Chapter 15: Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of selected Lymphatic Organs
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
spleen
-the major function of this organ is to scrutinize the incoming blood for aged and malformed erythrocytes
-Will remove RBC and recycle their iron and begin disposal of bilirubin.
-On the lookout for any pathogens organisms or toxic materials in the blood.
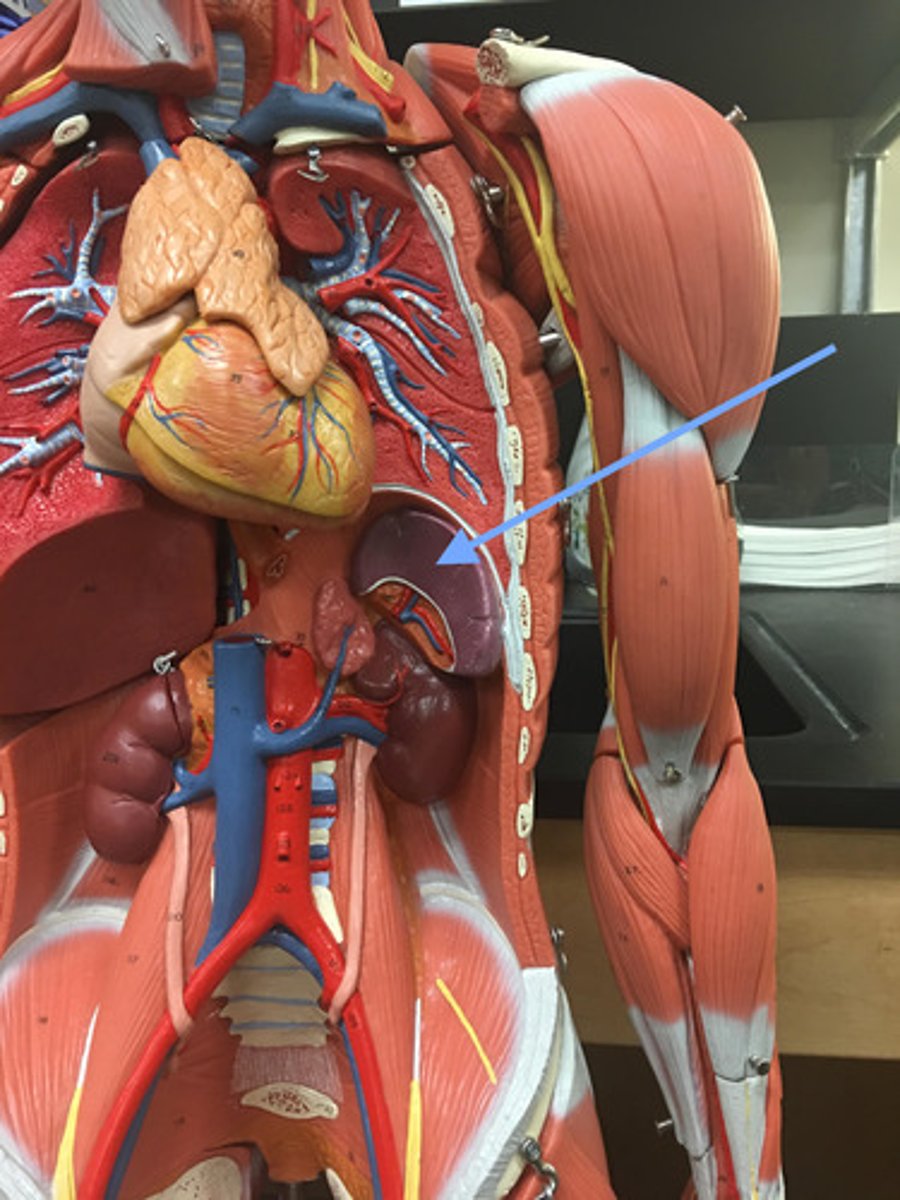
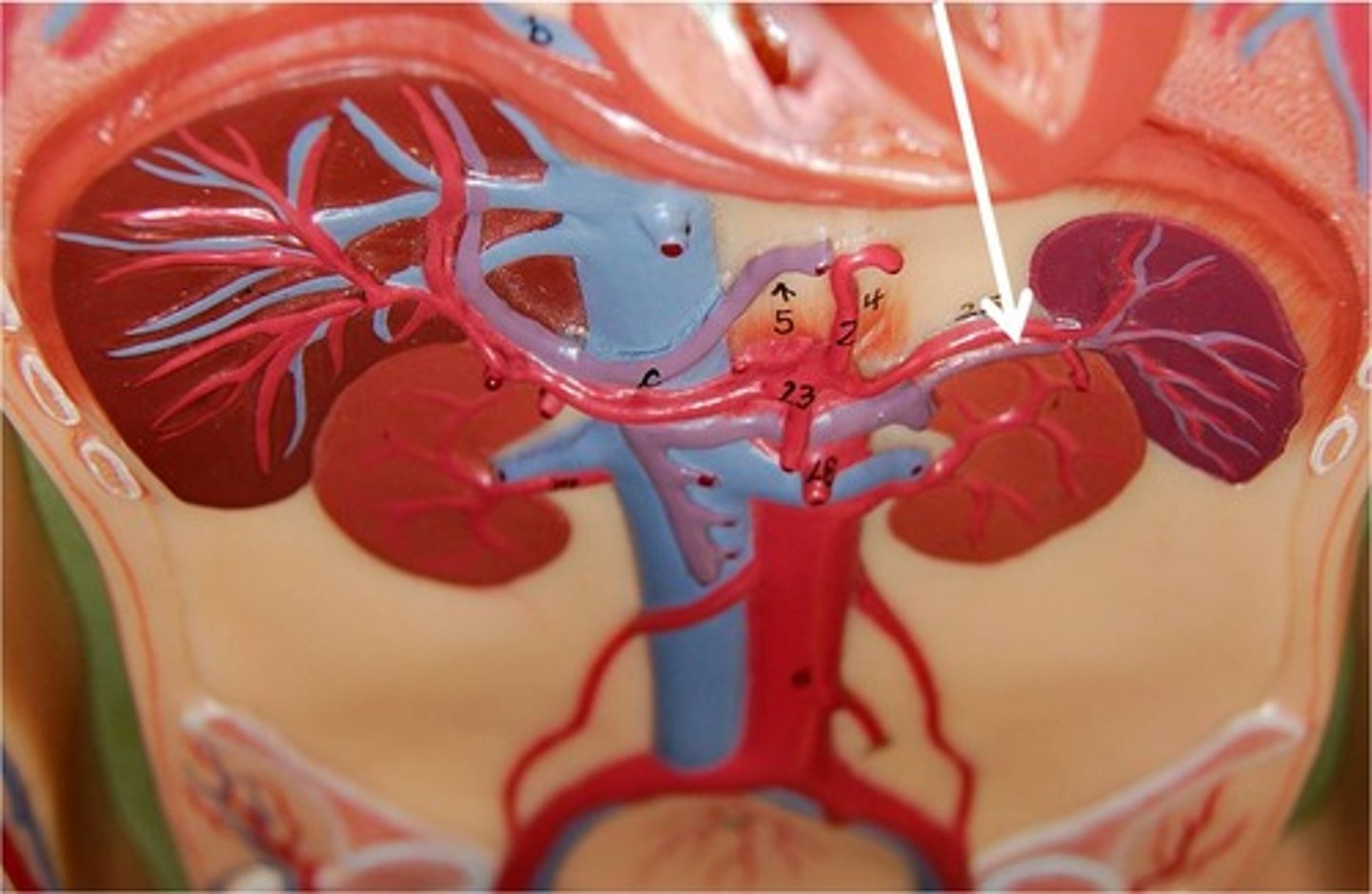
splenic artery
-extends from the celiac trunk to the splenic hilum.
-supplies to the spleen
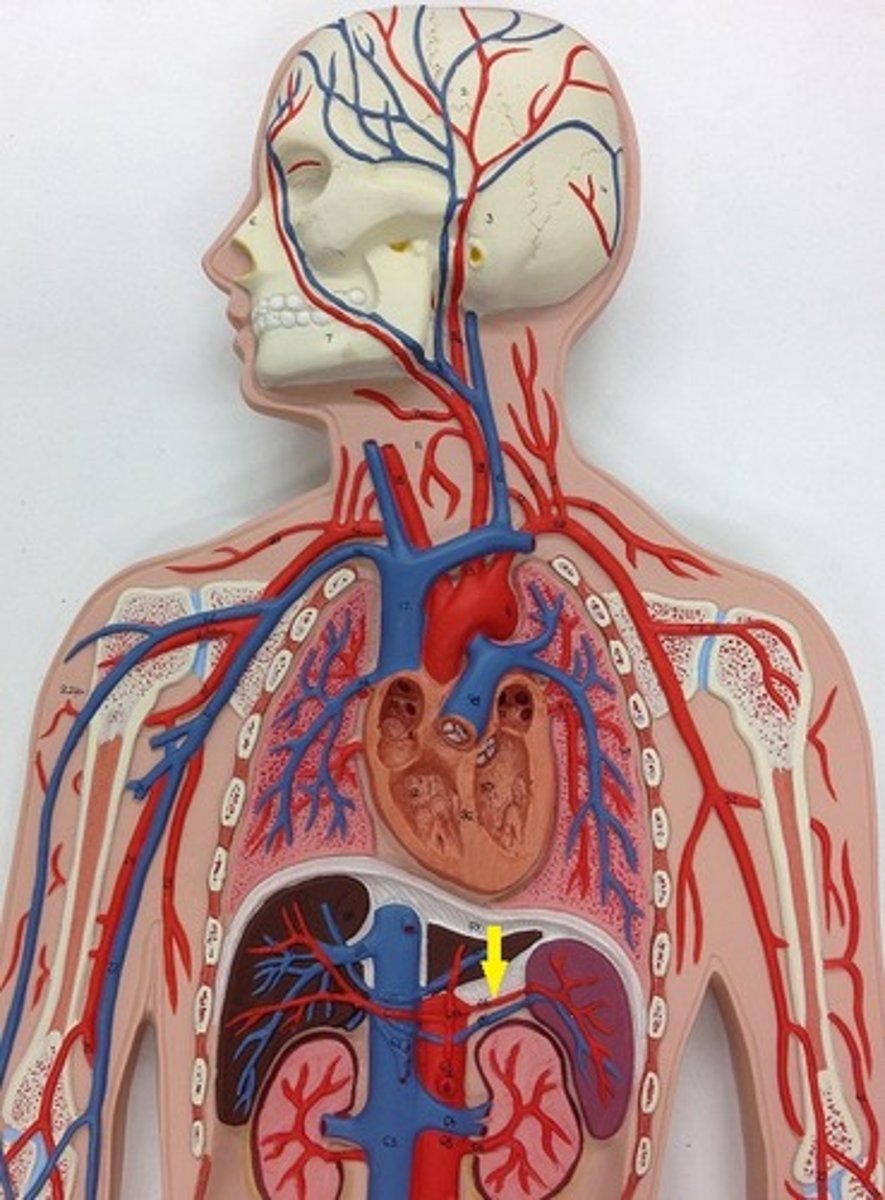
splenic hilum
site located in the middle of the spleen where blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves enter or exit the organ.
