Lecture 4: GAD
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are some characteristics of the worry experienced in GAD?
Even if some people think in images, worrying is usually done in words
* Intrusive
* Perceived as uncontrollable (but actually controllable)
* Associated with motivation to prevent potential danger
* Perceived as helpful
* "Normal" phenomenon, content of thoughts is the same compared to people without an anxiety disorder
* Transdiagnostic phenomenon
Aside from uncontrollable worrying, what are some other GAD traits in the DSM?
- Restlessness
- Fatigue, sleep problems
- Impaired concentration
- Irritability
- Increased muscle aches or soreness
- Daily life impaired by the complaints
How do we differentiate between people with GAD and “regular” worry?
People with GAD’s worry differs in that
- They think that worrying is going to cause problems ("I think I'm gonna have a heart attack if I keep worrying")
- Perceive worrying as part of self
- Worry constantly, always have something to worry about
Are positive meta-cognitions about worry specific to GAD?
No. This is something that we all have
If someone who is anxious keeps having panic attacks, how can we differentiate between GAD and panic disorder?
If anxiety leads to panic attacks, but the person doesn’t have panic attacks for no reason, it’s GAD. This is because panic attacks are a transdiagnostic factor.
What is the difference between the anxiety found in GAD and the anxiety found in OCD?
GAD also has compulsions, but they have different FUNCTIONS
Function of compulsions in OCD is to reduce perceived threat
Function of compulsions in GAD is to reduce the worrying
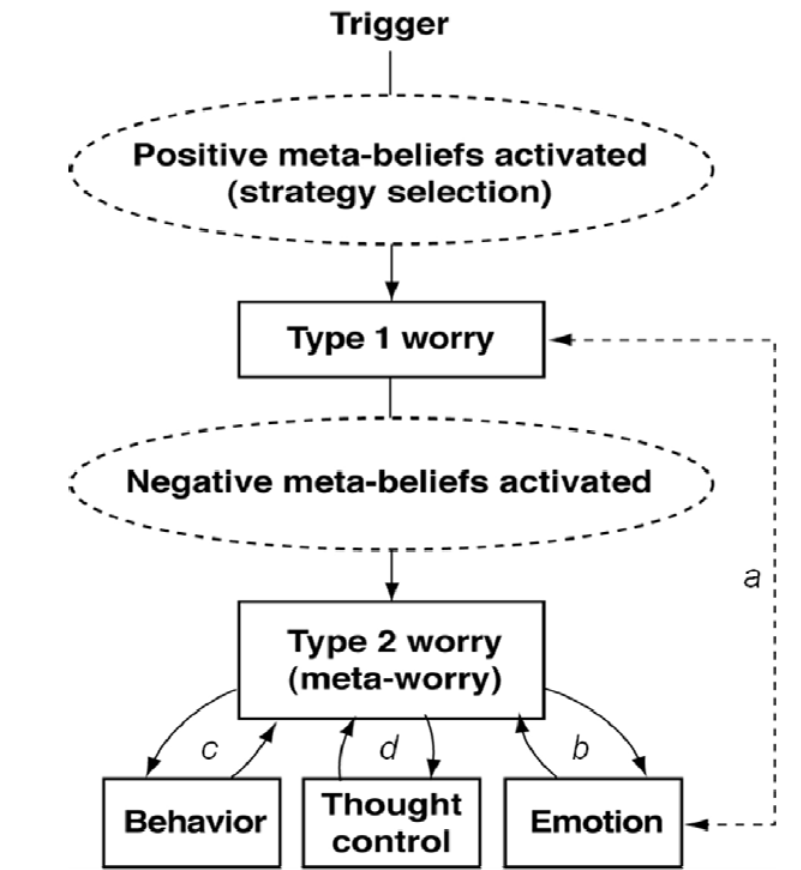
What is the meta-cognitive model?
A model that explains how positive meta-beliefs about worry contribute to increased worry (Type 1 worry) and then negative meta-beliefs contribute to type 2 worry leading to anxiety symptoms (Anxious behaviour, emotion and attempts at thought control)
Why don’t we talk too much about the content of the worrying in therapy for GAD?
Because the content changes all the time by nature of the disorder
What are steps 1-3 of metacognitive therapy?
Step 1: Identify the trigger (automatic thought that precedes the worrying)
Example: "Did my daughter arrive at school safely?"
Step 2: Identify what the person thinks next (catastrophizing)
Example: What if she got kidnapped?
Focus on the content of the worrying not for your own sake or because of the model, but to build a therapeutic relationship
Step 3: Ask about emotions
Make sure they are not actually describing the content anymore, but actual emotion
What are steps 4-6 of metacognitive therapy (meta-cognitions)
Step 4: Ask about worrying about worrying
"Did you think something would happen if you kept worrying"
If the person doesn't worry about worrying, likely no GAD - this is the step you will get stuck at
If the person does have GAD, they will say sth like "I can't function, I'll go crazy, I'll get a headache"
Step 5: Activating negative metacognitions
"What is the worst thing that could happen if you keep on worrying"
Is it something you could stop?
Step 6: Activating positive meta-cognitions (Asking them what the positive sides are to worrying)
Possible the client will say there are none, in that case, ask tentatively or trust the process (will come up later)
"Prepares me for the worst that could happen"
What are steps 7-8 of metacognitive therapy?
Step 7: Avoidance or safety behaviours
Avoidance: Call in sick to work
Safety behaviours: Keep track of where everyone is, check everything is ok
Step 8: What do you do when you start worrying to deal with it? (Different to Step 7 because avoidance and safety behaviour prevents worrying before it's present)
E.g. Seeking distraction, doing sports, substance use
How can we detect meta-cognitions?
Asking about the judgement of worrying
List of advantages and disadvantages
Finding thought-control behaviour and asking the function of it. (e.g. why do you try to stop yourself from worrying)
Doing an experiment:
for example concentrating on worrying
Questionnaires for example metacognitions questionnaire
What are other strategies to prevent worrying?
Expanding coping strategies with standard CBT techniques
Reduce avoidant behaviour
Letting go of thoughts (detached mindfulness)
Imagine positive outcomes
Relapse/recidivism prevention