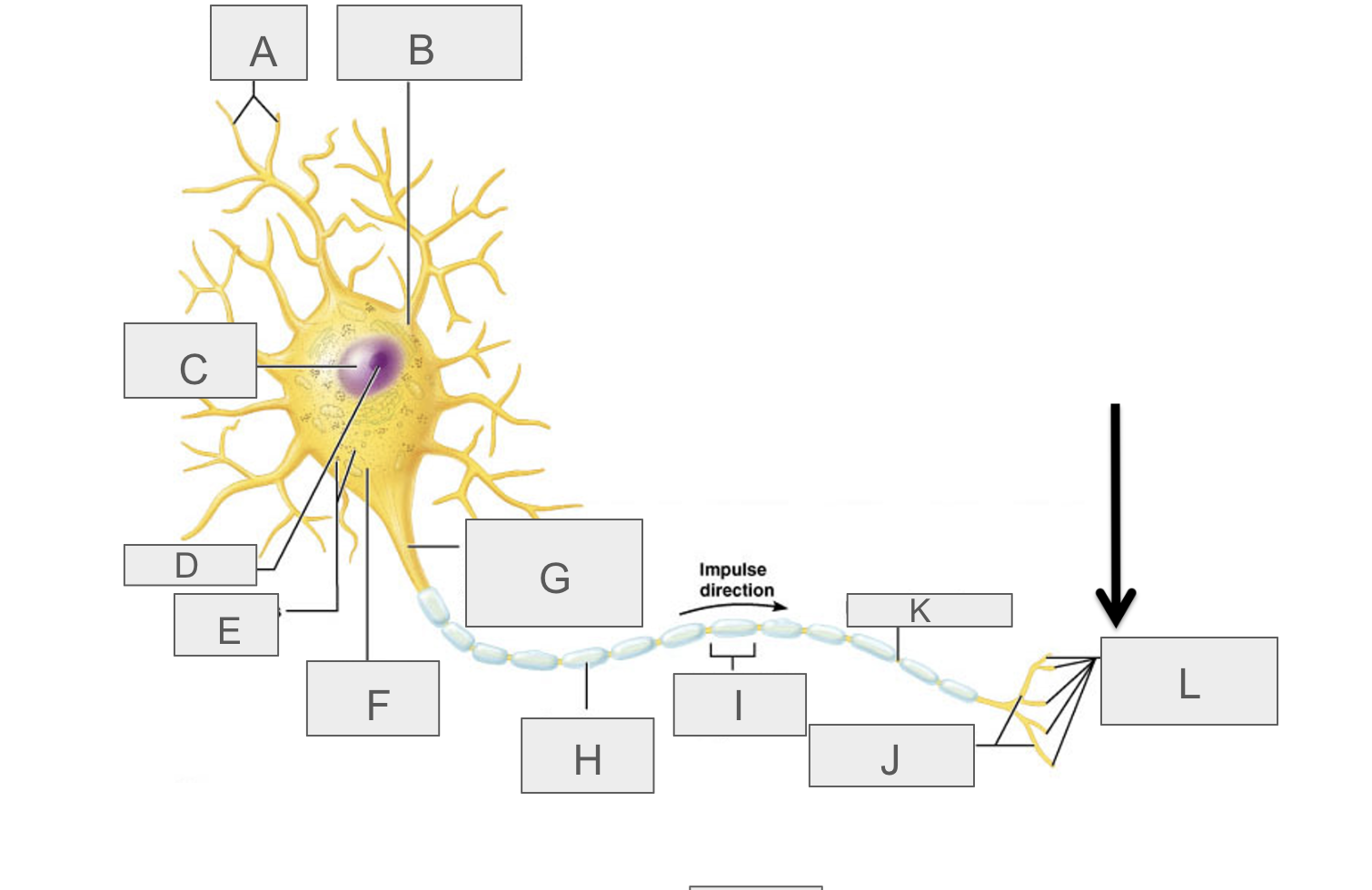
what is H?
