CCMA Unit 1: Foundational Knowledge & Patient Care Coordination
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary and concepts related to the foundational knowledge and patient care coordination for Certified Clinical Medical Assistants.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms

Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA)
A nationally recognized professional certification awarded by the National Healthcareer Association (NHA). It validates that a medical assistant possesses the essential skills to perform both clinical tasks (like phlebotomy) and administrative duties (like billing).
Scope of Practice
The definitive legal and ethical boundaries within which a medical assistant must operate. These vary significantly by state law and usually prohibit the assistant from performing tasks such as diagnosing, prescribing medication, or performing surgery.
Telehealth
A modern healthcare delivery system that utilizes digital communication technologies (video conferencing, remote monitoring) to provide clinical services without an in-person visit. This is essential for rural access and chronic disease management.
Patient-Centered Medical Home (PCMH)
A collaborative care delivery model where a primary care provider coordinates a team of health professionals to provide comprehensive, accessible, and continuous care focused on the patient's individual needs and preferences.
Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs)
Voluntary groups of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers who come together to give high-quality, coordinated care to their Medicare patients. The goal is to avoid unnecessary duplication of services and prevent medical errors
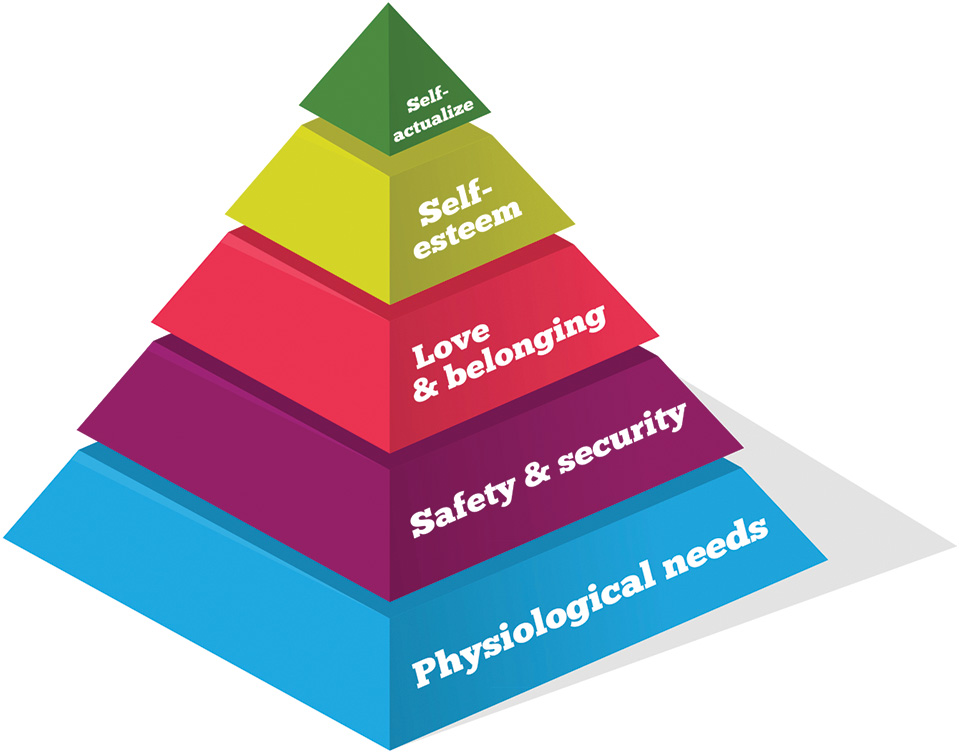
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
A psychological theory used in healthcare to understand patient motivation. It consists of five levels: 1. Physiological 2. Safety 3. Love/Belonging 4. Esteem 5. Self-Actualization. Clinical priority is always given to the base of the pyramid (physiological needs).
Continuing Education Units (CEUs)
Educational credits required for the maintenance of professional certifications. For CCMAs, earning 10 CEUs every 2 years is typically required to ensure the assistant stays current with evolving medical technology and protocols.
Vital Signs
Measurements of the most basic body functions used to monitor health status. Includes: Temperature (Normal: \approx 98.6^{\circ}F), Pulse (60-100 bpm), Respiration (12-20 breaths/min), and Blood Pressure (Normal: < 120/80 mmHg).
Professional Development
The ongoing process of improving and increasing capabilities of staff through access to education and training opportunities in the workplace. This includes specializations in Phlebotomy or EKG.

Healthcare Team
A diverse group of healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, medical assistants, and administrative staff, who work together toward the common goal of optimal patient health.

Administrative Assisting
The management of the medical office's front end, including registration, insurance verification (billing), managing Electronic Health Records (EHR), and coordinating referrals.
Patient Navigation
The practice of helping patients 'navigate' the complexities of the healthcare system by identifying and removing barriers such as transportation, cost, or lack of health literacy.

Health Education
The provision of health-related information to patients to help them make informed decisions and manage chronic conditions (e.g., teaching a patient how to use a glucose monitor).
Clinical Responsibilities
Direct patient care tasks performed 'in the back' of the office, which include preparing patients for exams, administering injections, performing EKGs, and wound care. -
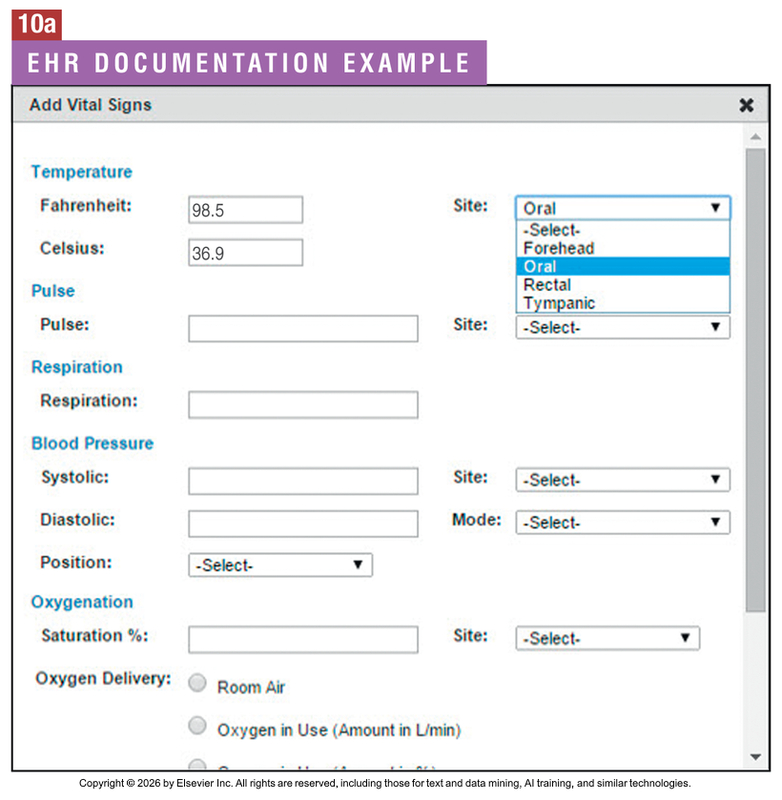
Documentation
The systematic recording of all patient care and interactions in the medical record. It often follows the SOAP format: Subjective (S), Objective (O), Assessment (A), and Plan (P).
Healthcare Payment Models
The various structures used to pay healthcare providers, currently shifting from 'Fee-for-Service' (quantity) to 'Value-Based Care' (quality and patient outcomes).