Epidemiology Exam 1
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
define epidemiology
the science, or the collection of methods, used to explain the distribution and determination of health-related outcomes in populations
what are the components of the epidemiology triad?
sick animal
agent
host
environment
what is the purpose of epidemiology?
determine the magnitude of disease in populations
study the natural history and prognosis related to disease
identify causes and predictors of health outcomes
evaluate preventive and therapeutic factors
collect quantitative data as the foundation for public policy
define incubation period
the interval from effective exposure to an infectious agent and the onset of related disease
define induction period
the interval from effective exposure to a non-infectious agent and the onset of related disease
define pre-patent period
the interval from effective exposure to the infectious agent and the detection of the agent in the tissues or secretion of the host
define pathogenicity
the ability of an agent to produce clinical disease
define virulence
the ability of an agent to produce severe disease
define infectivity
the ability of an agent to enter, survive, and multiply in the host
define infectious
the ability to transmit infection (indirectly or directly)
define contagious
the ability to transmit infection through direct contact
define latent infection
persistence of an infectious agent within the host without active replication/ shedding
pre-patent period is a type of
latent infection
define carrier state
persistence of an infectious agent within the host without clinical signs or symptoms with active replication and shedding or with the potential to replicate and shed in the future
define reservoir
the biological niche that supports the infectious agent under natural conditions before “escaping” into the animal or human population of interest
define source
the actual object (substance, animal, person) from which the infection is acquired
define vehicle
an inanimate substance that serves to pass an infectious agent to susceptible individuals
define fomite
inanimate object that is capable of transmitting an infectious agent
define vector
animate object that is capable of spreading infection
cases that occur irregularly without a discernable pattern can be described as
sporadic
cases the occur regularly with a perdictable pattern can be described as
endemic
cases that occur clustered in time and space can be described as
epidemic
define pandemic
an epidemic affecting many countries in the world
what are the important characteristics to include when describing an epidemiological situation?
animal: what are the characteristics of those affected
place: where were the individuals when they became affected
time: when did the individuals become affected
define outbreak
a sudden rise in the incidence of disease but is often used for limited geographical distributions
define cluster
an aggregation of cases in place and time that are believed to be greater than expected
define point source
all animals exposed within a short period of time
define line source
point source but with extended time of exposure
what are the stages of the epidemic curve?
endemic level
ascending part of the curve
plateau
descending branch
secondary peak
what is the cause of the secondary peak?
introduction of new susceptible animals or secondary transmission
describe a seasonal variation series
dry vs. wet
summer vs. winter
describe a cyclical trend series
longer than a seasonal time period
ex: lynx and hare populations
describe secular trend series
linear trend
long time periods
describe erratic variations
“white noise”
remaining variation after modeling other components
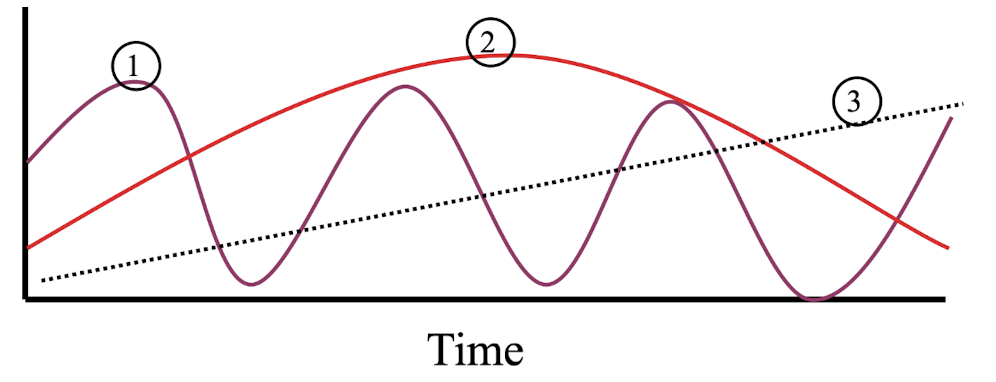
1 is pointing to
seasonal variation
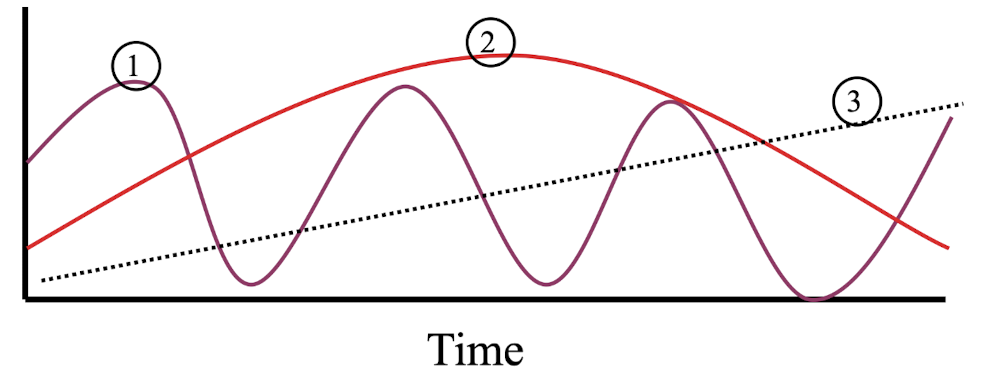
2 is pointing to
cyclical trend