myelin sheath
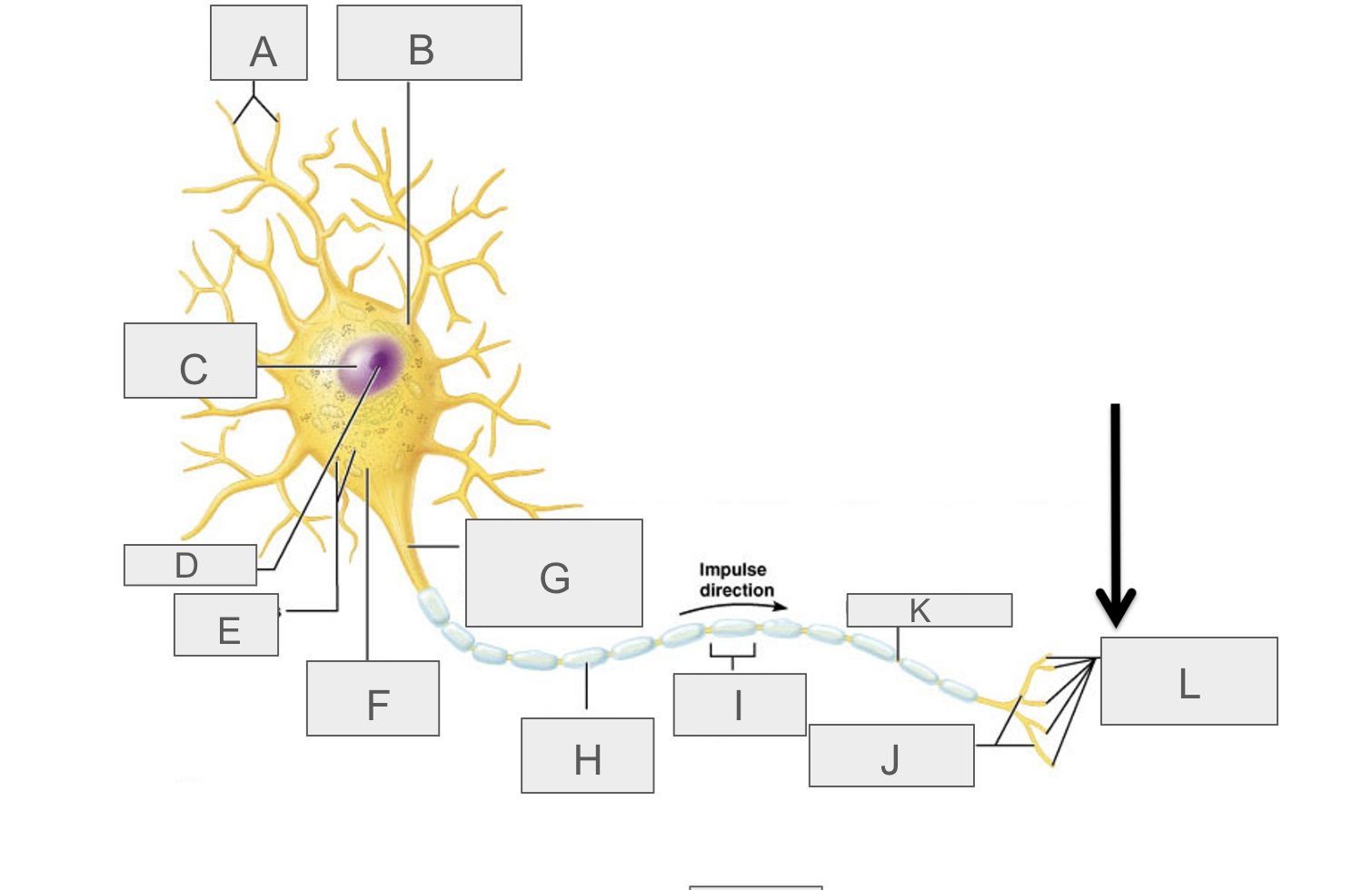
what is I?
schwann cell
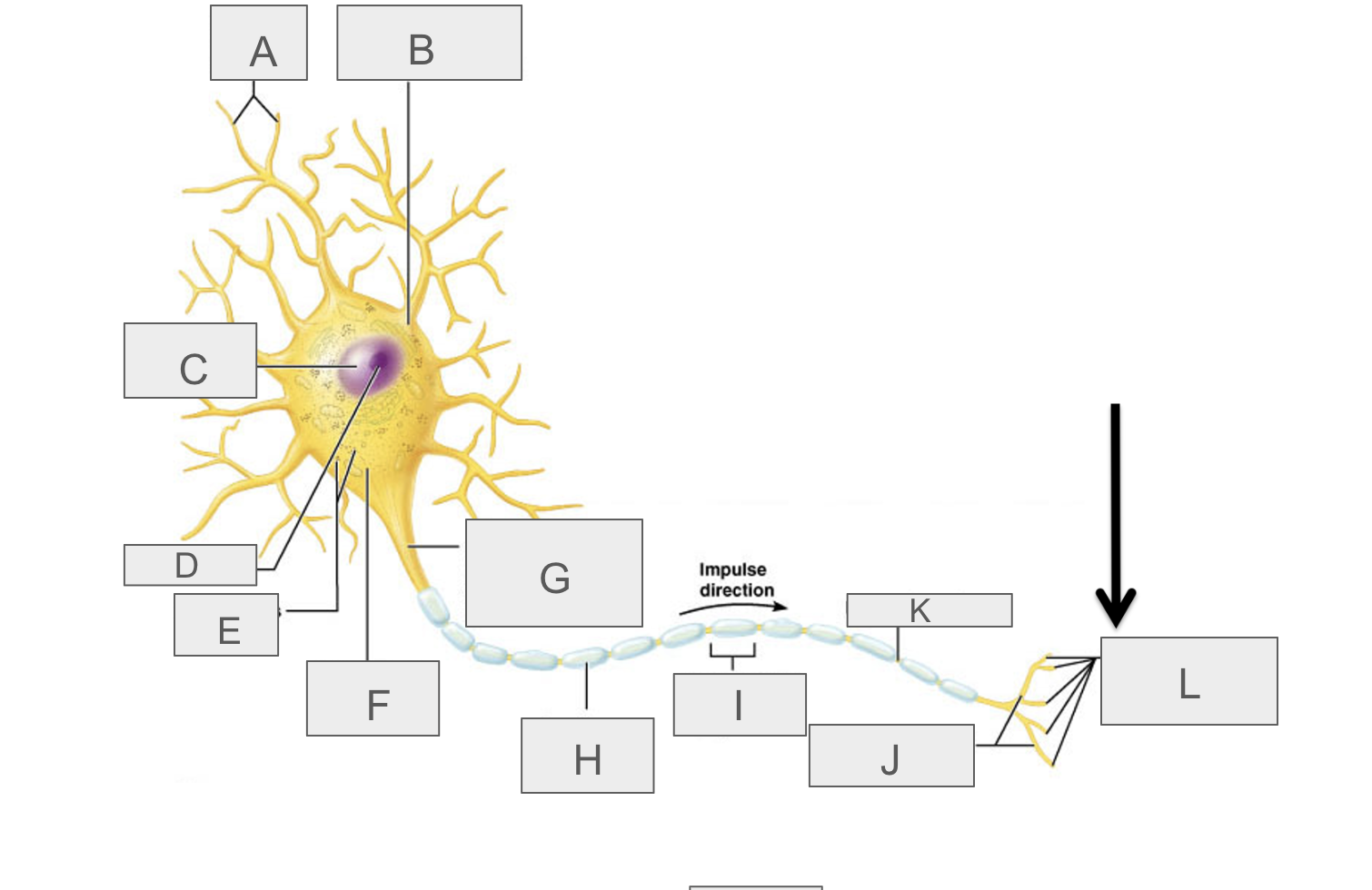
What is J?
