Week 7 -Digestive System (Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Accessory Organs)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
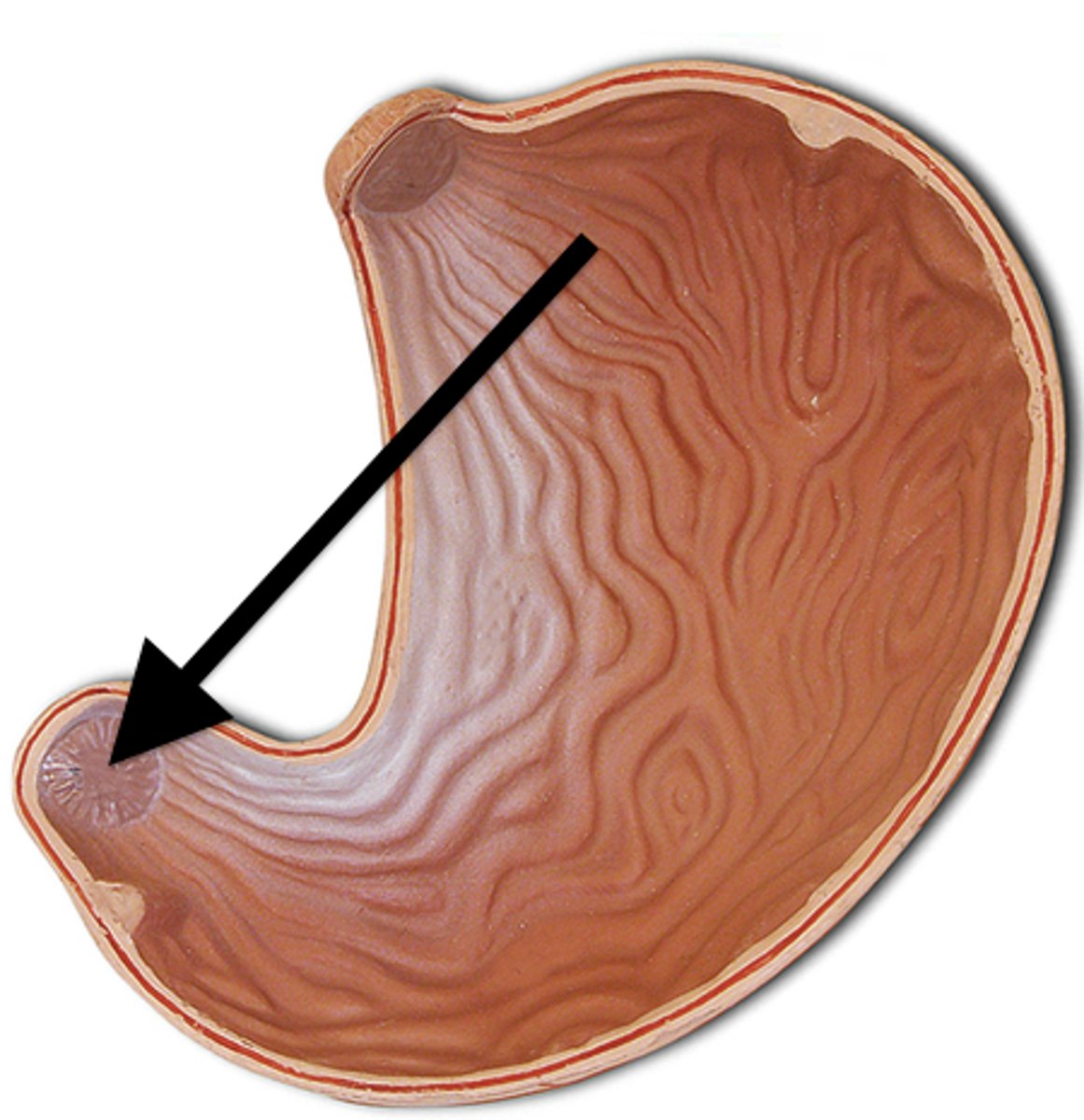
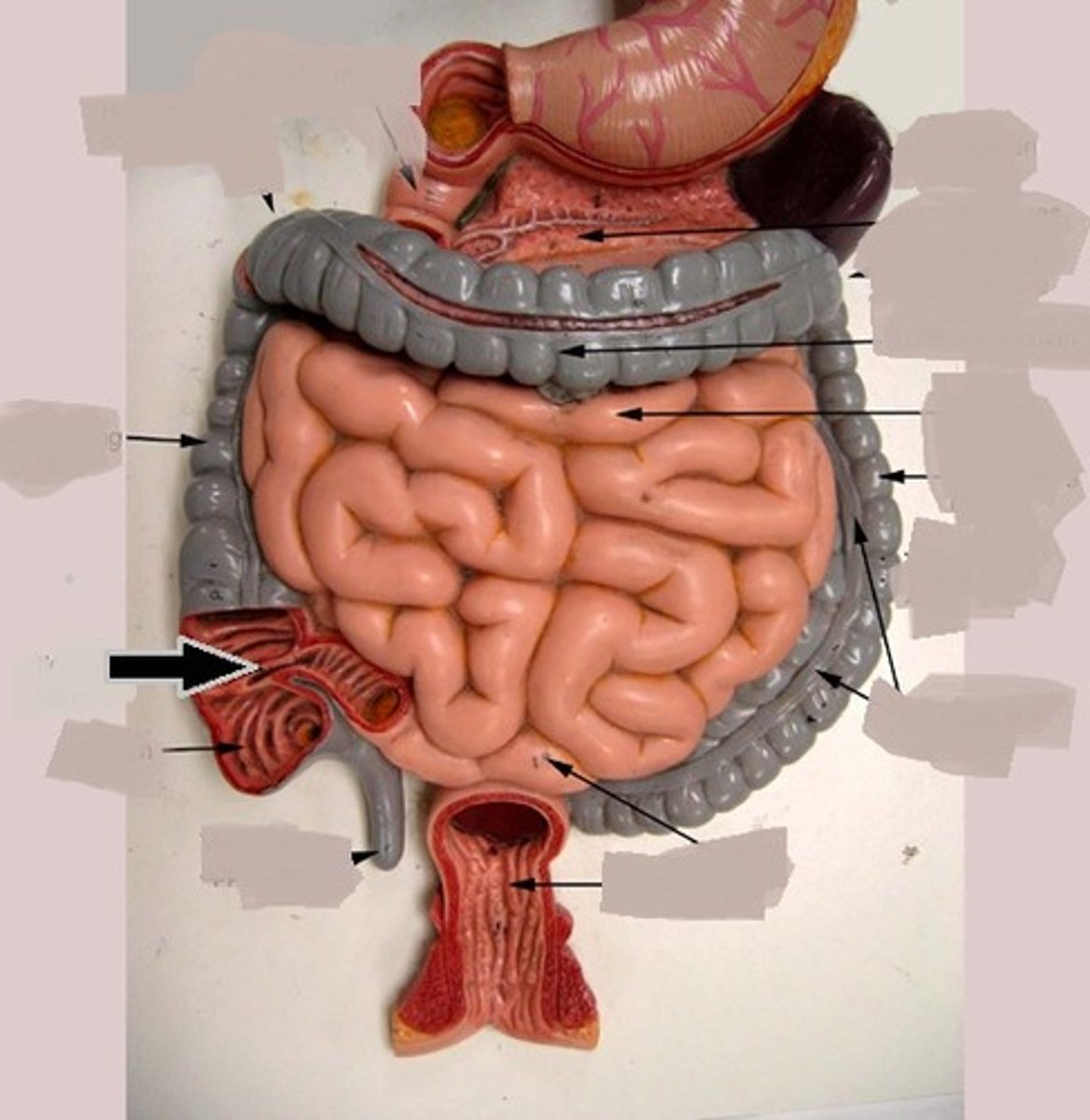
fundus
dome-shaped region of the stomach
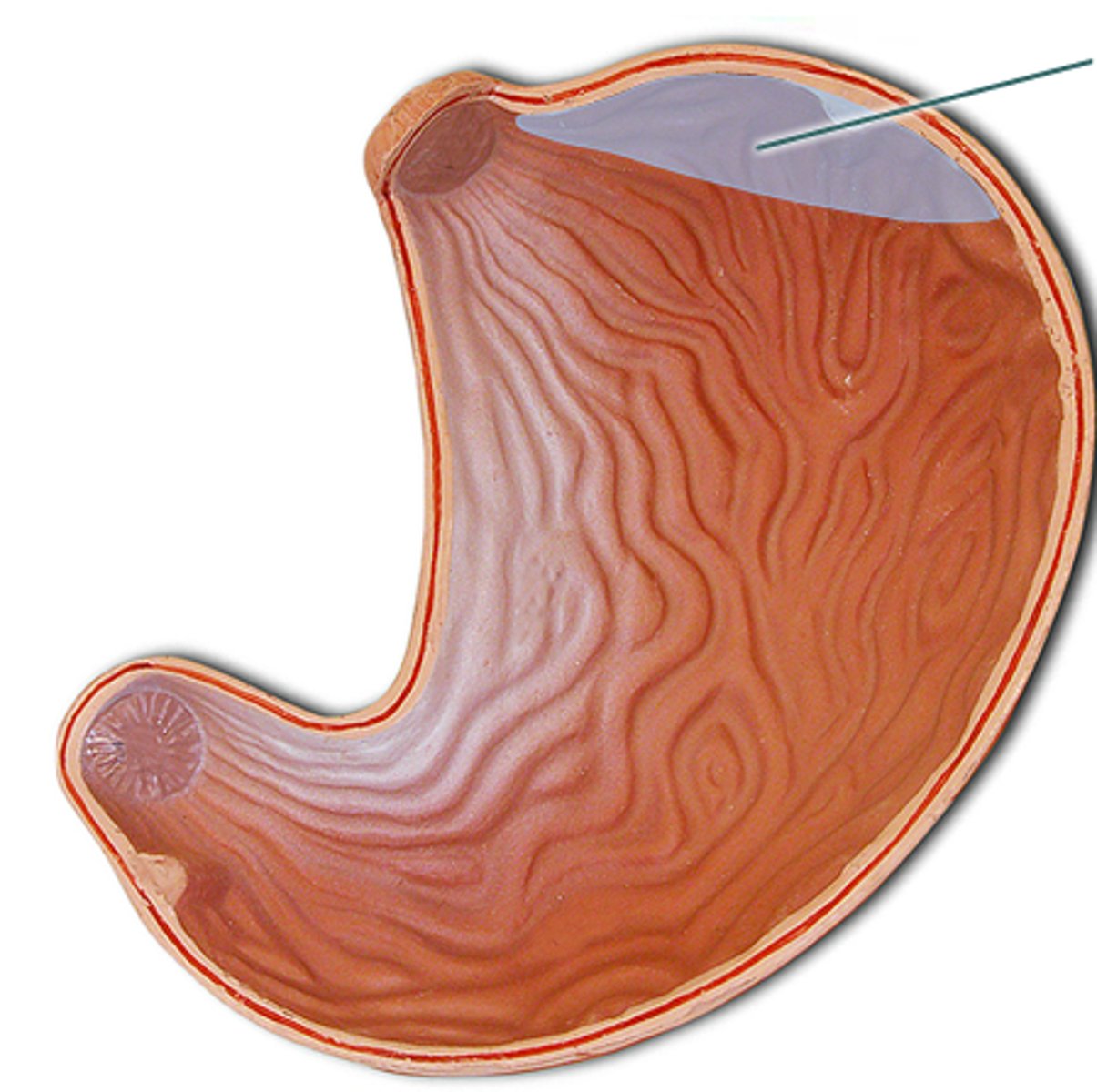
pylorus
lower, funnel-shaped part of the stomach that is continuous with the duodenum
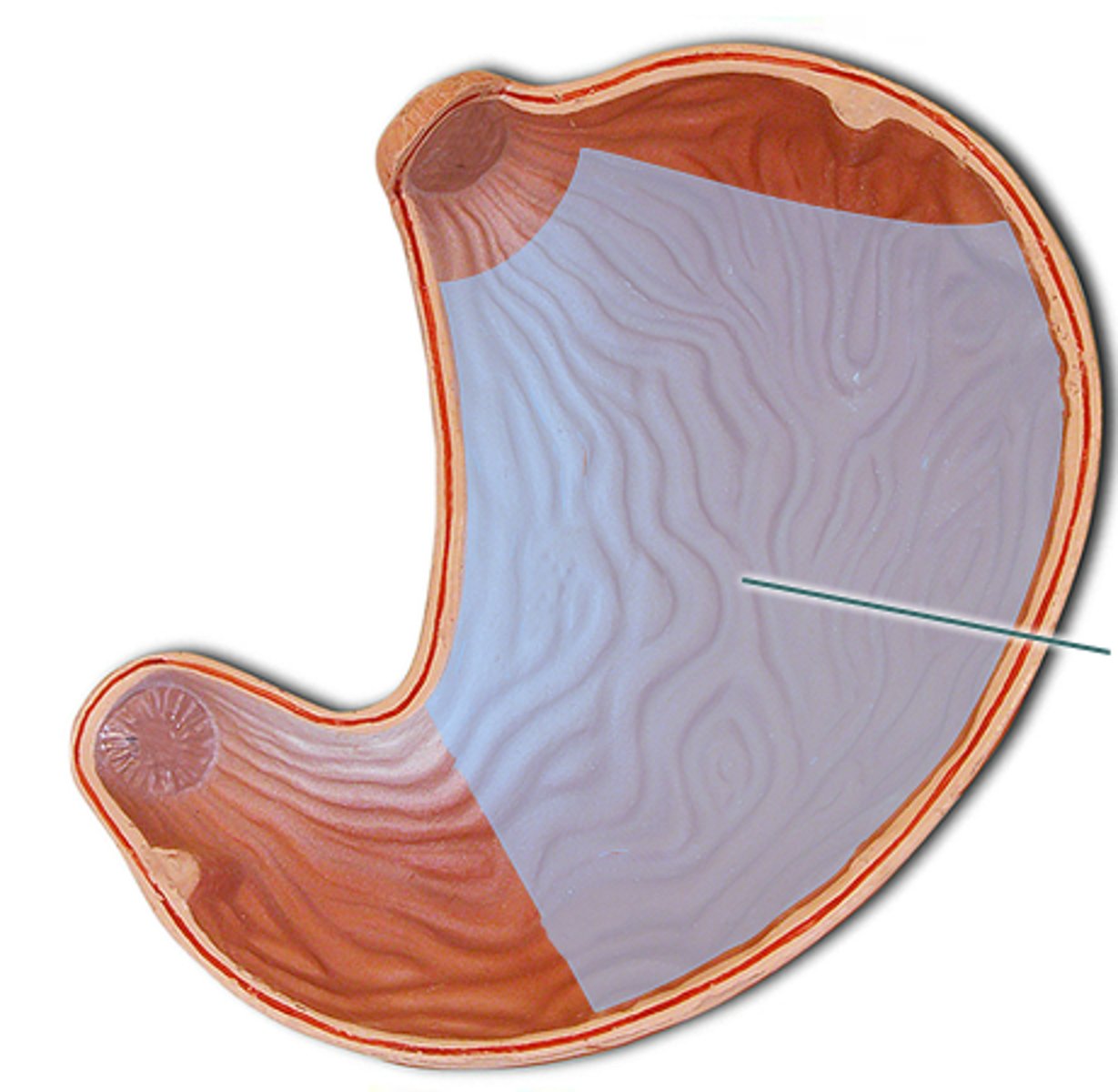
body
mid-portion of the stomach
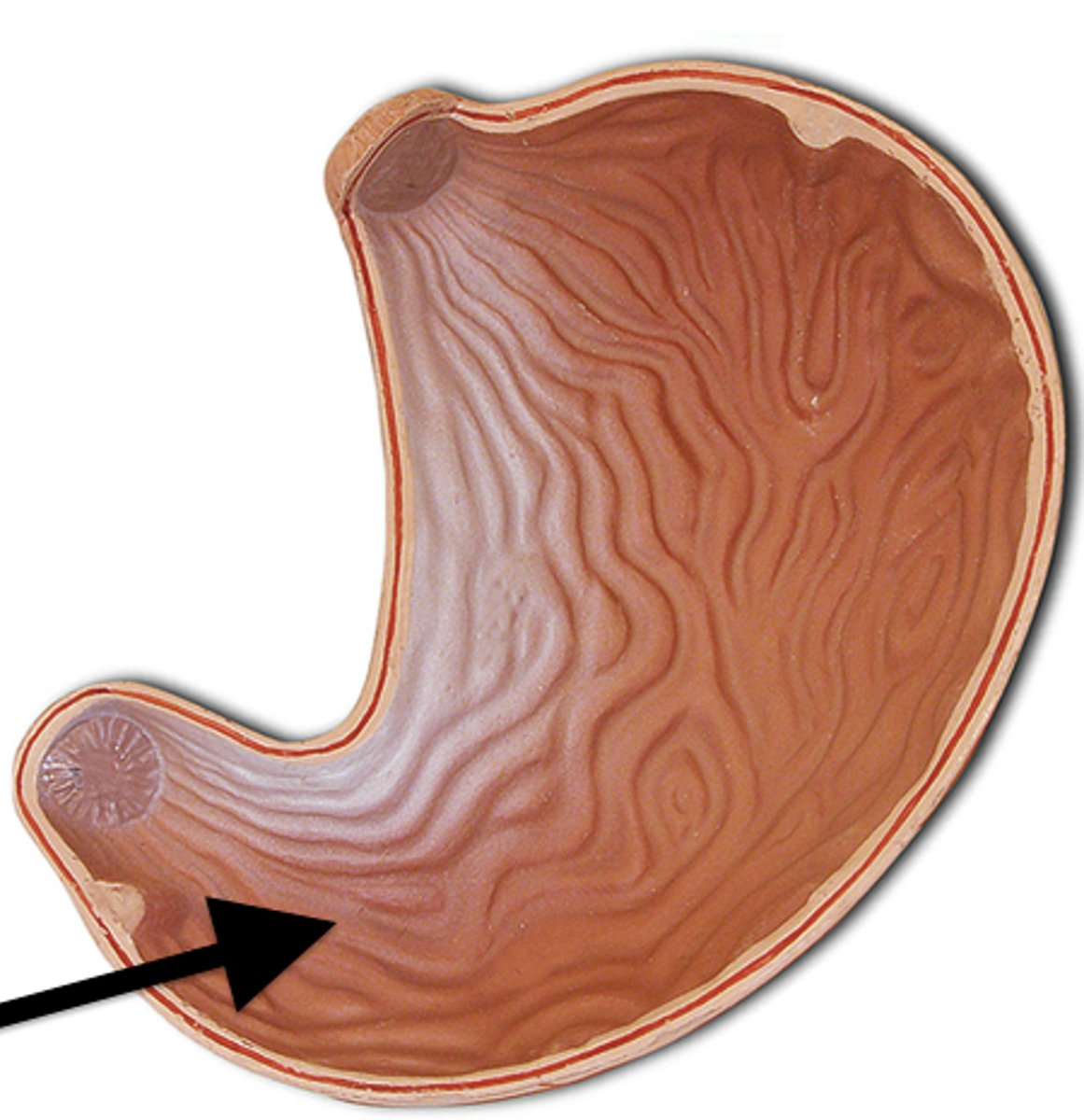
