Oncology 3 (Multiple Myeloma)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what are myeloma-related disorders (MRDs)?
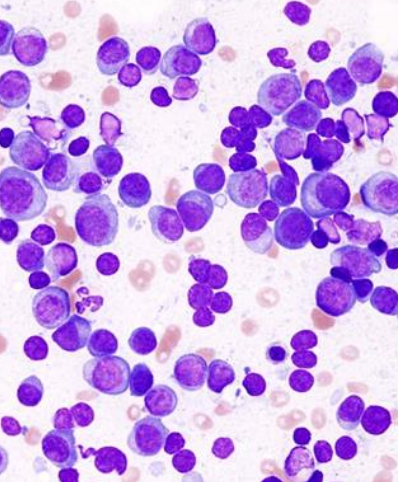
neoplastic population of plasma cells or immunoglobulin-producing B-lymphocyte precursor lineage
most are monoclonal
what are some MRD syndromes?
-multiple myeloma
-IgM (waldenstrom's) macroglobulinemia
-extramedullary plasmacytoma
-solitary osseous plasmacytoma
-Ig-secreting lymphomas (B-cell) and leukemias
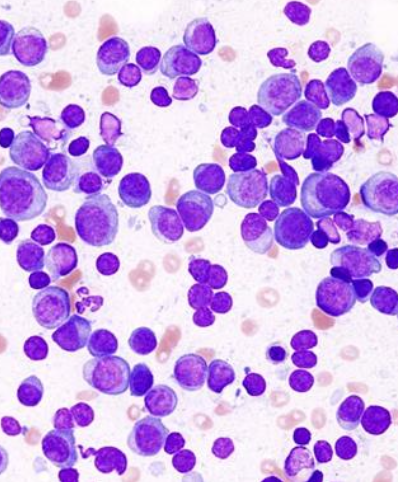
what is multiple myeloma?
originates from proliferation of malignant plasma cells that have undergone antigenic stimulation in peripheral lymph nodes
systemic
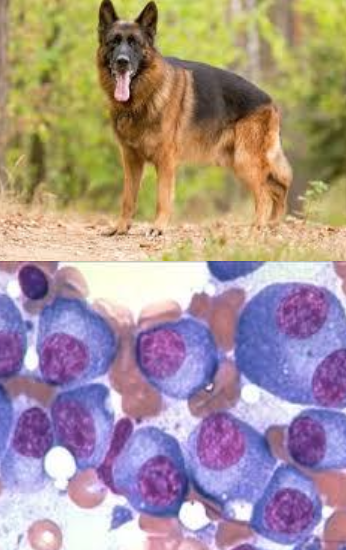
at what age do dogs and cats present with multiple myeloma?
dogs - 8-9 yo
cats - 10-14 yo
what are the clinical signs of multiple myeloma?
-lethargy/weakness
-bone pain/lameness (poss. pathologic fracture)
-bleeding
-PU/PD
-anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea
-palpable organomegaly
-chronic infection
-neuro signs
-lymphadenopathy
-sudden blindness
how can clinical signs of multiple myeloma differ in dogs vs cats?
dogs: multiple sites of bone marrow infiltration
cats: widespread abdominal organ involvement without significant bone marrow infiltration
what is the clinical presentation of multiple myeloma?
malignant cells typically produce an overabundance of a single type or component of immunoglobulin
called the M component- often first noted as hyperglobulinemia
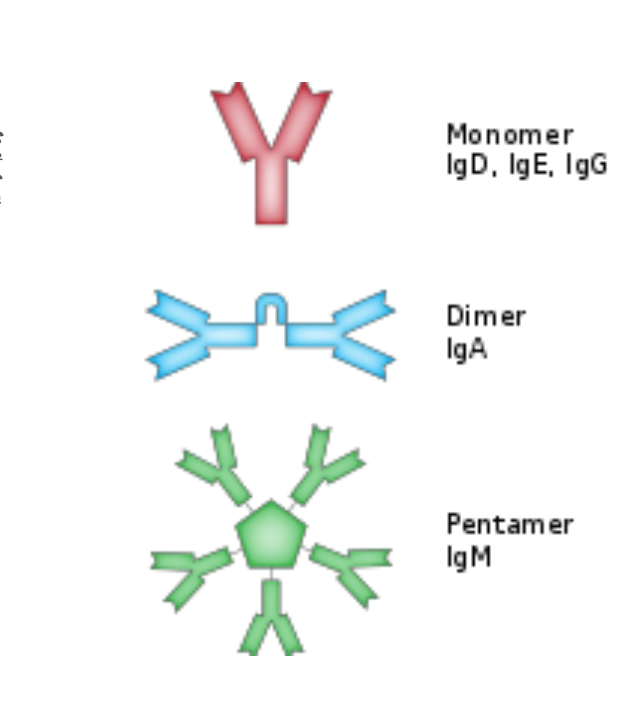
True or False? Skeletal lesions are rare with IgM (Waldenstroms) MM
True
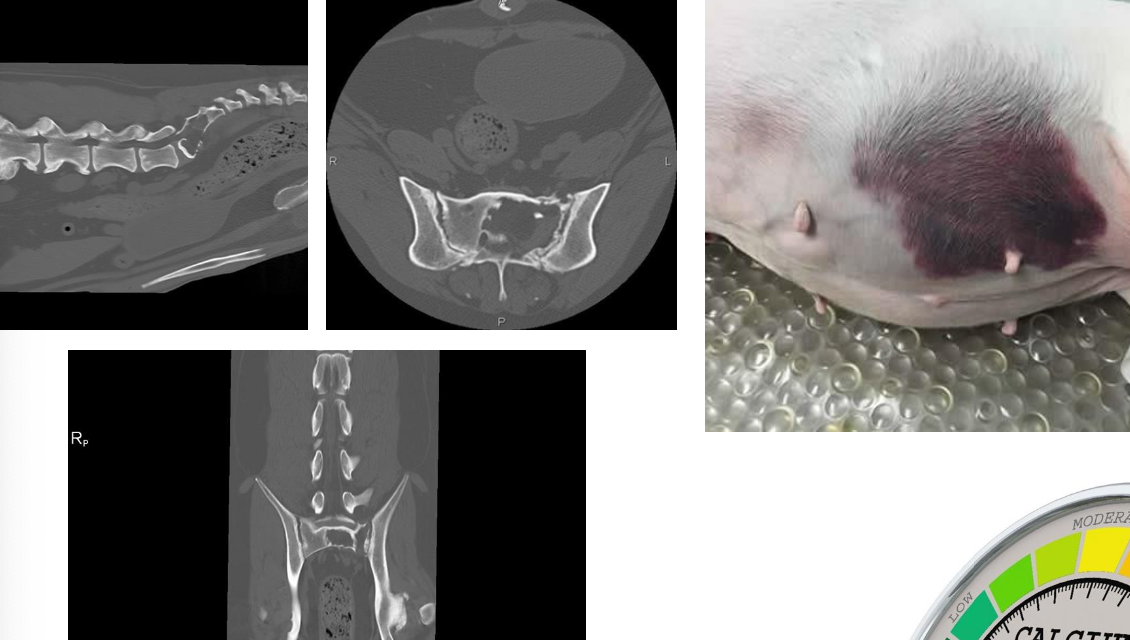
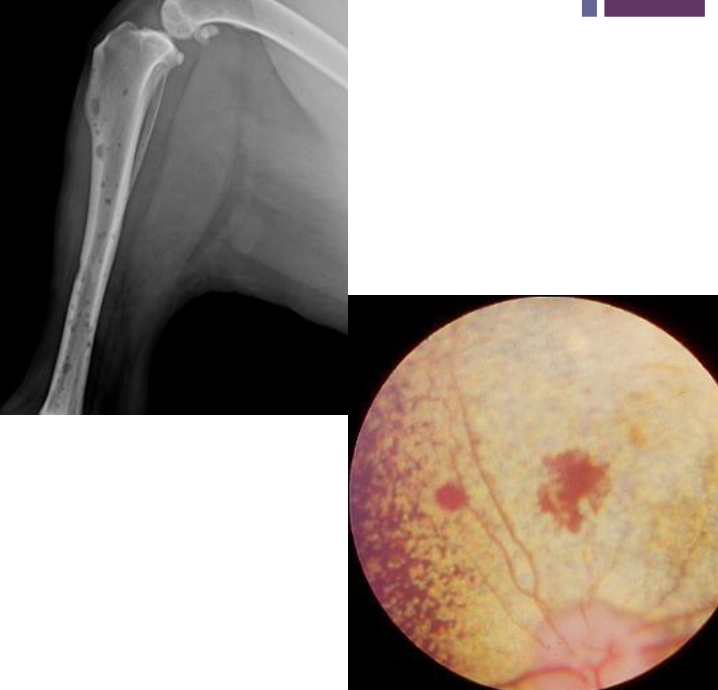
How can radiographic bone lesions appear?
Can be isolated, discrete lesions or diffuse osteopenia
Common sites have active hematopoiesis → vertebrae, ribs, skull, proximal and distal long bones