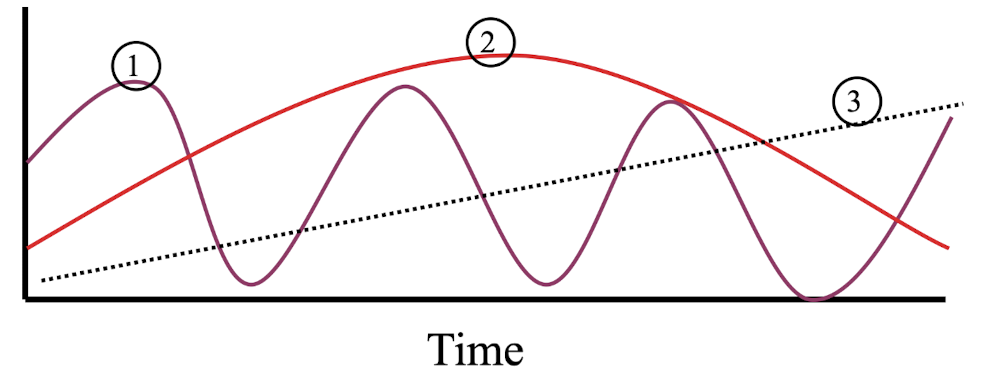
3 is pointing to
secular trend
what are the types of data classifications?
qualitative vs. quantitative
categorical (discrete) vs. continuous
nominal/ ordinal/ interval/ ratio
define qualitative data
denotes description or subjective impression
define quantitative data
denotes measurable numerical outcome
define discrete data
gaps between possible values (ex. birth order)
define continuous data
no gaps between possible values (ex. weight)
define nominal data
names, no true order (ex. nationality)
define ordinal data
ordered list, spacing between levels is not definable (ex. social class, prognosis)
define interval data
spacing between levels equal and can be quantified (ex. temperature); equality of differences; however, zero point can be arbitrary
define ratio data
highest level of measurement; equality of differences and ratios; there is a true zero point (ex. height, weight, length) something can be twice as long but (typically) not twice as hot
describe categorical variables (discrete)
information that can be sorted into categories
types of categorical variables- nominal and ordinal
describe continuous variables
always numeric
can be any number, positive, or negative (could be defined as continuous over a restricted range- weight is always positive)
there are no gaps between values, but the precision of the measuring instrument is a limiting factor
describe dichotomous data
categorical variable with only 2 levels
answer to a yes/ no question
presence or absence of a particular trait or characteristic
a proportion is defined as
a/ (a + b)
a ratio is defined as
a / b
a rate is defined as
a / (time at risk of becoming a)
define uncertainty
used to describe the potential development of disease in individuals
ratio refers to
population and not the individual
define odds
probability that something will occur : probability that something will not occur
define the normality assessment
a statistical procedure done to assume that the data that is under analysis have arisen from a normal population of values
what are methods to evaluate the normality assumption?
plotting histograms
descriptive statistics
formal test for normality
define statistic
is a random value, and its value will change from sample to sample even though the true population value does not change
define parameter
is the true population value; therefore, a statistic is the same as a parameter estimate
mean, median, and mode should be
equal
skewness and kurtosis should be
zero
define infectiousness
relates to the ability of an animal to transmit the infection to a new susceptible host
factors that drive disease transmission include
presence and number of infectious individuals
level of immunity in the population
probability of adequate contact
define adequate contact
contact that when it occurs between an infectious and a completely susceptible host will cause disease transmission
describe direct contact
infected and susceptible animal having the ability to physically touch (immediate proximity to one another)
transmission often by respiratory route (or venereal disease)
describe indirect contact
contact with a contaminated environment (feed, water)
vector or fomite transmission
airborne transmission over greater distances (not close proximity)
mosquitoes and ticks are examples of
biological vectors
biting flies are examples of
mechanical vectors
what are factors that drive disease transmission?
presence and number of infectious individuals
level of immunity (resistance) in the population
probability of adequate contact
define R0
the expected number of secondary cases produced by a single (typical) infection in a completely susceptible population
R0 = 1
endemic disease state
R0 > 1
increase number of cases, epidemic if susceptible population
R0 < 1
disease will not be maintained in the population
to prevent an epidemic, the immune proportion should be
(R0-1)/R0