A&P2 Lab Practical 1
1/295
Earn XP
Description and Tags
use written only
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
296 Terms
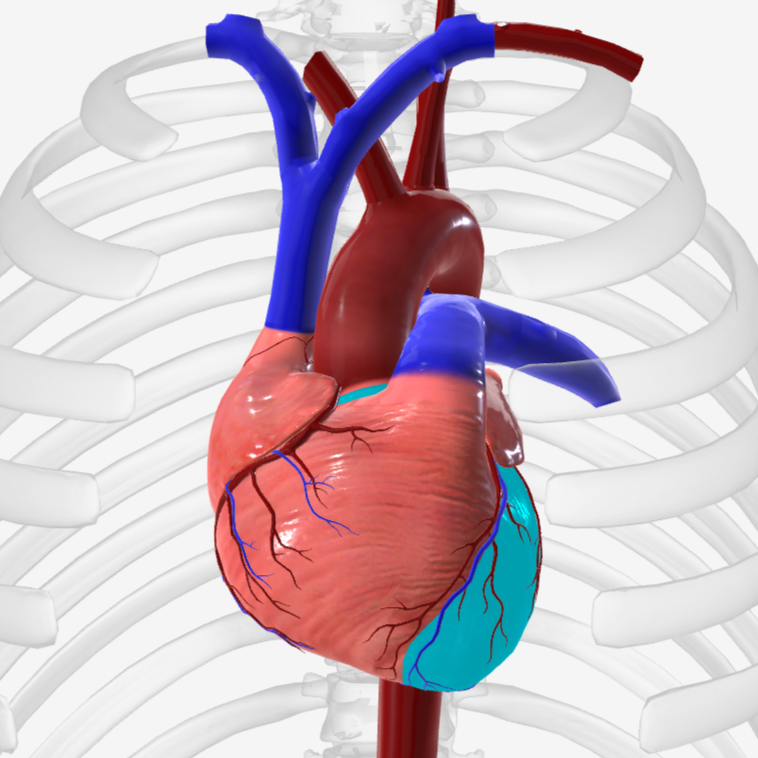
left atrium
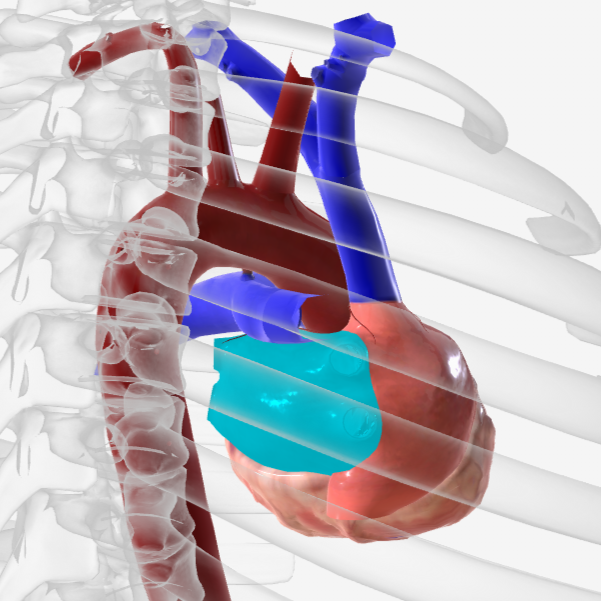
right atrium
right auricle
left auricle
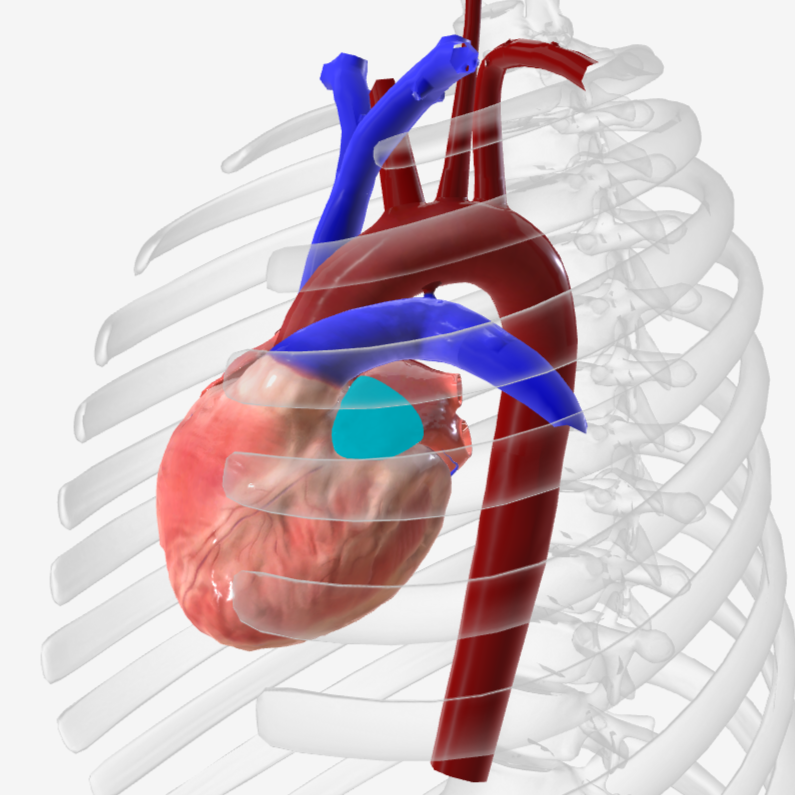
right ventricle
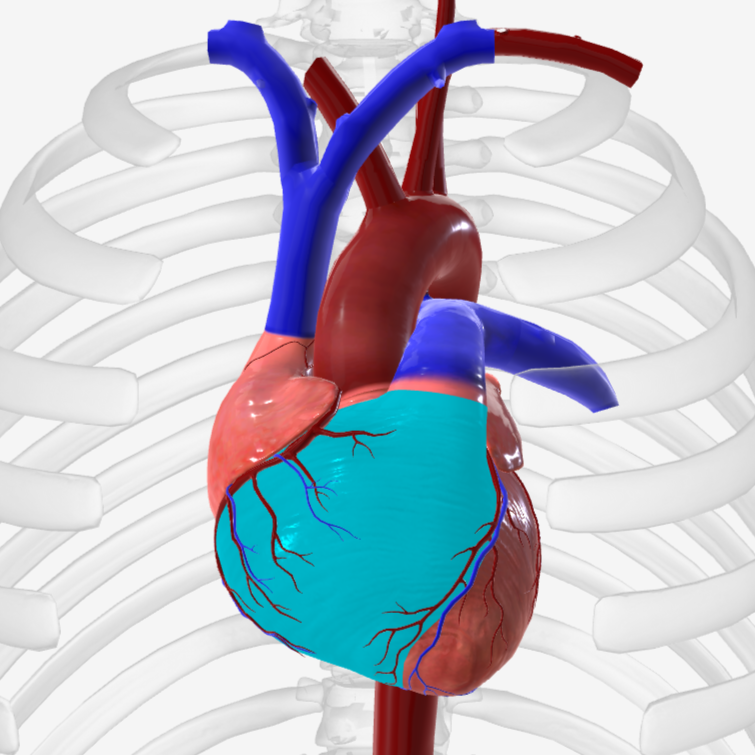
left ventricle
bicuspid/mitral valve
tricuspid valve
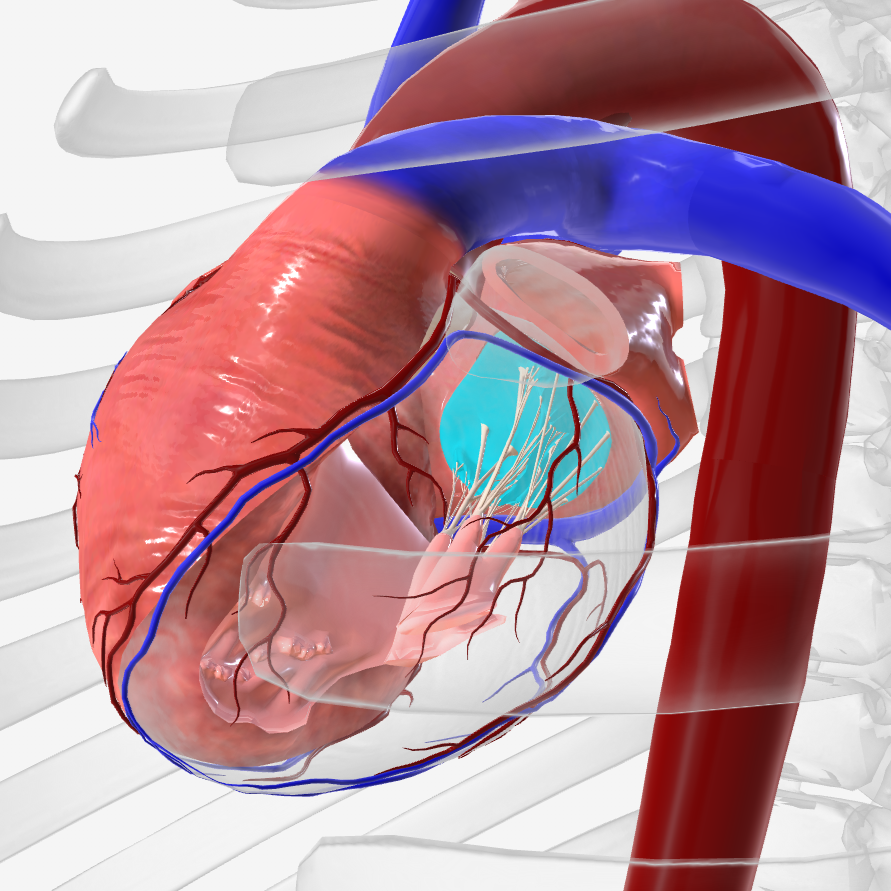
chordae tendineae
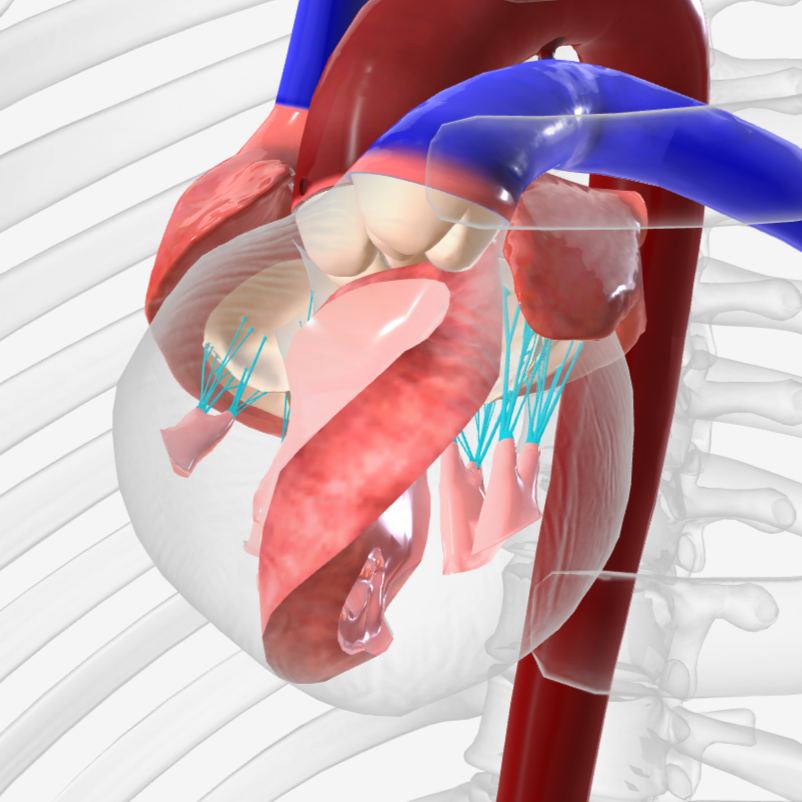
papillary muscles
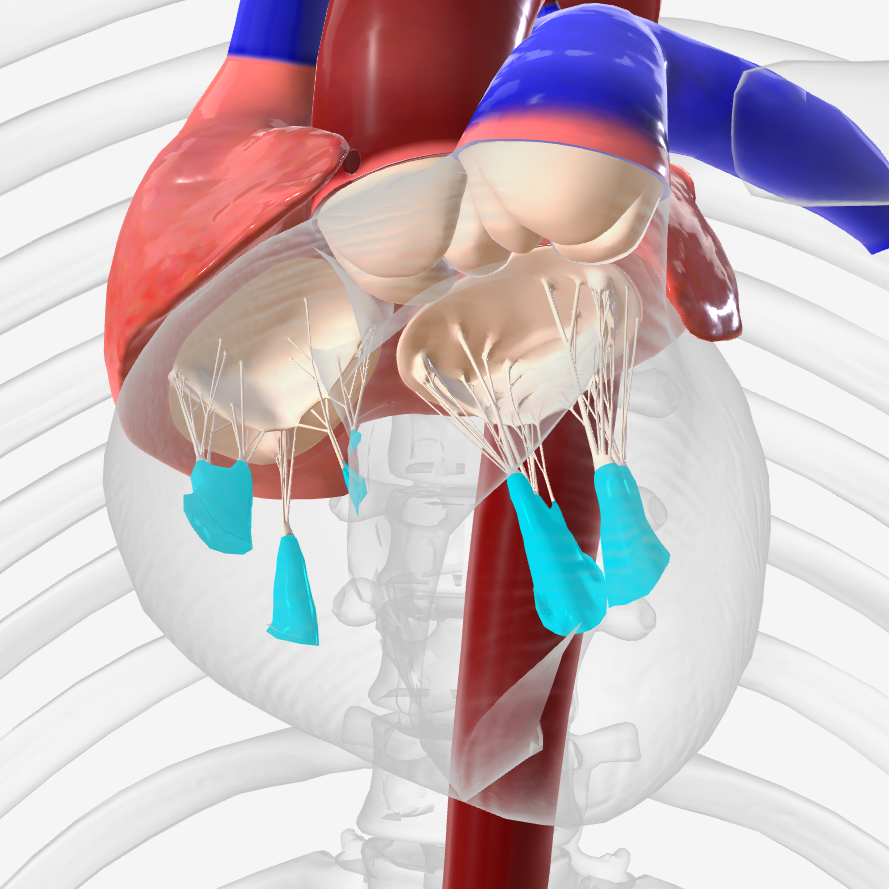