splenic vein
-Fuses with the superior mesenteric to carry newly filtered blood to the hepatic portal which will bring it to the liver
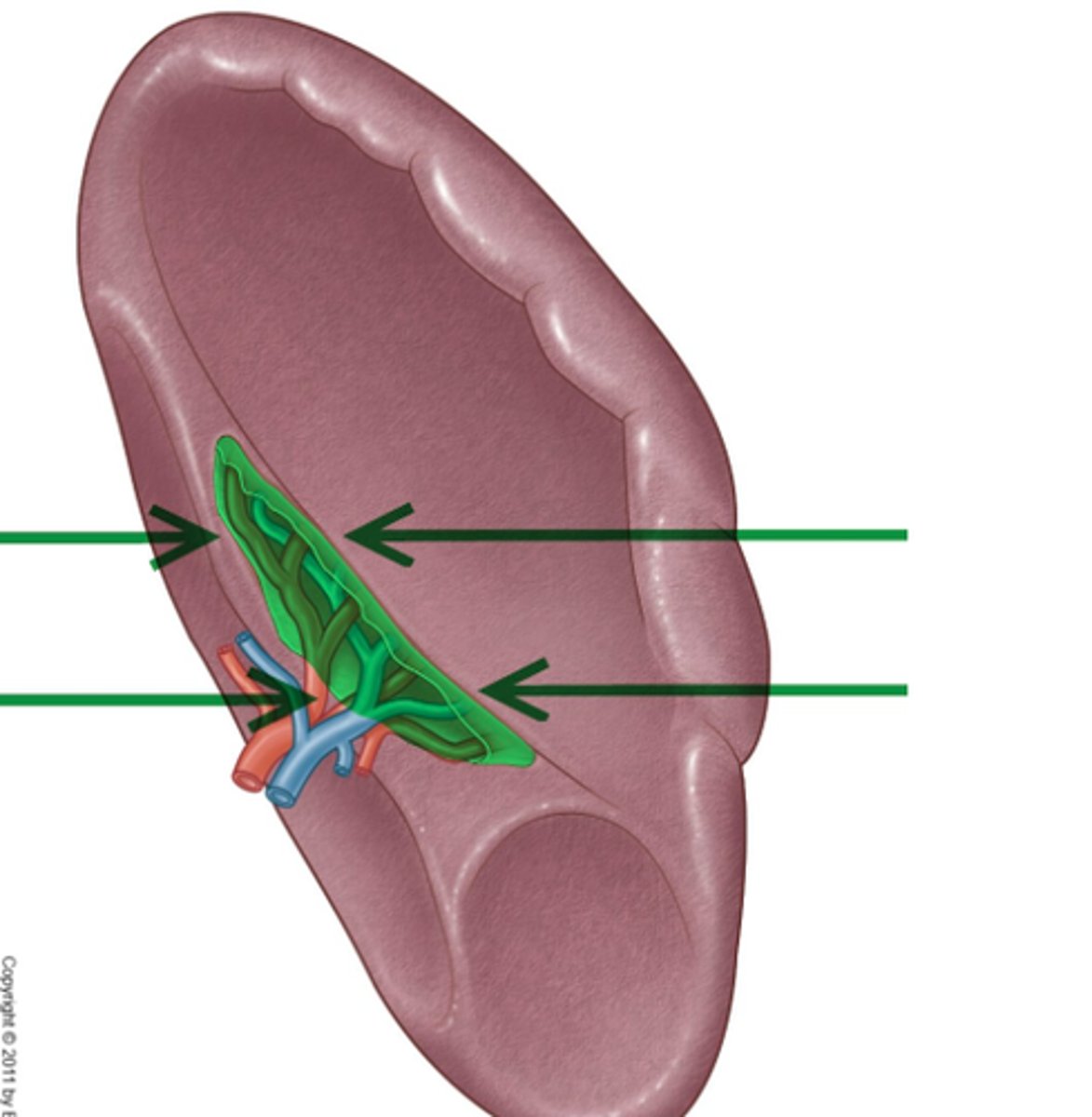
red pulp (spleen)
-is the dark red tissue in the spleen containing sinusoidal capillaries, connective tissue fibers, and immune cells like macrophages, plasma cells, and lymphocytes.
