Cogeneration and Combined Cycle Power Plants (Lecture Notes-5)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
cogeneration
schemes that involve the combined production of heat and power are variously known as CHP plant, cogeneration plant, or total energy plant
back-pressure turbine
class of turbine often found in combined heat and power cogeneration cycles, which exhaust into a condenser at a relatively high pressure (greater than atmospheric) so that the heat rejected in the condenser is relatively high grade (high temp) making it useful for heating purposes
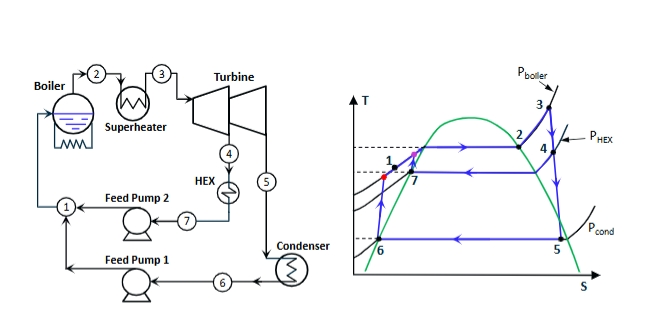
extraction or pass-out turbine
an alternative cogeneration turbine type in which some of the steam exits the final stage of the turbine and is expanded to a low pressure condenser in ambient condition, the remainder of the steam being extracted from part-way along the turbine at some intermediate temperature for use in process heating
thermal advantage
useful parameter when assessing cogeneration for domestic heating
thermal advantage is defined as:
heat produced by CHP plant for district heating/additional heat needed in the network to compensate for the lost electricity

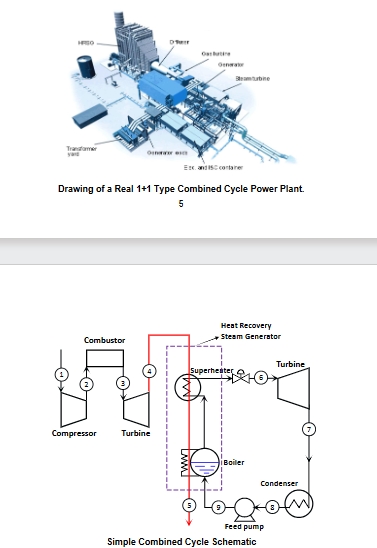
combined cycle power plants
a method for obtaining higher efficiency in a thermal power plant by combining gas and steam turbine technology, high temperature exhaust gas from the gas turbine is used to generate steam in a heat exchanger (HRSG) at temperatures that are high enough for additional work to be produced from the steam turbine
what are the pros and cons to combined cycle plants
the most efficient (usually >50%) thermal power plants but require a lot of infrastructure and so carry high capital and maintenance costs
heat recovery steam generator (HRSG)
this the heat exchanger used to transfer the heat from the exhaust gases of gas turbine cycle to the water/steam cycle
steam-tail
the steam turbine cycle in a combined cycle plant is sometimes referred to as the steam-tail. these are relatively simple cycle, normally consisting of a standard superheated steam cycle, reheating and feedwater heating is not required because the job of the steam tail is simply to convert the maximum amount of otherwise waste heat from the gas turbine exhaust into additional useful emchanical work
what are the most common fuels used to generate heat
oil and gas
what is thermodynamically wasteful
as when oil and gas combust the energy is released at temperatures far above that is needed so it is wasteful to use this heat directly to heat water and produce process steam
what is the higher temperature energy used for
be used to produce high-temperature steam which can then be expanded through a turbine to produce the desired process steam (this will require the turbine to exhaust into a condenser at a relatively high pressure)
back pressure turbine
a turbine which exhausts into a condenser at a relatively high pressure, therefore the class of turbine in this type of combined heat and power cogeneration cycle, in which the rejected heat is employed usefully
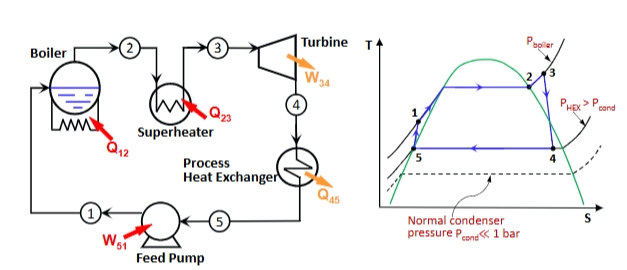
when is the use of a back pressure turbine practical
the use of a back-pressure turbine is practical if the power and heat requitements are fairly steady and well matched
when is an extraction or pass-out turbine used
when more flexible operation is needed, or when the power requirements are larger than those that can be obtained from a simple back-pressure turbine
how does an extraction or pass-out turbine used
some of the steam exits the final stage of the turbine and is expanded to ambient conditions in a low pressure condenser, the remainder of the steam is extracted from part-way along the turbine expansion at some intermediate temperature as needed for the process heating, the extracted steam is condensed in the process heat exchanger and finally returned to the boiler via a sperate feed pump
what does the extraction or pass-out turbine enable
this scheme enables variations in power and heat requirements to be at least partly accommodated by controlling the amount of extracted steam
CHP, cogeneration plant or total energy plant
schemes involving the combined production of heat and power
in cold climate countries where are back-pressure turbines used
in relatively large power stations located near cities
district heating schemes
rejected heat is conveyed to buildings by hot water mains
what is lost during district heating schemes
some electricity generating capacity is lost due to the district heating this must be made up from other power stations in other parts of the electricity grid
what is the thermal advantage used for
a crude measure of the saving in fuel consumption

what do combined cycle power plants deliver?
more power output for the same fuel consumption albeit at the cost of requiring more infrastructure (higher capital and maintenance costs)
combined cycle plants
a method for obtaining higher efficiency in a thermal power plant by combining gas and steam turbine technology
combined cycle
Exhaust exits from gas turbines at temperatures that are high enough for it to be
useful in generating steam that can produce additional work in a separate steam turbine
cycle. This type of dual power generation cycle is known as a combined cycle.
heat recovery steam generator (HRSG)
heat exchanger used to transfer the heat from the exhaust gases to the water/steam cycle
what do combined cycle stations offer
flexible operation (they can be started up much more rapidly than coal or nuclear fuelled steam power plant) to take advantage of high electricity prices at peak load times
what is a downside to combined cycle power plants
the capital and maintenance costs of combined cycle power plants are relatively high due to the large of infrastructure
what is a pro to combined cycle power plants
as the ability to generate electricity when electricity prices are high (combined cycle stations do not run continuously generating base load power) and the high thermal efficiency mean that the economics do work, and owners can make money competing alongside more conventional plant, providing that gas prices are not too high
what can a 1+1 combined cycle arrangement look lie
see image
assumption of adiabatic isentropic flow for an ideal gas eqn
see image
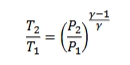
rp
pressure ratio
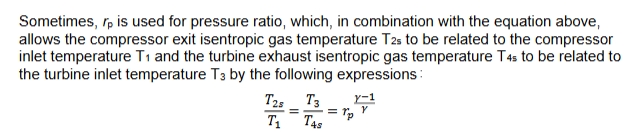
ideal gas work input to the compressor expression
w=hout-hin
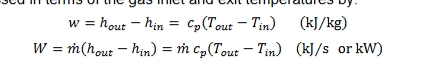
isentropic efficiency of the compressor
T2s-T1/T2-T1
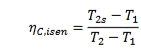
isentropic efficiency of the turbine
T4-T3/T4s-T3