Week 8 Presentation: Disability, Community, Culture, and Identity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Definition(s) of “Disability”: Socially Constructed Nature of Disability (Nagi, 1991)
Disability refers to social rather than organismic functioning
It is an inability or limitation in performing socially defined roles and tasks expected of an individual within a sociocultural and physical environment
Brings in task and role function
Definition(s) of “Disability”: Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
A physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more of the major life activities of an individual
A record of such an impairment
Being regarded as having such an impairment
Focus is major life activities
Important role of OT in evaluating and recording these effects on major life activities
OT’s can be involved in the disability determination process
Definition(s) of “Disability”: Social Security Act
A person is disabled under the Act if he/she can’t work due to a severe medical condition that has lasted, or is expected to last, at least one year or to result in death
The person’s medical condition must prevent him/her from doing work that he/she did in the past, and it must prevent the person from adjusting to other work
Rules how much money they can make and remain on this act
SSDI payments
SSI
Work
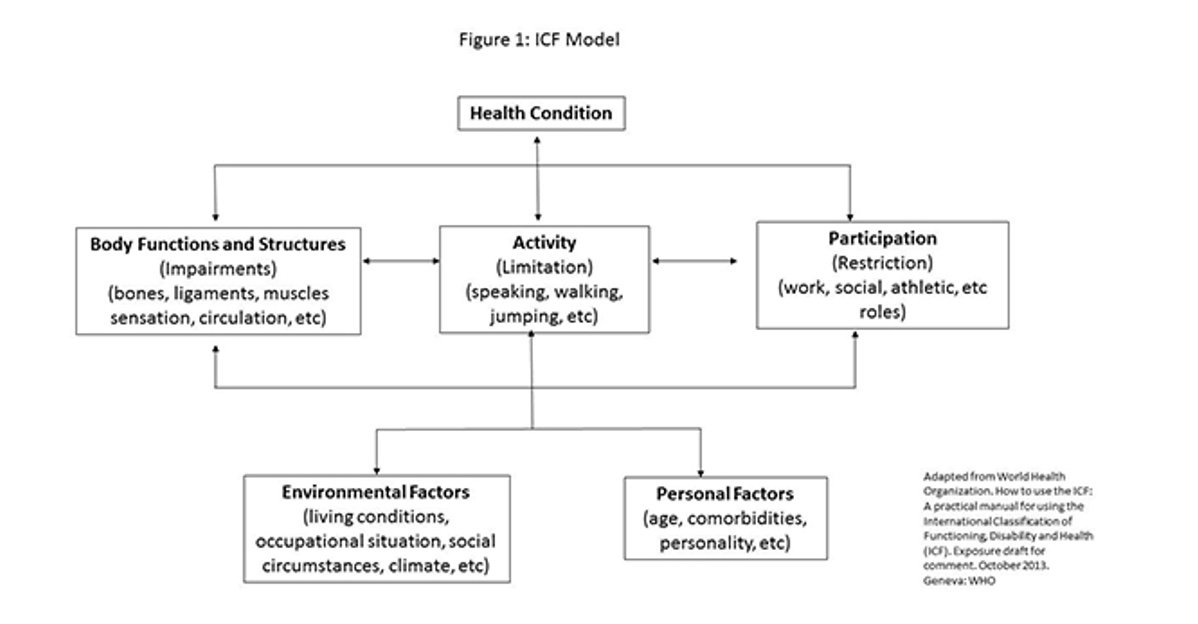
Definition(s) of “Disability”: World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)
Umbrella term for impairments, activity limitations, and participation
Impairment
Results from problems with body functions or structure
Activity limitation
Occurs when a person has trouble executing a task or action
Participation
A person’s difficulty engaging in a “life situation” (or roles/occupations)
WHO-ICF Model
Focused on how individuals participate in those roles and occupations
Person Environment Occupation (PEO) Model
Concept of occupational performance supports our social construct of disability
Are they able to perform?