terminal branches
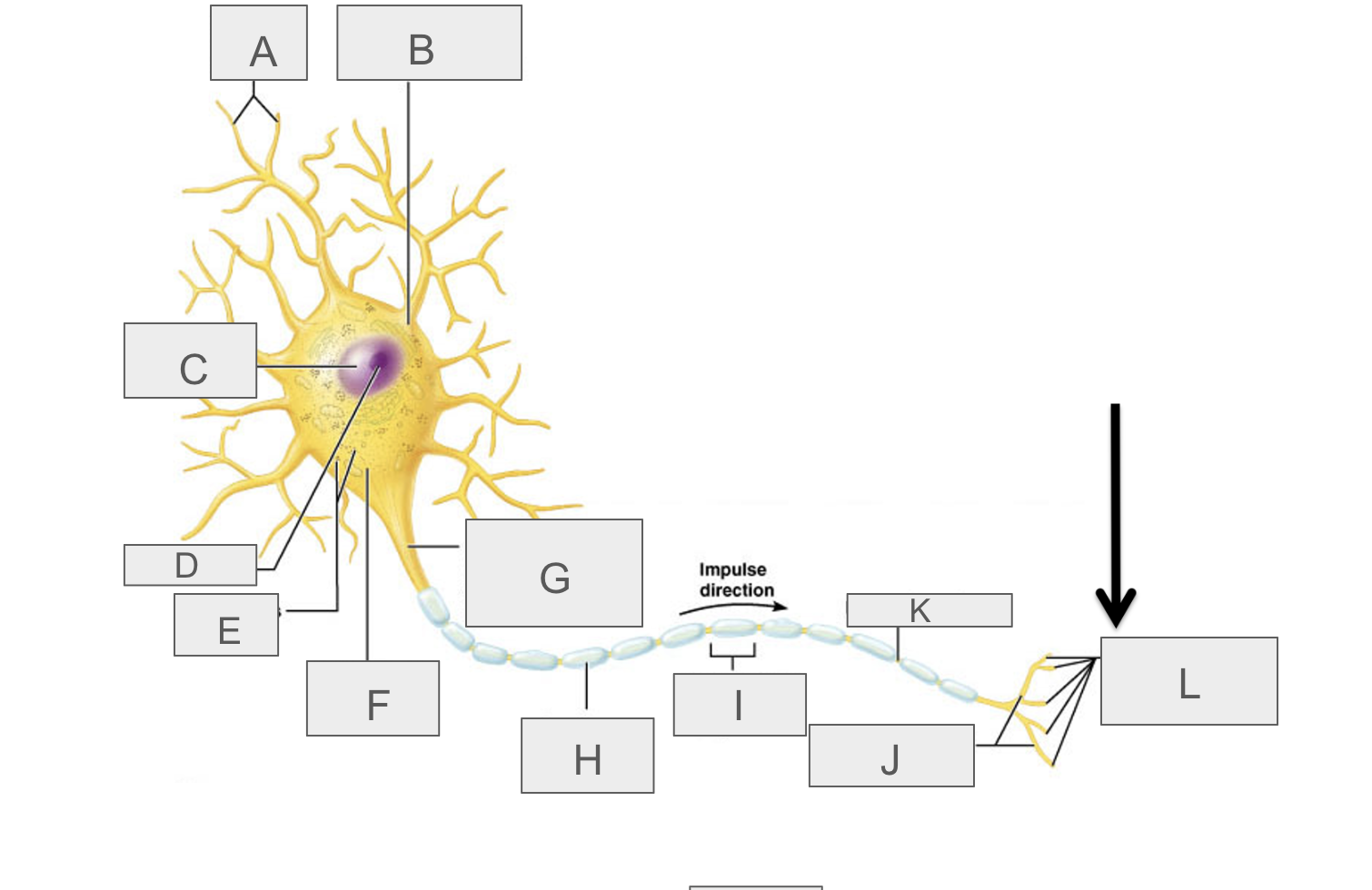
what is K?
