Form and Function: Animals
1/284
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
285 Terms
Asymmetrical
Animals, structures or organs which cannot be divided into similar halves by any plane
Bilateral
Animals, structures or organs which can be divided into two equal and similar halves by a single plane
Radial
Having similar parts arranged concentrically around a longitudinal axis, typically the oral-aboral axis. Can be divided into identical pie-shaped pieces along their radial axes. If an animal can be divided into eight identical wedges, it is called octaradial. Animals divisible by five are pentaradial and so on
Anterior
Nearer the front or that which is foremost in locomotion. The head end in quadrupeds and ventral surface in bipeds. Opposite of posterior
Cephalic
Pertaining to the head. Opposite of caudal. Also called cranial
Posterior
Nearer the back. Tail or hind end in quadrupeds and the dorsal surface in bipeds. Opposite of anterior
Caudal
Pertaining to the tail or posterior end of the body. Opposite of cephalic
Dorsal
Toward or pertaining to the upper surface. Opposite of ventral
Ventral
Toward or pertaining to the lower surface. Opposite of dorsal
Medial
Pertaining to the middle part of the body. Contrasted with lateral
Lateral
The side of the body. Contrasted with median. In a bilateral organism, the sides of the body are referred to as right or left. Note that this refers to the organism's right and left sides, not your own
Proximal
Nearer the point of attachment, for example, the shoulder is the proximal end of the arm. Opposite of distal
Distal
Away from the point of attachment. Opposite of proximal
Longitudinal
Lengthwise; parallel to the long axis of the body.
Circular
Around the long axis of the body in the transverse plane
Oral
