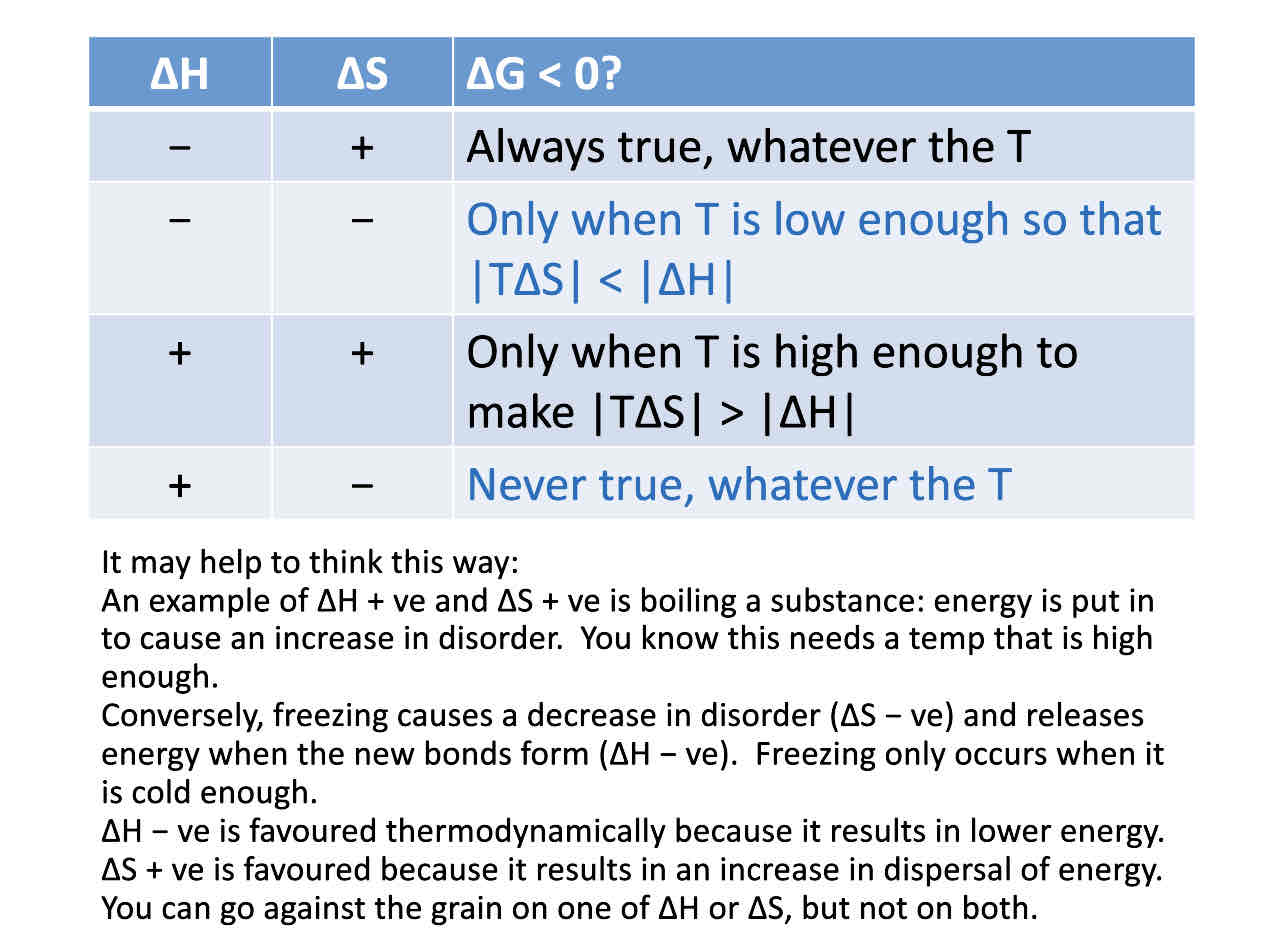
5D lattice enthalpy change
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is lattice enthalpy change
The enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of one mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
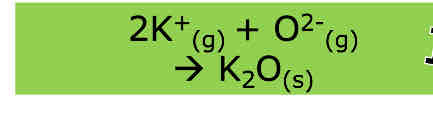
What is enthalpy of ionisation energy
The enthalpy change required to remove one electron from each atom/ion in a mole of gaseous atoms/ions to form one mole of gaseous ions of equal charge
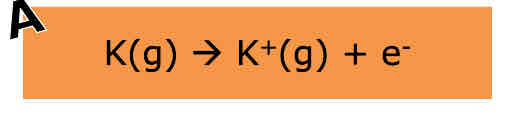
What is enthalpy of electron affinity
The enthalpy change required to add one electron to each atom/ion in a mole of gaseous atoms /ions to form one mole of gaseous ions with an equal charge
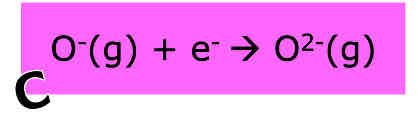
