AP Bio Unit 5 CELL SIGNALING
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
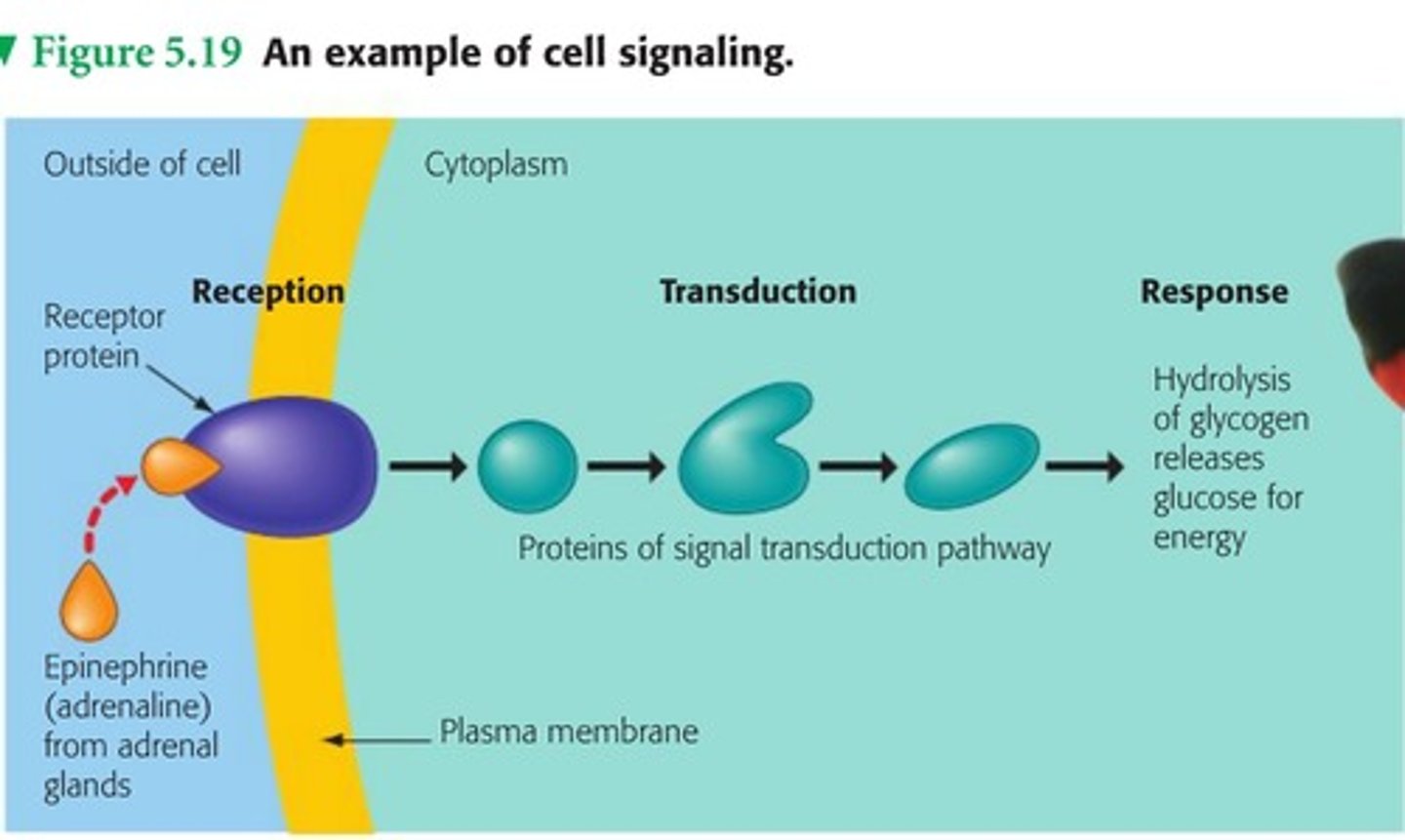
Reception (signal transduction pathway)
target cell's detection of a signaling molecule coming from outside the cell;
The binding between a signal molecule (ligand) and receptor is highly specific (lock & key) and generally causes a shape change in the receptor, activating the receptor
Ligand
Signaling molecule
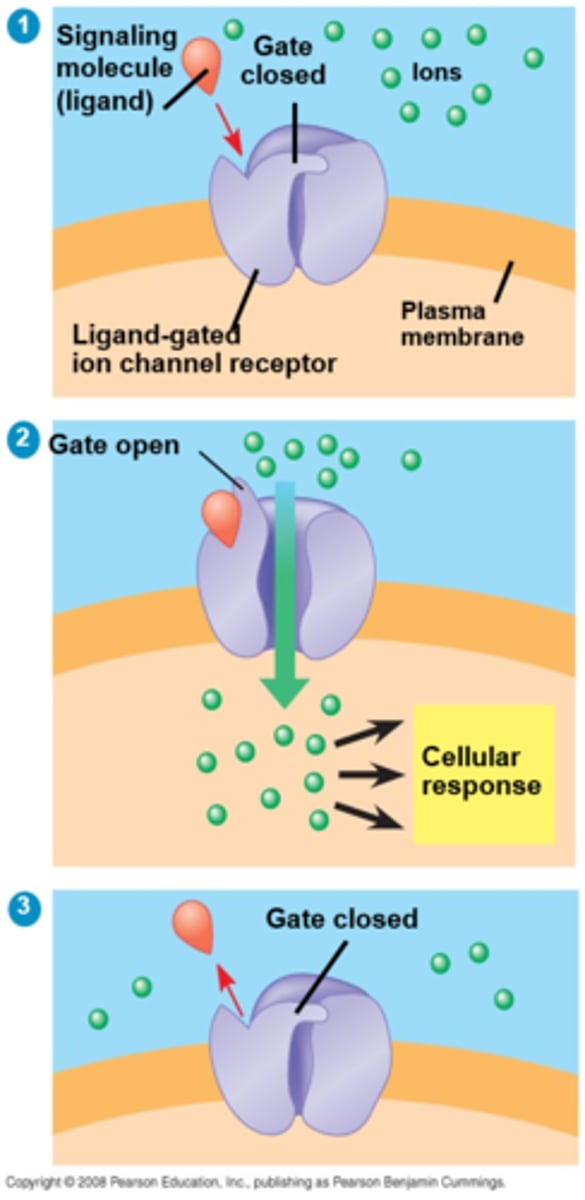
Ligand ion channel receptor
When a ligand binds to the receptor, the gate allows specific ions, such as Na+ or Ca2+, through a channel in the receptor
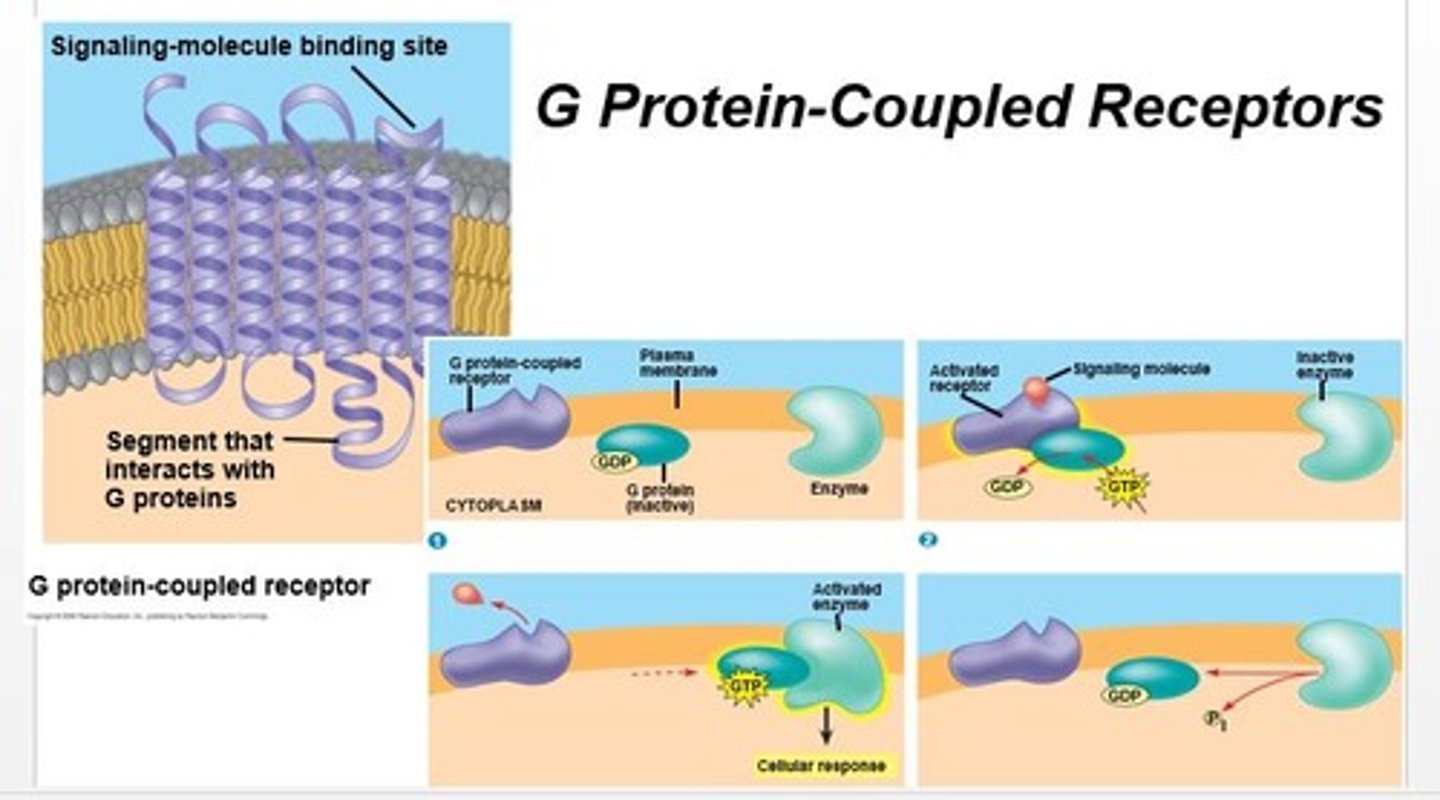