Pertaining to the mouth. Area around the mouth. In radially symmetric animals, the surface bearing the mouth
Aboral
Pertaining to the region not associated with the mouth. Opposite of oral. A term used mainly to describe radially symmetric animals.
Saggital Plane
Pertaining to the median vertical longitudinal plane of the body. It divides the body into symmetrical right and left halves. Also called midsagittal. A plane parallel to the midsagittal is a parasagittal plane
Frontal Plane
A plane parallel to the ventral or dorsal surface of any bilaterally symmetrical animal; at right angles to the sagittal plane
Transverse Plane
Any plane at right angles to the sagittal and frontal planes. A cross section
Anterior-Posterior Axis
An axis extending from the anterior to the posterior end
Dorsal-Ventral Axis
An axis extending from the dorsal to the ventral surface
Oral-Aboral Axis
An axis extending from the oral to the aboral surface in radially symmetric animals
Radial Axis
An axis extending from the centre of a radially symmetric animal to the periphery
Metazoans
Multicellular animals
34
___ phyla of multicellular animals
Cambrian Explosion
basic body plans have not changed since the ___________
Cambrian Explosion
Most phyla appeared during this period
Protozoa
single celled eukaryotes (protoplasmic)
• Complete organism within one cell (Protists)
• E.g., Paramecium
Metazoa
multicellular animals with greater complexity
• Individual cells cannot survive on their own
• Cells are specialized for certain functions
• Parenchyma: functional cells
• Stroma: support cells
Parenchyma
Functional cells
Stoma
Support cells
Symmetry
refers to the correspondence of size and shape on opposite sides of a plane
Bilateral
Most animals with a head
Spherical
Any plane passing through the center divides a body into equivalent, or mirrored, halves. Rare in animals