pyloric sphincter
sphincter that controls stomach emptying
rugae
folds of gastrointestinal mucosa and submucosa in the empty stomach and other organs
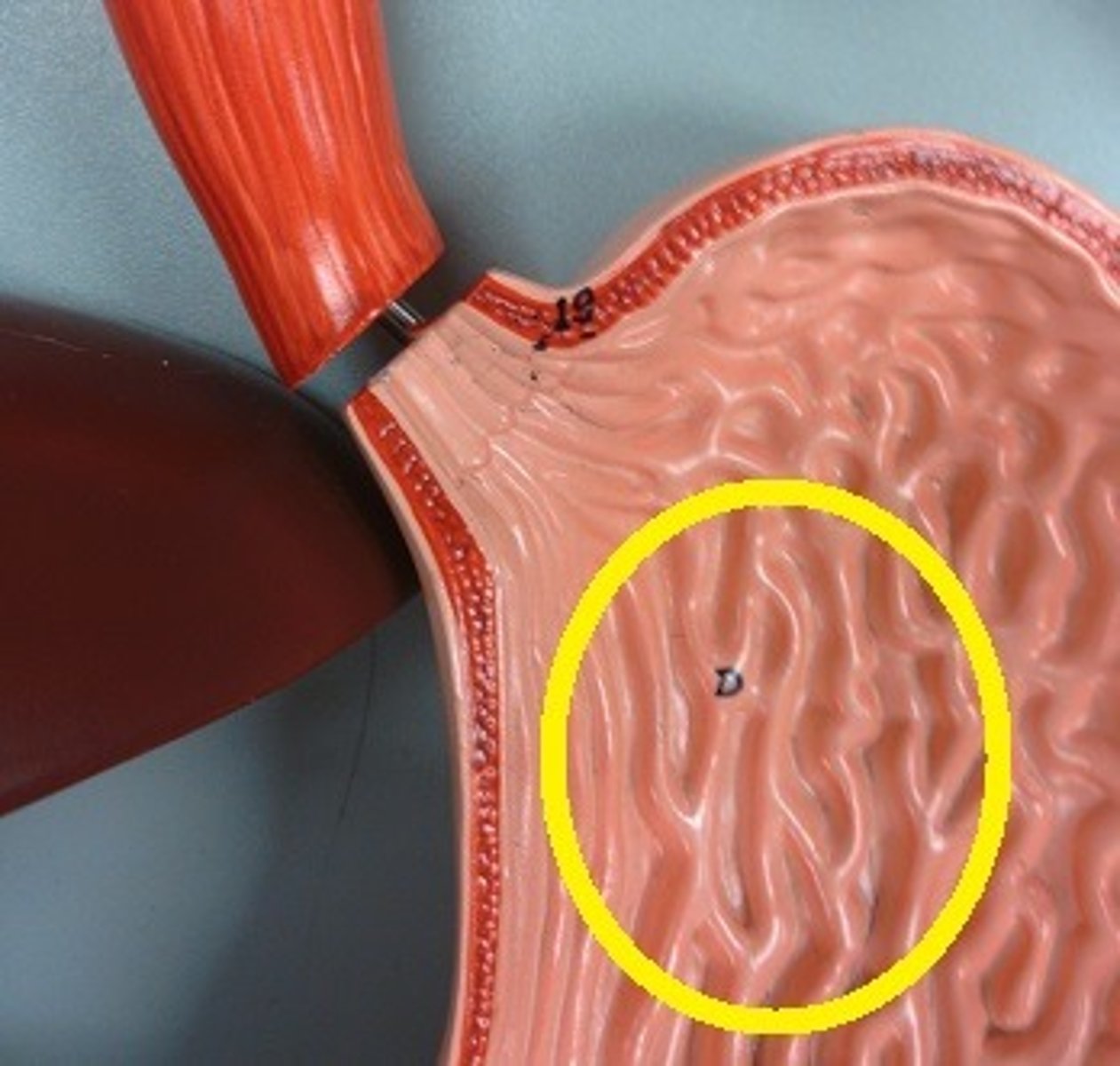
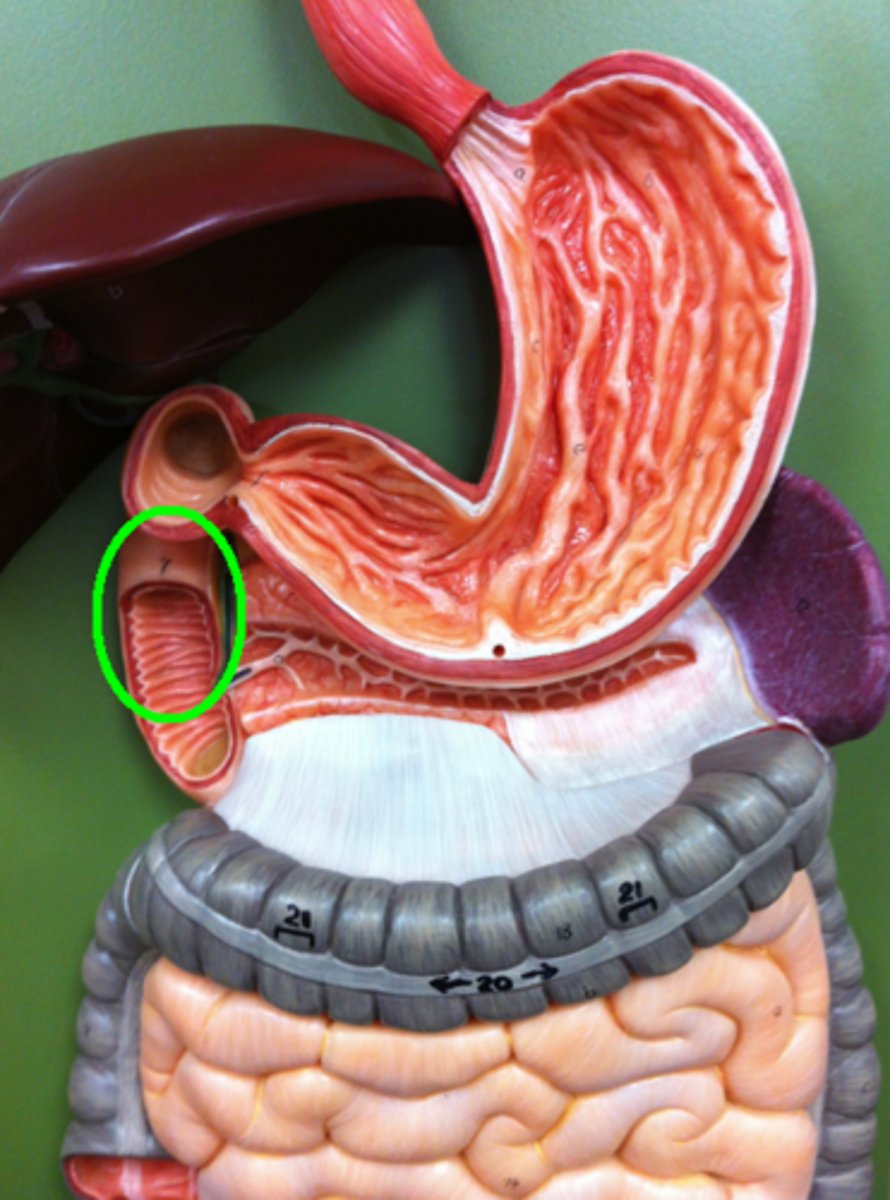
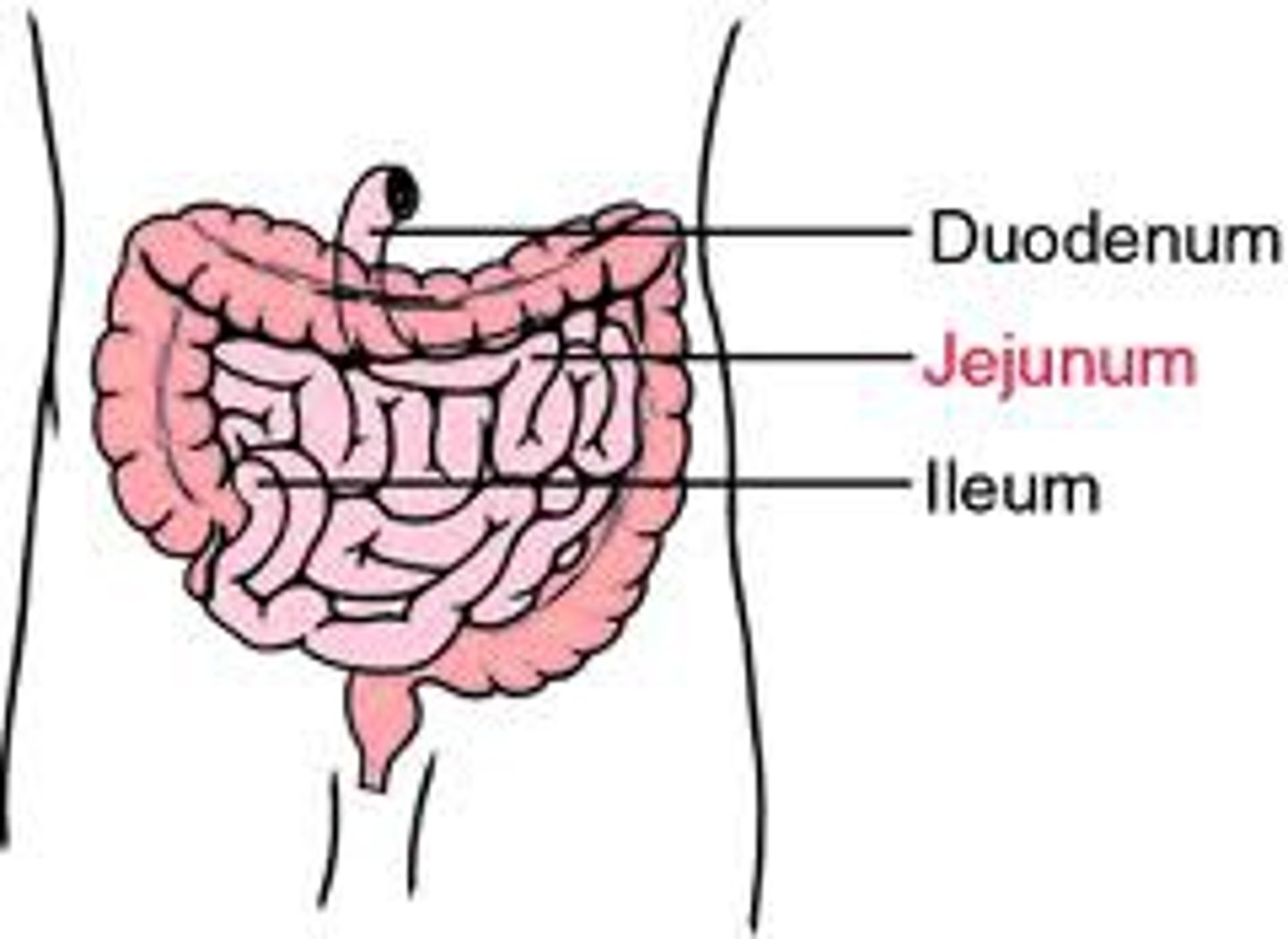
duodenum
first part of the small intestine, which starts at the pyloric sphincter and ends at the jejunum
jejunum
middle part of the small intestine between the duodenum and the ileum
ileum