What is enthalpy of atomisation
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from an element in its standard state under standard conditions
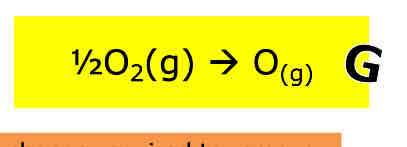
What is enthalpy change of formation
The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements under standard conditions
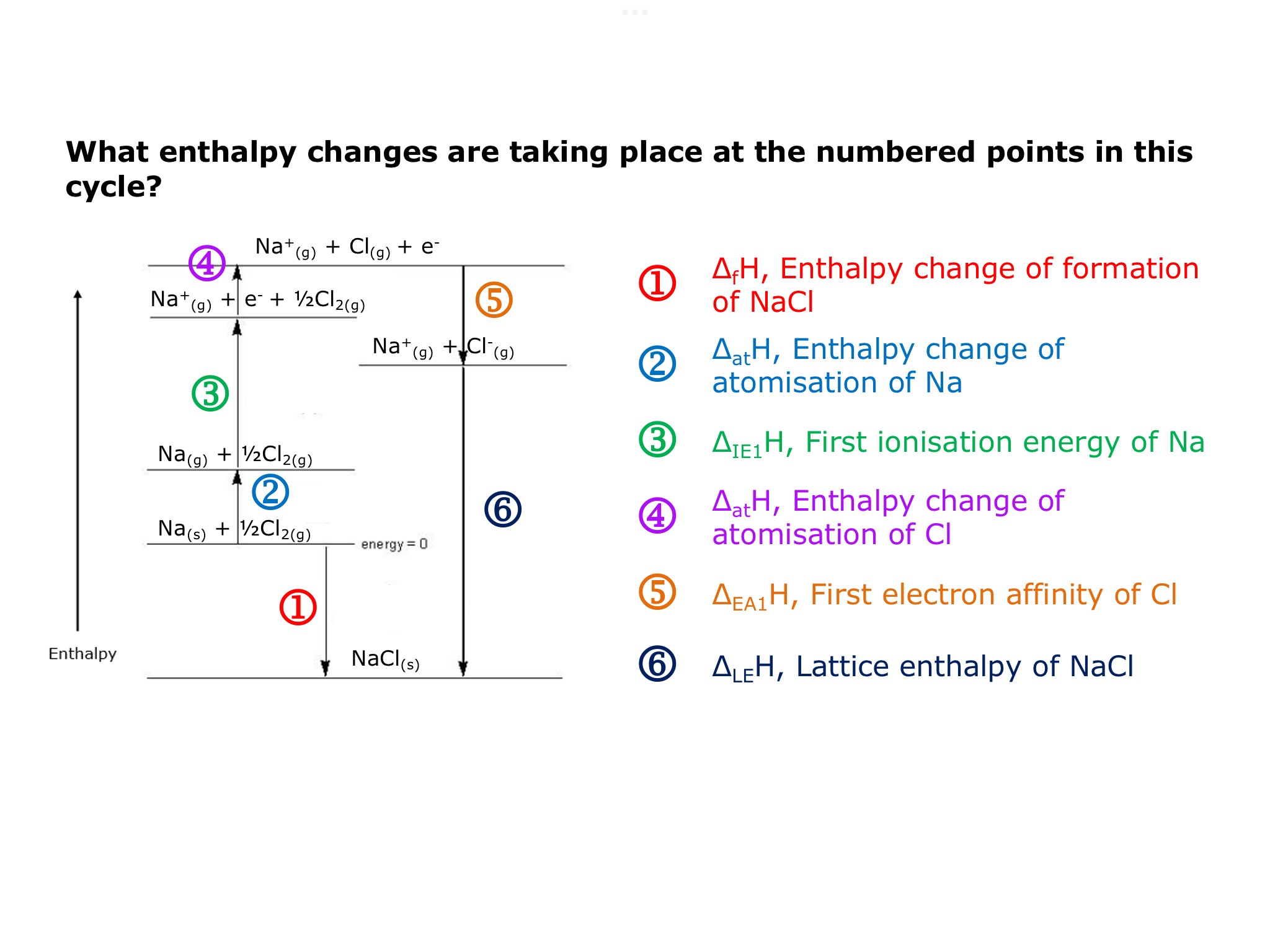
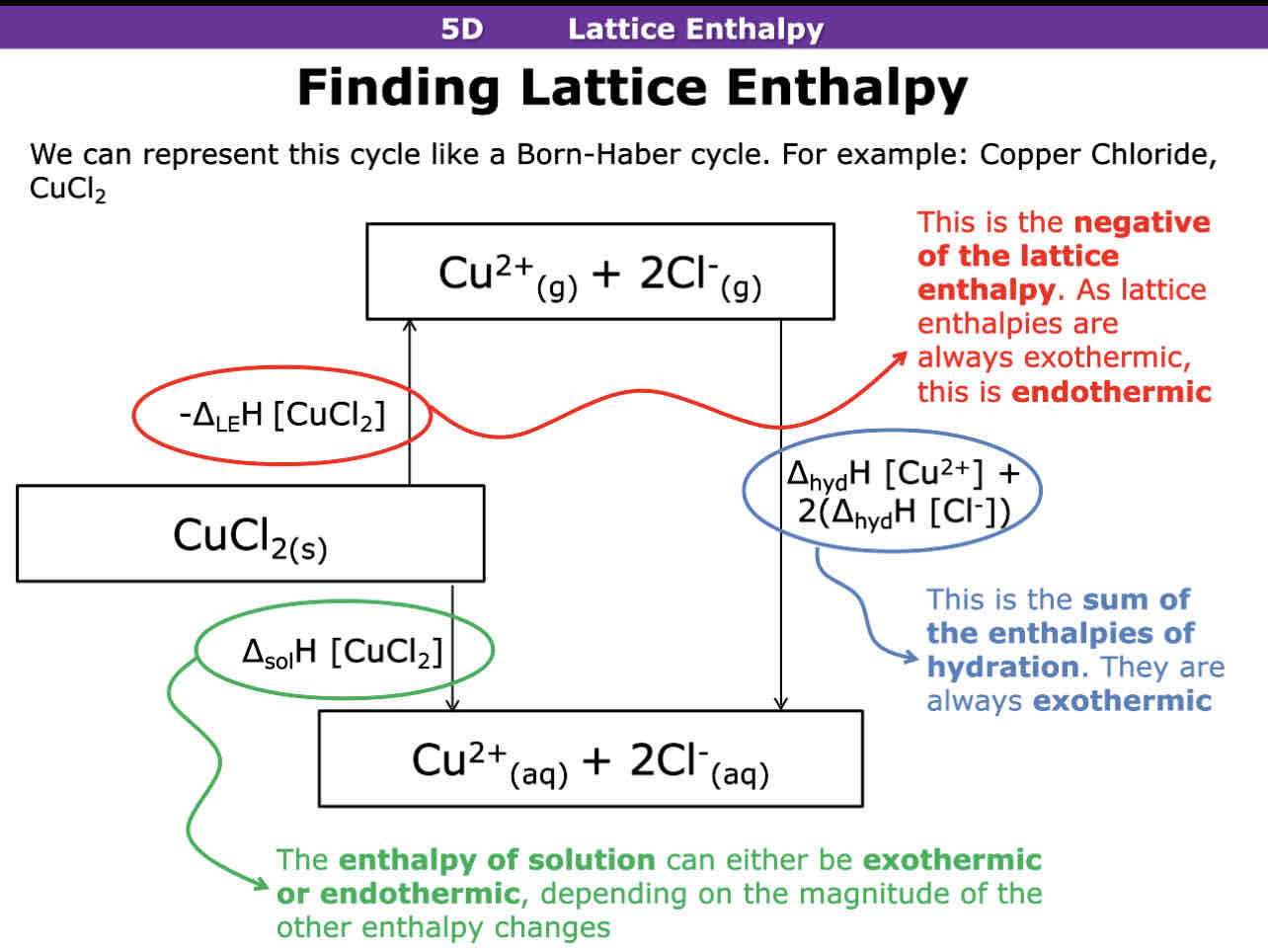
How does born Haber cycle work

Structure of born haber cycle
What is standard enthalpy change of solution
The enthalpy change when one mole of solute dissolves to form a dilute solution
What is standard enthalpy change of hydration
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions forms a solution
What happens when an ionic solid dissolves in water