Zygote
Fertilized egg, single cell
Blastula
Cluster of cells
Gastrula
2-3 layered embryo; germ layers
Ectoderm
Forms the exoskeleton
Mesoderm
Develops into organs
Endoderm
Forms the inner lining of organs
Diploblastic
• Only 2 germ layers: endoderm and ectoderm
• Cnidarians (sea anemones, e.g.), flatworms
Triploblastic
• 3 germ layers: mesoderm (develops from the endoderm)
• Organs, organ systems
• Most animals
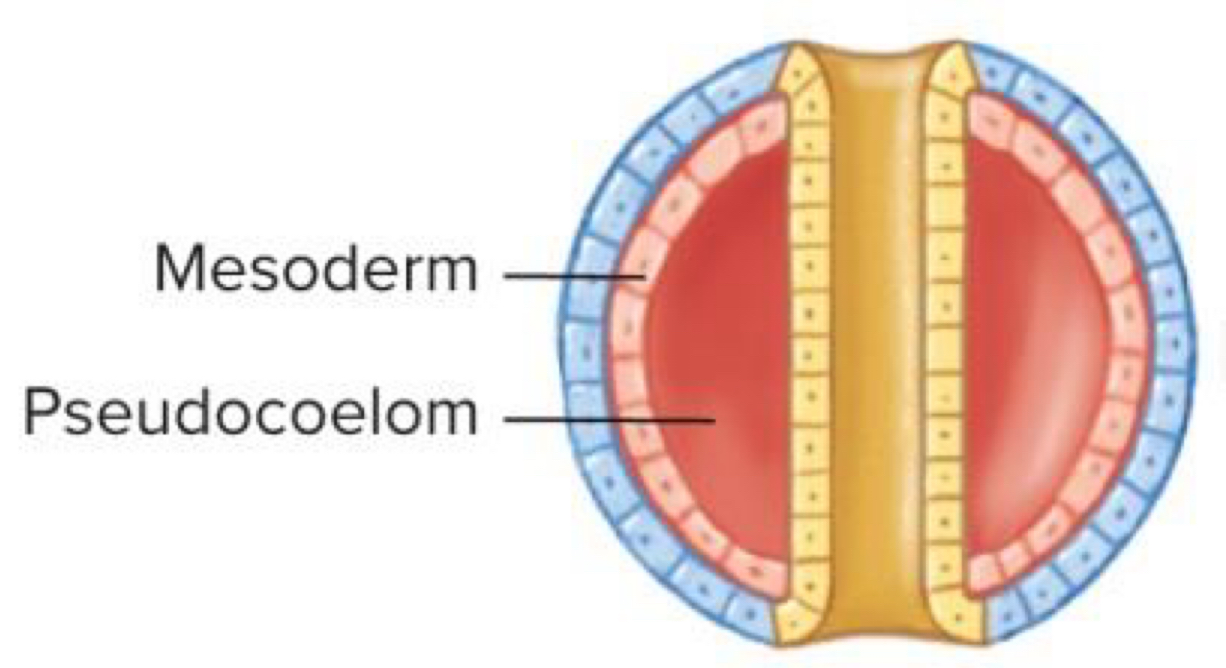
Pseudocoelomate Body
Mesoderm lines outer edge of blastocoel
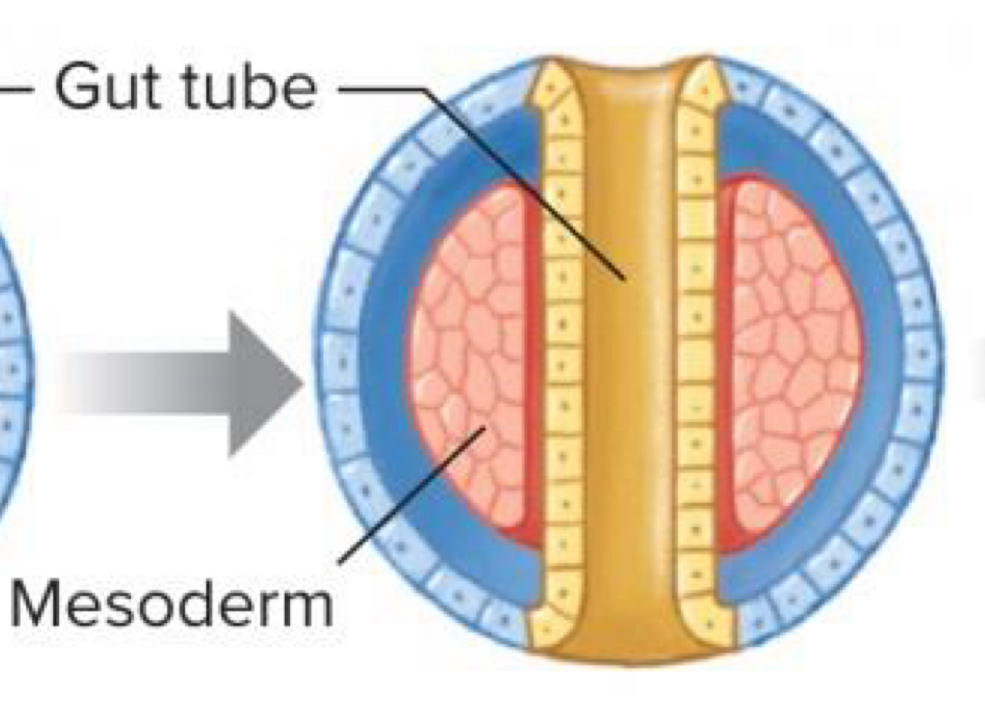
Acoelomate Body
Mesoderm completely fills blastocoel
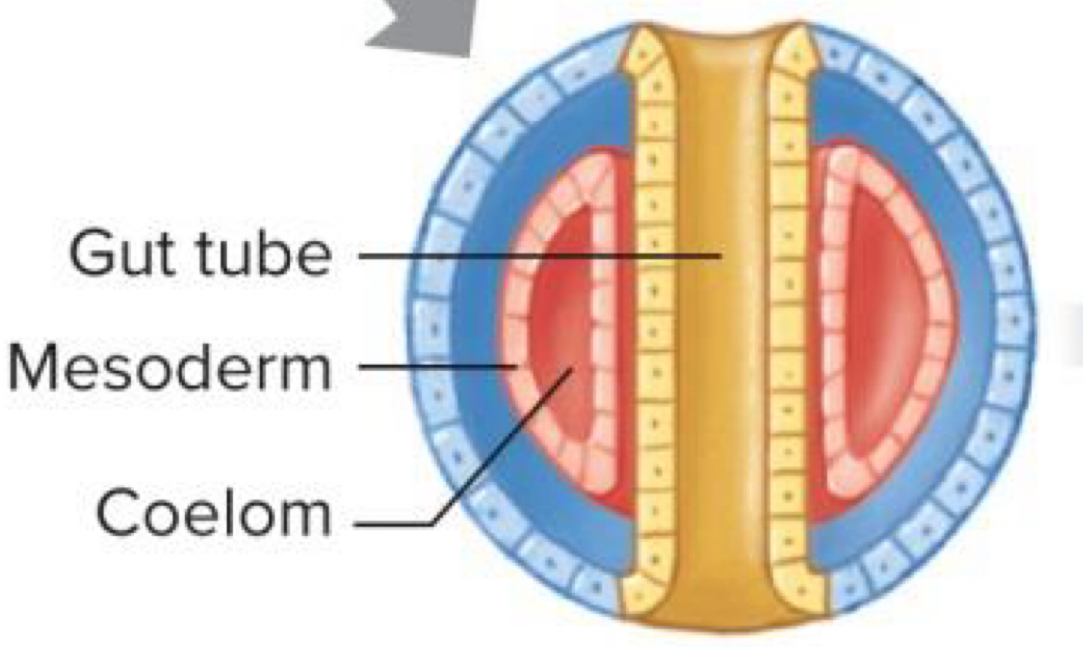
Coelomate Body
Coelomic cavity forms inside mesoderm
3
Triploblastic animals are further classified into ____ types
Extracellular Components
• body fluids (intracellular and extracellular)
• extracellular structural elements
Cellular Components
• tissue
Intracellular Fluids
within the individual cells
Extracellular Fluids
between cells or within cavities. In animals with a closed circulatory system:
• Blood plasma
• Interstitial fluid – between cells
Structural Components
• Connective tissue
• Cartilage
• Bone
• Cuticle
Epithelial Tissue
forms the covering on all internal and external surfaces of the body, lines body cavities and hollow organs and is the major tissue in glands
Connective Tissue
diverse body tissue that connects, supports, protects, and binds other tissues and organs, forming the body's framework
Nervous Tissue
the main tissue of the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, nerves) responsible for controlling body functions by rapidly transmitting electrical and chemical signals, coordinating movement, sensations, and thought
Sponges
Have zero germ layers
No
Can diploblastic animals have organs?