How does the M component affect blood?
bleeding diathesis due to interference with coagulation
hyperviscosity syndrome (HVS) more commonly occurs with IgM, possibly IgA
What specific clinicopathologies are associated with multiple myeloma?
radiographic bone lesions
bleeding diathesis
hyperviscosity syndrome (HVS) → bleeding, neurologic, ocular, renal, cardiac
renal disease → Bence Jones proteinuria
hypercalcemia
cytopenias
what is the diagnostic criteria of multiple myeloma in dogs?
2+ criteria met:
1. monoclonal gammopathy
2. lytic bone lesions
3. bence jones proteinuria
4. bone marrow plasmacytosis
what is the diagnostic criteria of multiple myeloma in cats?
2+ criteria met:
1. monoclonal gammopathy
2. visceral plasma cell proliferation
3. bence jones proteinuria
4. bone marrow plasmacytosis (less common than in dogs)- suggested that 10% infiltration consistent with MM
how are globulins calculated on a serum chemistry panel?
globulins = total protein - albumin
what diagnostic tests are used to diagnose multiple myeloma?
-cytology of malignant site
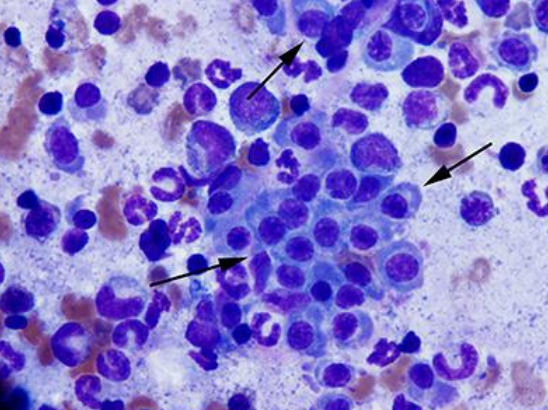
-bone marrow aspirate (over 20% plasma cells in dogs, 10-20% in cats)
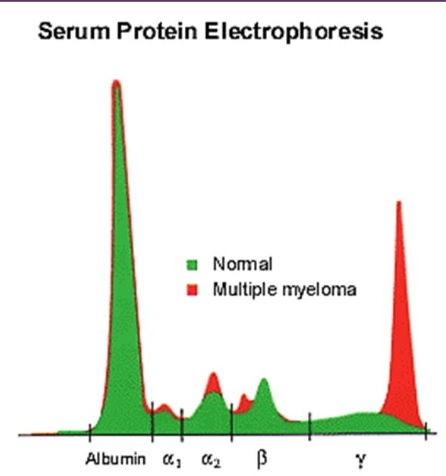
-serum protein electrophoresis (monoclonal gammapothy, occasionally biclonal)
-bence jones proteinuria (monoclonal light chains in urine- not detected on typical UA)
-immunoglobulin quantification and PCR
what diagnostic tests for multiple myeloma are used to assess extent of disease?
CBC, serum biochem, UA (PT/PTT if signs of bleeding)
fundoscopic exam
imaging:
-thorax (rads/CT)
-abdomen (rads, US, CT- especially in cats since they tend to have the visceral form)
-skeleton (CT, rads)
these diagnostics are important for diagnosis, tx, and monitoring
what is the main treatment for multiple myeloma?
chemotherapy → effective at reducing myeloma cell burden and relieving bone pain

