Chemistry-VSEPR/Polarity/IMF's
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
In polar compounds how are electrons shared
unequally
electronegativity
how much electrons are pulled and therefore one molecule holds on to the electrons longer creating a negative charge
= sharing of electrons
non-polar
un = sharing of electrons
polar
Dipole
has 2 poles
0-0.5
nonpolar
0.5-2
polar
2.0-3.3
ionic compound
how does shape affect polarity
a bent shape means a polar molecule
a linear shape most likely means nonpolar
How are nonbonded (unpaired) electrons different from bonded electrons
they take up more space
What are the 4 types of electrons
non bonded (lone pairs)
single bond
double bond
tripple bond
what are electrons domains
the type of electrons that exist around the central atom/ space where electrons exist
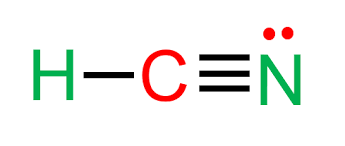
How many e.d. are present
2
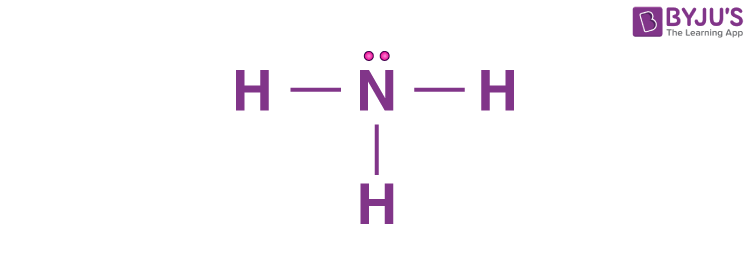
How many e.d. are present
4
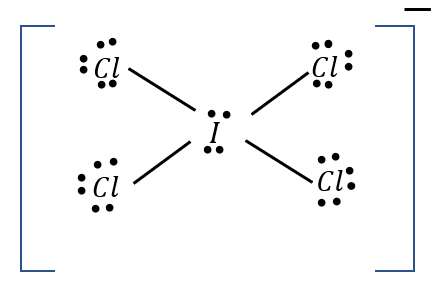
How many e.d. are present
6
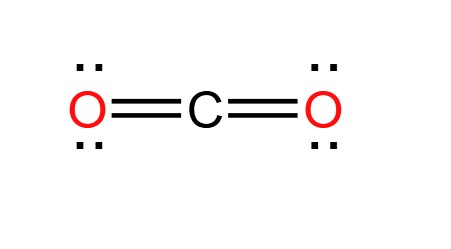
How many e.d. are present
2
how many electrons can the s orbital hold
2
how many electrons can the p orbital hold
6
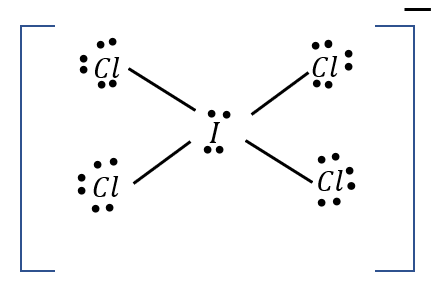
what is the hybridization of this atom?
sp3d2
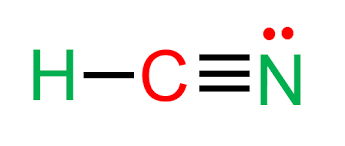
what is the hybridization of this atom?
sp
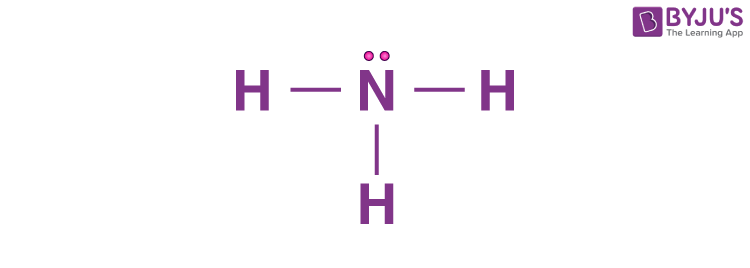
what is the hybridization of this atom?
sp3
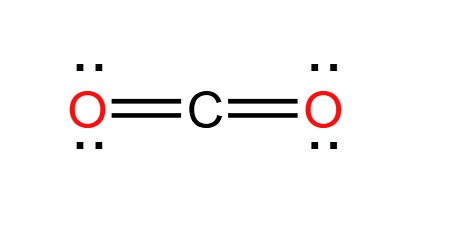
what is the hybridization of this atom?
sp
true or false: lone pairs repel more strongly than bonded pairs
true
What is VSEPR notation
AXaEb
What does A stand for in AXaEb
the central atom
What does X stand for in AXaEb
the number of bonded pairs (this goes to a)
What does E stand for in AXaEb
the number of lone pairs (this goes to b)
Do you write the subscript for 1 in VSPER notation?
no, just the letter
Where there are 0 lone pairs or bonds do you write the letter in VSPER notation?
no
True or false: lone pairs affect bond angles
True
What is the difference between intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces
INTRAmolecular forces-connects chemical bonds (like super glue)
INTERmolecular- forces that bine compounds
examples of INTRAmolecular forces
ionic and covalent bond
what are INTERmolecular forces represented by?
a dotted line
What do intermolecular forces affect?
Physical properties: melting point, boiling point, and surface tension
what is surface tension
the ability for an object to rest on top of a liquid.
