Vertebral Column and Muscles of the Back
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
The only plane that intersects 2 halves and creates equal planes is ___
the medial plane
Any plane that is slightly off the medial plane (off to the side) is the ___
sagittal plane
When looking at CTs or MRIs, this is the ___
transverse plane
The sole of the foot can also be referred to as the ___
plantar surface of the foot
Proximal means ___
Distal means ___
closer to; further away
The knee is ___ to the hip
distal
The hip is more ___ to the belly button than the knee
more proximal
Posterior means ___
Anterior means ___
dorsal; ventral
Layers of skin:
superficial (top)
intermediate
deep (inner)
Top of hand is called ___
Bottom on hand is called ___
dorsum; palm (sole for foot)
What is it called when you straighten your arm?
extension
-bending arm up is flexion
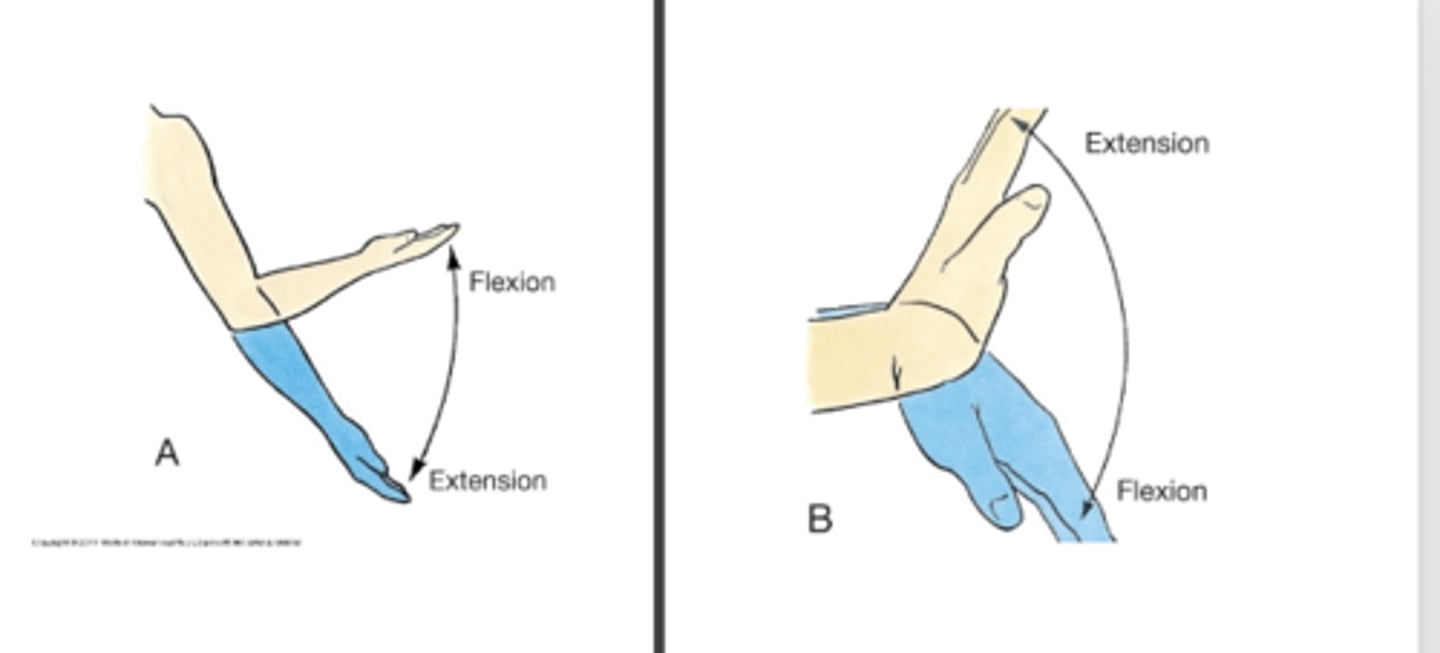
Flexion is ___
Extension is ___
moving the upper and lower limb forward; opposite, moving upper/lower limbs backwards
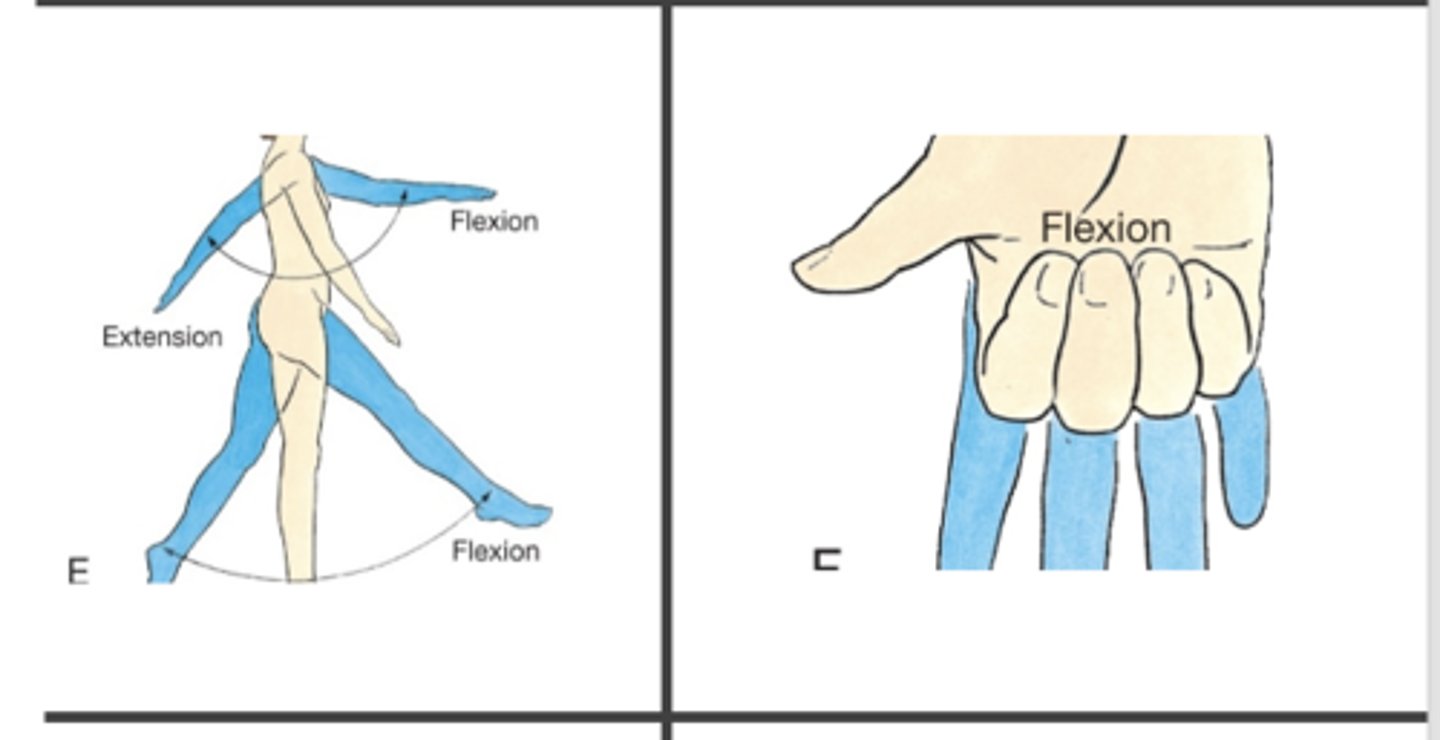
Curling body forward (like a C) is called ___
Flexion
-flexion is bending back leg (knee joint)
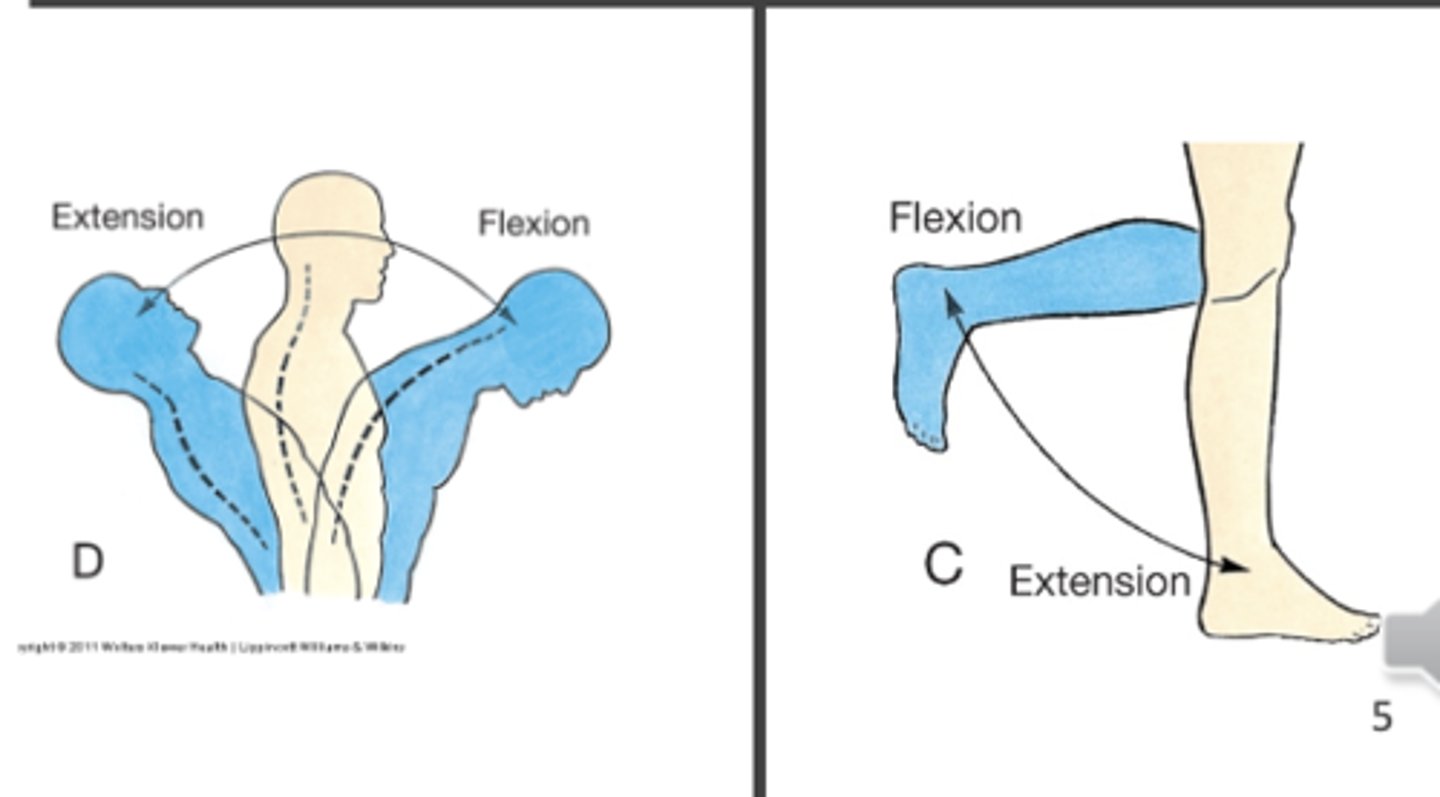
Moving something away from the midline is ___
Abduction