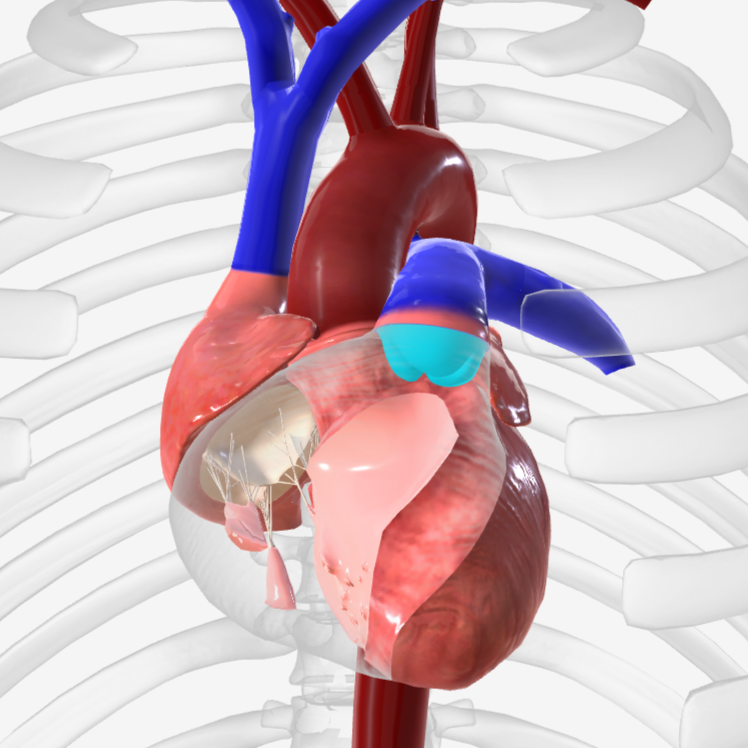
pulmonary (semilunar) valve
aortic (semilunar) valve
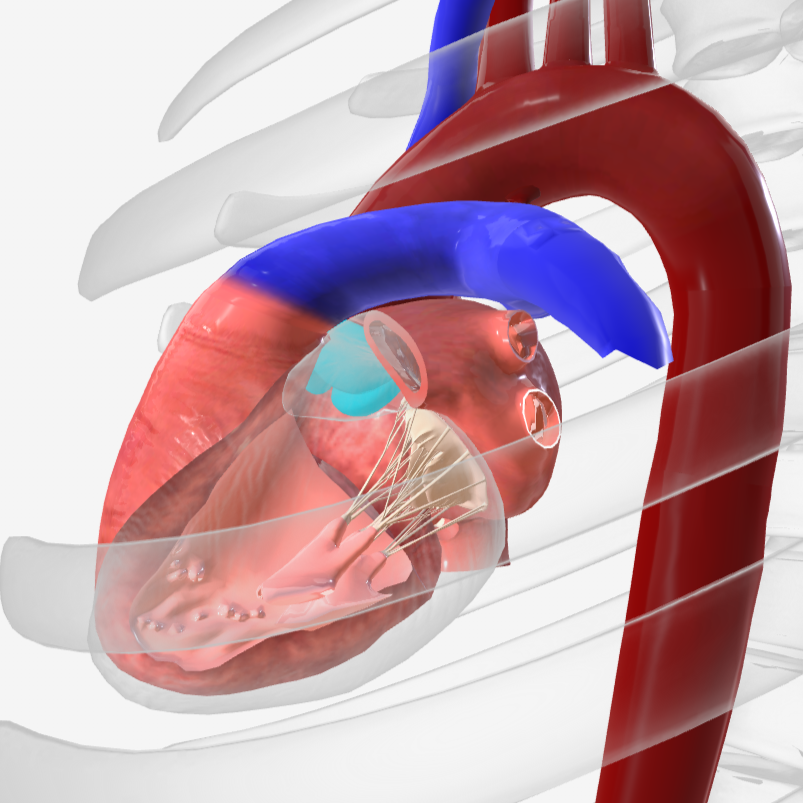
interventricular septum
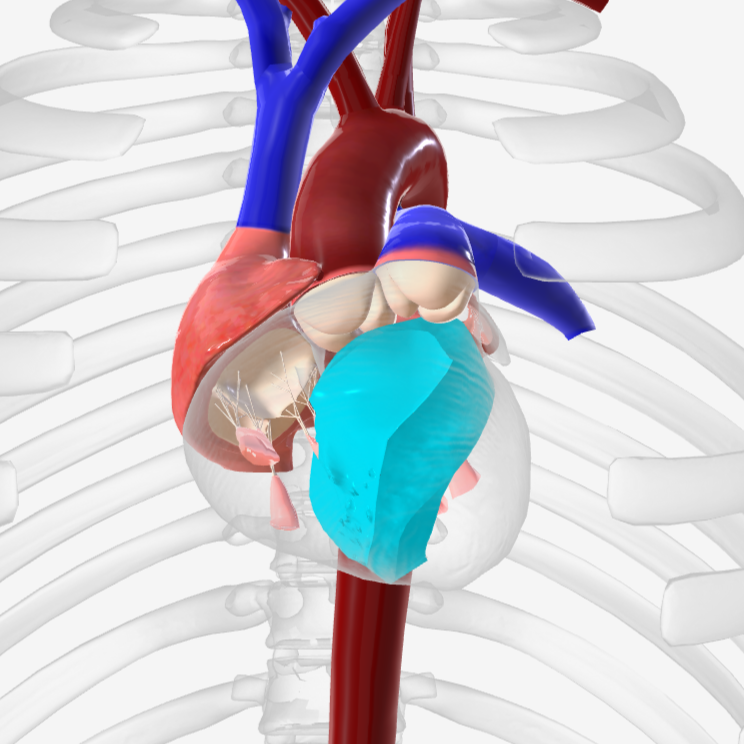
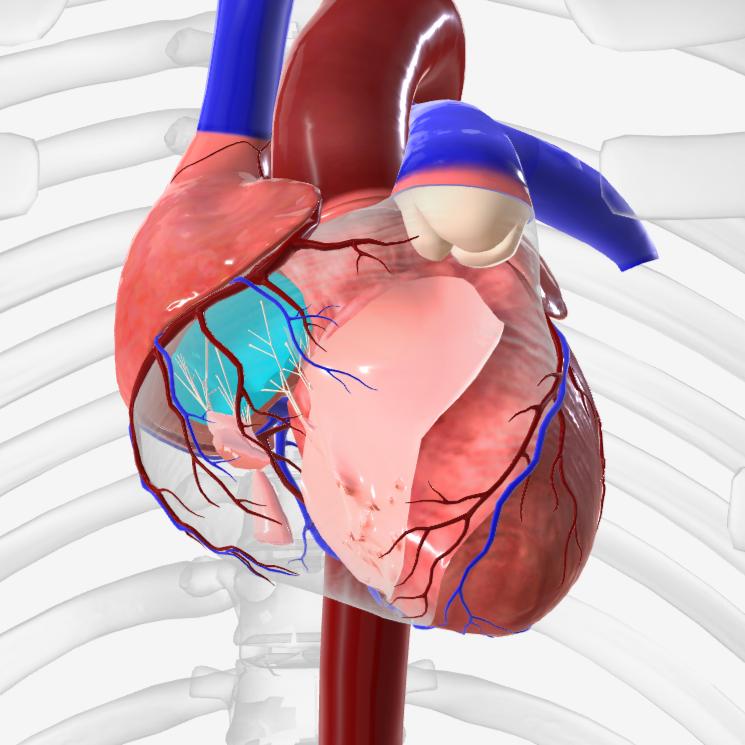
aorta
brachiocephalic trunk
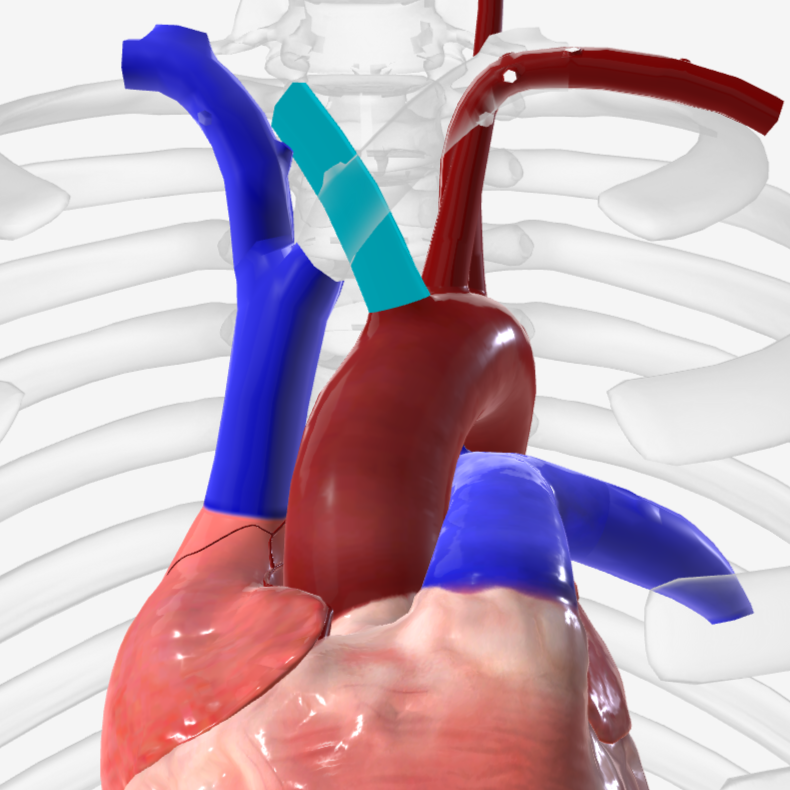
pulmonary trunk
pulmonary arteries
pulmonary veins
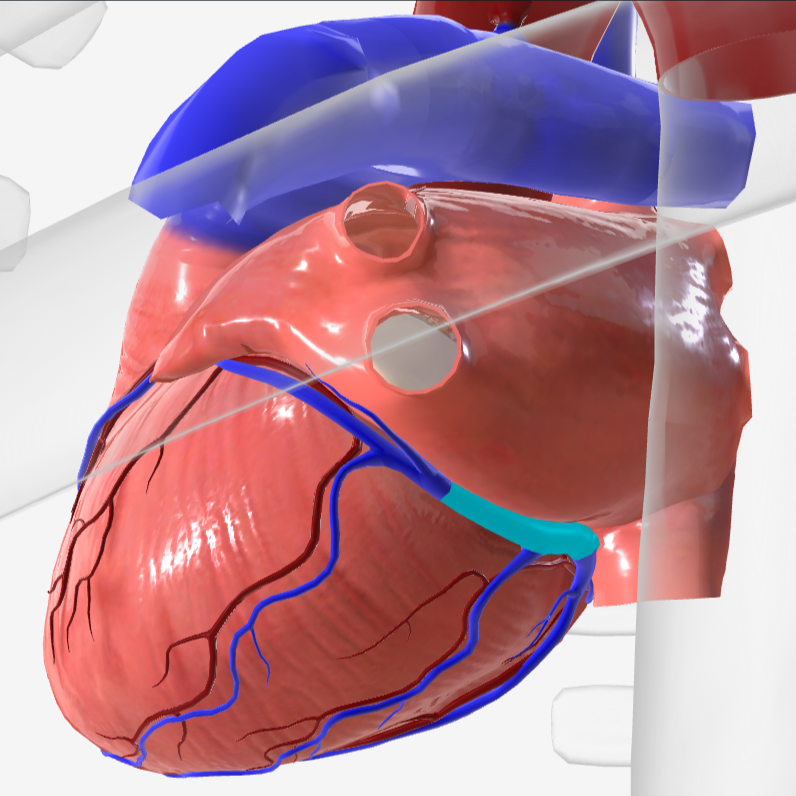
coronary arteries
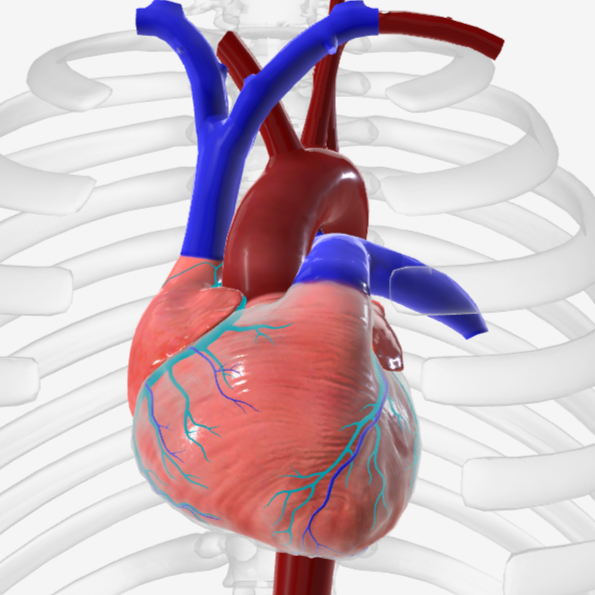
coronary sinus
endocardium
what is layer 1?
myocardium
what is layer 2?
epicardium
what is layer 3?