what is the chemotherapy treatment of choice for multiple myeloma?
melphalan (an oral, alkylating agent)
+ prednisone use concurrently
what rescue setting chemotherapeutic drugs are used for multiple myeloma?
other alkylating agents like:
-cyclophosphamide
-chlorambucil
-CCNU
-tanovea (off label use)

what is the treatment for bone pain caused by multiple myeloma?
-oral analgesics
-palliative radiation therapy
-bisphosphonates

what is the treatment for hyperviscosity syndrome (HVS)?
fluid therapy (saline is preferred) ± plasmapheresis
how is immunological impairment treated/managed in multiple myeloma?
monitor for infection, in humans no benefit to prophylactic abx
what is the prognosis of multiple myeloma in dogs?
good for initial tumor control with melphalan and prednisone
long term prognosis is poor

what is the overall response rate, remission rate, and MST of multiple myeloma in dogs when treated with melphanan and prednisone?
ORR: 92%
CRR: 43%
MST: 540 days (18 months)

what are poor prognostic factors of multiple myeloma?
hypercalcemia
extensive bone lysis
bence jones proteinuria

what is the prognosis of multiple myeloma in cats?
less responsive to therapy (melphalan and prednisolone)
- about 60% initially respond (most are partial responses)

what is the MST of cats with multiple myeloma?
4 months (>1 yr survival reported)

what are poor prognostic factors of multiple myeloma in cats?
hypercalcemia
bony lesions, pathologic fracture
azotemia
anemia