Moving something toward the midline is ___
Adduction
Moving your foot towards the dorsal side of foot is ____
dorsiflexion
-moving down (planting on ground) is plantarflexion
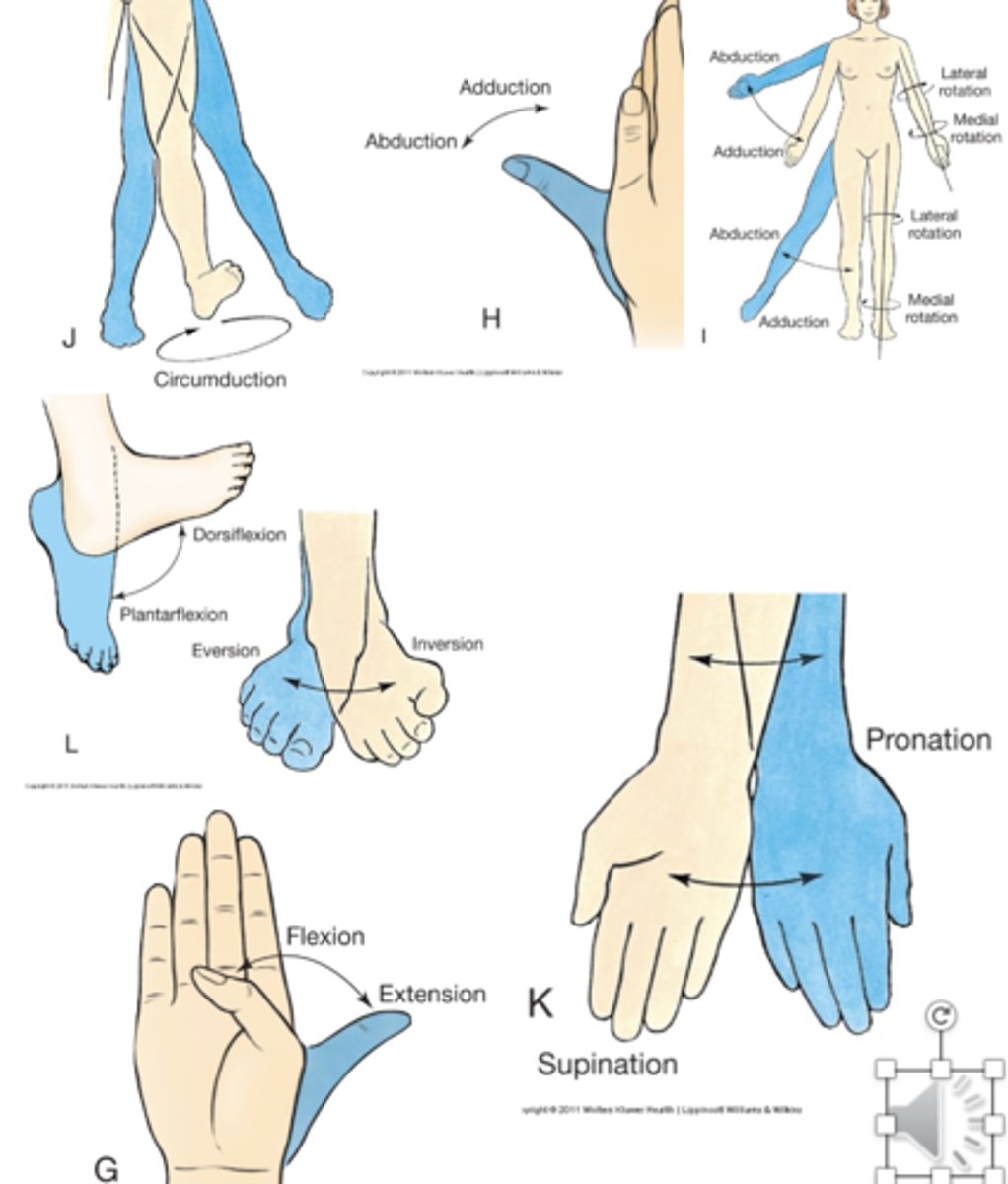
Supination is ___
holding a bowl of soup (in palm of hand)
-Pronation is flipping wrist so palm is down
"Normal" range of motion is evident in ___
young healthy individuals and reduced by >50% with increasing age
-influenced by intervertebral discs, structure of the zygoapophysial joints, ligaments associated with the vertebral column, attachment to other bony structures, and associated muscle and adipose tissue
Regions of Vertebrae:
-Cervical (7)
-Thoracic (12)
-Lumbar (5)
-Sacrum (fused 5)
-Coccyx (3-5)
The strongest vertebrae are in the ___ region
Lumbar region
-weight bearing increases as you go down spine
The lumbar curvature is more denoted in ___
females
-exaggerated during pregnancy (excessive lordosis)
The sacral curvature is diff in females as it is less acute which ___
limits protrusion of the coccyx into the birth canal
The concavity of the thoracic and sacral region are ___
anterior (kyphosis)
-while being posteriorly placed in the cervical lumbar region (lordosis)
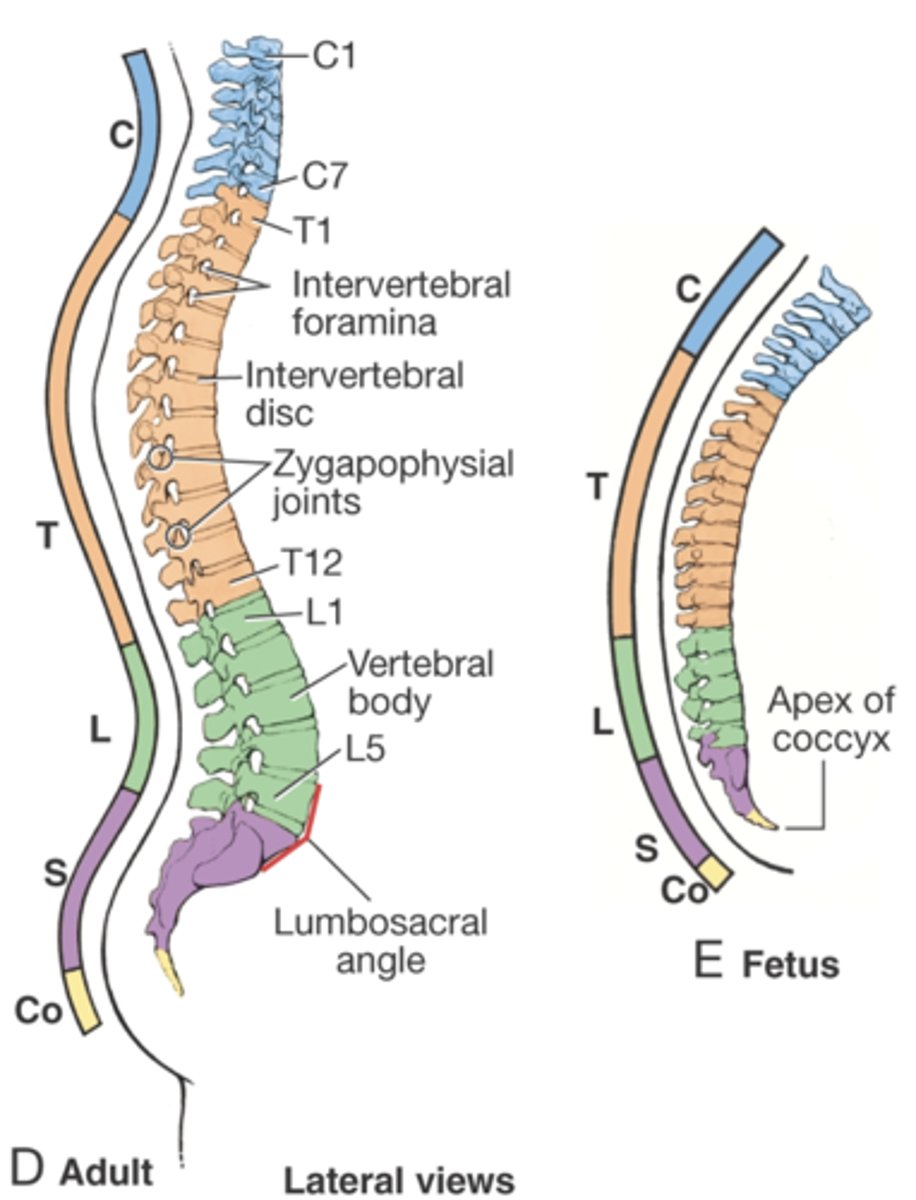
When do the primary curvatures of the back exist?