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
1. Ligand molecule binds to specific G protein-couple receptor, changing its shape, & activating it
2. GPCR binds & activates G protein
3. G protein then leaves receptor & binds to enzyme, changing its shape, and activating it
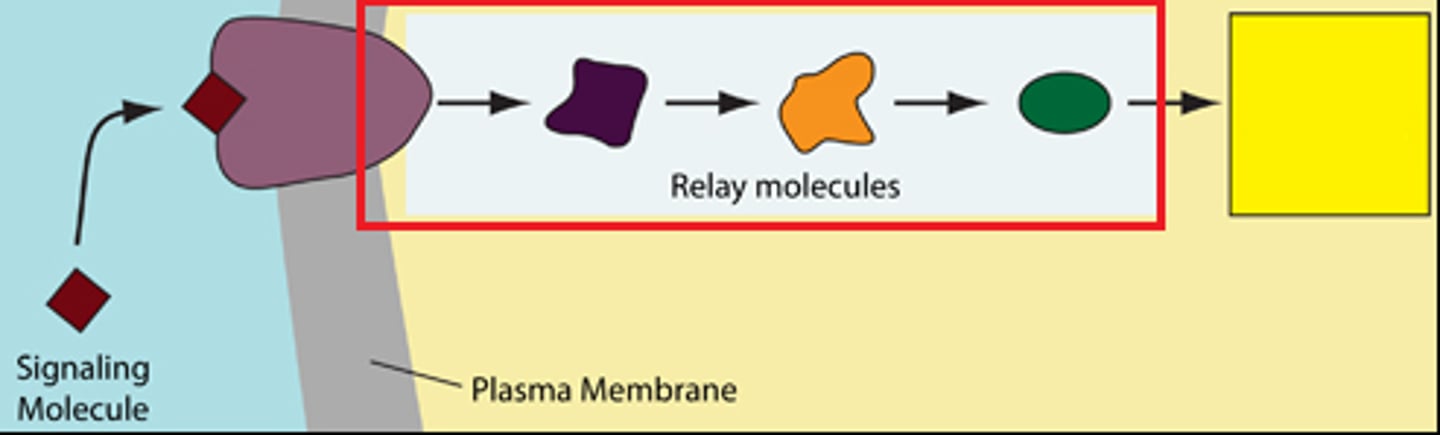
Transduction
Step or series of steps that converts the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response
Protein kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein
Signal transduction pathway
1. reception
2. transduction
3. response
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal conditions as environment changes; examples include body temperature, glucose levels, osmolarity, pH