Independence
Ableism
Discrimination and prejudice experienced by people with disabilities and in favor of being able-bodied
View people with disabilities as having or being a defect that needs to be fixed, as opposed to a view of disability as a dimension of difference
Views of inferiority and devaluation have had a profound impact on creation and implementation of public policy toward people with disabilities
6 Forms of Ableism that OT’s Should Resist
Failing to offer a full range of accessibility options (wheeled mobility, low vision, hearing loss, SPD…)
Using discriminatory (ableist) language in pejorative ways
Being careful on the words you use
Acknowledging that many temporarily able-bodied individuals rarely check their privileges (use accessible bathroom stalls, using disability-only parking, etc.)
The assumption that disabled have no agency or autonomy by automatically assuming that they need help
The assumption that it is ok to ask how a person’s disability occurred
Assuming that disability is obvious and apparent
Models of Disability
Moral model of disability
Welfare model of disability
Medical model
Social model
Minority group model
Moral Model of Disability
Early model
Disability is explained by a divine action to provide the person with a challenge to overcome
Welfare Model of Disability
People with disabilities are considered part of the “worthy poor”
Worthy
Through no part of their own are worthy to receive government support and benefits that support their existence (even in institutions)
Created work disincentives in the US; invoke pity/contempt by able-bodied
Vocational Rehab and Workers comp emerged to support their employment
These define levels of disability based on an economic value
Medical Model
“Medicalization”
The individual with an illness or impairment is deficient and abnormal
A professional is required to heal, fix, or cure the deficiency though medication, surgery, technology, therapy
Independence is the ultimate goal and measure of success
Needing to be fixed
Focus on independence
Social Model
Focuses focuses on the interaction of the person with their environment and the resulting effect on what the disabled person can do to participate in society
Disability is simply another type of difference on the human continuum of difference and disablement is a result of oppressive social structures
Minority Group Model
Systemic oppression, marginalization, alienation, social and political isolation
Develop disability culture, disability pride, disability identity
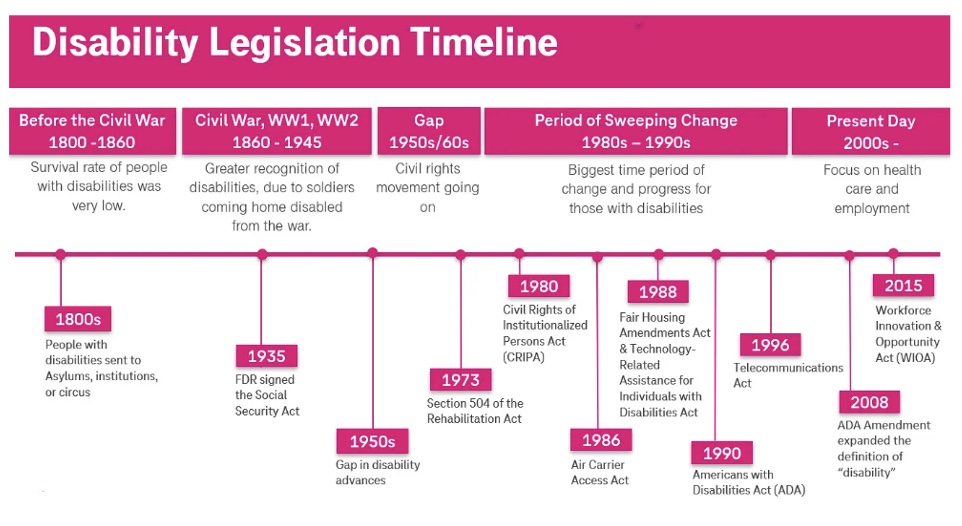
Legislation and Policies
1973 Rehabilitation Act Section 504
1990 Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
1973 Rehabilitation Act Section 504
Prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities in federal agencies, contractors, and those receiving federal grants, including universities
1990 Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Creates equal opportunities for people with disabilities in USA in the areas of employment, public services, public accommodation, transportation, and telecommunication
Enabled having to have telephones interact with different disabilities, being able to have wheelchair access and different types of access, transportation, etc.
Events Impacting People with Disabilities