during fetal development
-thoracic and sacral curvatures maintained throughout life
When do secondary curvatures of the back develop?
later on and are dependent on growth and development of intervertebral disc
When does the cervical curvature begin to develop?
when infants begin to hold up their heads
When does the lumbar curvature develop?
with initiation of walking
What does a vertebra consist of?
1. a body (more dense anteriorly)
2. an arch (consist of lamina and pedicle)
3. 7 processes (spinous, 2 transverse, and 4 articular (2 superior/2inferior))
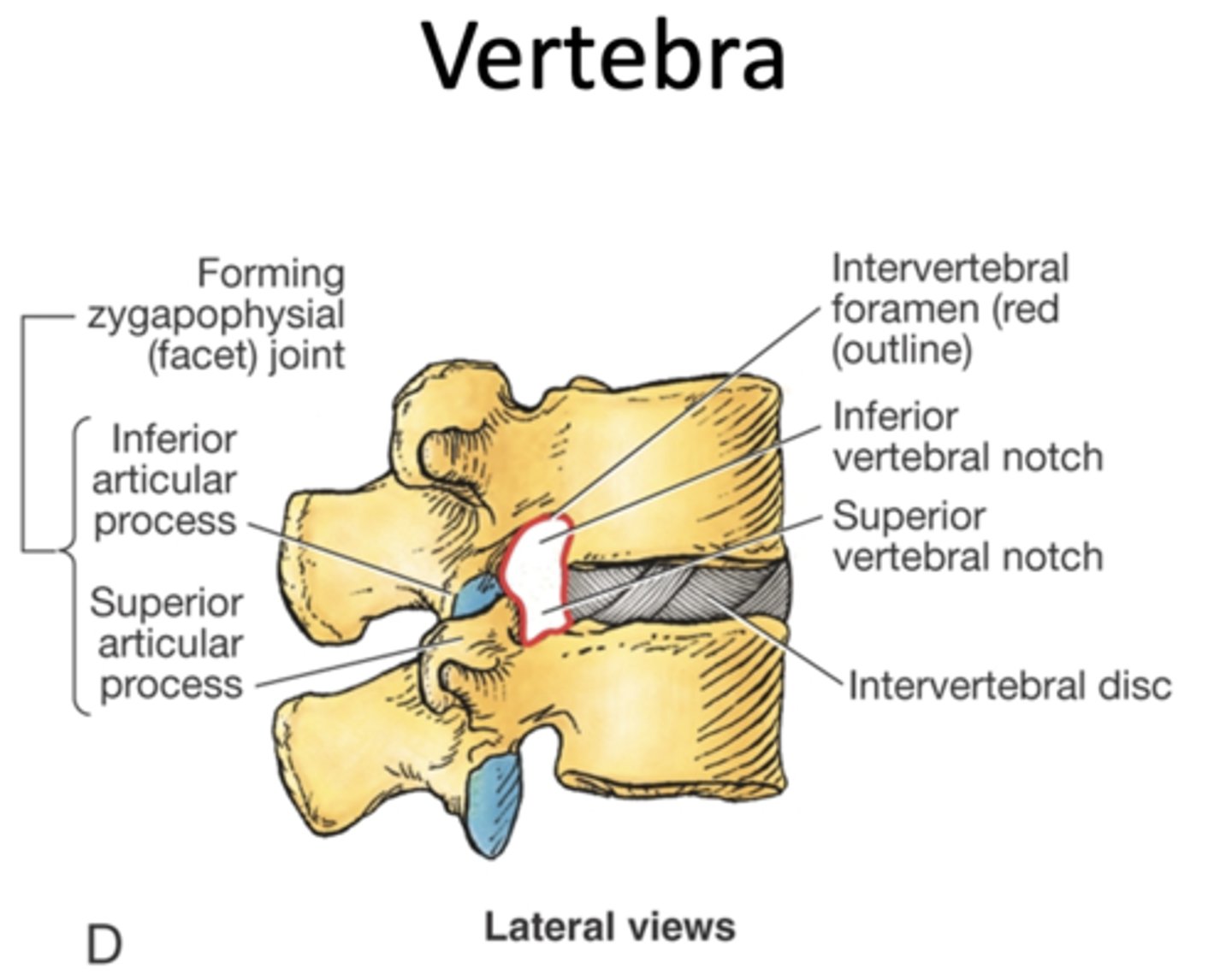
The vertebral arch and posterior aspect of body created the boundaries of the ___
vertebral foramen
-with all of the vertebral foramina stacked --> vertebral canal
The inferior vertebral notch of the superior vertebra in relationship to the superior vertebral notch of the inferior vertebra creates the ___
intervertebral foramen
-allows for passage of spinal nerves
Specific Characteristics of Cervical Vertebrae:
1. body is the smallest of all of the regions of the vertebral canal
2. vertebral foramen is large and has triangular shape
3. The transverse processes of C1-C6 have foramen (allow for ascension of vertebral arteries)
4. spinous processes of C3-C5(6) are bifid in nature
5. C3-C7 are considered “typical”
6. C1-C2 are "atypical"
7. C1: Atlas, C2: Axis
8. flexion is greatest in this region
Characteristics of C1 Atlas:
1. Ring-like
2. No spinous process or body, but rather has an anterior and posterior arch
3. The superior articular facets, in association with the occipital condyles, create the atlanto-occipital joints
4. The inferior articular facets, in association with C2, create the atlanto-axial joints.
Characteristics of C2 Axis:
1. considered the strongest cervical vertebra
2. the dens (odontoid process) is believed to be the body of C1
The atlas pivots around the ___
dens with lateral/medial rotation
-dens articulates with anterior arch of C1
Characteristics of Thoracic Vertebrae:
1. Body is heart shaped and has costal facets where the ribs articulate
2. The vertebral foramina is smaller
3. The spinous processes are long with a posteroinferior slope (which limits flexion). The tip reaches the vertebral body inferior to it
4. T1-T10 have transverse costal facets which articulate with a portion of the ribs
5. The transverse processes are long