node of ranvier
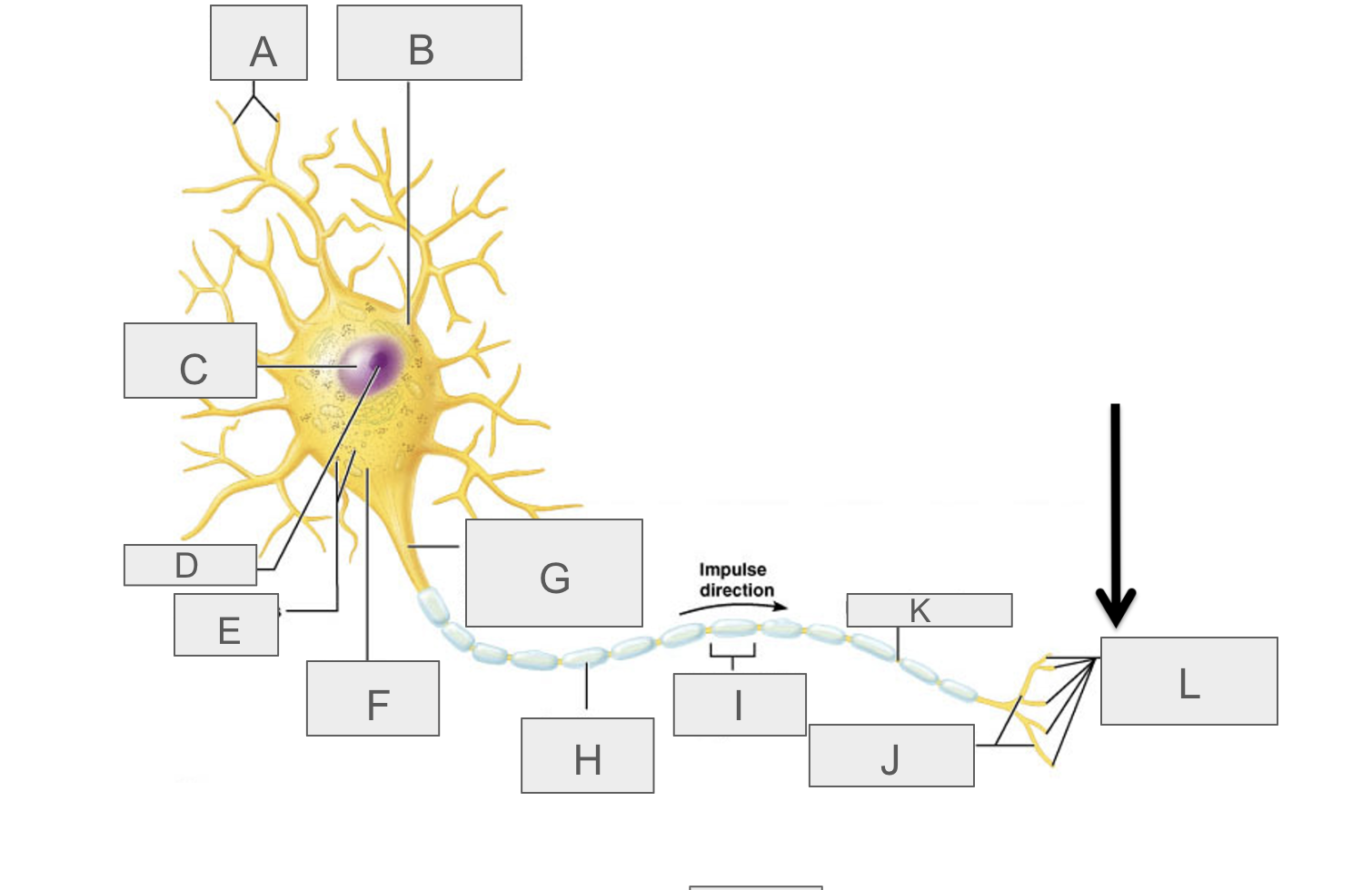
what is L?
axon terminal
what is found in the axon terminal?
synaptic vesicles of neurotransmitters (ACh)
what is the space between axon terminals and muscle fibers?
synaptic cleft
what are the junctional folds of sarcolemma for?
increasing surface area for binding of ACh
what is the resting membrane potential?
-70 mV (more negative inside than outside)
what is the resting membrane potential maintained by?
sodium potassium pump
what is it called when Na+ moves in to a cell?
depolarization
what is it called when K+ moves out of a cell?
repolarization
what happens during depolarization?
inside of membrane becomes more positive than RMP
what happens during repolarization?
membrane returns to RMP from a depolarized state
what happens during hyperpolarization?
inside of membrane becomes more negative than RMP
what is the minimum stimulus required to initiate an electrical event in muscle fiber that will result in contraction?
threshold
what is the required membrane potential for a muscle cell to depolarize?