-It destroys old red blood cells, removes pathogens and toxins
-facilitates lymphocyte movement between splenic tissue and blood.
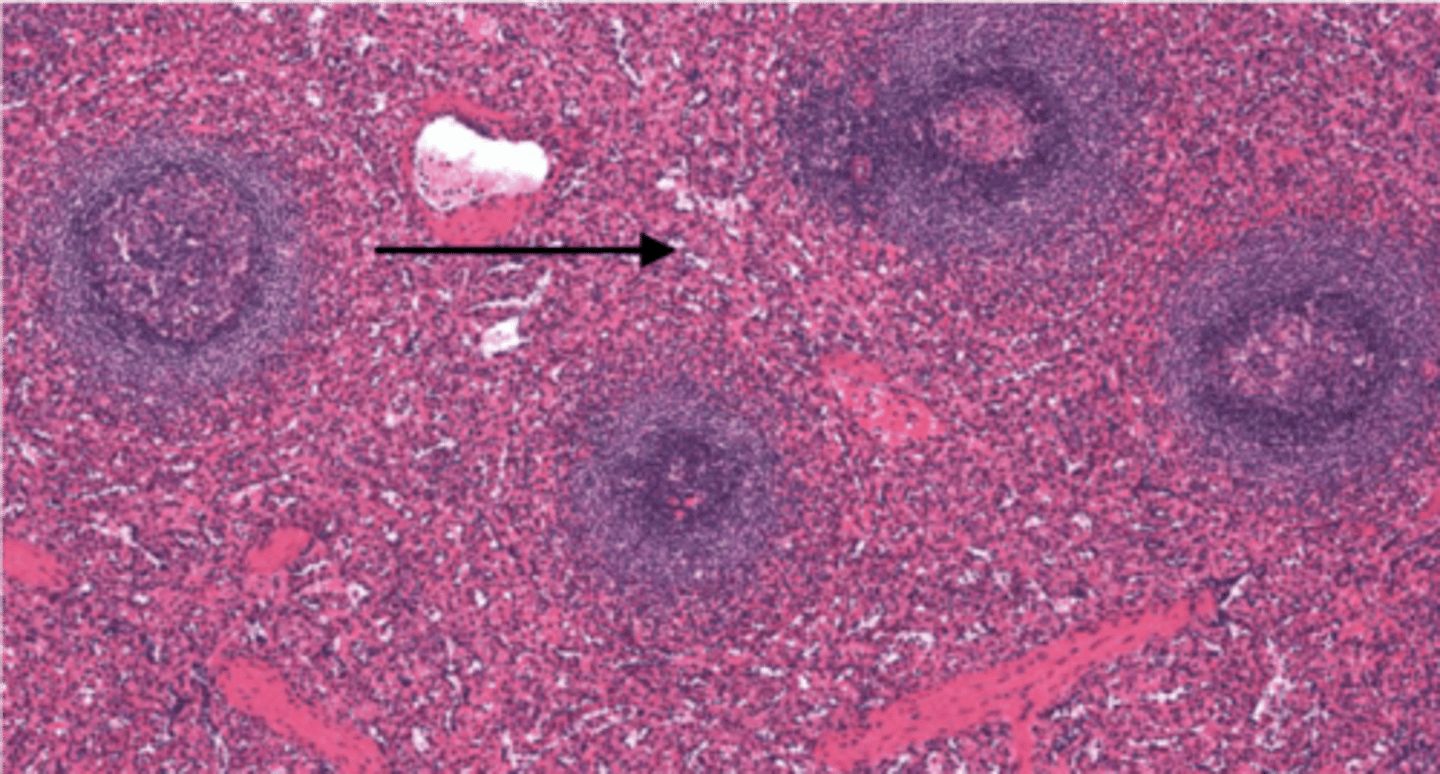
white pulp (spleen)