Characteristics of Lumbar Vertebra:
1. Body is massive and dense
2. Spinous processes are blunted
3. The vertebral foramina are the largest in this region and triangular in shape
4. The transverse processes are long and slender
Characteristics of Sacral Vertebrae:
1. provide stability for the pelvis, with transmission of body weight via the sacroiliac joints
2. The base of the sacrum (S1) articulates with L5. It’s anterior edge projects and is referred to as the promontory
3. The superior-lateral edge of the sacrum is called the ala (Latin for wing)
S1-S3 have both ___ and ____ for the sacral vertebrae
lamina and pedicles
-absence of these structures creates a hiatus on posterior aspect of the sacrum
-Coccyx: remanent of the tail-life embryonic caudal eminence
Ligaments and Intervertebral Disc:
1. anterior longitudinal ligament: fibrous band that covers and connects the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and the associated IV disc
2. posterior longitudinal ligament: not a wide or strong as the anterior. Runs in the vertebral canal, covering the posterior aspect of the vertebral bodies (from C2-sacrum)
3. Ligament flavum: yellow, elastic ligament covers the lamina of the vertebral canal
4. intervertebral disc: Anulus Fibrosus (outer portion) and Nucleus pulposus (central core: contains water, elastin and proteoglycans)
What is the function of the anterior longitudinal ligament?
traverses from the pelvic surface of the sacrum to the anterior tubercle of C1 (including the occipital bone)
-limits the extension of the vertebral column
What is the function of the Posterior longitudinal ligament?
important for the prevention of hyperflexion of the vertebral column and posterior herniation of IV disc
What is the function of the ligamentum flavum?
important for protection of the IV discs during sudden flexion of the column
-also preserves the curvatures of the column and assist with straightening the back after flexion
Arterial Supply of Vertebral Column:
•Periosteal branches
•Equatorial branches
•Spinal branches:
–Anterior vertebral canal br
–Posterior vertebral canal br
Periosteal and Equatorial branches:
arises from cervical and segmental arteries
Spinal Branches:
arise from vertebral, ascending cervical [neck], posterior intercostal [thorax], subcostal, lumbar [abdomen], iliolumbar and lat/med sacral a [pelvis].