-55mV
what happens once a threshold is met?
an action potential will fire and travel through entire muscle
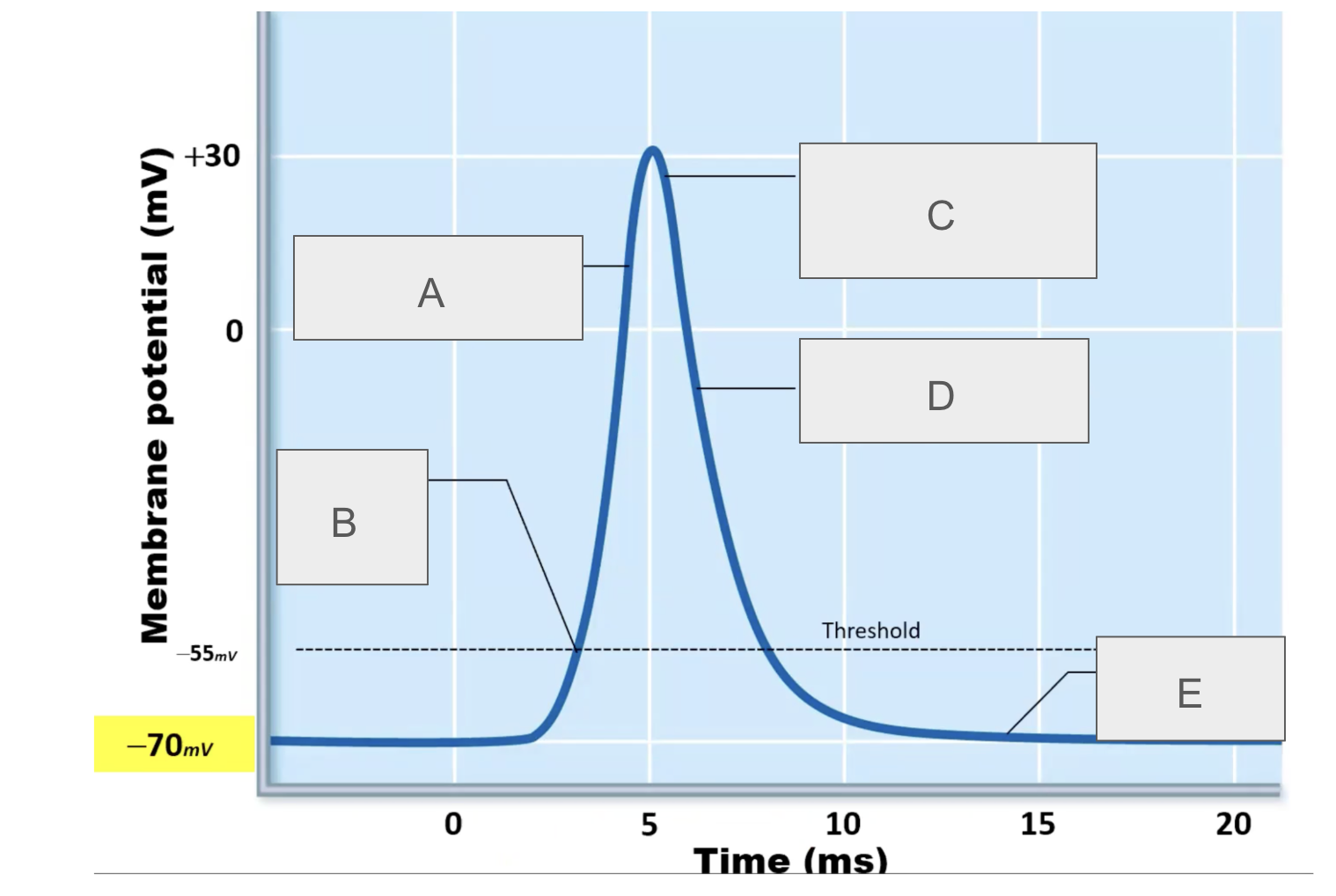
what is happening at A?