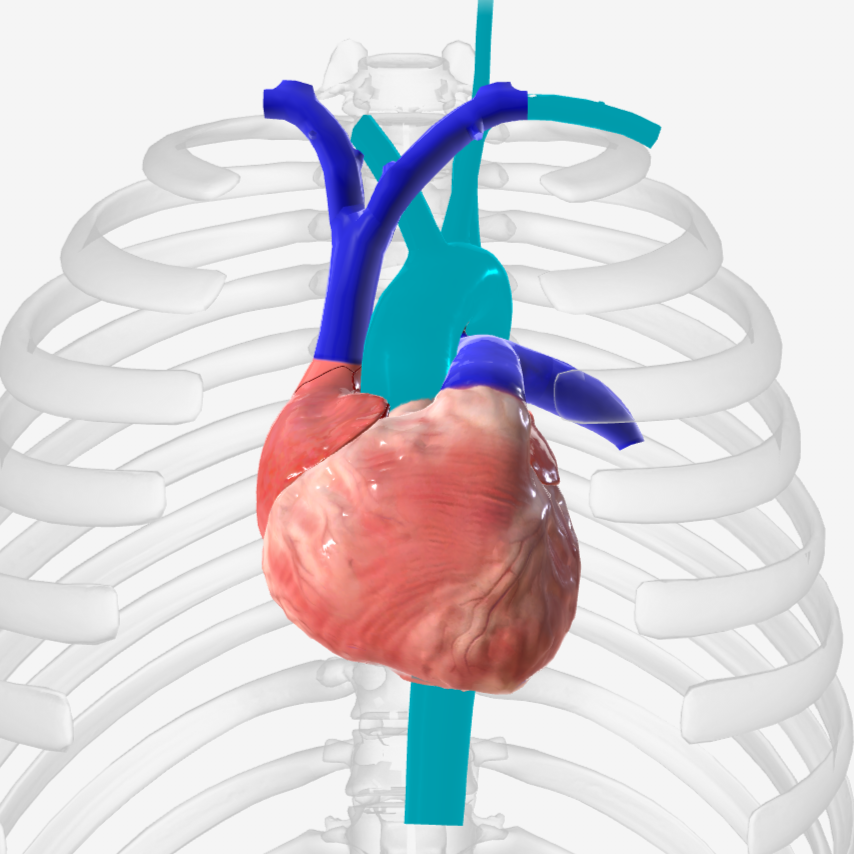
superior vena cava
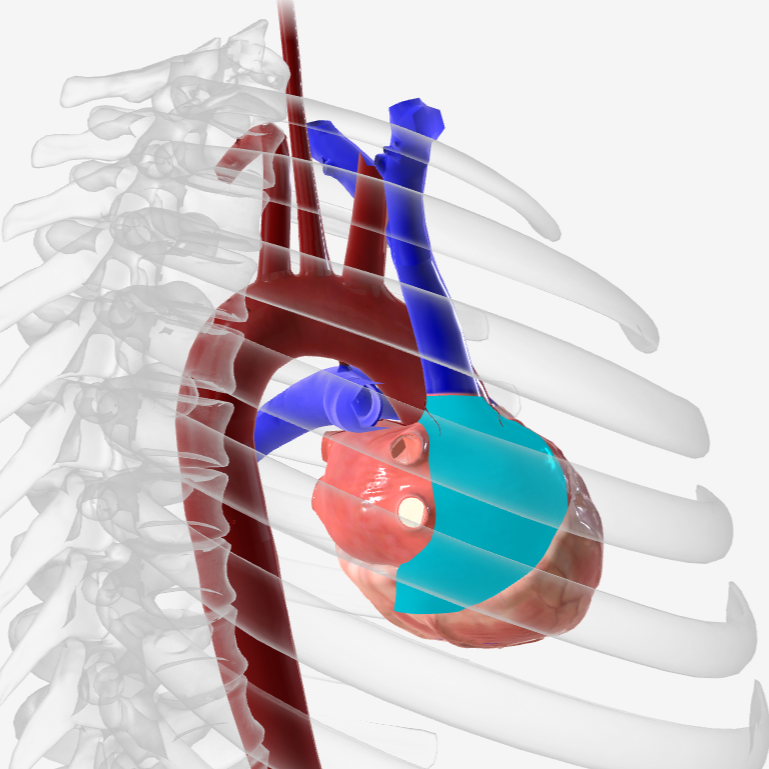
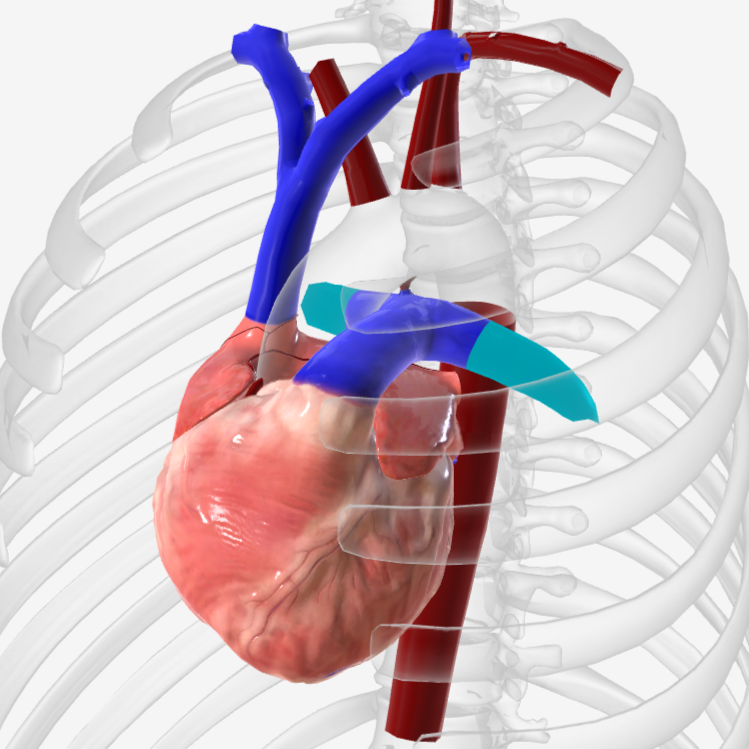
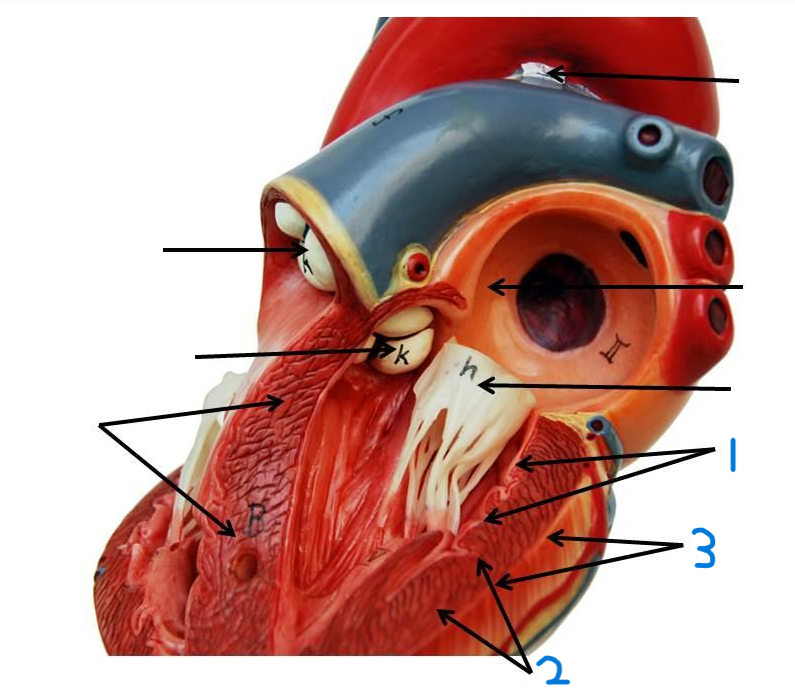
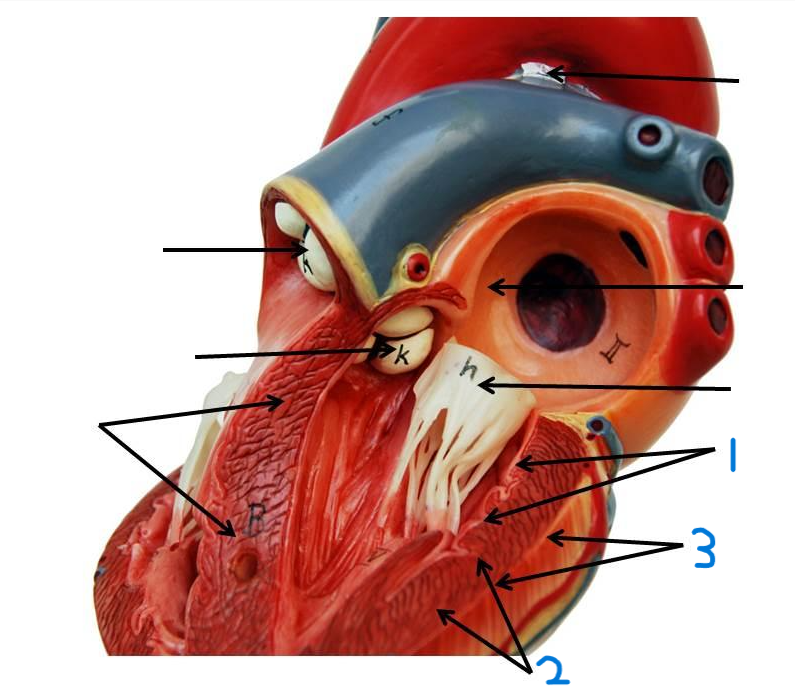
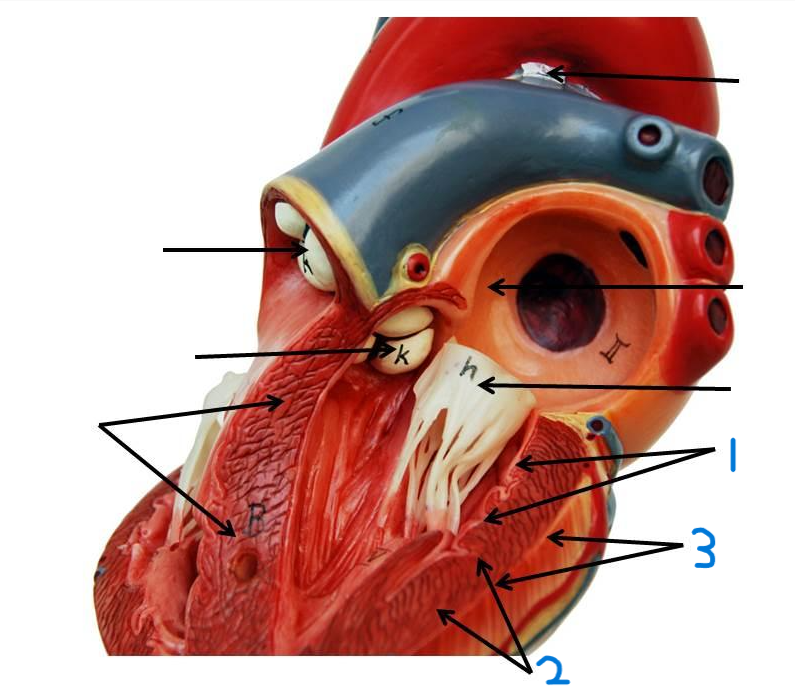
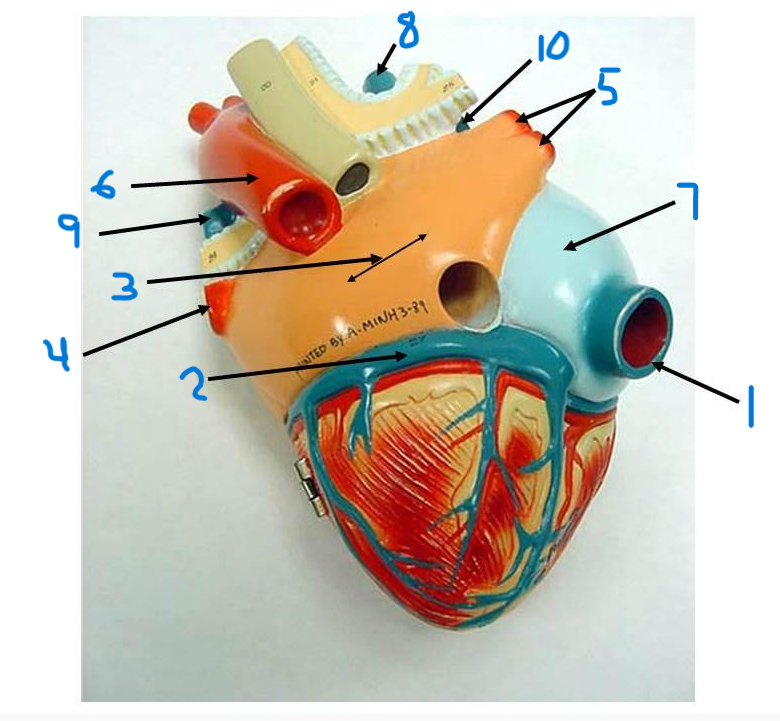
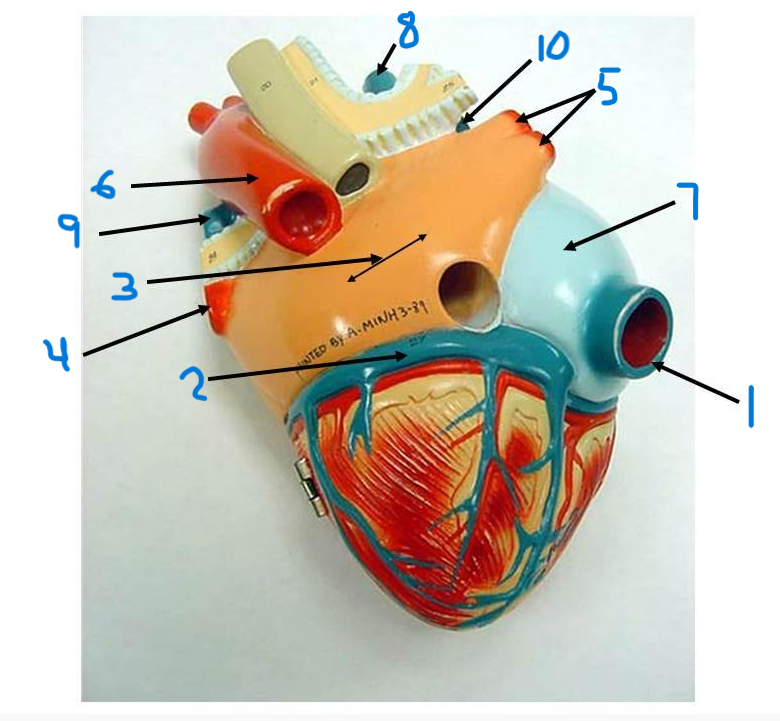
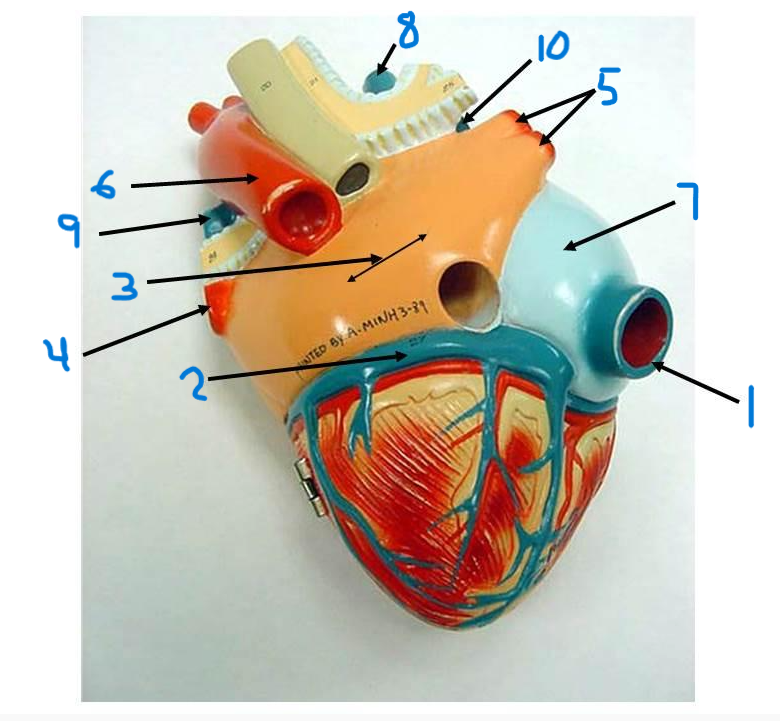
what is structure 1?