Venous Drainage of Vertebral Column:
•Spinal v.: Internal vertebral (epidural) venous plexus (anterior/posterior) AND External vertebral venous plexus (anterior/posterior)
•Basivertebral v.
•Intervertebral v.
Basivertebral vein:
drain into internal venous plexi --> external venous plexi
Intervertebral vein:
receives blood from the spinal cord and the vertebral plexi, exits through the intervertebral foramina and drains into the vertebral/segmental v. of the neck and trunk
What is the nuchal groove?
site of nuchal ligament in the back
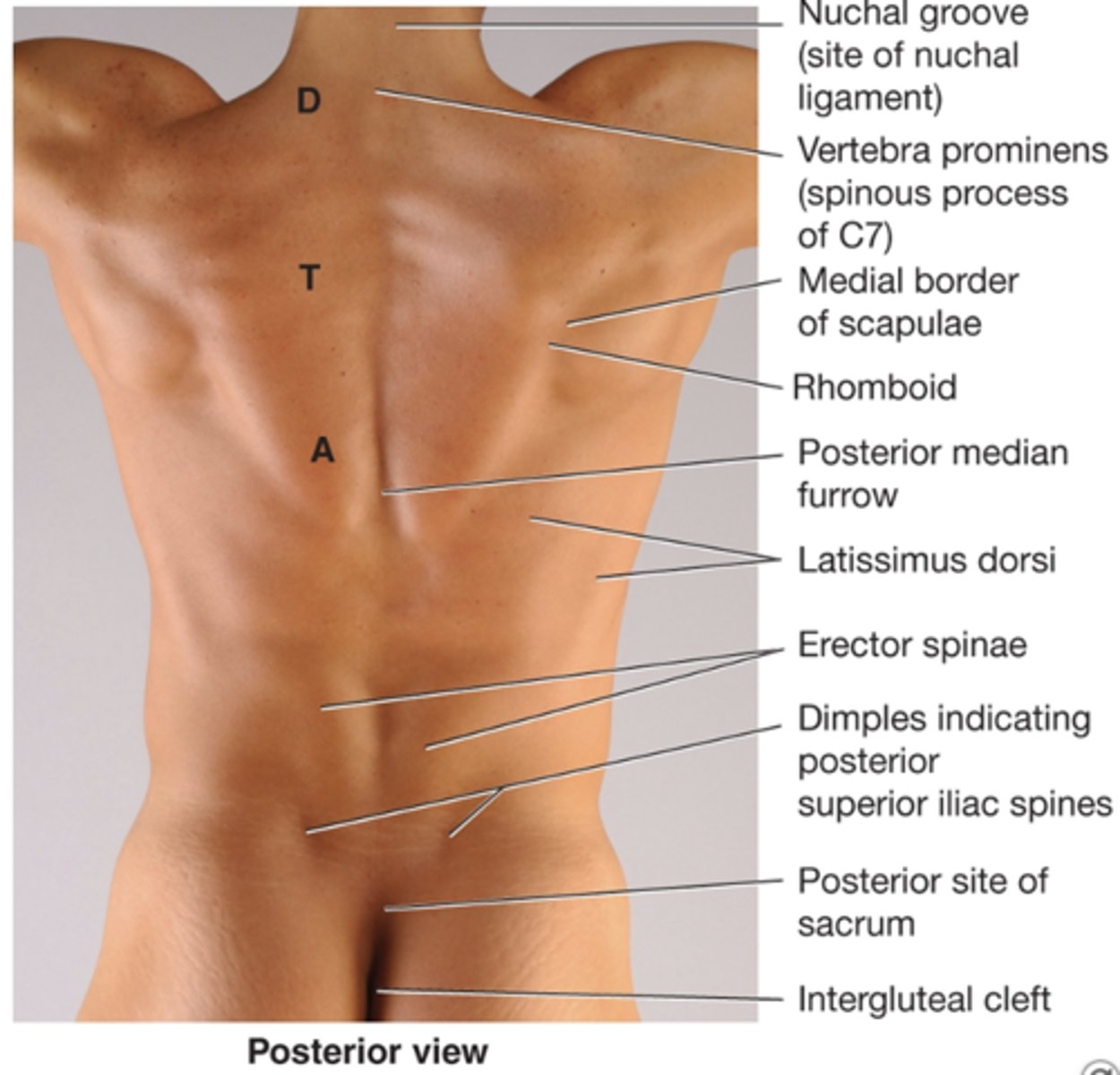
In the trapezius muscle:
D: descending
T: transverse
A: ascending
What are extrinsic back muscles responsible for?
limb movement and control
-also respiratory movement
What are intrinsic back muscles responsible for?
act on spinal column to produce movement
-responsible for posture
Superficial Extrinsic Division of back muscle:
Functions primarily to produce and control limb movement
-innervated by ventral rami (1 exception is trapezius CN XI)
Muscles of the Superficial Extrinsic division:
•Trapezius m.