depolarization due to sodium entry
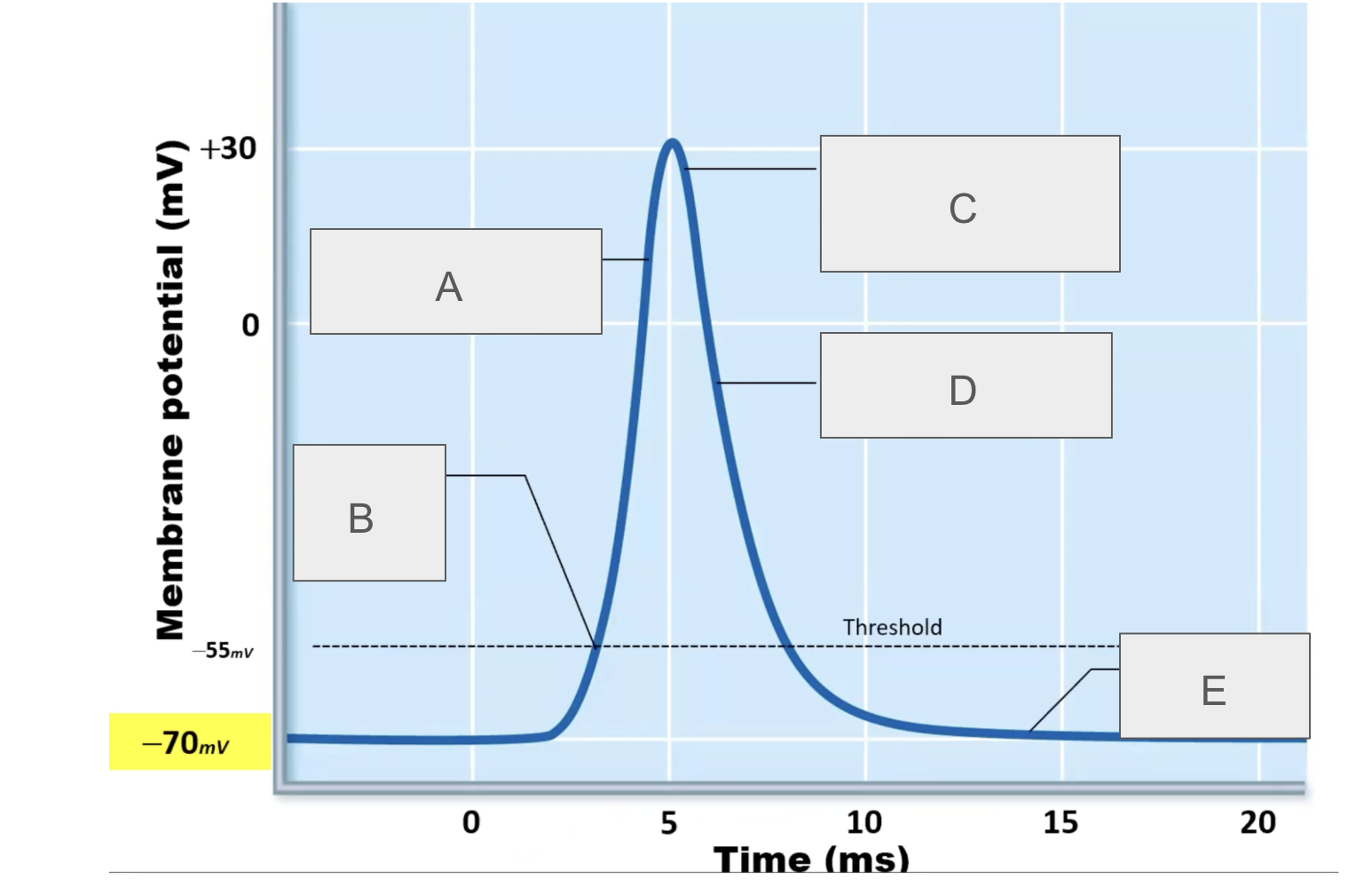
what is happening at B?
sodium channels open
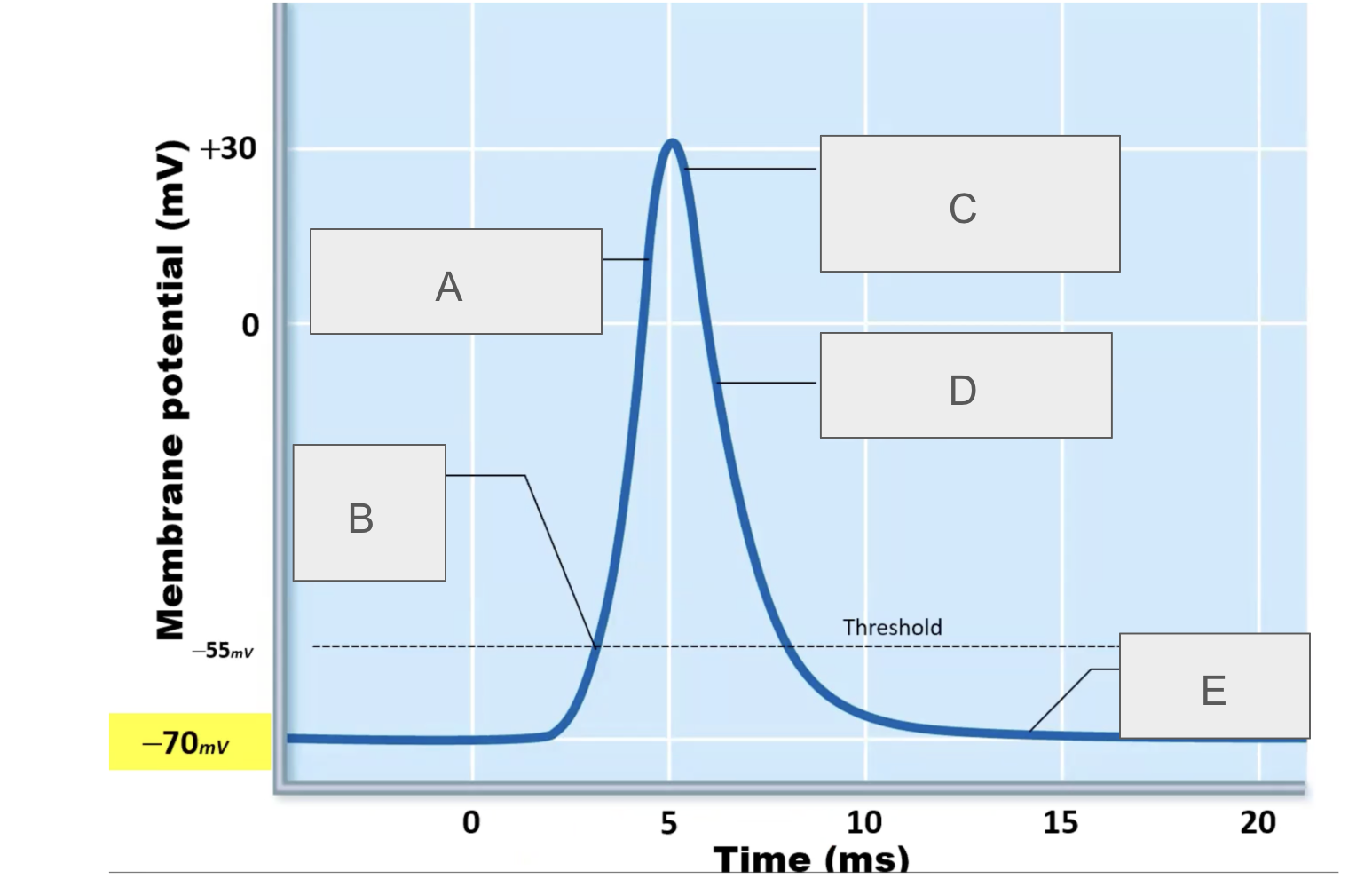
what is happening at C?