end of the small intestine between the jejunum and the large intestine
ileocecal sphicter
sphincter located where the small intestine joins with the large intestine
plicae circulares
deep folds in the mucosa and submucosa of the small intestine
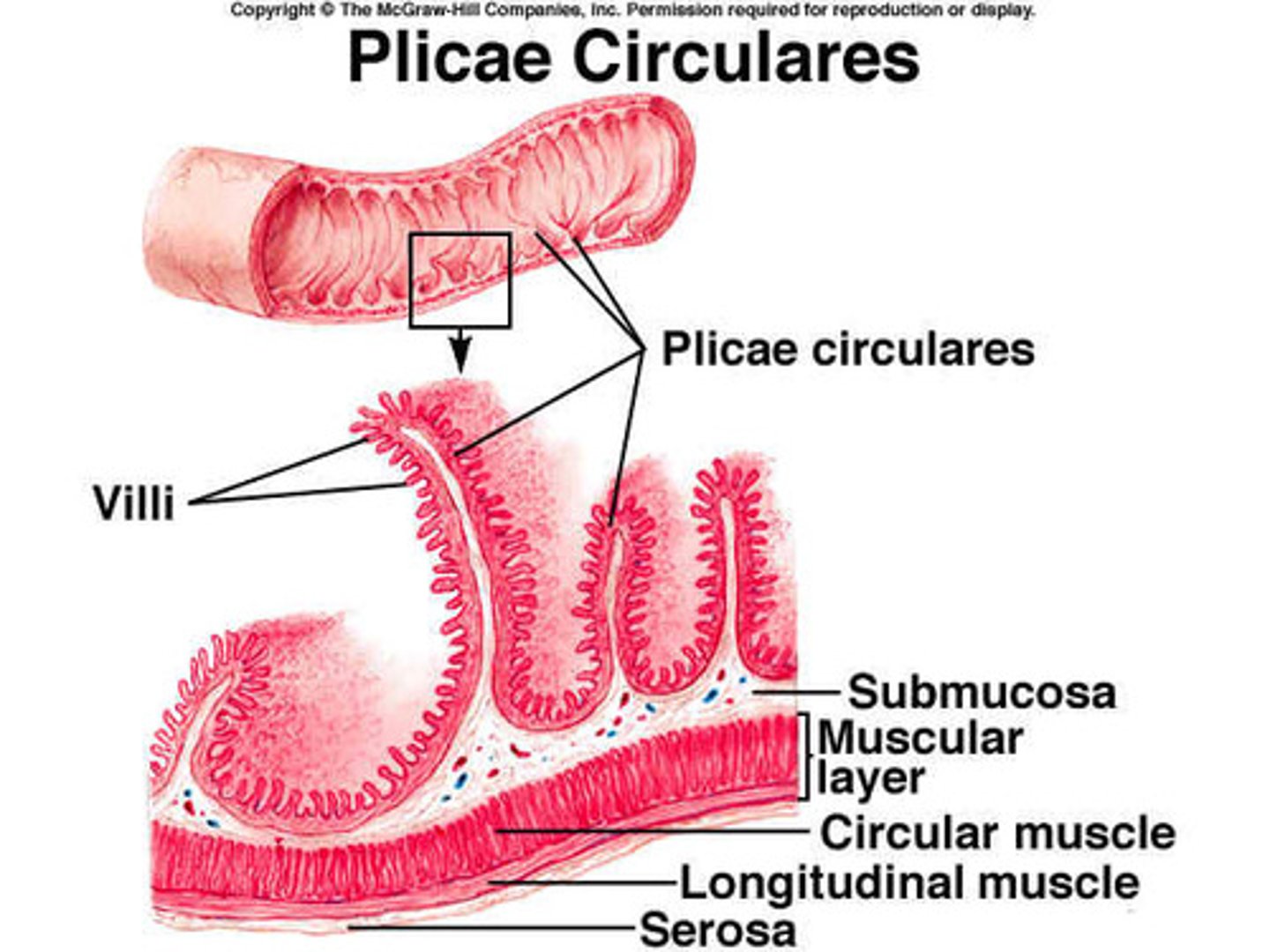
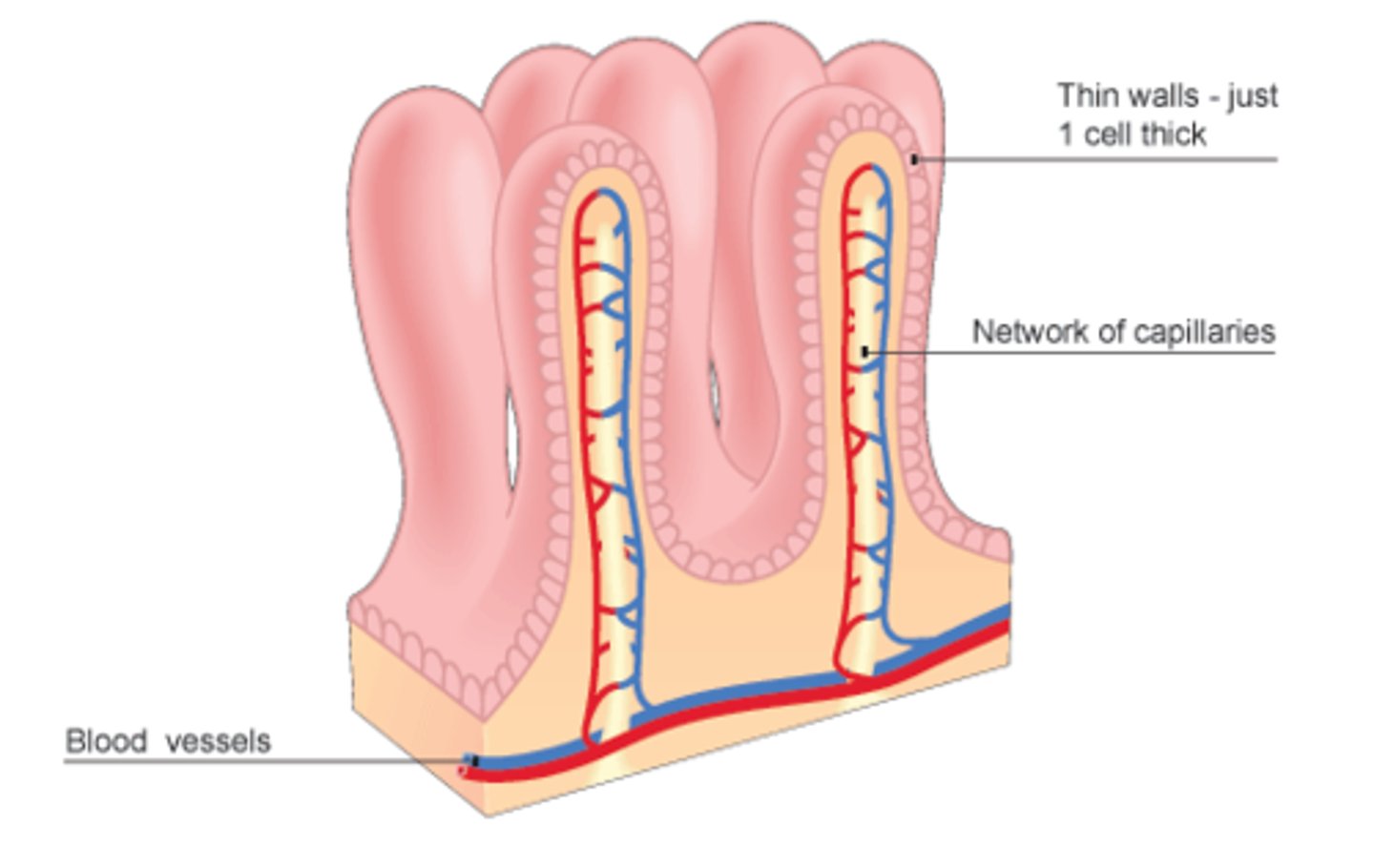
villi
projection of the mucosa of the small intestine
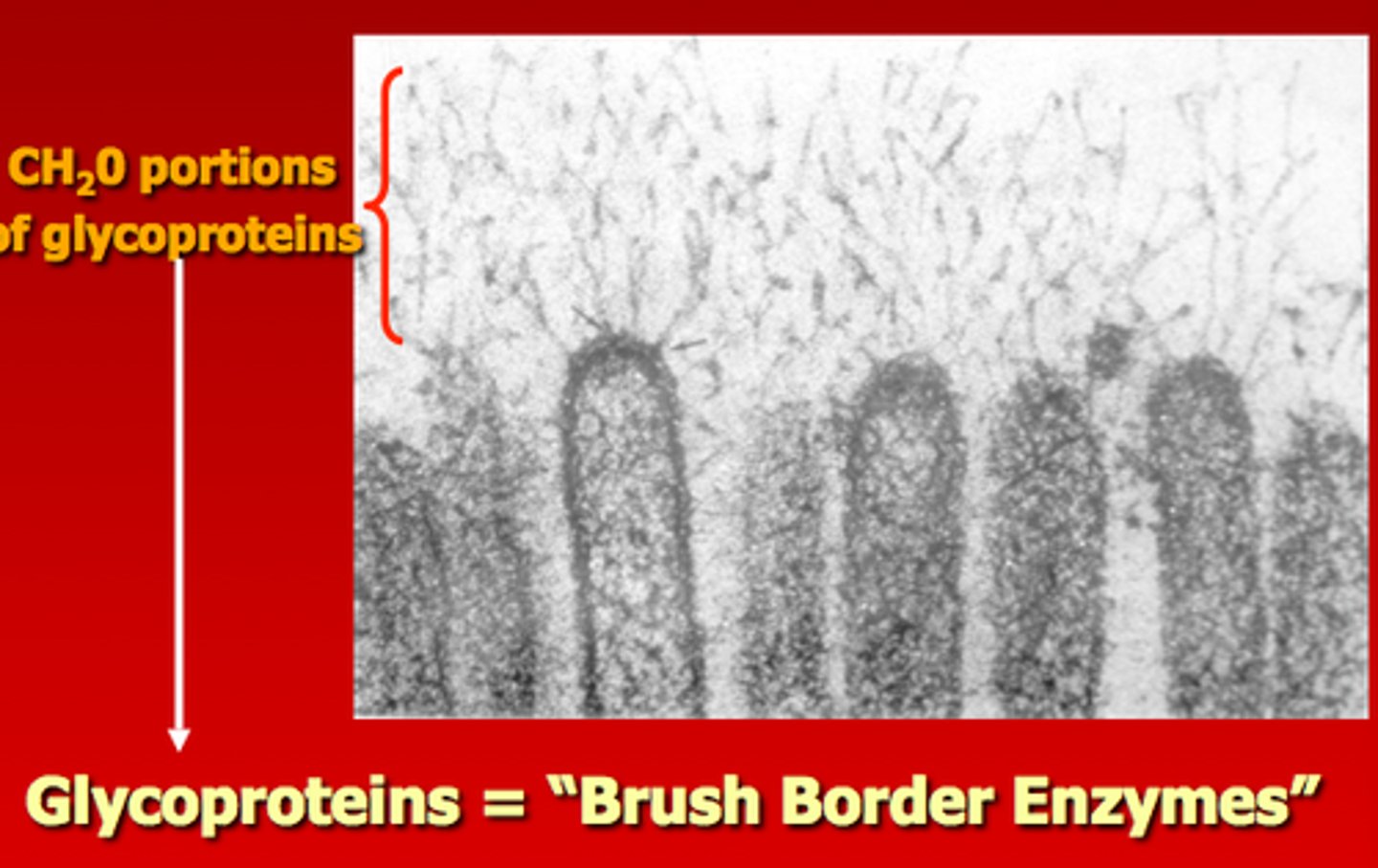
microvilli
small projection of the plasma membrane of the absorptive cells of the small intestinal mucosa