pulmonary trunk
what is structure 2?
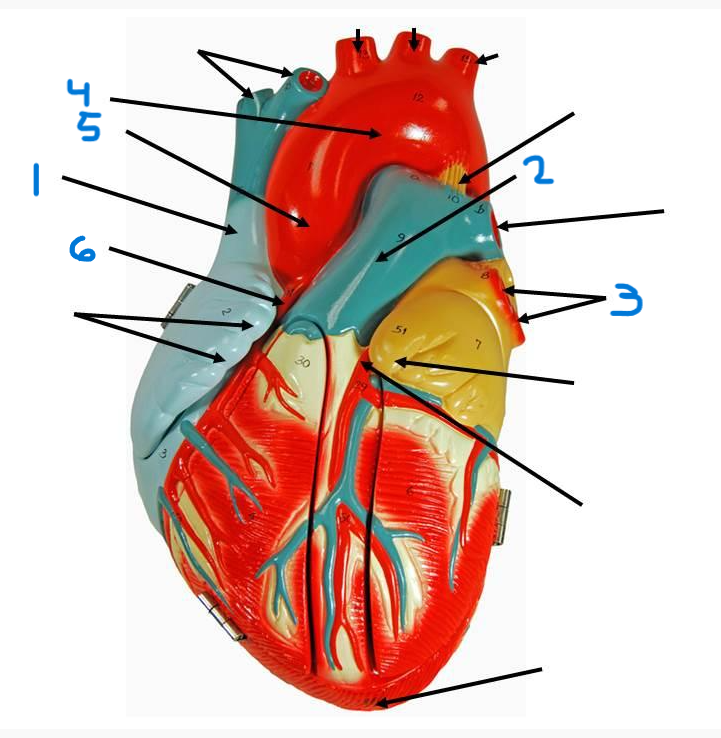
left pulmonary veins
what is structure 3?
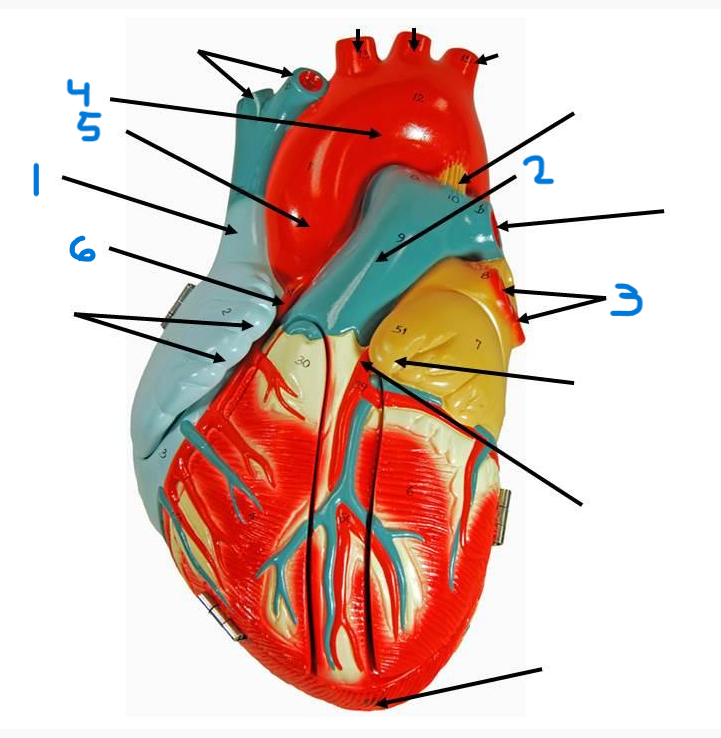
aortic arch
what is structure 4?
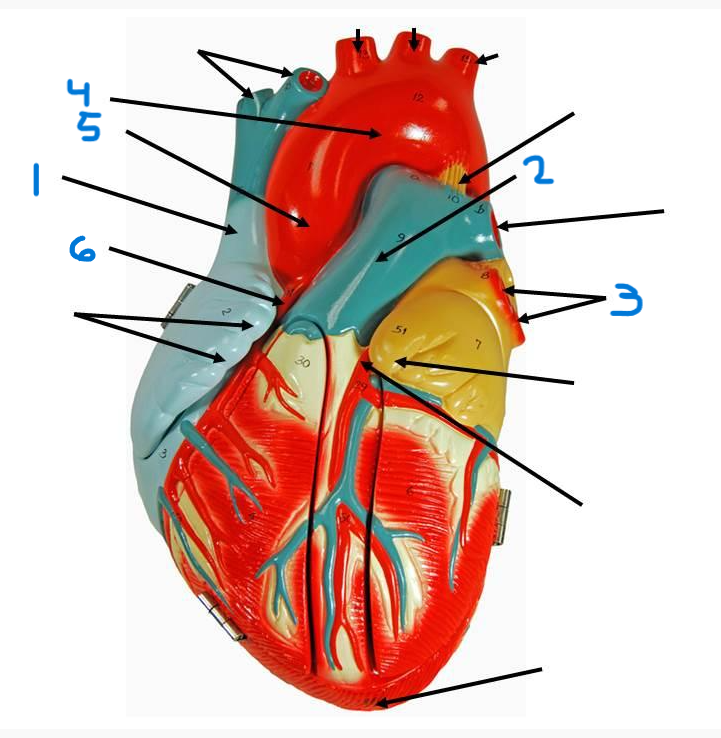
ascending aorta
what is structure 5?
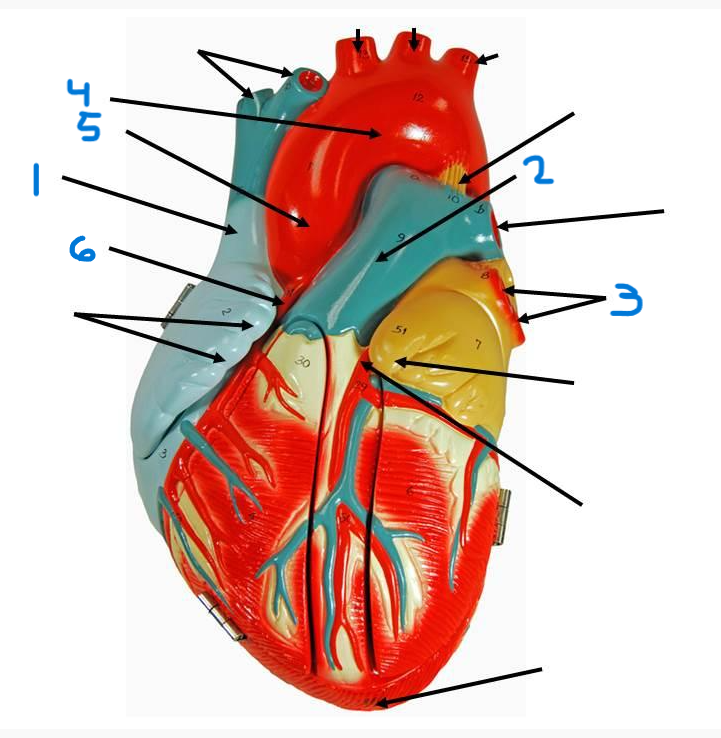
right coronary artery
what is structure 6?
