Transcription and RNA Processing
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what are proteins?
polypeptides that are made up of amino acids
amino acids are linked by peptide bonds
what is gene expression?
the process that DNA directs the synthesis (creation) of proteins
this includes transcription and translation
happens in all organisms
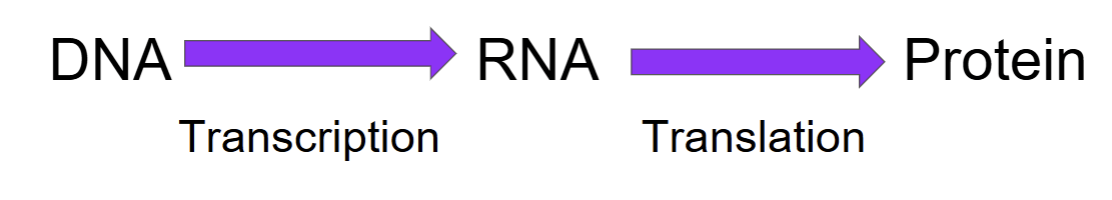
what is transcription and translation?
transcription
making RNA by copying information from DNA
allows for the “message” of DNA to be transcribed
happens in the nucleus
translation
making polypeptide using information from RNA
happens in the ribosome
nucleotide sequence becomes an amino acid sequence
what are the 3 types of RNA used in transcription and translation?
messenger RNA (mRNA)
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
transfer RNA (tRNA)
messager RNA
mRNA is made during transcription by copying DNA
It carries the instructions from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where proteins are made.
transfer RNA
imporant for translation
each rRNA carries a specific amino acid
that can attach to the mRNA via their anticodon
complementary codon
mRNA
this allows for information to be translated into a peptide sequence
ribosomal RNA
rRNA forms ribosomes
linked amino acids together
genetic code
DNA contains the sequence of nucleotides that code for proteins
the sequence is read in groups of 2 called triplet code
during transcription, only one DNA strand is being transcribed
this is the template strand
also knowen has noncoding strand, minus strand, or antisense strand
genetic code pt.2
mRNA is the opposite (antiparallel and complementary) of the DNA strand.
A pairs with U, and C pairs with G
mRNA is read in groups of three bases called codons
Each codon tells the cell which amino acid to add
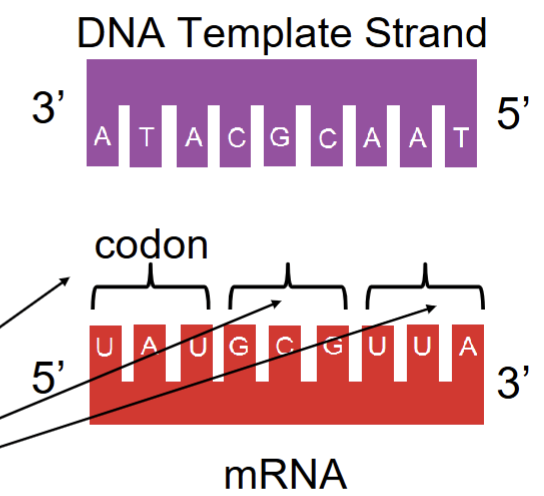
genetic code pt.3
there are 64 different codon combinations
61 code for amino acids
3 are STOP codons
same for all living things
redundancy: more than one codon can code for the same amino acid
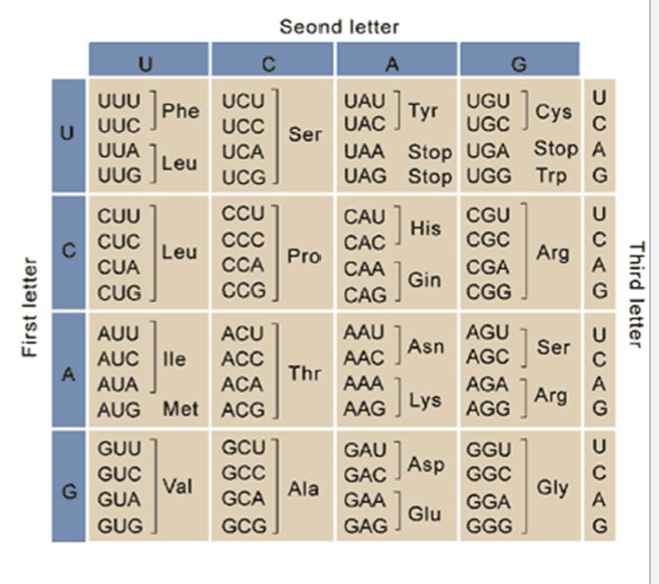
genetic code pt.4
reading frame
how codon are grouped
where the ribosome starts reading the mRNA in sets of three
codon is one of those three-letter groups, but the reading frame is the overall structure that keeps everything in the right order
the codons must be in the correct spot during translation to make the correct proteins

what are the steps of transcription?