has whitish appearance in a fresh spleen. Lymphocytes, macrophages surrounding small branches of splenic artery
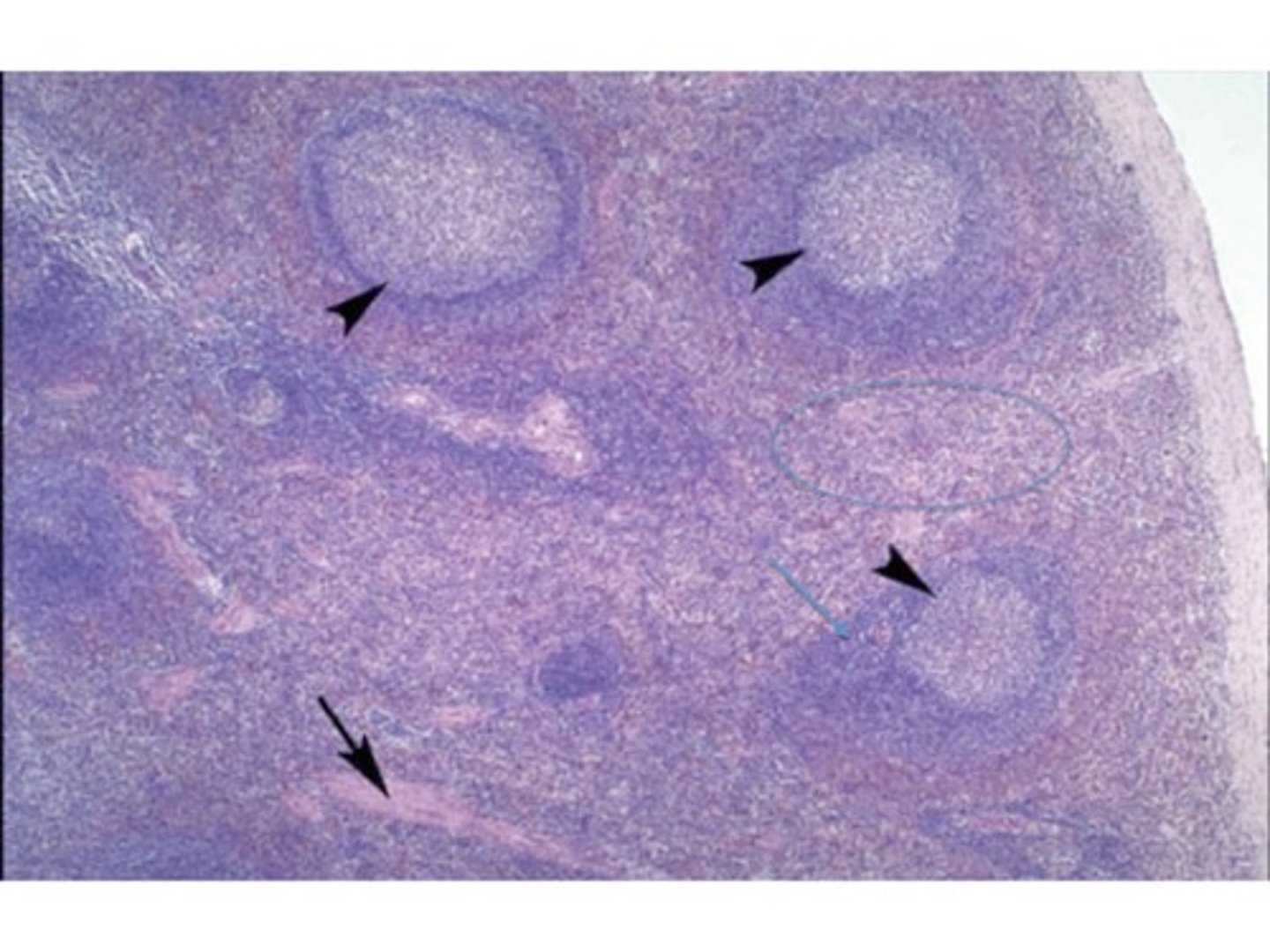
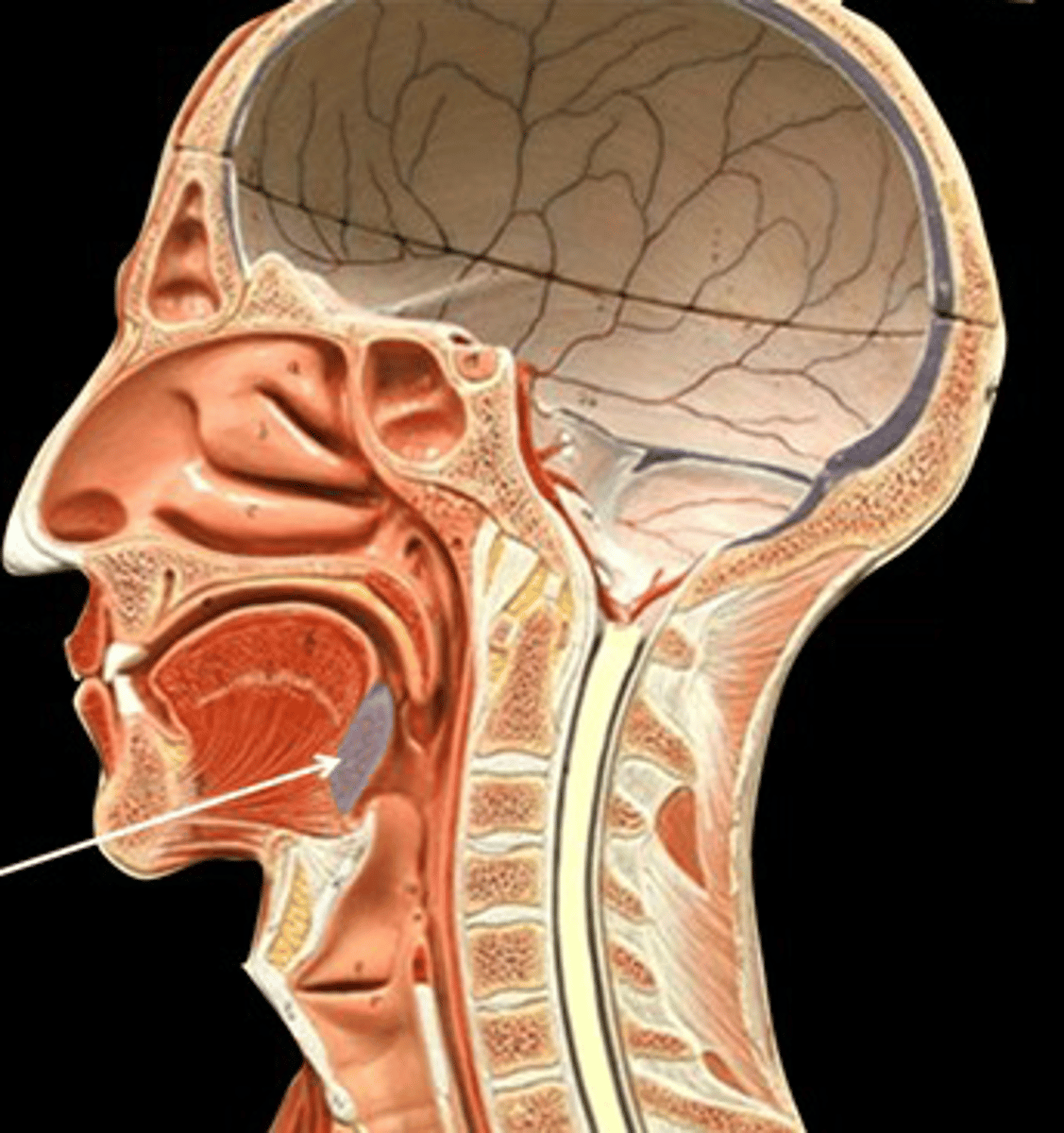
tonsils
form a ring of lymphatic tissue around the openings to the pharynx.