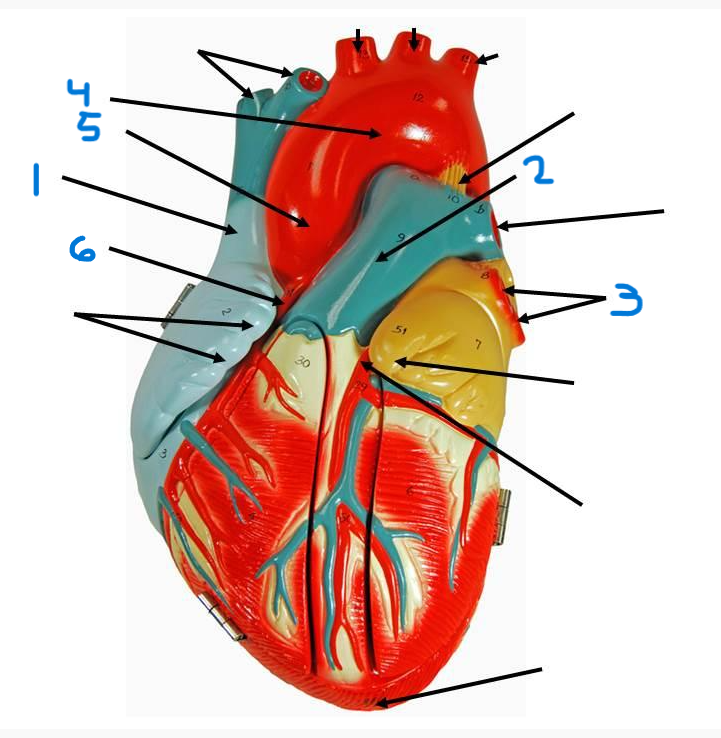
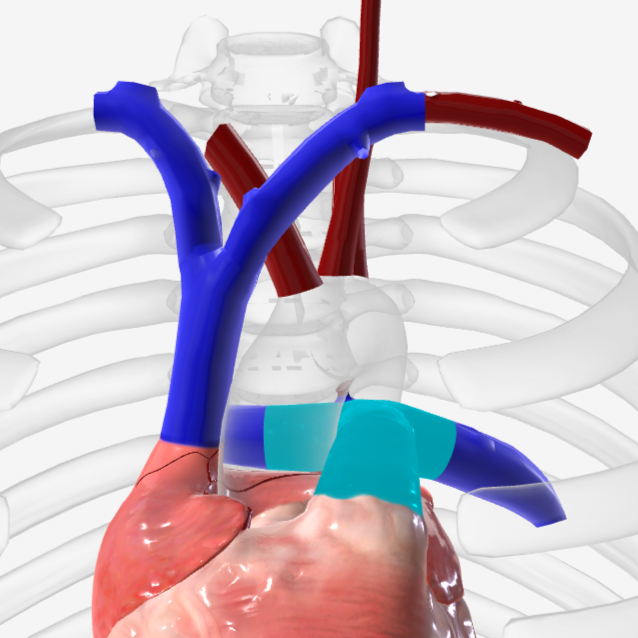
inferior vena cava
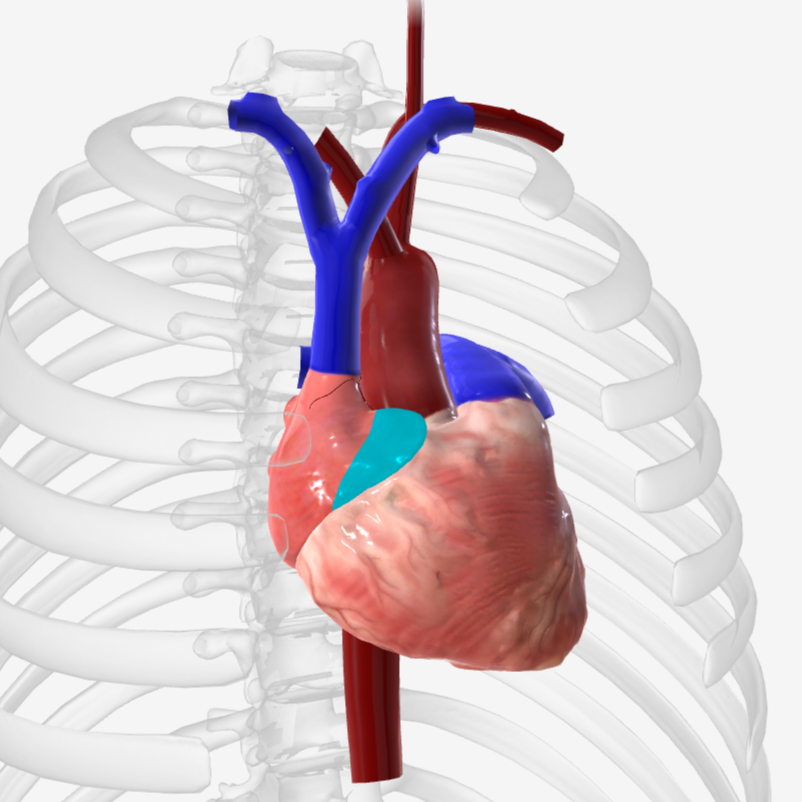
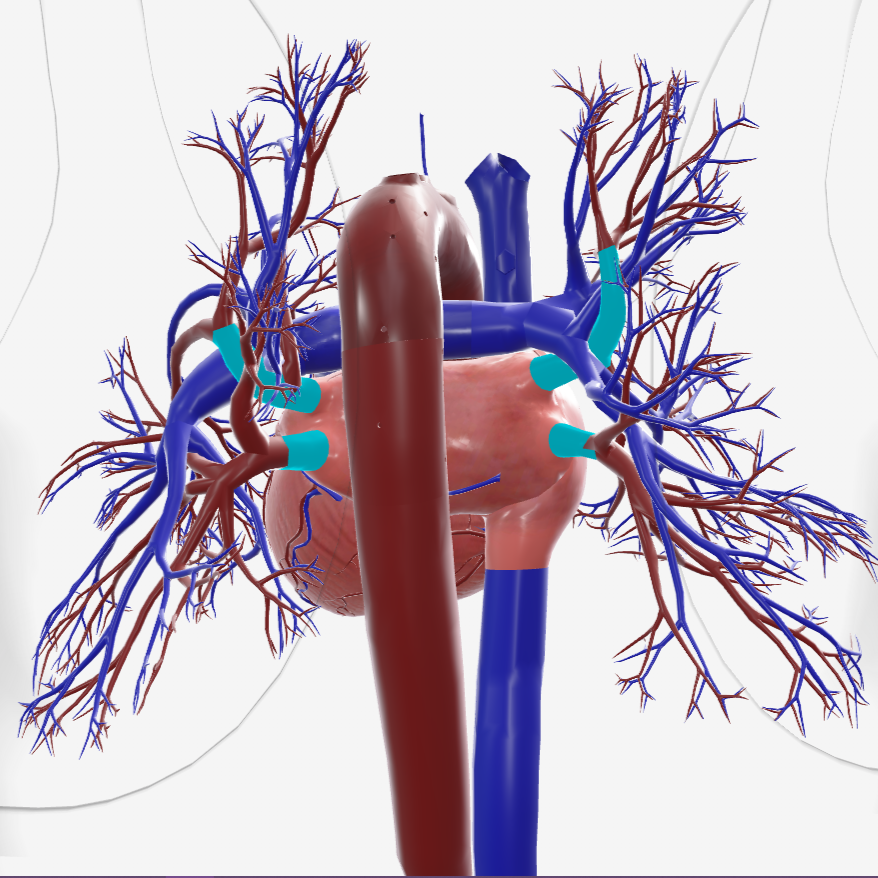
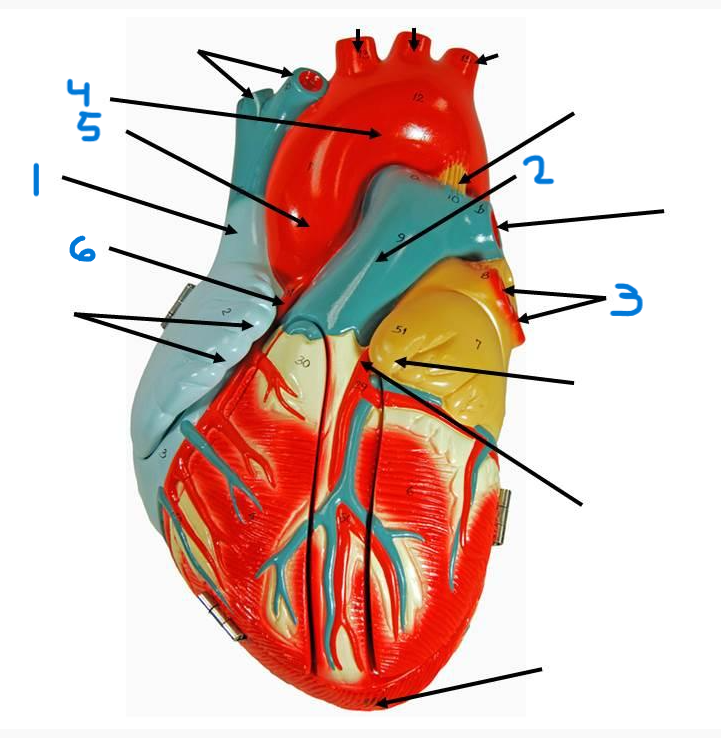
what is structure 1?
coronary sinus
what is structure 2?
left atrium
what is structure 3?
left pulmonary veins
what is structure 4?
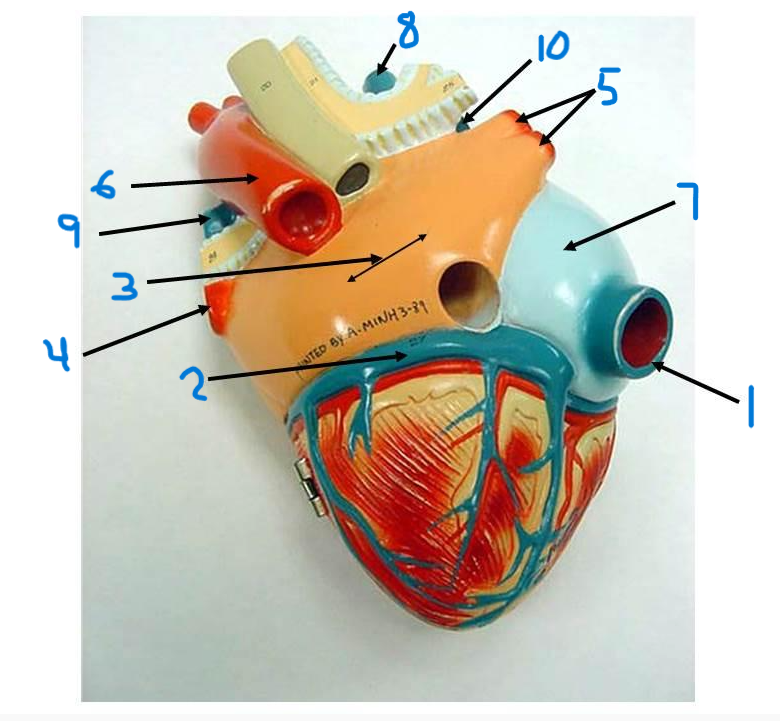
right pulmonary veins
what is structure 5?
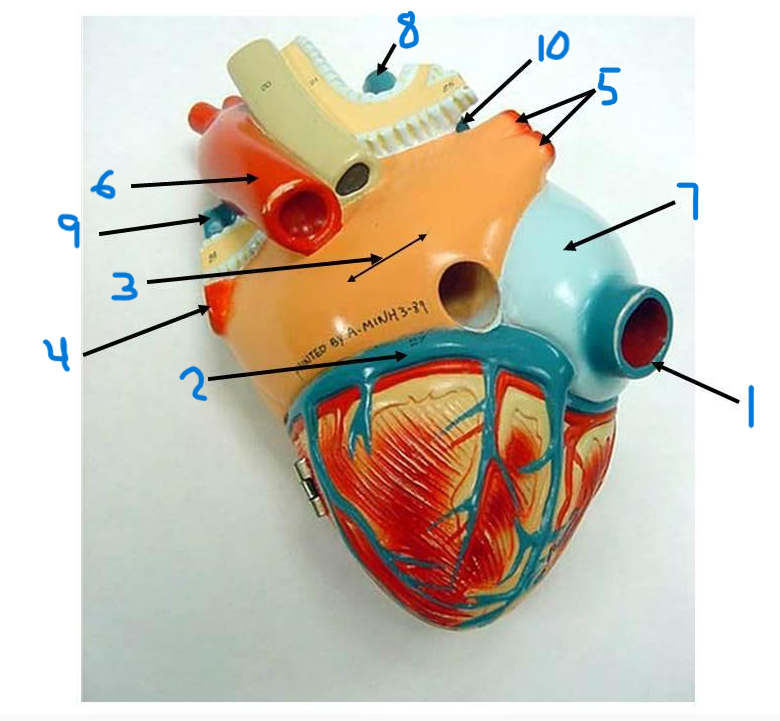
descending aorta
what is structure 6?
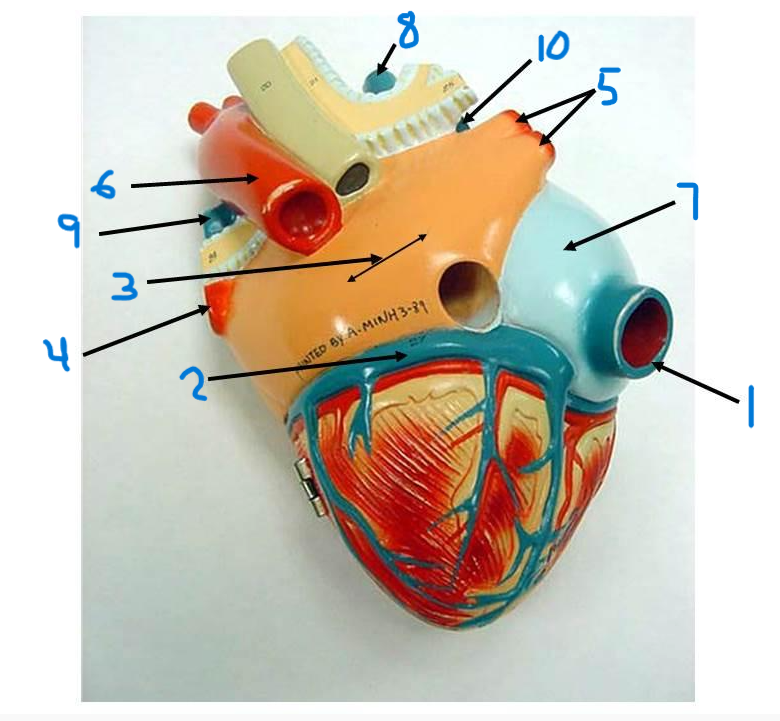
right atrium
what is structure 7?