What IMF can every molecule make
LDF
What are the strongest IMF’s
ionic forces
Ion-ion
forces between ionic compounds
ion-dipole
force of attraction between ion and covalently bonded polar molecule.
example of ion-dipole
ionic compound being dissolved in a polar solvent.
Dipole-dipole
attraction between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules
what bond does every polar molecule have
dipole-dipole
Hydrogen bond
molecule must have hydrogen covalently bonded to Nitrogen,Oxygen, or Fluoride
Nitrogen,Oxygen, or Fluoride must have a lone pair attached to it.
Are hydrogen bonds strong
yes
do hydrogen bonds have a high melting point
yes
weakest IMF
LDF
LDF
molecule with an instantaneous dipole
instantaneous dipole
all electrons move to 1 side at some point (even if not a dipole)
induced dipole
follows after an instantaneous dipole
Do LDF’s last long
no, they end just as quickly as they start
What are factors that affect LDF’s
size of the molecule (the larger the molecule the stronger the LDF
True or false: the more polar the molecule, the stronger the dipole-dipole force
True
True or false: the more polar a molecule is the higher the boiling point
true
Cl combinding with H2O is an example of what IMF
Ion-Dipole
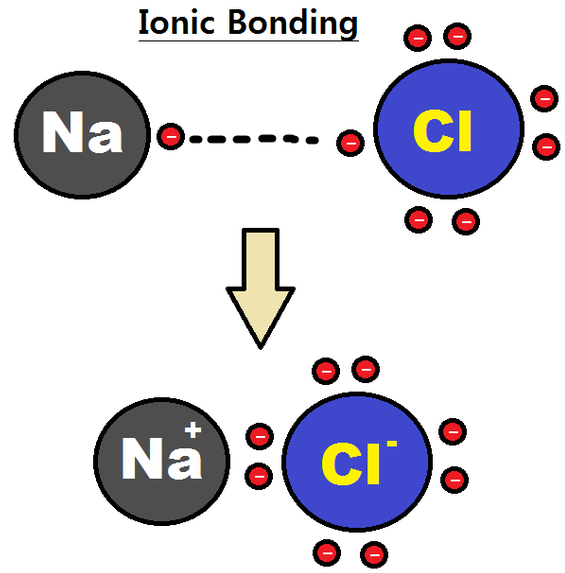
This is an example of what IMF
ion-ion
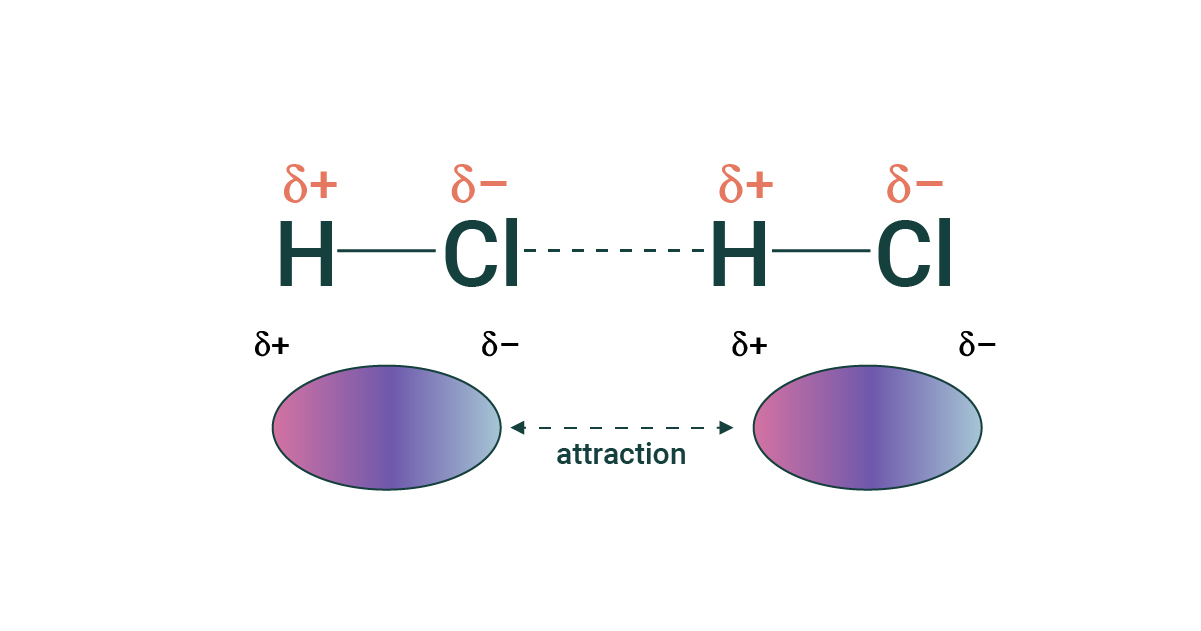
This is an example of what IMF
dipole-dipole
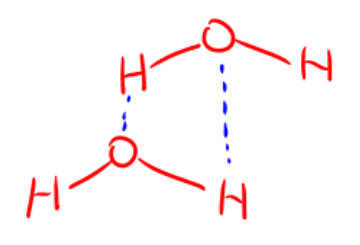
This is an example of what IMF
hydrogen bonding
what does the symbol for a dipole look like (positive or negative)
δ
the stronger the IMF, the high the what?
melting and boiling point or higher surface tension.