Pseudocoelomate, Acoelomate, Coelomate
3 types of triploblastic animals
Grade of organization, symmetry, germ layers and body cavities
Animal phyla are distinguished from each other by their body plans; this includes:
Protoplasmic, cellular, cell-tissue, tissue-organ, organ-system
The five major grades of organization are…
Protoplasmic
Characterizes unicellular organisms. All life functions are confined within the boundaries of a single cell, the fundamental unit of life. Within a cell, protoplasm is differentiated into organelles capable of performing specialized functions
Cellular
An aggregation of cells that are functionally differentiated. A division of labour is evident, so that some cells are concerned with, for example, reproduction, and others with nutrition.
Cell-Tissue
An aggregation of similar cells into definite patterns or layers and organized to perform a common function, to form tissue
Tissue-Organ
An aggregation of tissues that forms organs in a further step in complexity. Organs are usually composed of more than one kind of tissue and have a more specialized function than tissues
Organ-System
Organs working together to perform some function, producing the highest level of organization - an organ system. Systems are associated with basic body functions such as circulation, respiration, and digestion
Eumetazoans
Animals at or beyond the cell-tissue grade of organization
11
______ different kinds of organ systems are described in animals
Bilateria
Bilateral animals form a monophyletic group of phyla called the…
Pectoral
In vertebrates _______ denotes the chest region or area associated with the anterior pair of appendages
Pelvic
In vertebrates, _______ denotes the hip region associated with the posterior pair of appendages
Blastopore
Typically becomes the adult mouth or anus
Segmentation
also called metamerism
Serial repetition of similar body segments along the longitudinal axis of the body
Metamere
Each segment of segmentation is called a _______, or somite
Segmentation
Permits greater body mobility and complexity of structure and function
Interstitial Fluid
Also called tissue fluid, occupies the space surrounding cells
Histology
The study of tissues
Epithelial, nervous, connective, muscular
4 types of tissue
Epithelium
A sheet of cells that covers an internal or external surface
Systematics
the study of the units of biodiversity, dealing with diversification of lineages through time
Carolus Linneaus
Created the current scheme (=binomial classification) that we still use today (1707-1778)
Taxonomy
Classification of animals
Phylogeny
evolutionary relationships
Characters
Can be morphological, chromosomal or molecular
Homology
Character similarity from a common ancestor
Convergent Evolution
Independent evolution of the same characteristic
Cladogram
Nested hierarchy of branches with similar derived characters
Phylogenetic Tree
Similar to cladogram but includes more information, usually genetic
Monophyly
Single common ancestor + all descendants
Paraphyly
Common ancestor and some of its descendants
Polyphyly
Grouping with no recent common ancestor
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukaryota
Domains of life
Genus
A group of related species with taxonomic rank between family and species
Holotype
The single museum specimen that formally carries the same of a recognized species
Species Epithet
The second (uncapitalized) word in the Linnaean binomial nomenclature of species, used to separate an individual species from other members of the same genus
Common Descent
Darwin’s theory that all forms of life are derived from a shared ancestral population through a branching of evolutionary lineages
Reproductive Community
A general criterion for the species category shared to some degree by all formal species concepts is that species constitute a reproductively bounded population or lineage of populations that does not freely merge with others in nature
Geographic Range
The specific geographic area occupied by members of a population, species, or higher taxon
Evolutionary Duration
The length of time that a species or higher taxon exists in geological time
Evolutionary Species Concept
Defines species as a single lineage of ancestral descendant populations that maintains its identity from other such lineages and has its own evolutionary tendencies and historical fate; differs from the biological species concept by explicitly including a time dimension and including asexual lineages
Cosmopolitan
Used to describe a species or higher taxon that has a very large geographical range, such as the worldwide distribution of humans