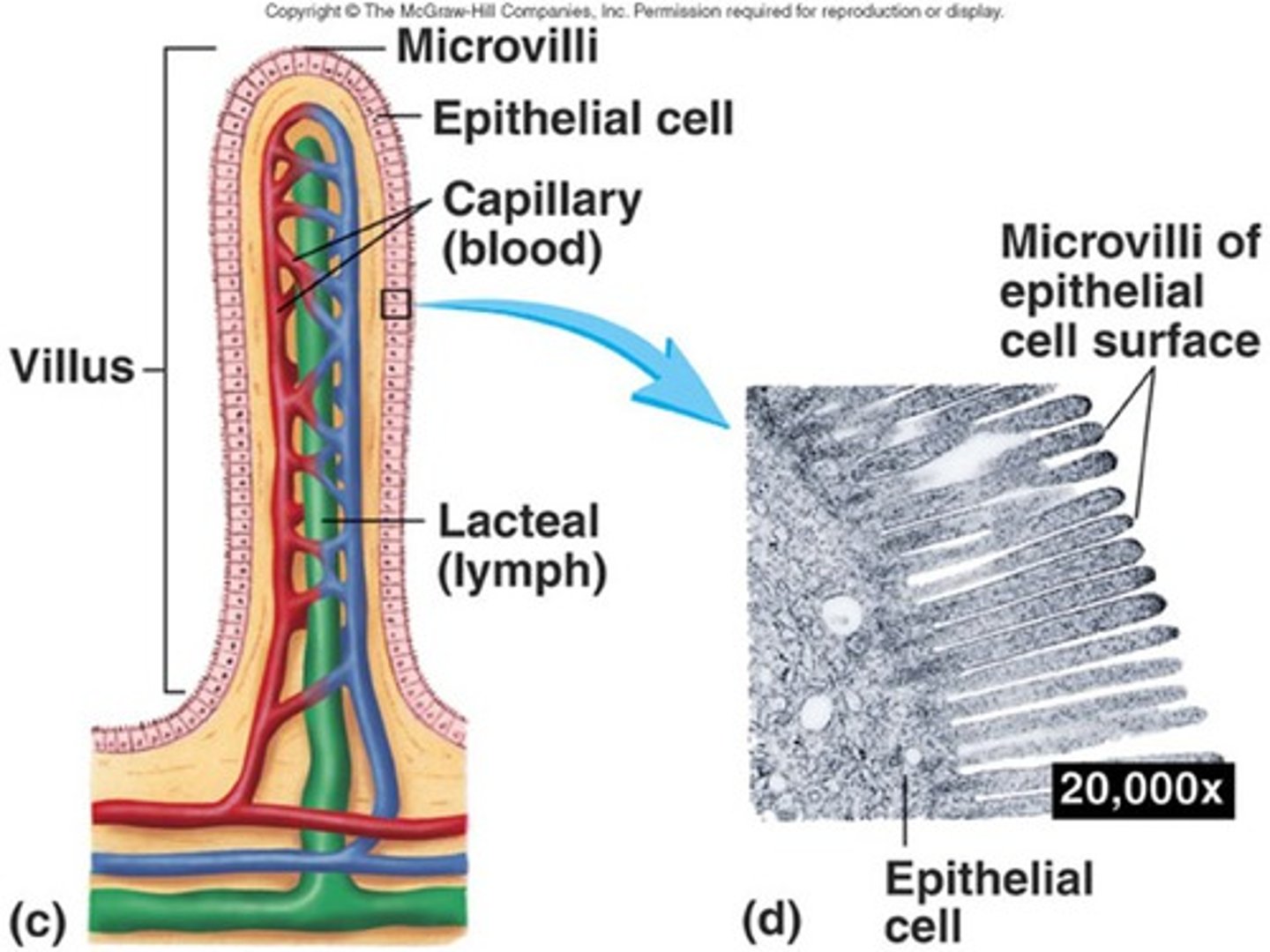
brush border
fuzzy appearance of the small intestinal mucosa created by microvilli
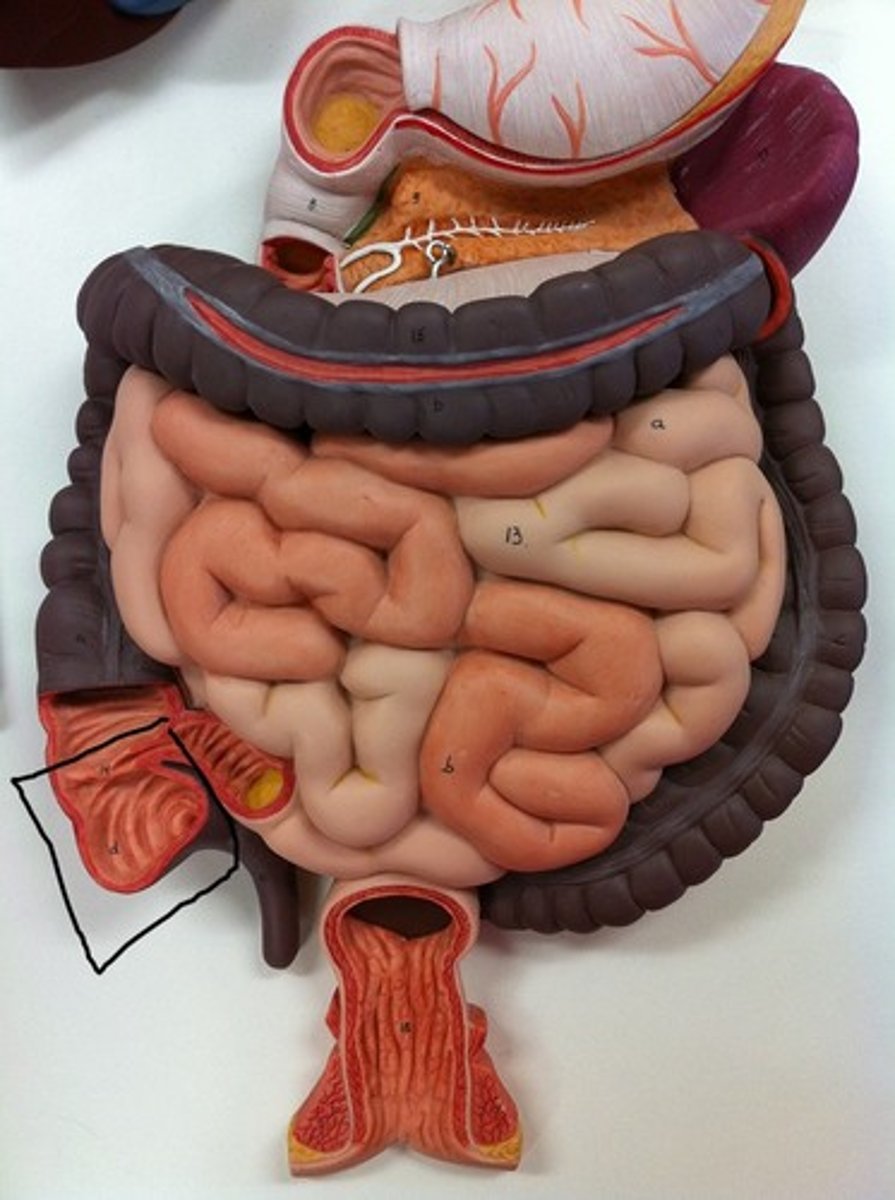
vermiform appendix
coiled tube attached to the caecum
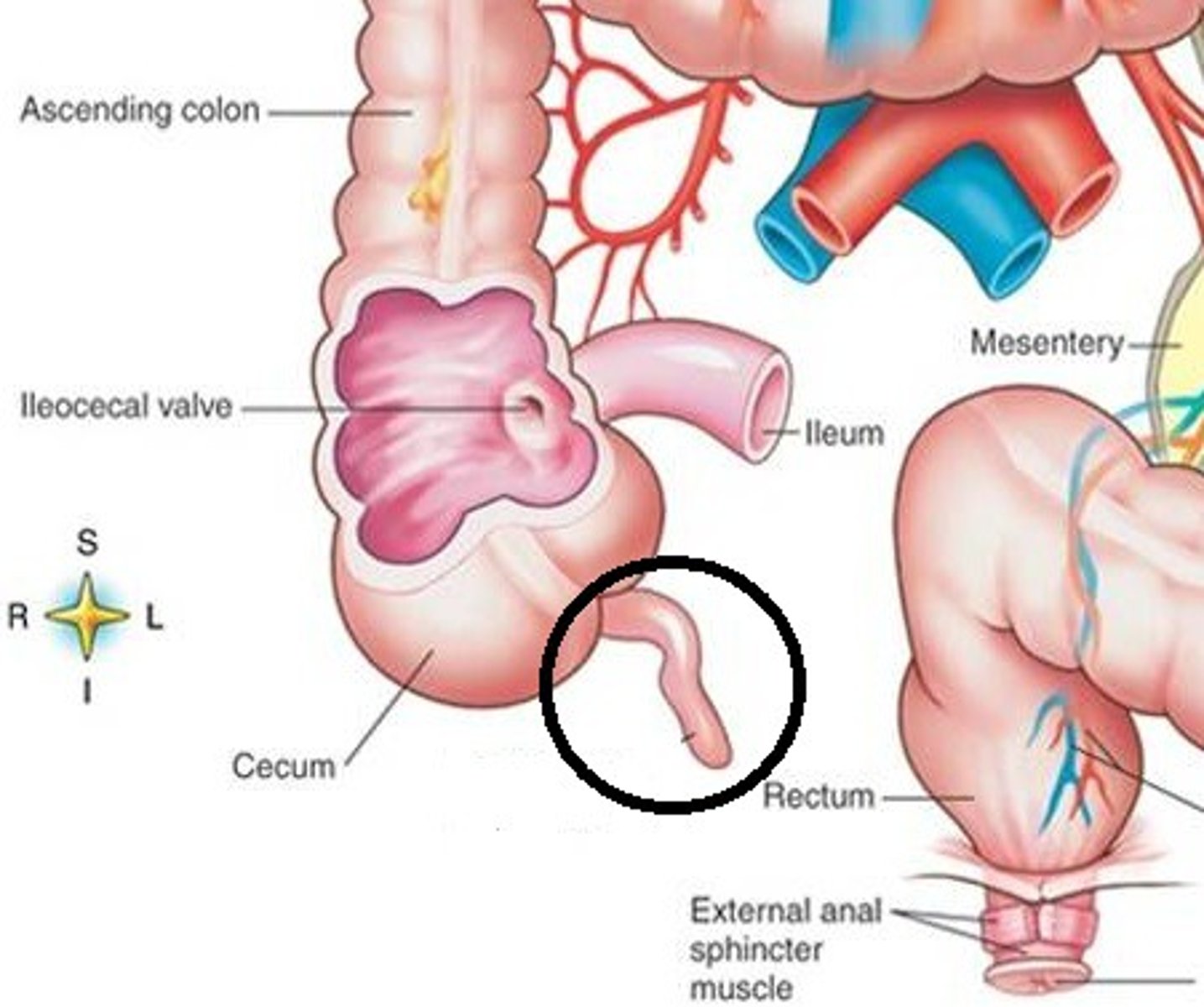
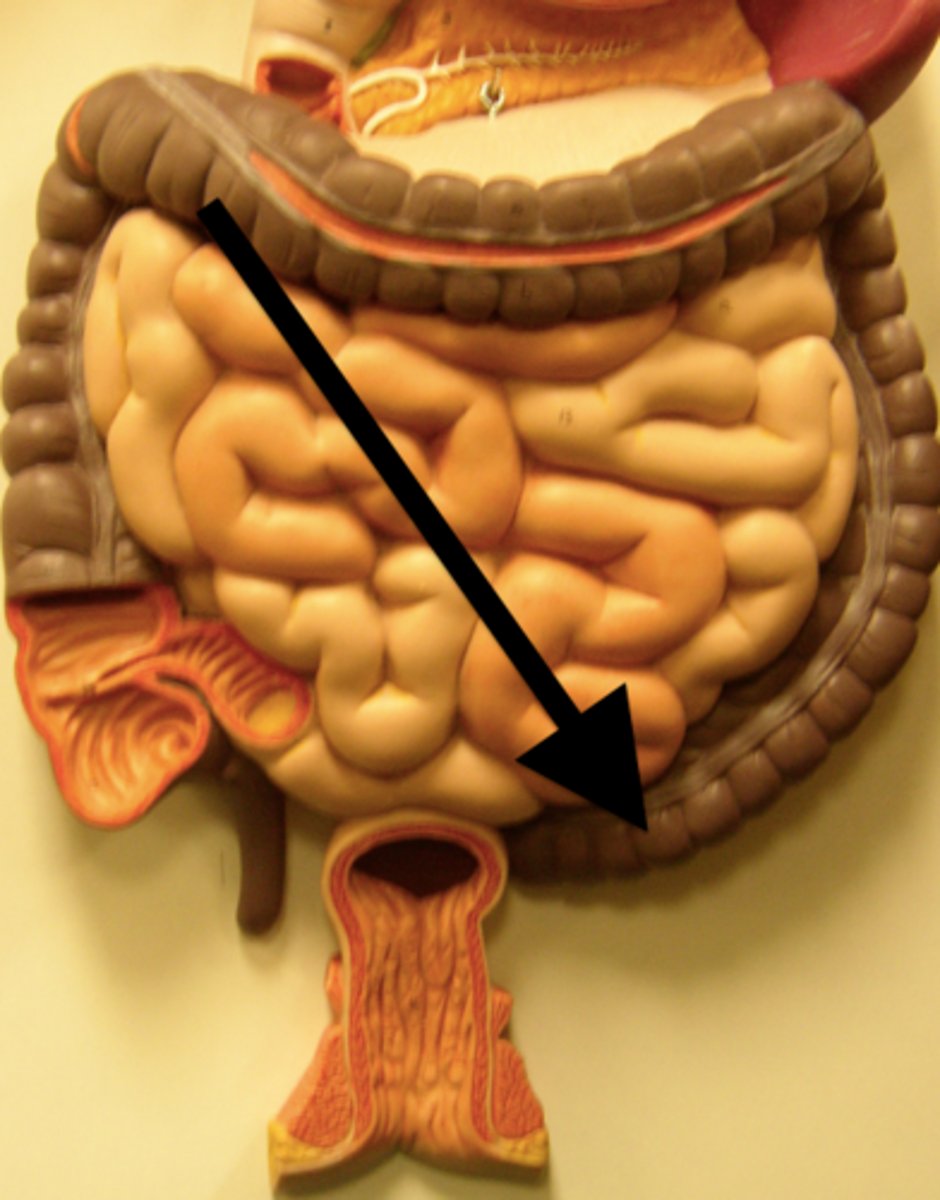
caecum
pouch forming the beginning of the large intestine
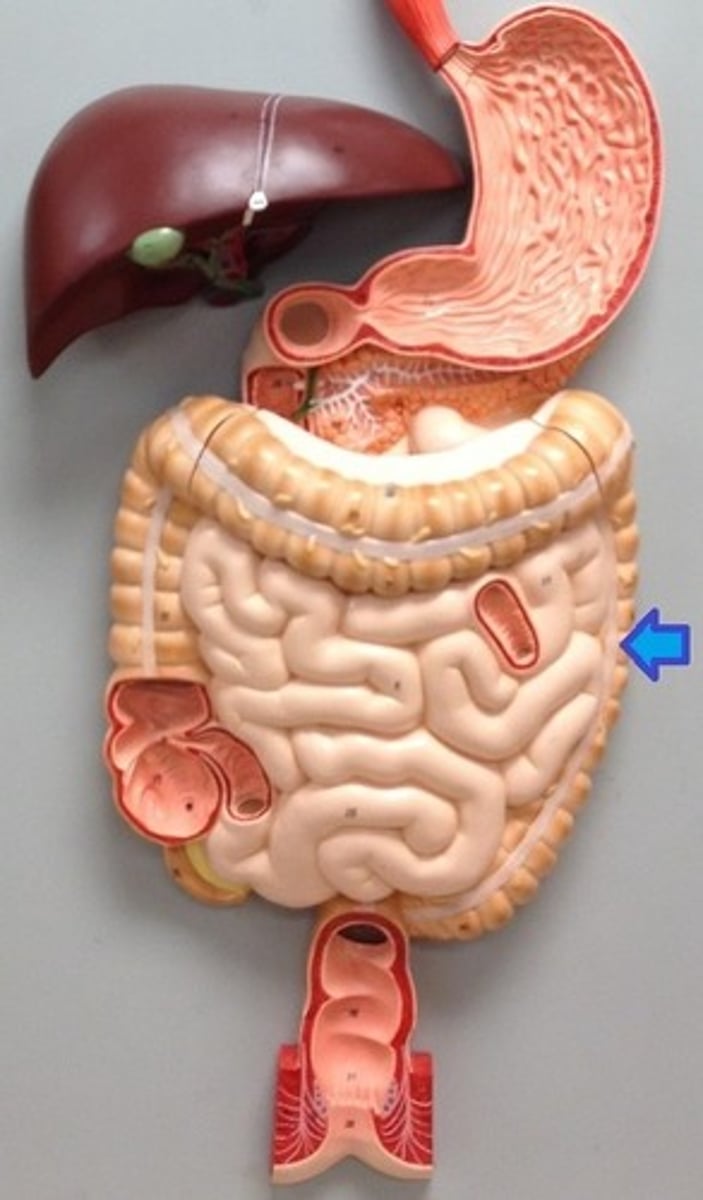
ascending colon
first region of the colon
transverse colon
part of the colon between the ascending colon and the descending colon