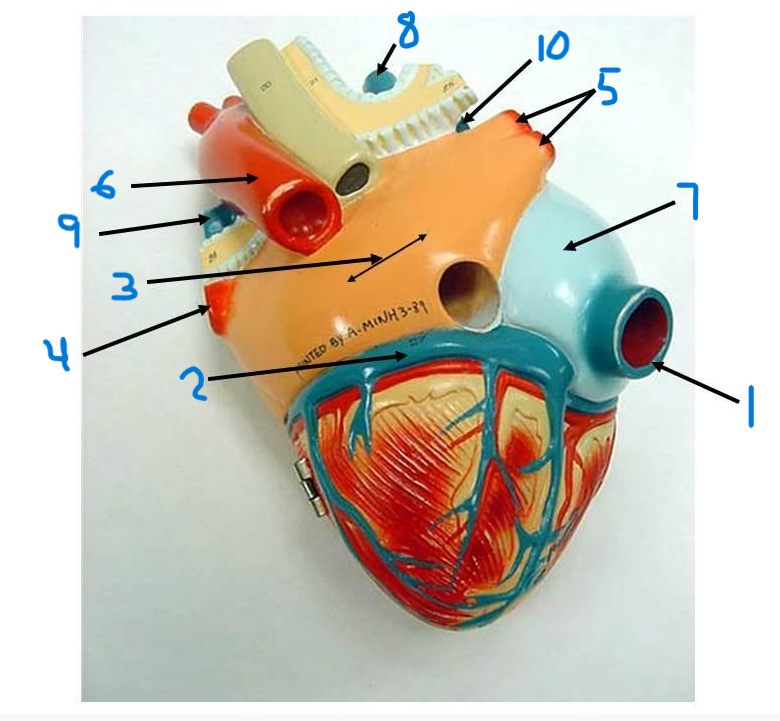
superior vena cava
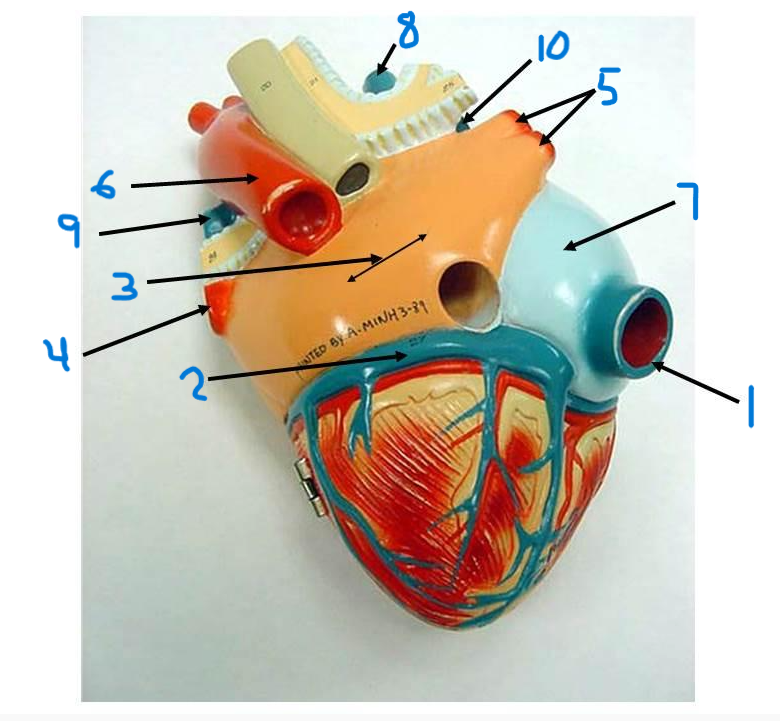
what is structure 8?
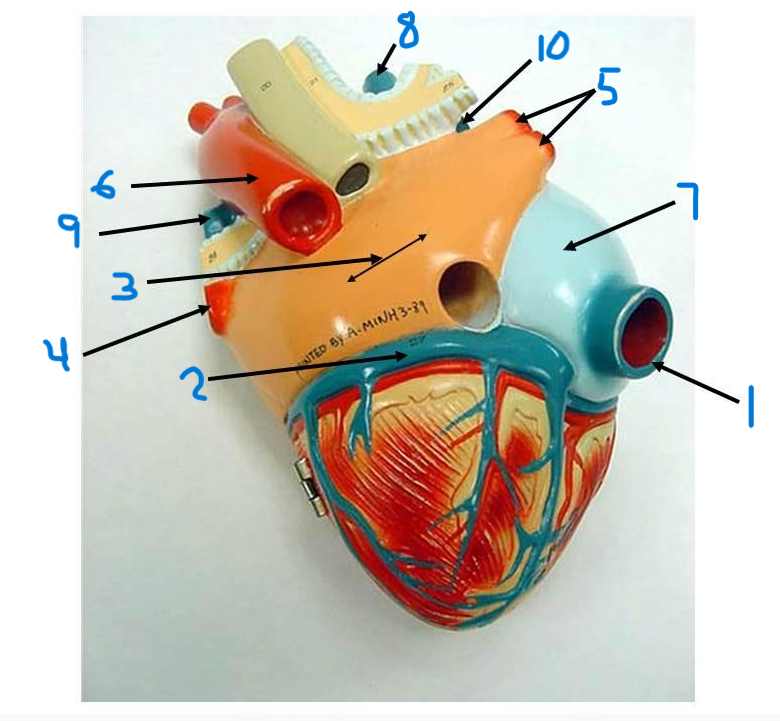
left pulmonary artery
what is structure 9?
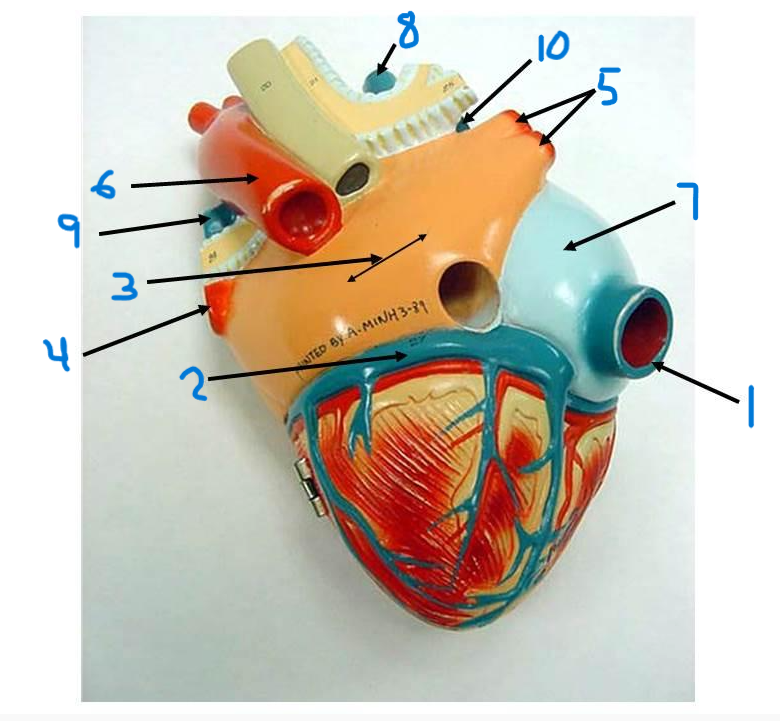
right pulmonary artery
what is structure 10?
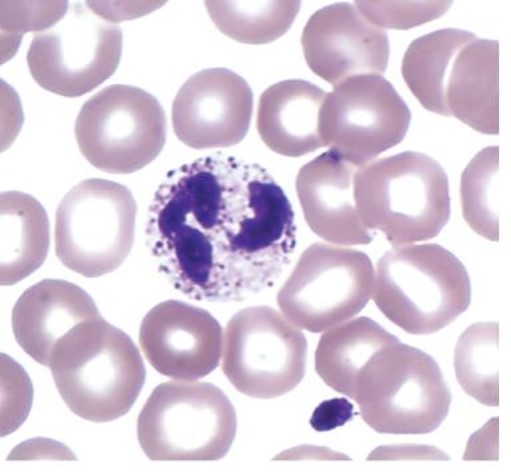
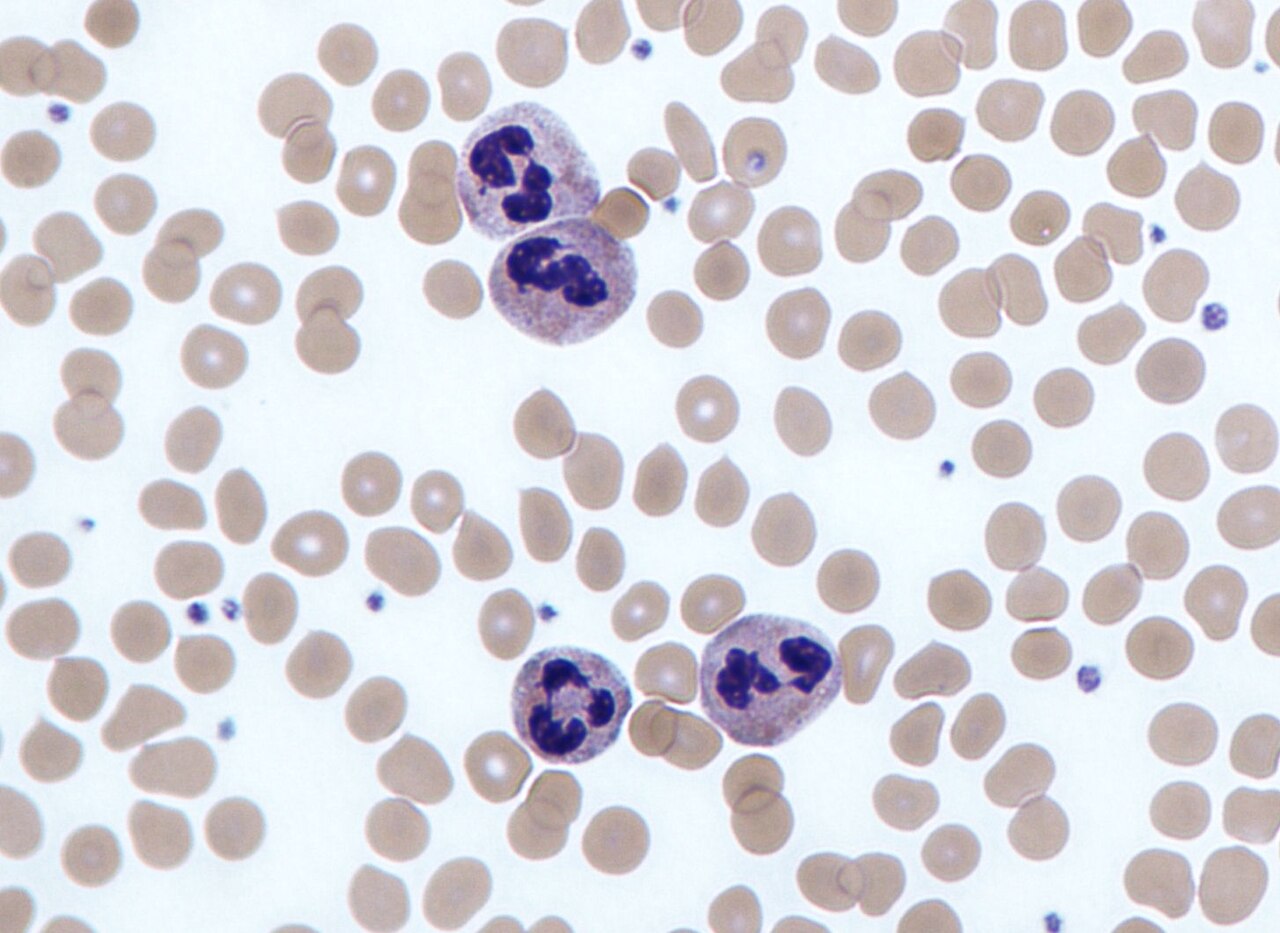
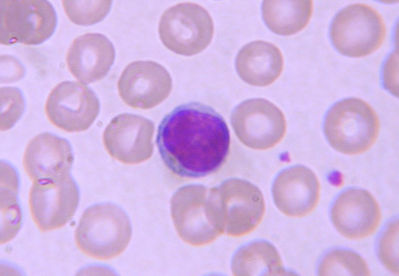
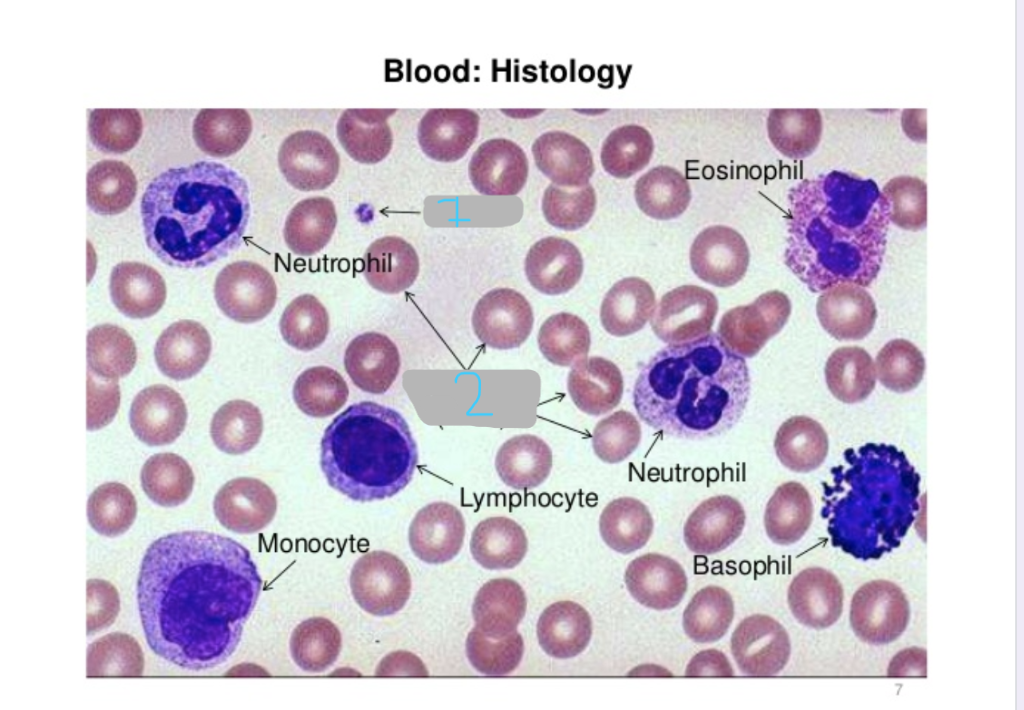
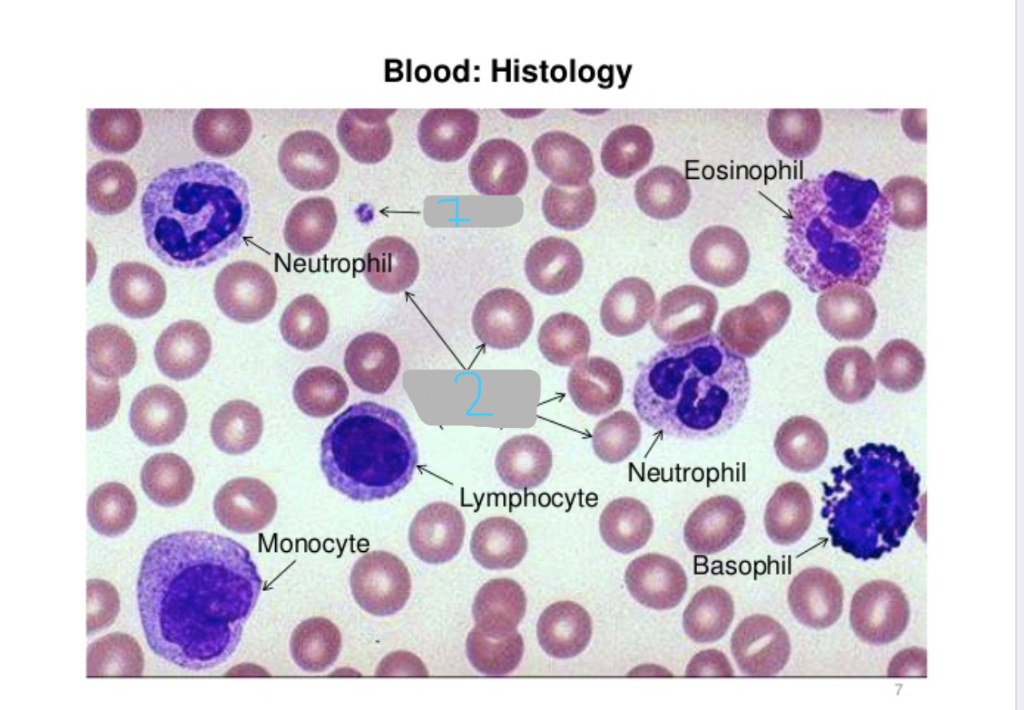
neutrophil
which leukocyte is this?