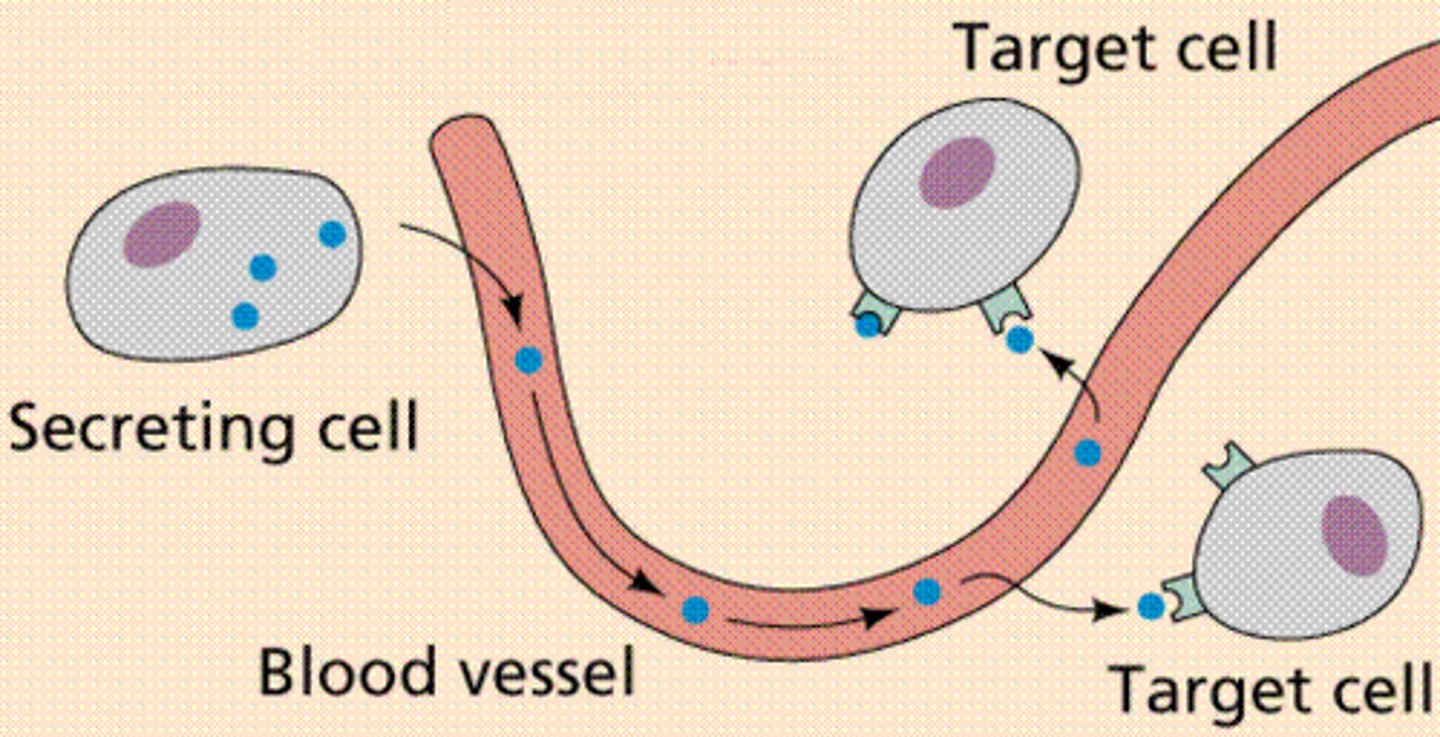
Hormone
Type of secreted chemicals by the endocrine system that are important in long-distance signaling- travel in body fluids and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body; examples include insulin (released with high blood glucose levels) and glucagon (released with low blood glucose levels)
Negative feedback
Maintaining set point; examples include body temperature, blood glucose levels, osmolarity, pH
Osmolarity
The solute concentration of a solution
Positive feedback
Amplifies/ reinforces stimulus; examples include ethylene, blood clotting
Intracellular domain
Inside portion of a membrane embedded receptor protein
Signal cascades
Amplify and distribute intracellular (inside the cell) signals; occurs in cytoplasm
cAMP
Secondary messenger that relays and amplifies intracellular (inside the cell) signals
Chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
Interphase
Cell grows, copies DNA, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
G0 stage
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
Growth factors
Proteins released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide
Cyclin
One of a family of proteins that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Cancer
A disease in which some body cells grow and divide uncontrollably, damaging the parts of the body around them.