Ionic lattice breaks up to release ions
Ions bond to water molecules forming the solution
Changes that may occur from solid ions going to aqueous ions
Solid ions to gaseous ions
Gaseous ions to aqueous ions
Is lattice enthalpy endothermic or exothermic?
Why?
Exothermic - because bonds are being formed
Is standard enthalpy of hydration endothermic or exothermic?
Why?
Exothermic - gaseous ions are forming bonds with water molecules
is enthalpy change of solution endothermic or exothermic
Can be either
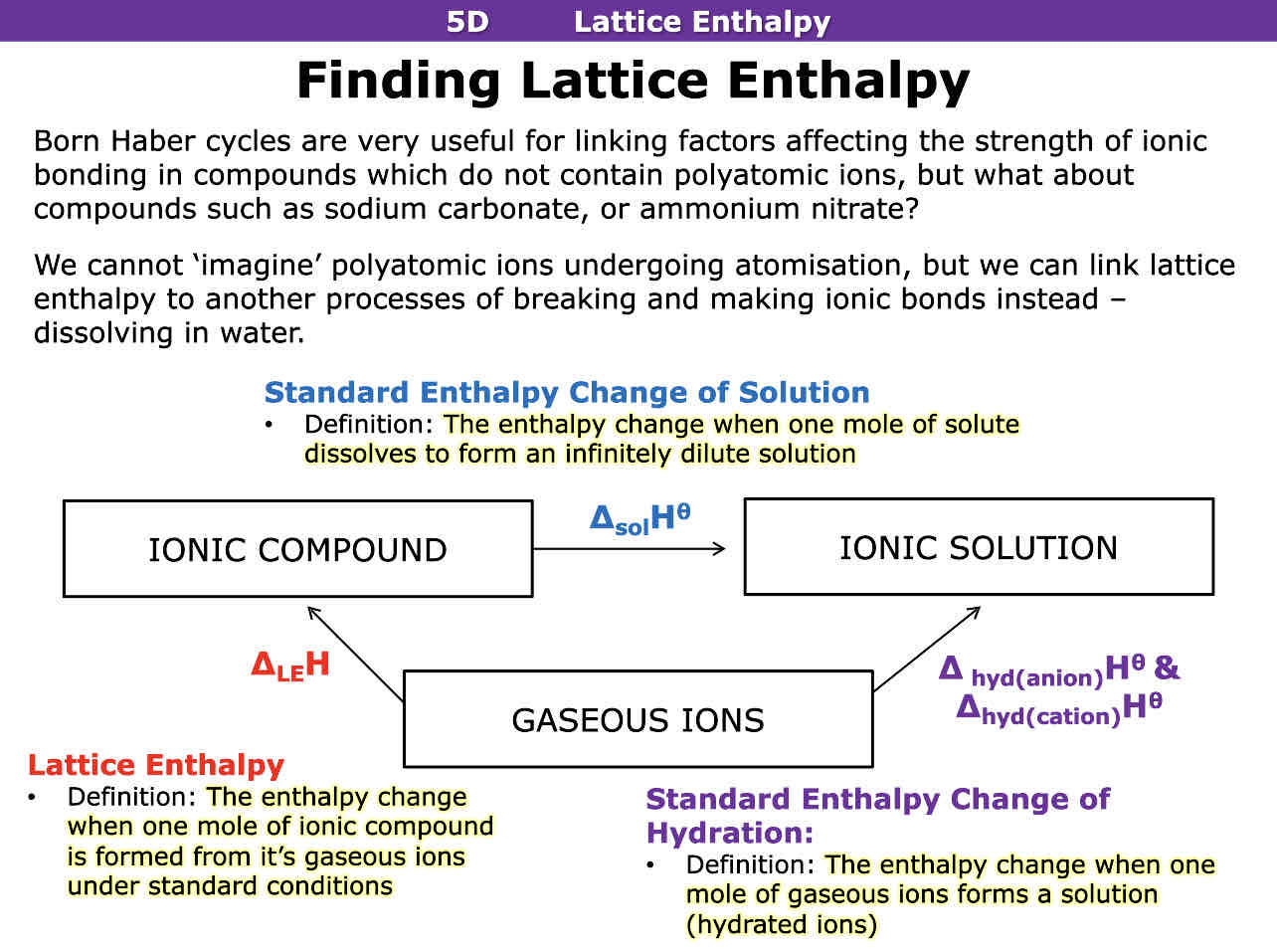
How do you calculate lattice enthalpy, enthalpy of solution or enthalpy of hydration
How to calculate enthalpy of solution
Q= m x c x delta t (change in temp) Solution mass x 4.18 x change in temp.