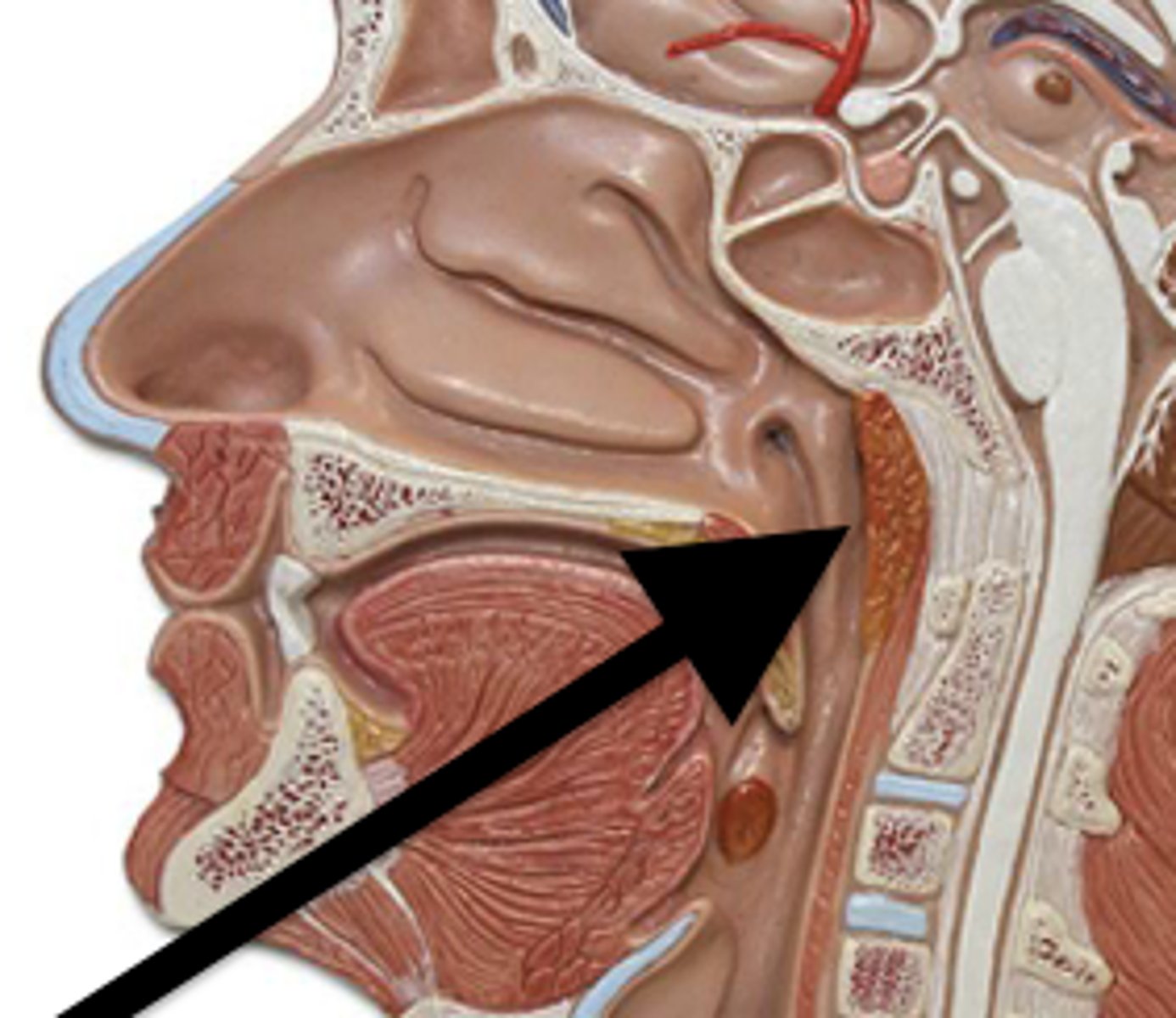
pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
sits on the posterior wall of the superior pharynx. This location allows it to filter inhaled air for pathogens.