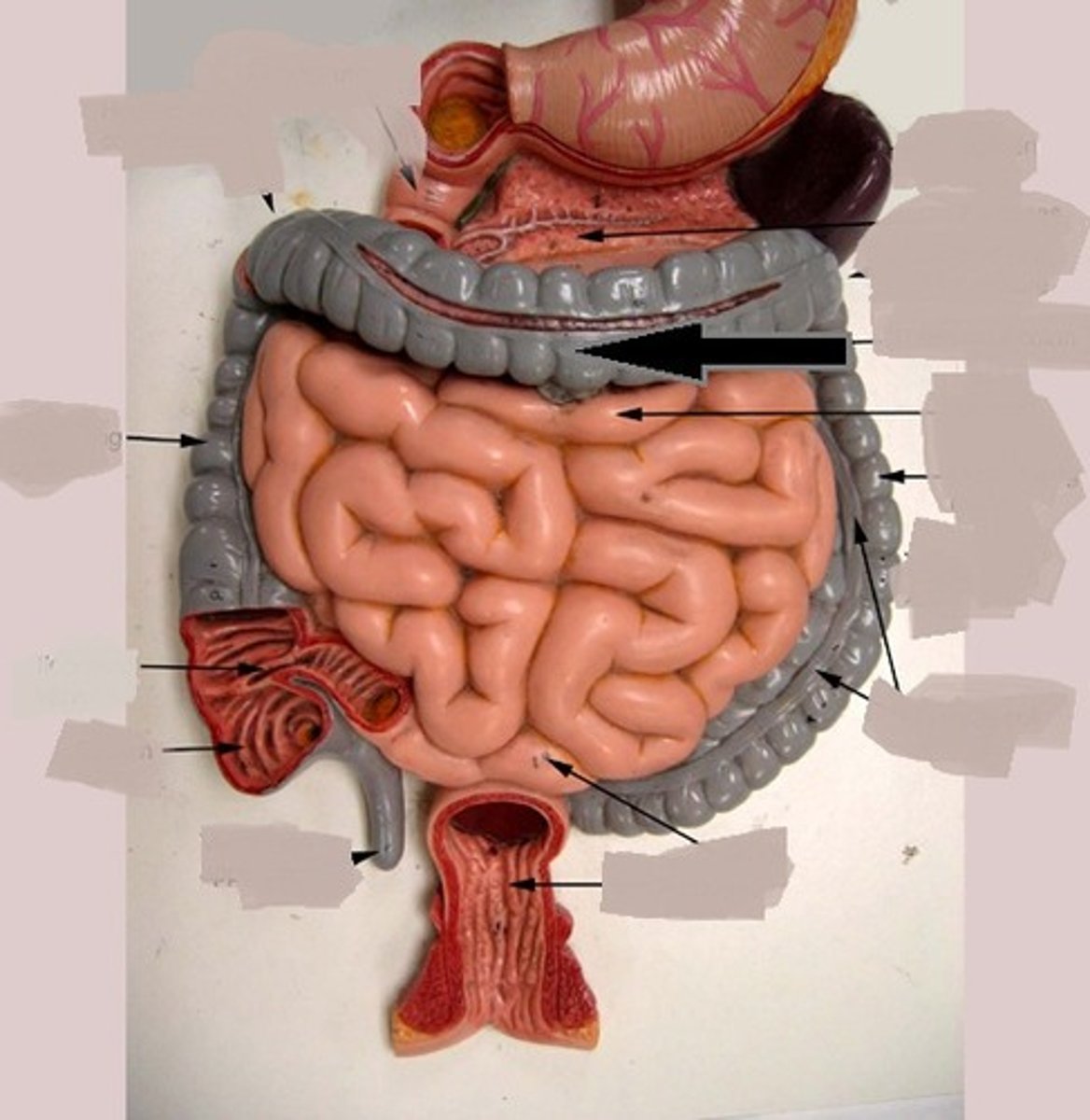
descending colon
part of the colon between the transverse colon and the sigmoid colon
sigmoid colon
end portion of the colon, which terminates at the rectum
rectum
part of the large intestine between the sigmoid colon and anal canal
anal canal
continuous with the large intestine with two muscle anal sphincter
internal anal sphincter
smooth muscle, involuntary
external anal sphincter
skeletal muscle, voluntary
defecation
