PHONETICS
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
speech chain production
thought in a speaker’s brain
linguistic representation
phonetic representation
neural impulses
muscular activity
resultant movements of the speech organs
speech chain acoustic signal
sound emitted from lips and nose of speaker
sound travel through air as pressure wave
different sounds produce different variations in the pressure wave
speech chain perception
sound strikes the hearer’s ear
ear turns vibration/ mechanical energy back into neural impulses
brain interprets neural impulses to reconstitute the phonetic representation
words are understood from the phonetic representation
the original thought is understood
initiation and phonation
require moving air, this movement is initiated in the lungs
abduction of the arytenoids
Arytenoids swivel to draw vocal folds apart
no vibration
no voicing
no sound produced at the glottis
voiceless sound
adduction of the arytenoids
arytenoids swivel to draw vocal folds together
vocal folds vibrate
vocal folds produce voicing
buzzing sound is produced at the glottis
sound is voiced
Bernoulli effect
high pressure air from lungs forces vocal folds open
air flows through the open glottis (during the open phase of voicing = no voicing)
high velocity of the air = low pressure between vocal folds
low pressures with natural elasticity of vocal folds = they snap shut
pressure below glottis builds up again and creates a cycle
3 types of phonation
modal voice, breathy voice (vocal folds vibrate but do not close completely or have a longer open phase), creaky voice (vocal folds held tightly by arytenoids so only vibrate at the front and more time closed than open)
cardinal vowels
the 4 vowels at the extremities of the tongue-arching model
secondary cardinal vowels
4 vowels in intermediate positions on the tongue-arching model
conoids
speech sounds produced with an obstruction in the vocal tract
consonants
sounds that act as syllabic margins
3 parameters of consonant classification
place of articulation, manner of articulation, voicing
3 main patterns of voicing of word-initial stops
prevoiced stops = vocal folds vibrate throughout entire sound
short-lag/ voiceless unaspirated stop = vocal folds start vibrating as stop is release or shortly after (e.g. /b/ in ‘bat’)
long-lag/ voiceless aspirated stops = vocal folds start vibrating after release, the period between release and voicing onset is filled with aspiration (e.g. /p/ in ‘pat’)
word-final voiced stops
vocal folds vibrate throughout closure and all/ most of hold phase
word-final voiceless stops
voicing stops at the end of closure phase
pre-fortis clipping
vowel before a voiceless stop is likely to be shorter than one before a voiced stop in word-final position
4 types of sound waves
periodic, aperiodic, transient, quiescent
simple wave
air molecules vibrate at a single frequency
complex wave
air molecules vibrate at different frequencies at the same time
fourier analysis
decompose a complex sound wave into a simple sound wave
harmonic
each single sine wave that is part of a decomposed complex sound wave
the higher the value of F1
the lower the vowel height
the higher the value of F2
the more front the vowel
lip rounding
general lowering of formants
broad band spectrograms
show formants
narrow band spectrograms
show harmonics
source and filter theory
vocal folds create certain basic harmonics, some of which are more enhanced when the sound wave passes through the oral cavity (formants) because of its shape
the lower your voice is
the more harmonics you are fitting in a frequency range
formula for formants
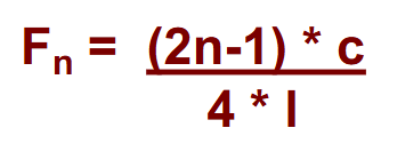
the smaller the space of air in the oral cavity
the higher the frequency