Marine Zoology & Ecology: Pelagic fishes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Pelagic meaning
relating to/living/occurring in the open sea
Characteristics of Open Ocean:
less productive
lower biomass
lower diversity
Adaptations: Body plan
streamlined, laterally compressed body
stiff fins
small pectoral fins
Adaptations: Colouration
countershading
Marlin- use iridophores to rapidly change colour
Adaptations: Body composition
scales oriented to disrupt boundary layer- reduced or absent
specialised denticles- sharks
oils/mucus coating to reduce drag
firm and muscular
powerful tails
Adaptations: Biolumniescence
camouflage: some can match ventral light intensity to downwelling light
attracting prey
courting/sexual dimorphism
schooling behaviour
Adaptations: Buoyancy
swim bladder
increased lipid storage
reduced density- body can be up to 95% water
Adaptation: Senses
large eyes
lateral line
Small pelagic fish: keystone role
in forage fish (schooling)
high oil content
tropical or subtropical
Small pelagic fish: food
consume zooplankton- prey for higher trophic levels
Small pelagic fish: Ecological role
energy transfer
Small pelagic fish: commercial role
food, oil or bait
Large pelagic fish: keystone role
apex predator
migratory fish
Large pelagic fish: food
smaller pelagic fishes
control species abundance at different trophic levels
Large pelagic fish: ecological role
population control of lower trophic levels
Large pelagic fish: commercial role
food, recreational fishing
Deep sea pelagic fish: distribution
patchy distribution
highly diverse
Deep sea pelagic fish: morphological traits
significantly different than epipelagic
Deep sea pelagic fish: survival strategies
Body morphology & colour
eye, mouth and teeth shape
lure appendages
prey illumination
counterillumination
Deep sea pelagic fish: body morphology & colour
great diversity of body shapes and colours
Deep sea pelagic fish: eye, mouth & teeth shape
several adaptations: tubular and enlarged eyes
large expandable mouth
long teeth
Deep sea pelagic fish: lure appendages
structures used to glow light & attract prey
symbiosis with bioluminescent bacteria
Deep sea pelagic fish: counterillunimation
camouflage involving use of ventral photophores to match dim light from surface
Ecological types of pelagic fish
oceanic & neritic
Ecological types of pelagic fish: Oceanic
spend most life in open ocean
true residents: tuna, swordfish, marlins, sunfish
partial: juveniles of benthic fish, whale sharks
Ecological types of pelagic fish: Neritic
spend most life in water above continental shelf & open ocean
most abundant fish in world: herring, sardines, anchovy
feed in highly productive inshore waters
Migration
follow food or move in search of spawning grounds
pelagic movements driven by changing conditions, often seasonal
Oceanic hotspots:
fixed structures
eddies
seasonally variable
Diel Vertical Migration
daily cycles of movement leads to formation of deep scattering layer
creates a nutrient cycle- leading to increased productivity and enhancing biodiversity
leads to pelagic carbon cycle
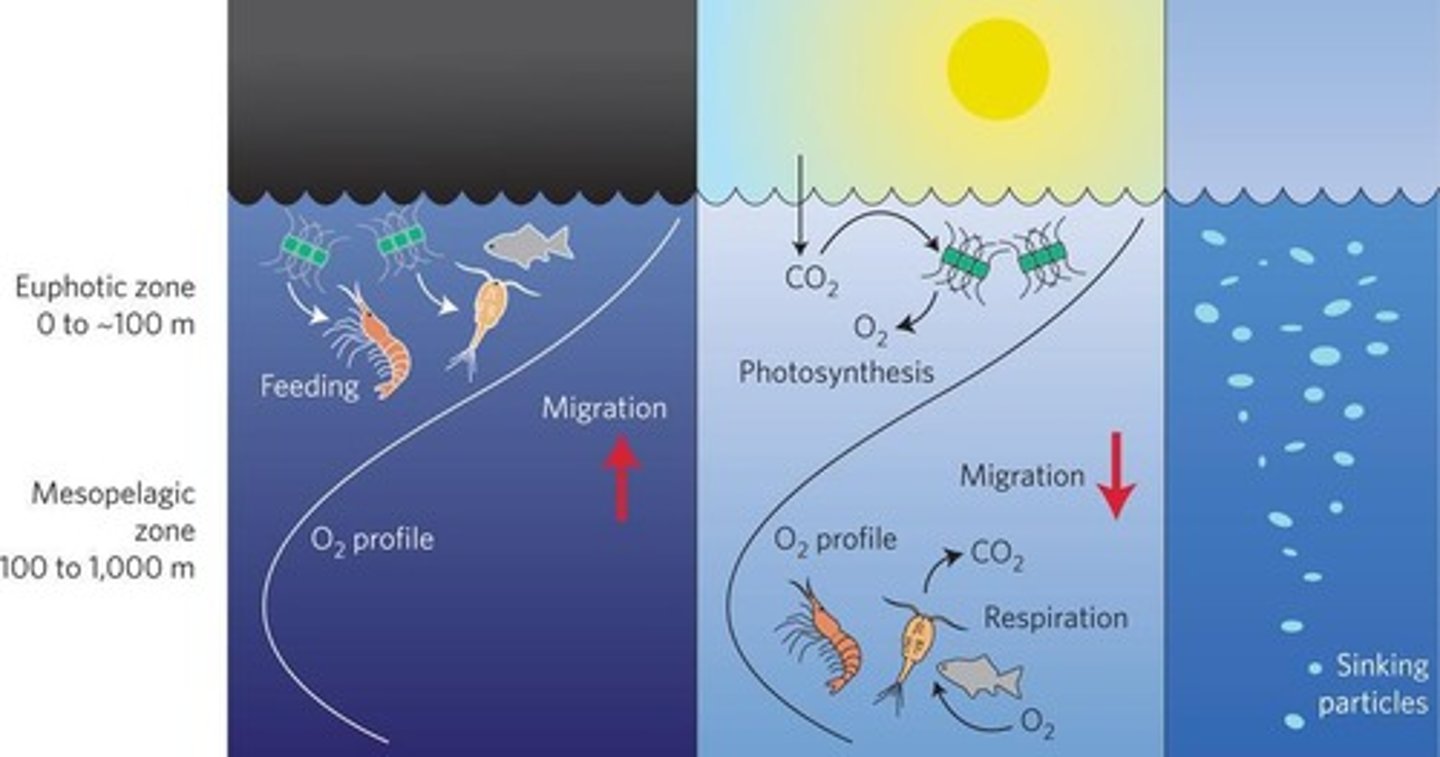
Pelagic carbon cycle: Trophic cascade carbon
food web dynamics- help maintain carbon storage and function of coastal marine ecosystem
Pelagic carbon cycle: biomixing carbon
turbulence & drag- movement of marine vertebrates
enhanced mixing of nutrient rich water from deeper in water column
enhance primary production
Pelagic carbon cycle: Bony fish carbonate
excrete metabolised carbon as calcium carbonate
enhance alkalinity- provide buffer against acidification
Pelagic carbon cycle: Whale pump
nutrients from faecal material of whale
enhance primary production by phytoplankton & uptake of dissolved CO2
Pelagic carbon cycle: twilight zone carbon
Mesopelagic fish feed in upper ocean layer at night
transport consumed organic C to deeper waters at day
Major challenges
overfishing
bycatch
climate change