•Latissimus dorsi m.
•Levator scapulae m.
•Rhomboid m. (major/minor)
Intermediate Extrinsic Division of back muscles:
Functions as superficial respiratory muscles
-innervated by intercostal nerves (ventral rami)
Muscles of the Intermediate Extrinsic division:
-Serratus posterior superior m.
-Serratus posterior inferior m.
Intrinsic (deep) Back muscles:
maintain posture and control the movements of the vertebral column
-innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Muscles of Intrinsic (deep) back muscles:
Superficial: Splenius m.
–Capitis
–Cervicis
Intermediate: erector spinae m.
Deep: Transversospinales muscle group
–Semispinalis
–Multifidus
–Rotatores
What is the collective name for a group of 3 muscles which lie in the space between the spinous processes of the vertebrae and the costal angles?
Erector spinae
The Transversospinales muscle group is composed of 3 specific muscles:
Semispinalis, Multifidus, Rotatores
-reside in the space between the spinous and transverse processes of the vertebral column
Trapezius Muscle:
innervation: CN XI
function: Elevation, depression, and retraction of the scapula
blood supply: transverse cervical artery
Where is the insertion of trapezius muscle?
lateral 1/3 of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula
Lattisimus Dorsi muscle:
innervation: throacodorsal nerve
Fx: Adduction of upper extremity, internal rotation, extend upper extremity
blood supply: thoracodorsal artery
Where is the insertion of the Lattisimus Dorsi?
intertuberular groove of humerus
Levator scapulae:
Innervation: Dorsal scapular n.
Fx: elevates scapula
Blood supply: dorsal scapular a
Rhomboids:
Innervation: Dorsal scapular n.
Fx: retract and rotate scapula; fix scapula to thoracic wall
Blood supply: Dorsal scapular a.
Rhomboid minor:
-Medial attachment: nuchal ligament and spinous processes of C7-T1
-Lateral attachment: medial end of scapular spine
Rhomboid major:
-Medial attachment: spinous processes of T2-T5
-Lateral attachment: medial end border of scapula from spine to inferior angle
Trapezius (sup and inf fibers) cause __ rotation of scapula
superior rotation
-rotation elevating glenoid cavity
Rhomboids cause ___ rotation of the scapula
inferior rotation
-rotation depressing glenoid cavity
Serratus Posterior Superior muscles:
-Innervation: 2-5th intercostal n.
-Fx: Elevate ribs
Serratus Posterior Inferior muscles:
Innervation: 9-11th intercostal n and subcostal n (T12)
Fx: Depresses ribs
Splenius muscles:
innervation: posterior rami of spinal nerves
Fx: extend head and neck (together) and laterally flex neck and rotate head (alone)
Blood supply: muscular branches of aorta and branches off posterior intercostal a
Erector Spinae:
Innervation: posterior rami of spinal n
Fx: laterally flex column (unilaterally) and controls flexion of spine by lengthening its fibers (bilaterally)
Blood supply: branches off aorta
What are the ILS muscles?
Iliocostalis, Longissimus, and Spinalis
Back Sprain:
injury to ligaments
-without dislocation or fracture
-from excessive extension/rotation
Back Strain:
stretching or tearing of muscle
-usually in lumbar region and involving the erector spinae m.
-MOST COMMON cause of lower back pain
-unbalanced weight on vertebral column pulls muscles (spasms occur)
What do you have to think about with lower back pain (LBP)?
bulging discs (herniation of nucleus pulposus)
-can compress spinal cord, spinal nerves, or nerve roots of cauda equina
What is a sciatica?
pain in the lower back and hip from compression of the L5 or S1 portion of the sciatic nerve
-can occur from herniation or the development of osteophytes (bony spurs) in the vertebral foramen
Spondylolysis:
-fracture of the vertebral lamina
-occurs at L5, thought to develop because of embryonic failure
-contributes to the development of spondylolisthesis
What is the most common embryonic anomaly of the vertebral column?
spina bifida
-failure of the laminae to develop and fuse
-L5 and/or S1
-24% of people
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap):
Aseptic procedure
-Between L3 and L4 -or- L4 and L5
Other nerve blocks:
-direct effect of the spinal nerves of the cauda equina as they exit the dural sac
-can also be done in the sacral canal or through the posterior sacral foramina