elimination of undigested substances from the body in the form of faeces
accessory digestive organ
includes teeth, tongue, salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas
pancreas
accessory digestive organ that secretes pancreatic juice
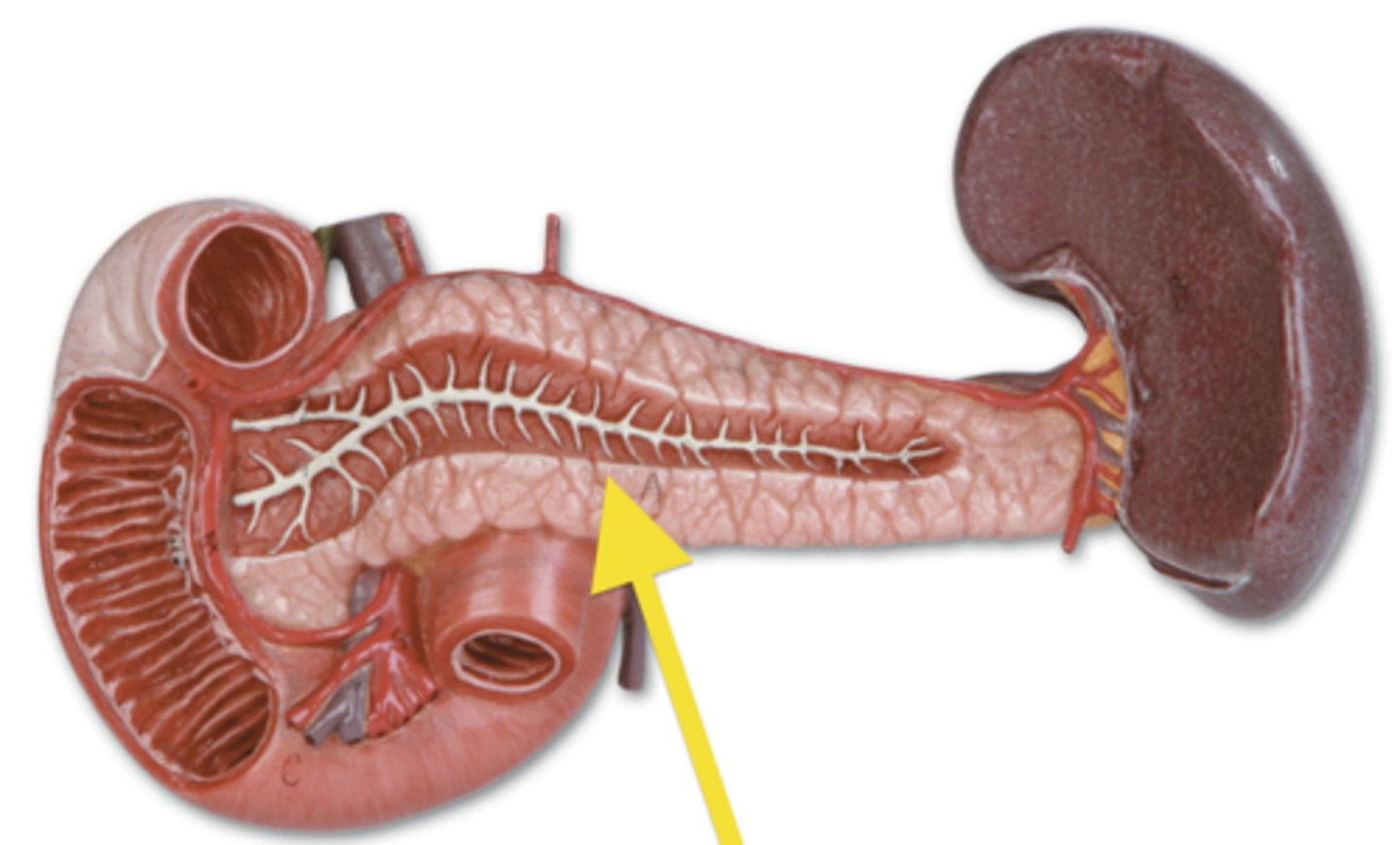
pancreatic juice
secretion of the pancreas containing digestive enzymes and bicarbonate
main pancreatic duct
duct through which pancreatic juice drains from the pancreas
hepatopancreatic ampulla