sodium channels close, potassium channels open
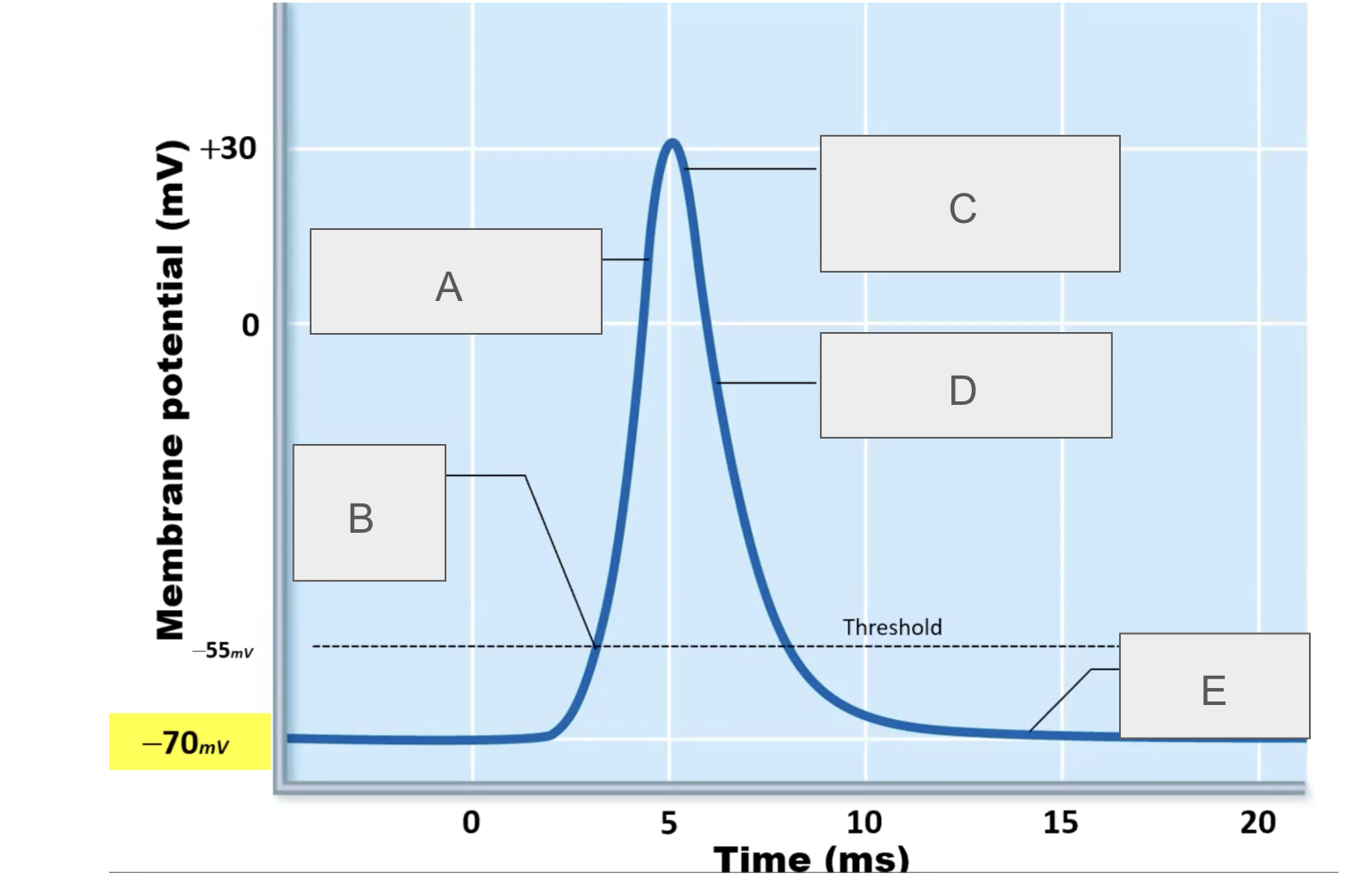
what is happening at D?