Mass of salt or mr to get moles
Do q/moles
Change sign
What are the factors that affect standard lattice enthalpy and enthalpy of hydration
Charge density - dependant on ionic radius or charge of ion
The smaller the radii and higher the charge means greater charge density
For standard lattice enthalpy the smaller the ionic radius and higher the charge means what
The greater the charge density of ions and stronger electrostatic attraction between ions so standard lattice enthalpy is more exothermic
For standard enthalpy of hydration the smaller the ionic radius and higher the charge means what
Greater charge density of ions involved
Stronger electrostatic attractions formed between ions formed between ions and water molecules so more exothermic
What is entropy
The quantitative measure of the degree of disorder in a system, the higher the entropy the more disordered the system is
Entropy units and equation

What has the most entropy solids liquids or gases
Gases = most
Liquids/ aqueous substances = middle
Solids = least
When talking about entropy talk about what
The disorder of the reaction and dispersal of energy
Do solids increase or decrease dispersal of energy
Decrease
What happens to entropy if moles of gas increases
Entropy increases

Predict entropy sign
If solids mention decrease in dispersal energy and decrease in disorder so delta S is negative
If gases mention an increase in dispersal energy and disorder so delta S is positive

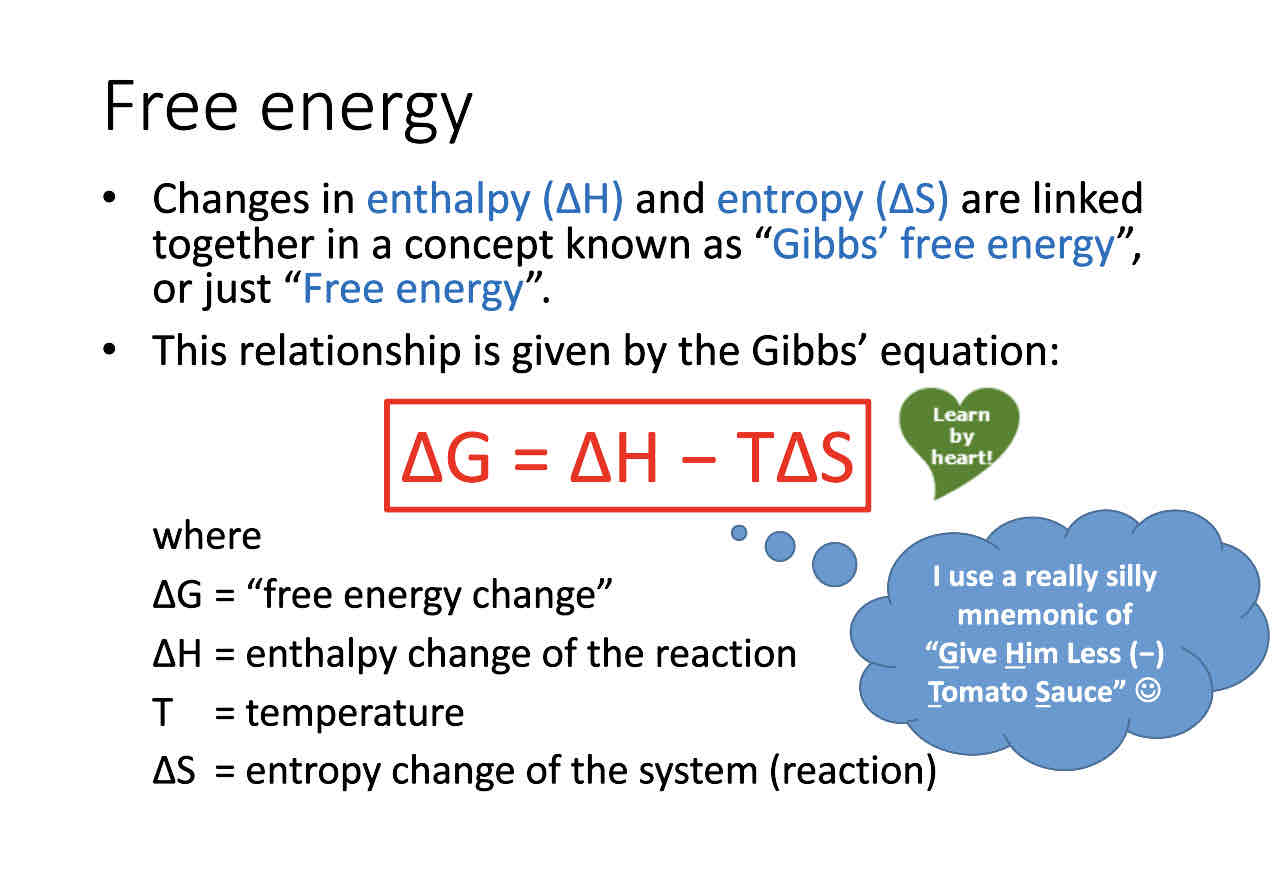
What is Gibbs equation
Delta G = free energy change
Delta H = enthalpy of reaction
T = temperature
Delta S= entropy
Units in gibbs equation
Delta G = kj mol ^-1
Delta H = kJ mol ^-1
Delta S is J so need to divide by 1000 to get kj k^-1 mol^-1
T = Kelvin
What is a feasible reaction
A reaction that is energetically possible
How do we know if a reaction is feasible
Delta G must be negative delta G<0
So of negative = feasible
If positive = not feasible
How do you calculate minimum temperature with gibbs equation
Delta H / Delta S

Explain question
Delta H is positive
Delta S is positive
Because reaction is feasible at high temperatures
In this case T delta S increases with temperature
At high temperatures delta G <0
At low temperatures delta G> 0