bulb-like point in the wall of the duodenum where the common bile duct and main pancreatic duct unite
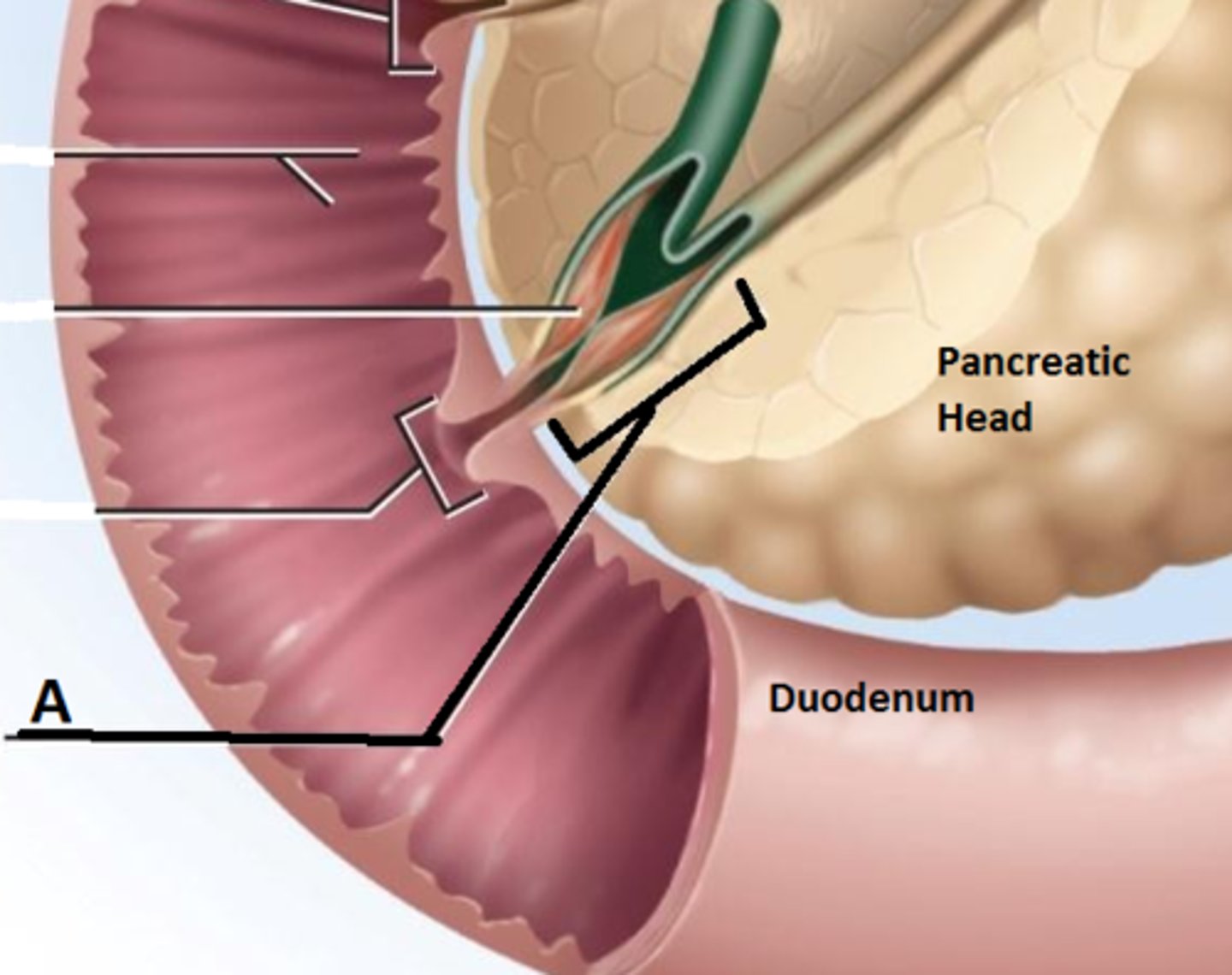
bile
alkaline solution produced by the liver and important for the emulsification of lipids
common bile duct
structure formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and the cystic duct of the gallbladder
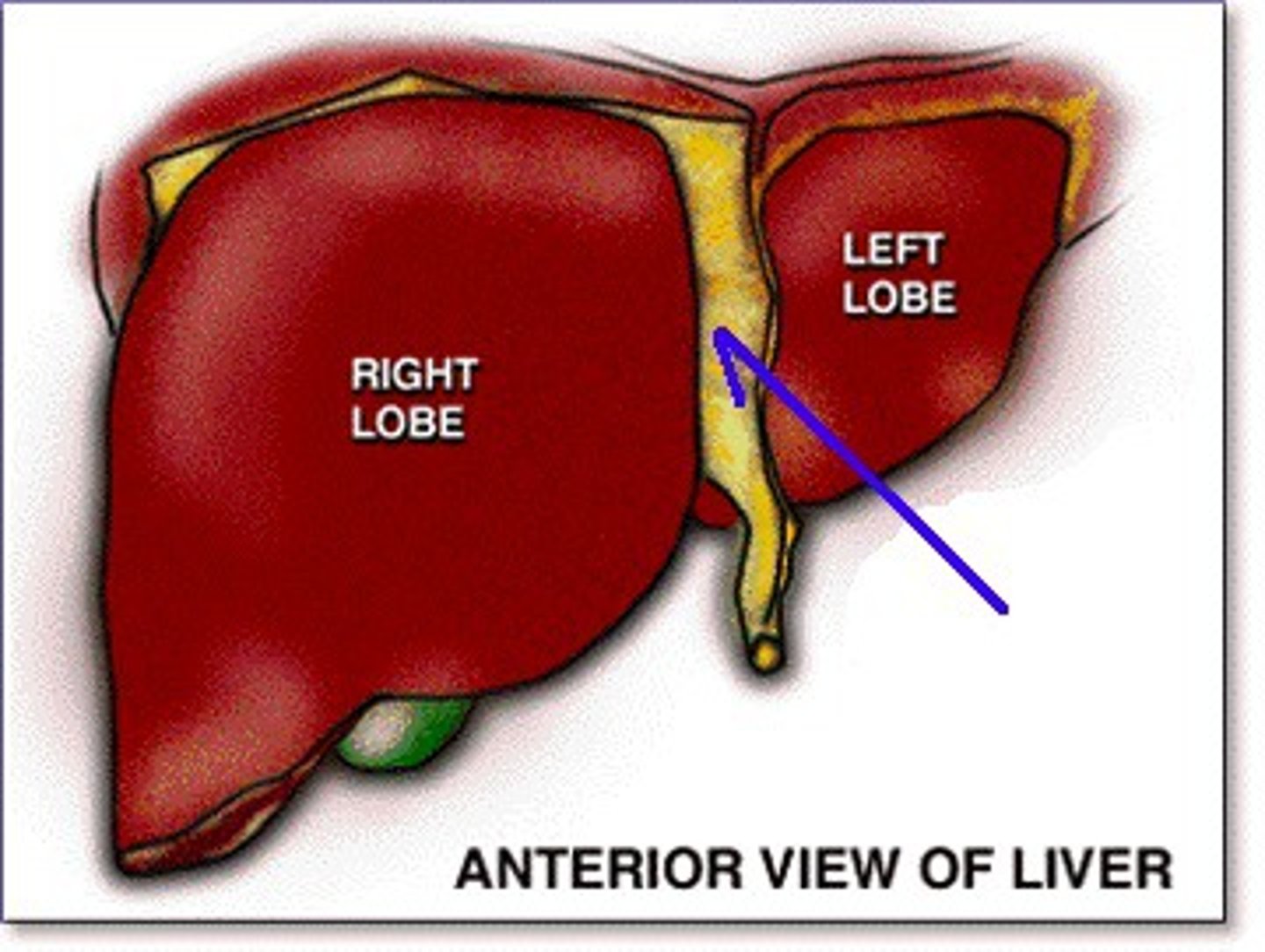
falciform ligament
Structure that separates right and left lobes of liver as a remnant of umbilical vein
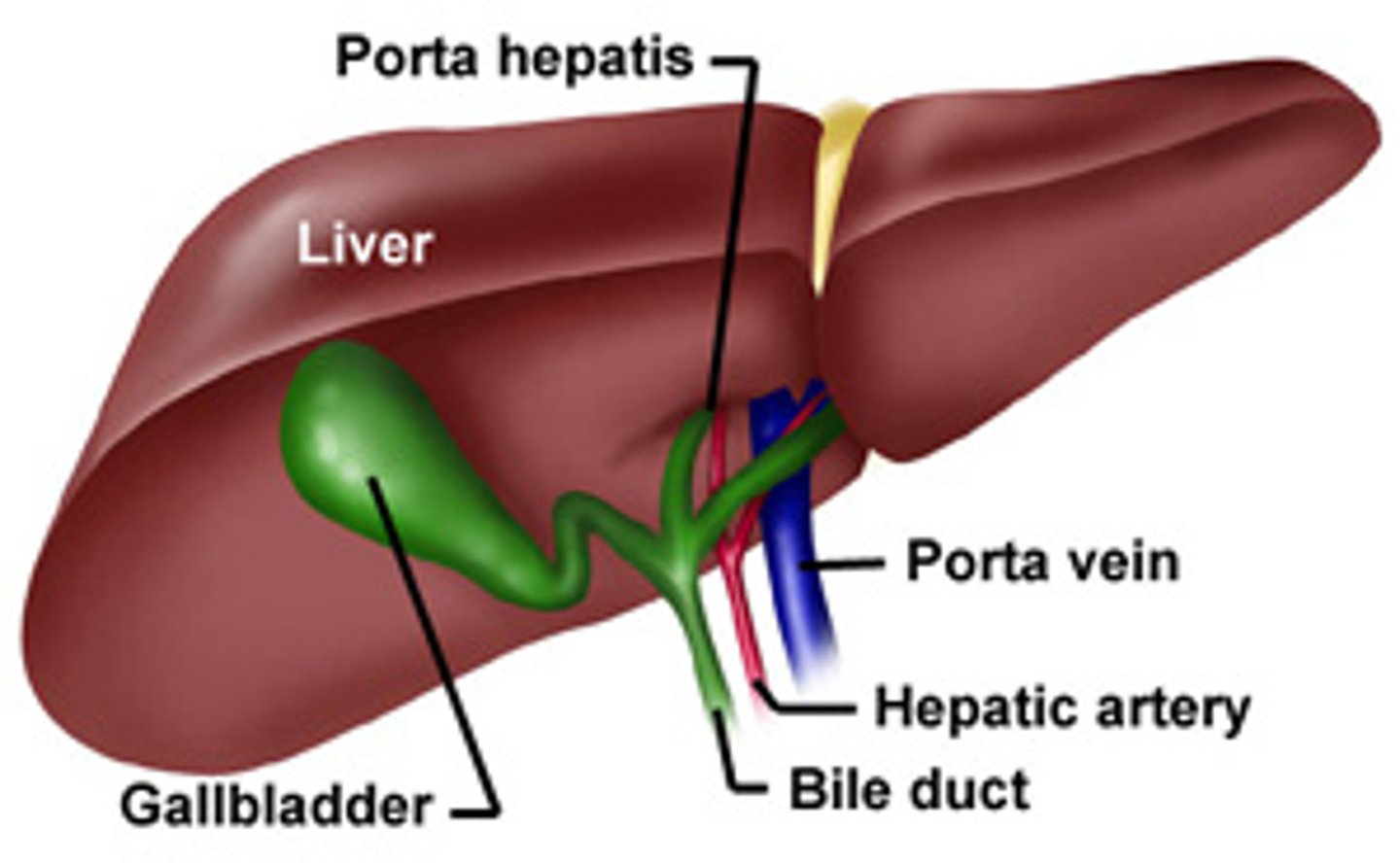