initiation
elongation
termination
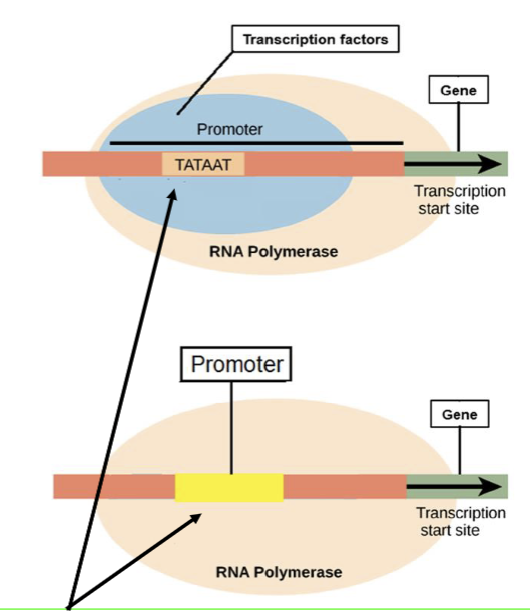
initiation
beings with RNA polymerase attaches to a promoter region of the DNA
does not need a primer to attach
promoter regions are upstream (before) the desired gene to transcribe
eukaryotes
promoter region is called the TATA box
transcription factors help RNA polymerase bind
prokaryotes
RNA polymerase can bind DIRECTLY to promoter
elongation
RNA polymerase opens the DNA and reads the triplet code of the template strand
moves in the 3’ to 5’ direction
so the mRNA transcript elongates 5’ to 3’
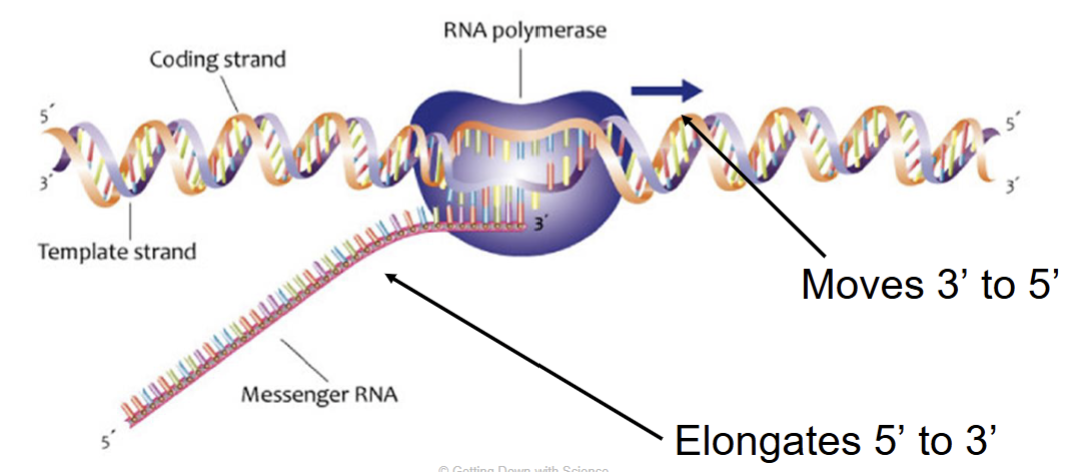
elongation pt.2
RNA polymerase moves downstream
opens small sections of DNA at a time
pairs complementary RNA nucleotides
the growing mRNA strand peels away from the DNA template strand
then DNA double helix comes back
many RNA polymerases can copy the same gene at once, making multiple mRNAs.
termination
prokaryotes
transcription proceeds through a termination sequence
causes a termination signal
RNA polymerase detaches
mRNA transcript is released and proceeds to translation
mRNA does NOT need modifications
eukaryotes
RNA polymerase transcribes a sequence of DNA at the end called the polyadenylation signal sequence
polyadenylation signal is a “wrap it up” signal for transcription in eukaryotes — it helps end transcription and prepare the pre-mRNA for processing.
pre-mRNA MUST undergo modifications before translation
pre-mRNA modifications
there are 3 modifications that happen to eukaryotes pre-mRNA before translation
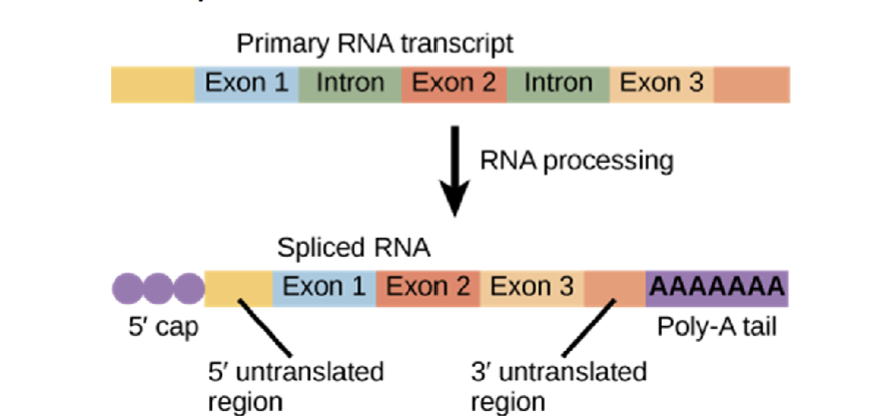
5’ cap
Poly-A tail
RNA splicing
what is 5’ cap (GTP) and Poly-A tail?
5’ cap (GTP)
the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA receives a modified guanine nucleotide “cap”
poly-A tail
the 3’ end of the pre-mRNA receives 50-250 adenine nucleotides
these help the mature mRNA leave the nucleus, help protect mRNA from degradation, and help ribosomes attach to the 5’ end of the mRNA when it reaches cytoplasm
what is RNA spilcing?
sections of the pre-mRNA are called introns and are removed so that exons are joined together (first image)
introns - do not code for amino acids
exons - expressed sections that code for amino acids
alternative slicing - means the same gene can be cut and rearranged in different ways → this makes different proteins from the same gene.
what happens when were all done?
now the pre-mRNA is now mature mRNA and can leave the nucleus and go to cytoplasm for translation at the ribosomes