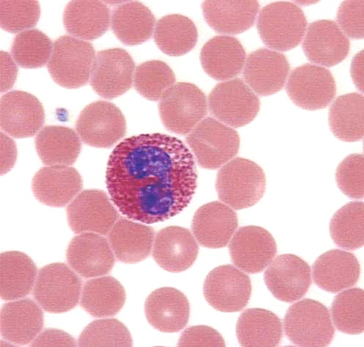
eosinophil
which leukocyte is this?
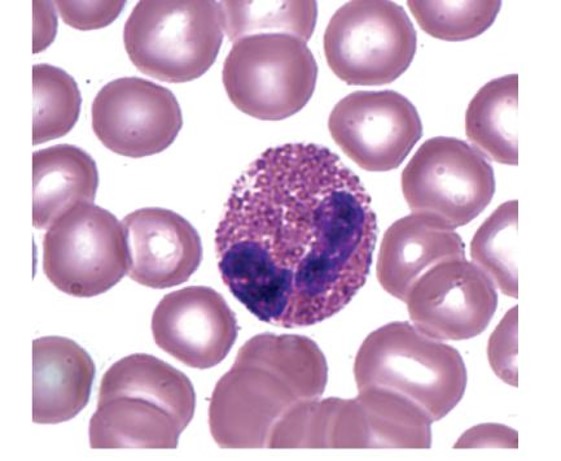
basophil
which leukocyte is this?
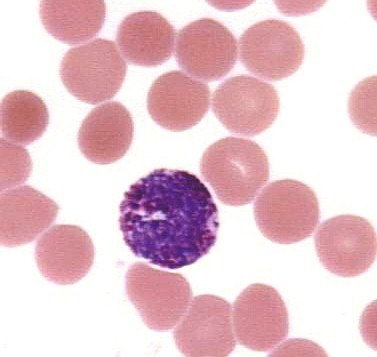
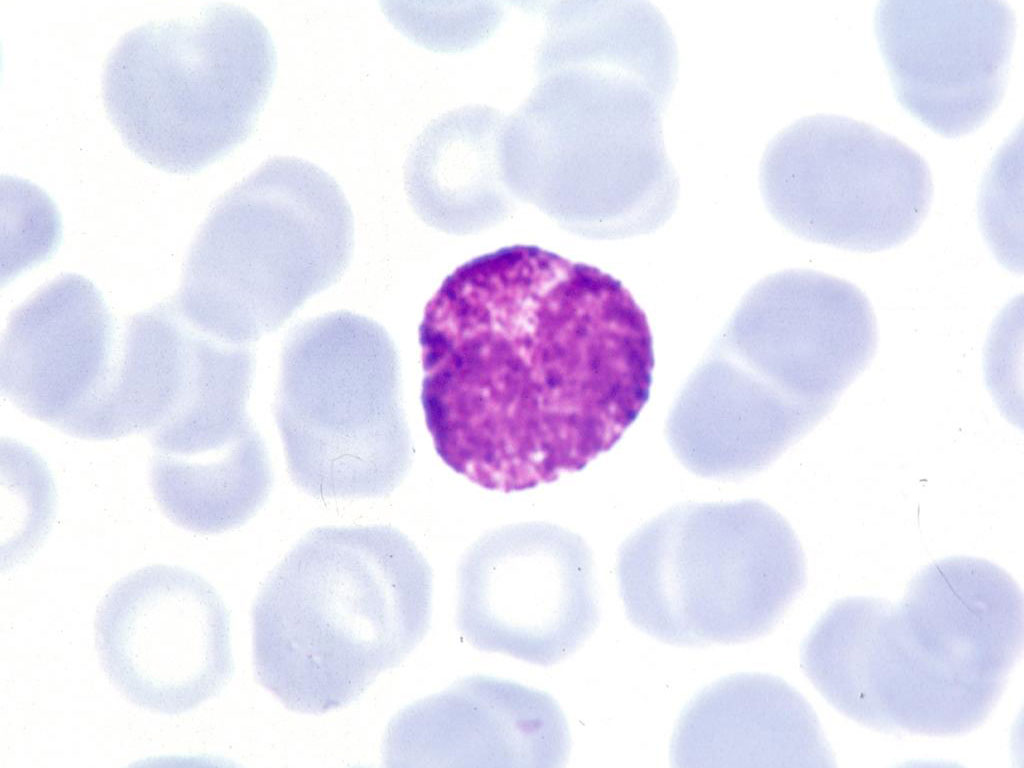
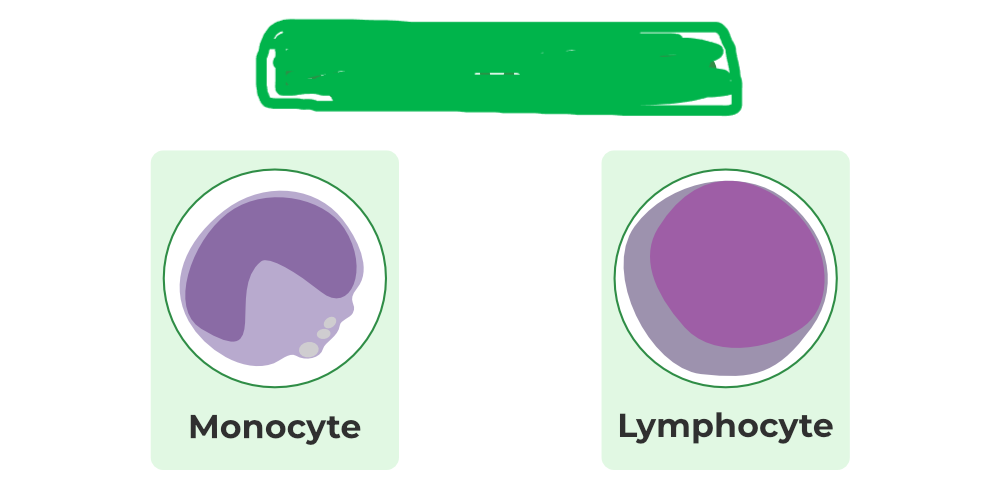
lymphocyte
which leukocyte is this?
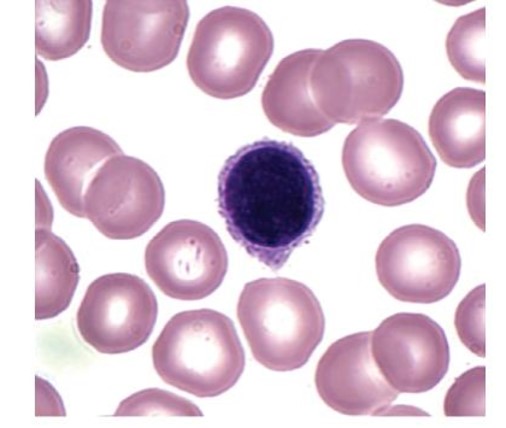
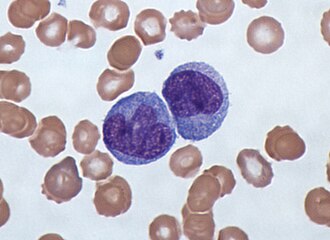
monocyte
which leukocyte is this?
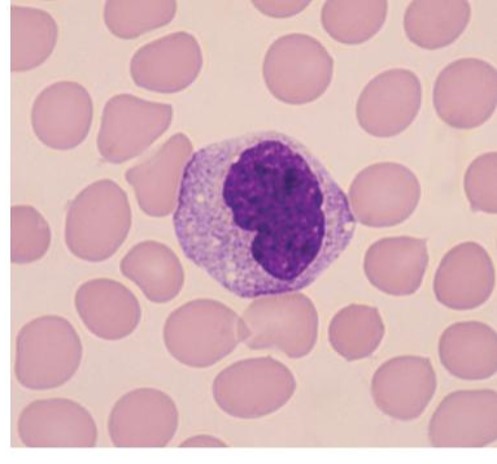
neutrophil
which leukocyte is this?
eosinophil
which leukocyte is this?
basophil
which leukocyte is this?
monocyte
which leukocyte is this?
lymphocyte
which leukocyte is this?
platelet
what is 1?
erythrocytes/red blood cells
what is 2?
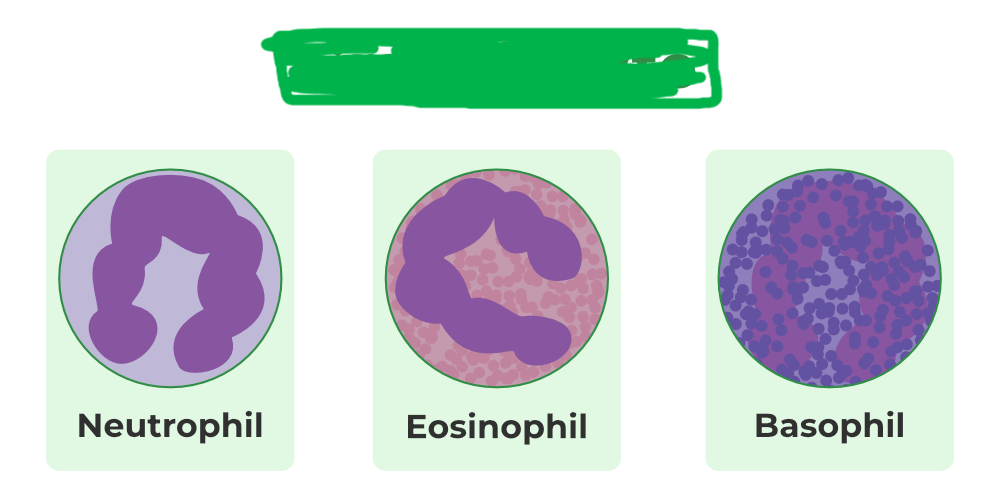
granulocytes/granular leukocytes
what group do these WBCs belong to?
agranulocytes / agranular leukocytes
what group do these WBCs belong to?
1%
White blood cells make up what percentage of blood volume?
never let monkeys eat bananas
what is the mnemonic used to remember the types of white blood cells and their relative abundance?
40-60%
The normal adult differential WBC count for neutrophils is…?
20-40%
The normal adult differential WBC count for lymphocytes is…?
2-8%
The normal adult differential WBC count for monocytes is…?
1-4%
The normal adult differential WBC count for eosinophils is…?
0.5-1%
The normal adult differential WBC count for basophils is…?
thrombocytes
platelets are also called…
megakaryocytes
platelets are fragments of their parent cells, called…
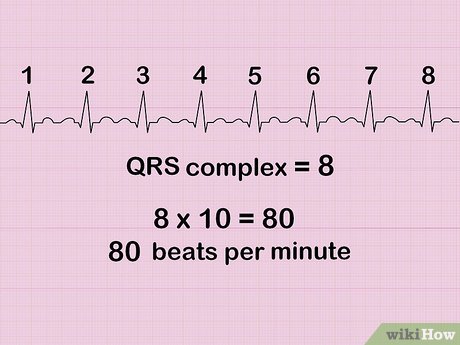
6 (six) seconds
how many seconds long is this strip?
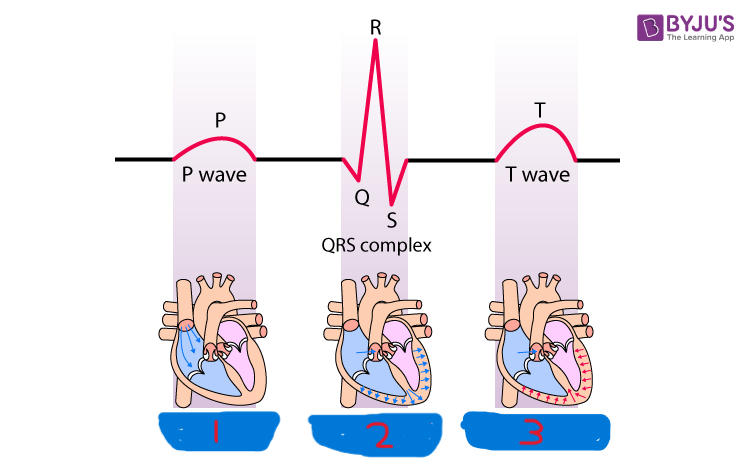
P wave
what is segment 1?