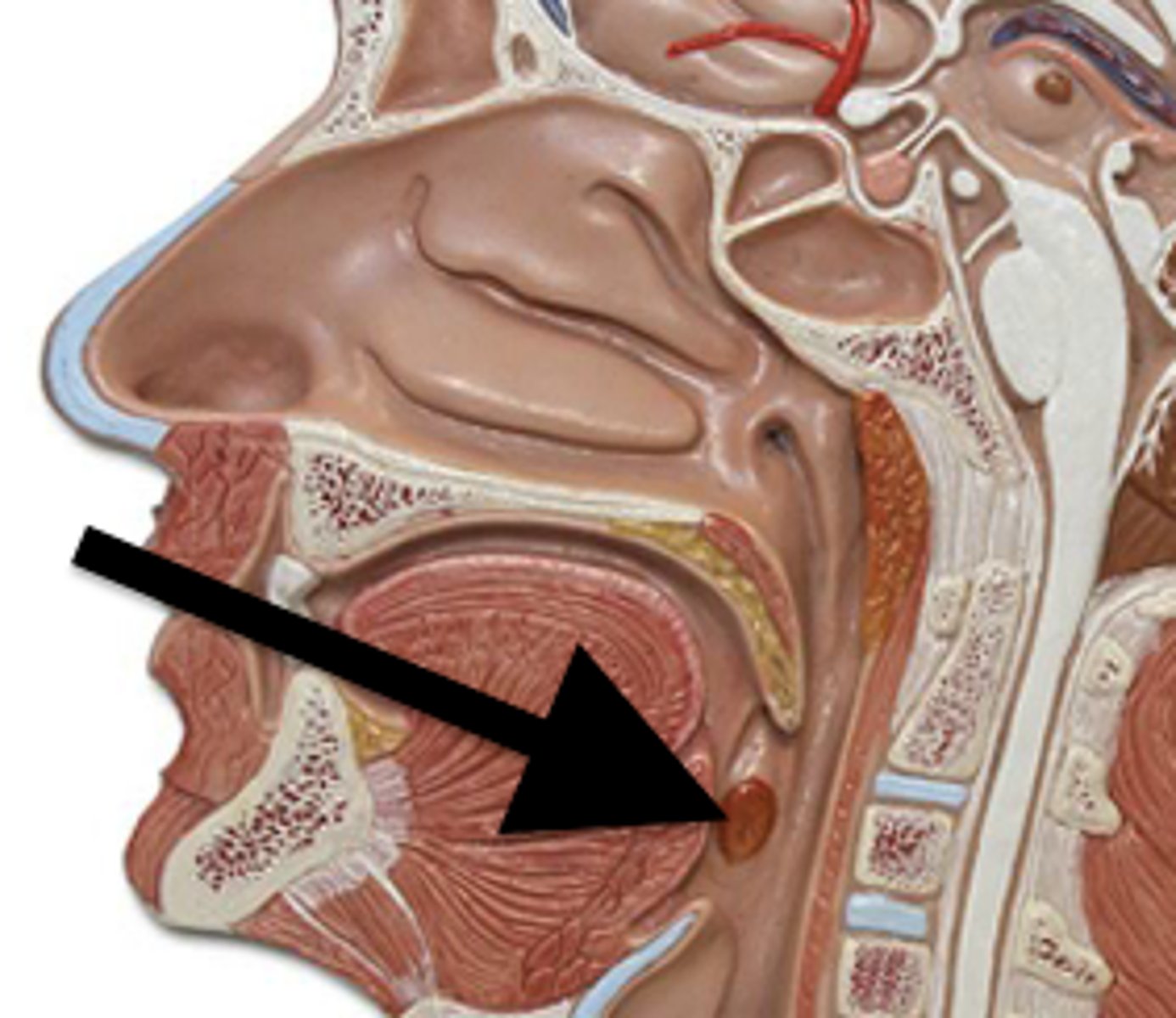
palatine tonsils
are found on the lateral walls of the oral portion of the pharynx (the oropharynx). These tonsils are in prime position to "catch" pathogens being ingested with food.