repolarization due to potassium exit
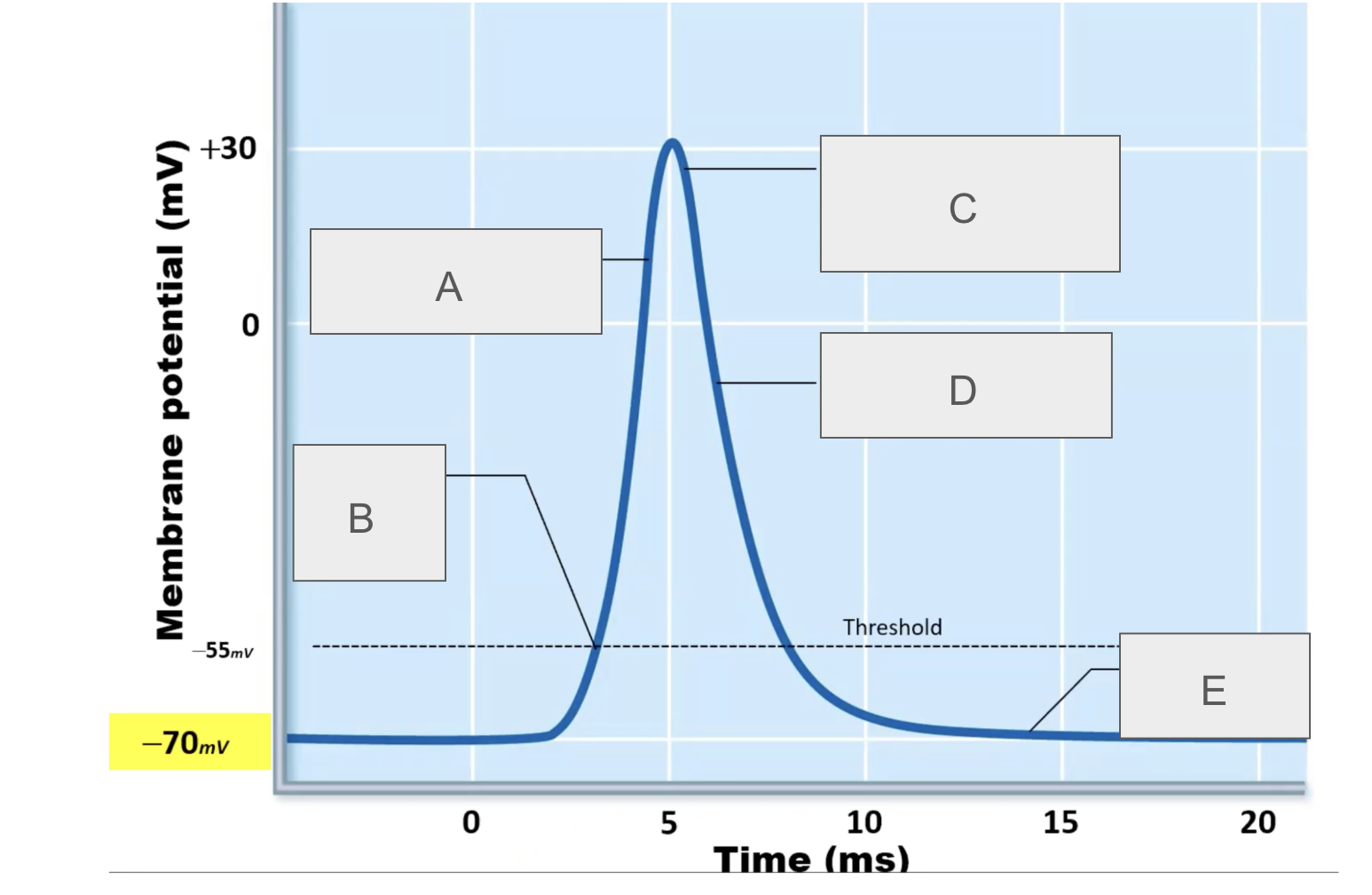
what is happening at E?
potassium channels open
what is the second phase of muscle contraction?
excitation
what is the first step of excitation?
action potential travels across the sarcolemma
what happens after the action potential travels across the sarcolemma?
action potential travels down t tubules
what happens after the action potential travels down t tubules?
sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium
what happens after the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium?
calcium binds to troponin and moves tropomyosin from myosin binding sites on actin
what happens after tropomyosin moves from myosin binding sites on actin?
myosin heads bind to actin, contraction begins
how many ATP’s are needed during contraction: cross bridge cycling
2
what happens after myosin head binds actin in phase 3: contraction?
power stroke
when is the second ATP used during phase 3: contraction
myosin heads detach from actin
what is the last step in muscle contraction?
myosin head resets
what will cause the cycle of muscle contraction to continue?
available ATP, calcium bound to troponin
what does exposure to botulinum toxin cause?
botulism
what does the botulinum toxin do?
blocks release of ACh from synaptic vesicles, paralyzing affected muscle