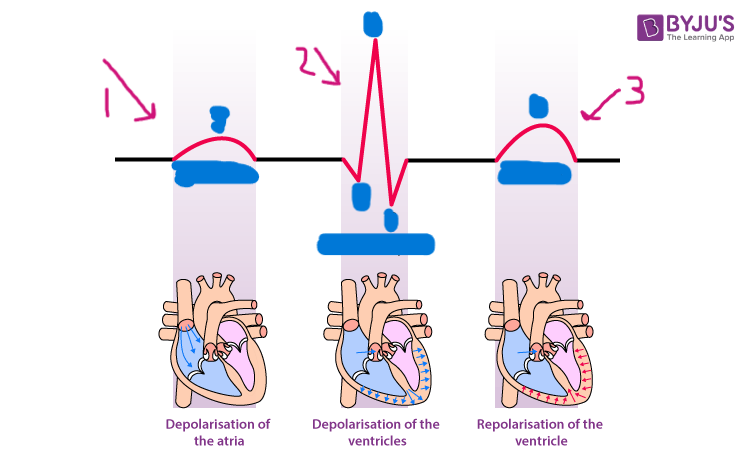
QRS complex
what is segment 2?
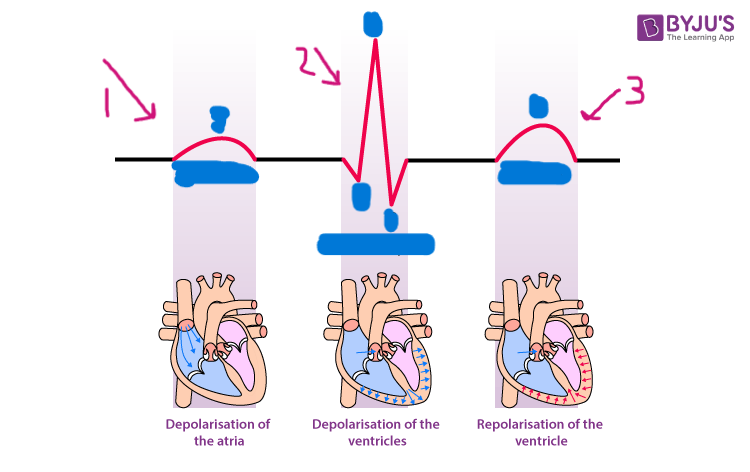
T wave
what is segment 3?
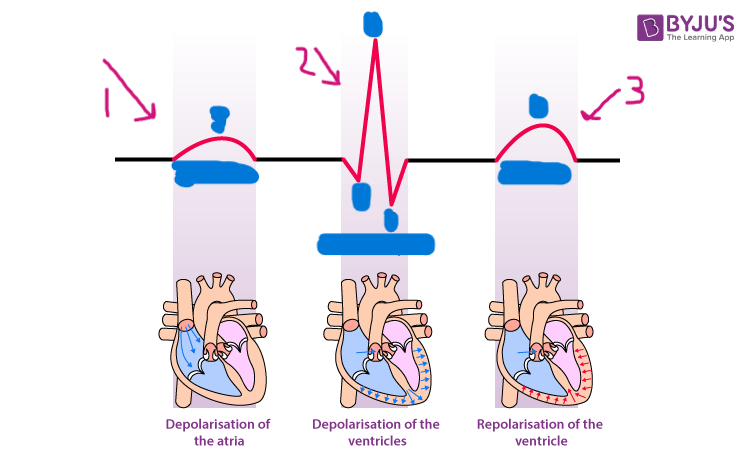
atrial depolarization
what happens during the P wave?
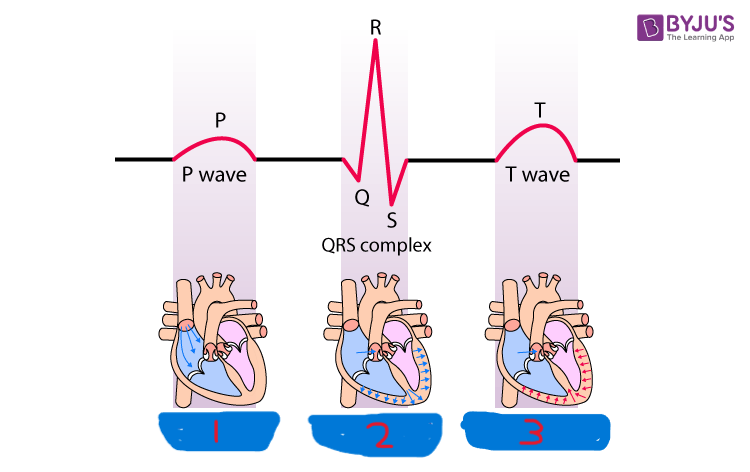
ventricular depolarization
what happens during the QRS complex?
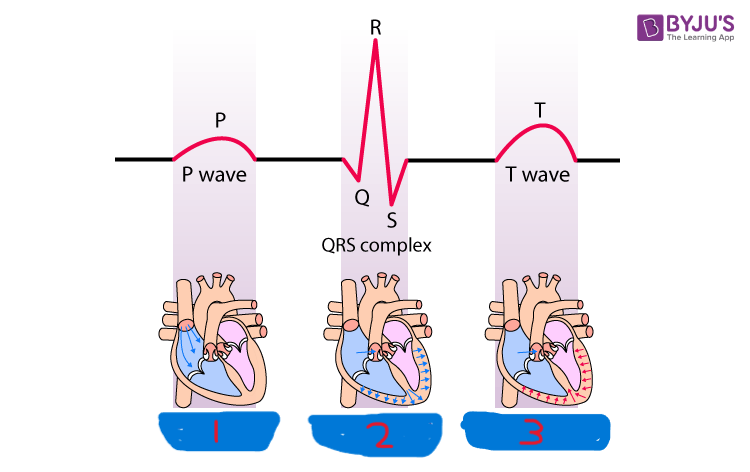
ventricular repolarization
what happens during the T wave?
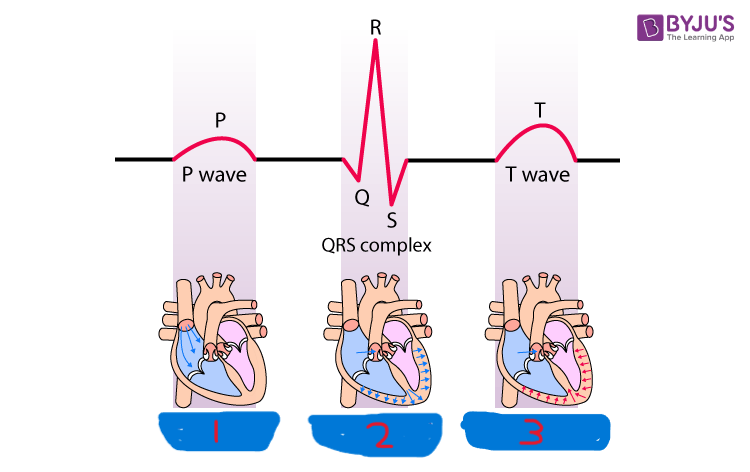
atrial repolarization
what isn’t shown during the QRS complex?
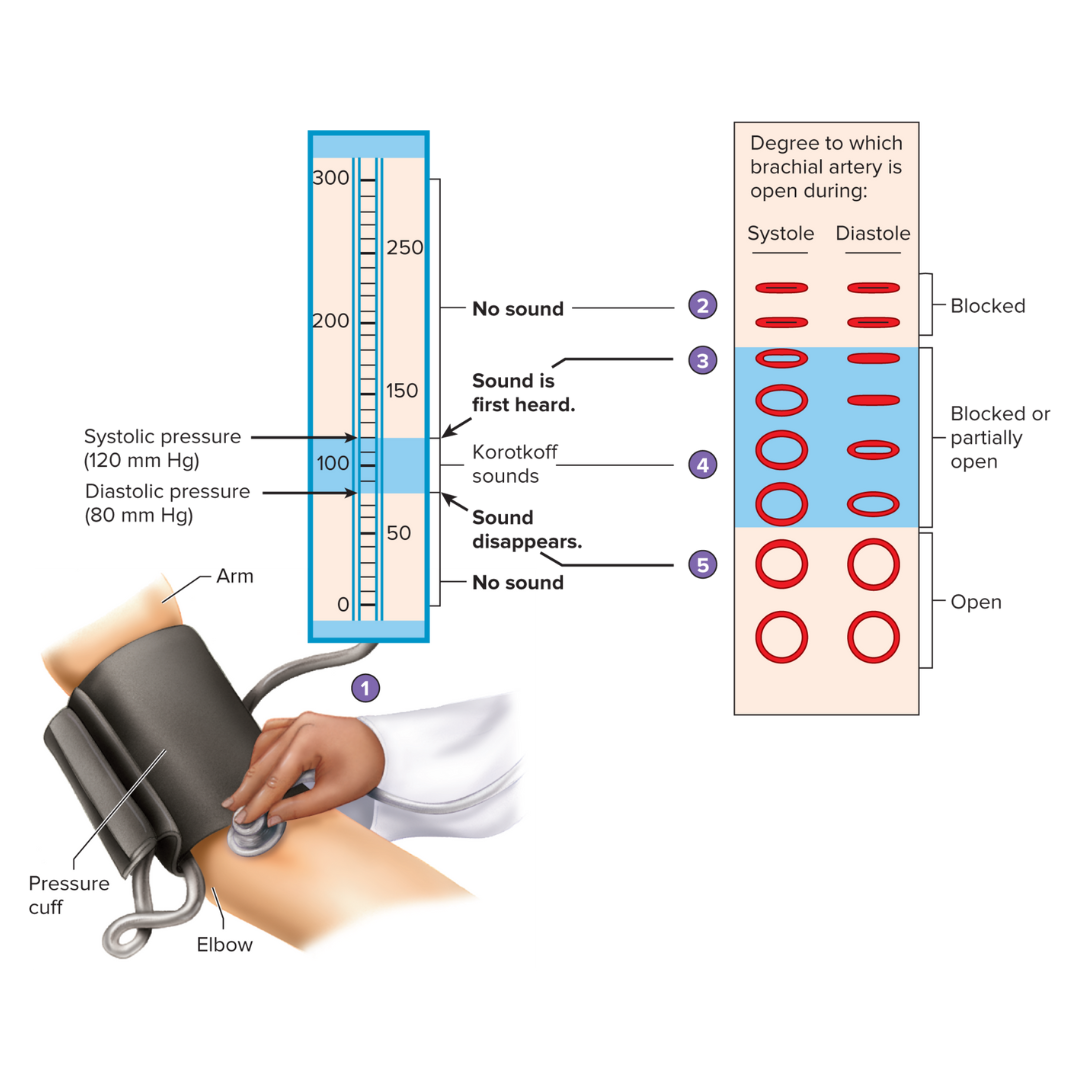
blood pressure readings
what is this describing? study the picture
agglutination
describe this phenomena…
When the binding of antibodies to the agglutinogens leads to clumping of RBCs in a process called…
type A blood
A antigen on RBCs
anti-B antibodies in the plasma
type B blood
B antigen on RBCs
anti-A antibodies in the plasma
type AB blood
both A and B antigens on RBC
no antibodies in the plasma
type O blood
neither A nor B antigens on the RBCs
both A and B antibodies in the plasma
Rh+ (Rh positive)
blood containing an Rh agglutinogen is considered…
Rh- (Rh negative)
blood lacking the Rh agglutinogen is considered…
true
True or false…
the production of Rh antibody requires prior exposure to the antigen
A+
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: A and Rh
Antibodies present in Plasma: Anti-B
A-
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: A
Antibodies present in plasma: Anti-B and Anti-Rh
B+
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: B and Rh
Antibodies present in plasma: Anti-A
B-
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: B
Antibodies present in plasma: Anti-A and Anti-Rh
AB+
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: A, B, and Rh
Antibodies present in plasma: none
AB-
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: A and B
Antibodies present in plasma: Anti-Rh
O+
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: Rh
Antibodies present in plasma: Anti-A and Anti-B
O-
name the blood group
Antigens/Agglutinogens present on RBCs: none
Antibodies present in plasma: Anti-A, Anti-B, and Anti-Rh
Anti-D
Anti-Rh can also be called…
negative agglutination
name the phenomena:
when no agglutination has occurred during a blood typing test, displaying that there are no agglutinogens on the RBCs in the sample
positive agglutination
name the phenomena:
when agglutination has occurred during a blood typing test, displaying that there is a certain agglutinogen on the RBCs in the sample
O-
What blood type is the universal donor?
AB+
What blood type is the universal recipient?
Rh-
Rh- can only receive blood from…
Rh+ and Rh-
Rh+ can receive blood from…
leukemia
cancers of the red bone marrow in which one or more white blood cells types is produced
thrombocytopenia
reduction in the number of platelets that leads to chronic bleeding through small vessels and capillaries
type A blood
can receive blood from: A, O
can donate blood to: A, AB
type B blood
can receive blood from: B, O
can donate blood to: B, AB
type AB blood
can receive blood from: A, B, AB, O (universal recipient)
can donate blood to: AB only
type O blood
can receive blood from: O only
can donate blood to: A, B, AB, O (universal donor)