porta hepatis
"gateway to the liver" where the hepatic artery proper and hepatic portal vein enter the liver
hepatic artery proper
artery that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver
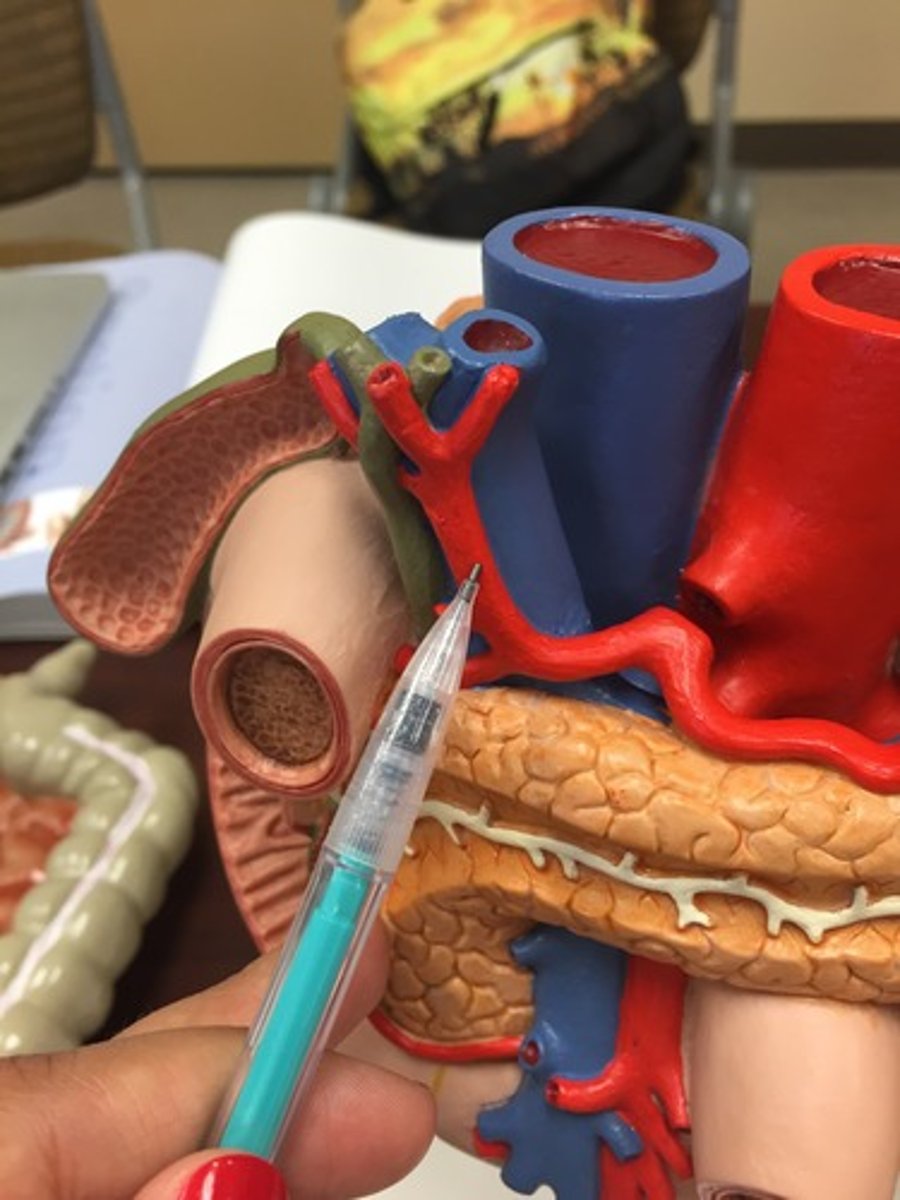
hepatic portal vein
vein that supplies deoxygenated nutrient-rich blood to the liver
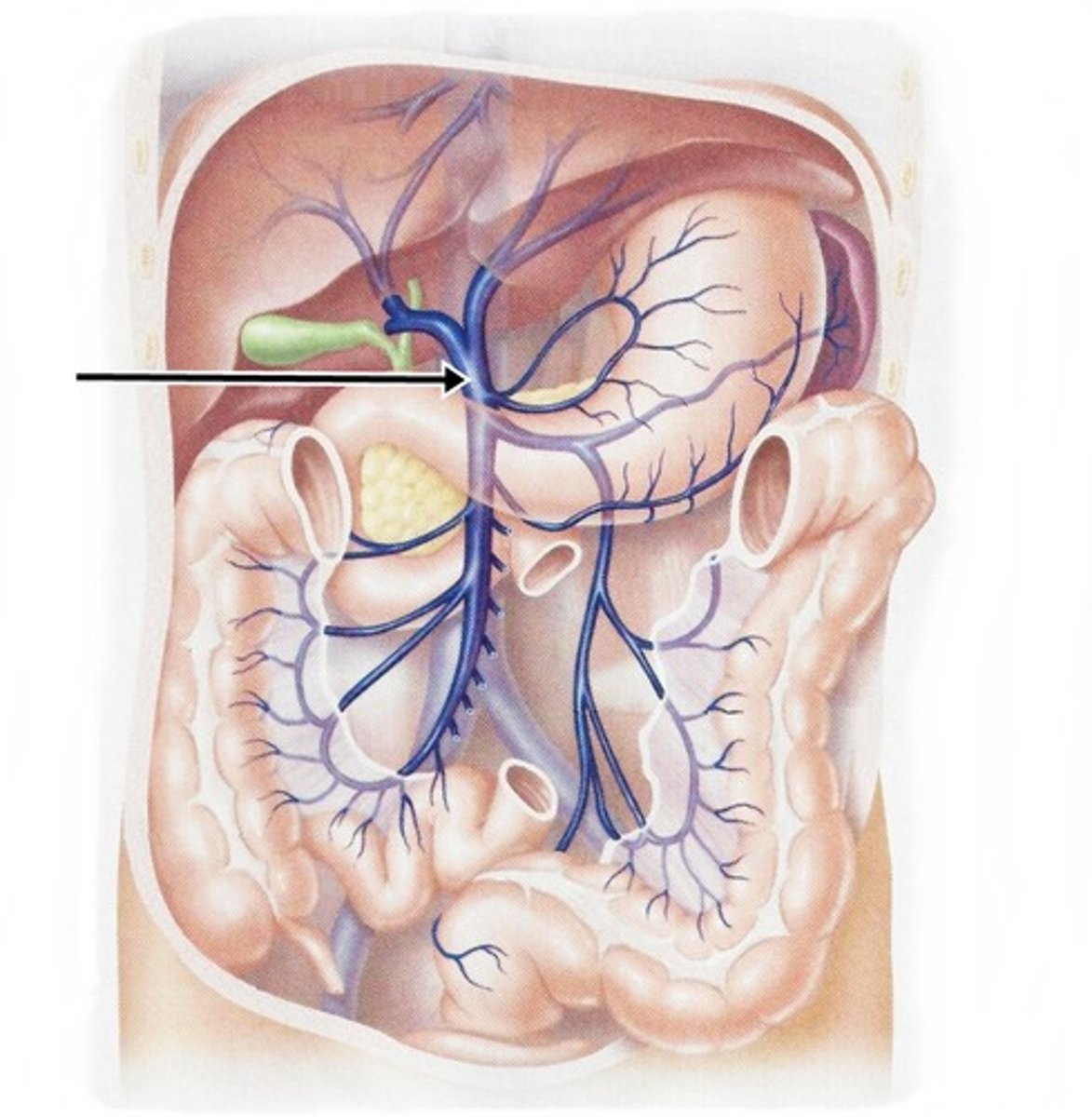
common hepatic duct
duct formed by the mergeing of the two hepatic ducts
cystic duct
duct through which bile drains and enters the gallbladder