lingual tonsils
reside on the superior surface of the posterior tongue. These tonsils are in prime position to "catch" pathogens being infested with food.
tonsillar crypts
contains lymphocytes and bacteria. Deep to the epithelium and adjacent to the crypts you can see dense lymphatic tissue
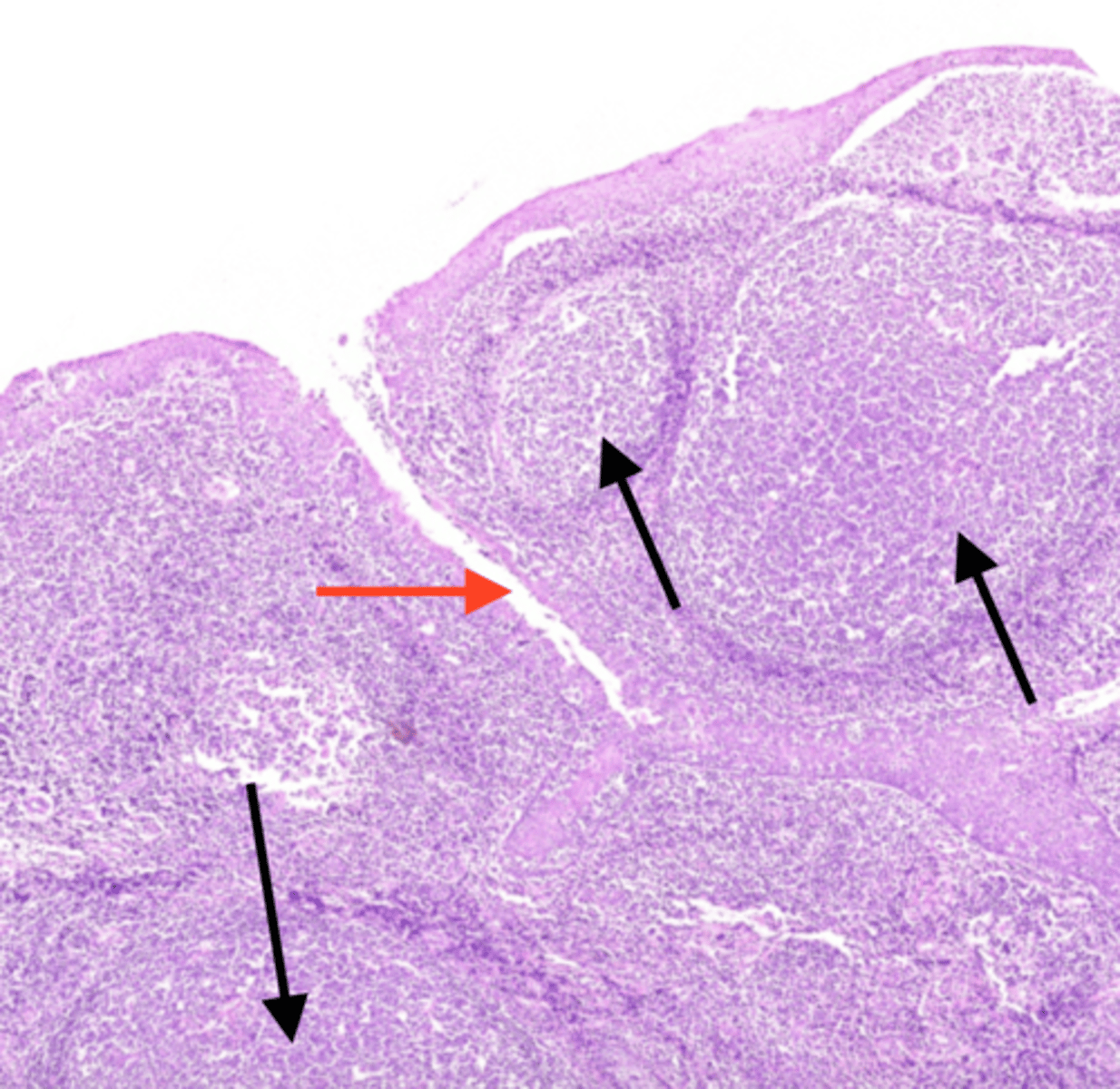
tonsillar capsule
made of dense connective tissue. It separates the tonsil from the subjacent tissues. Helps prevent the spread of infection.
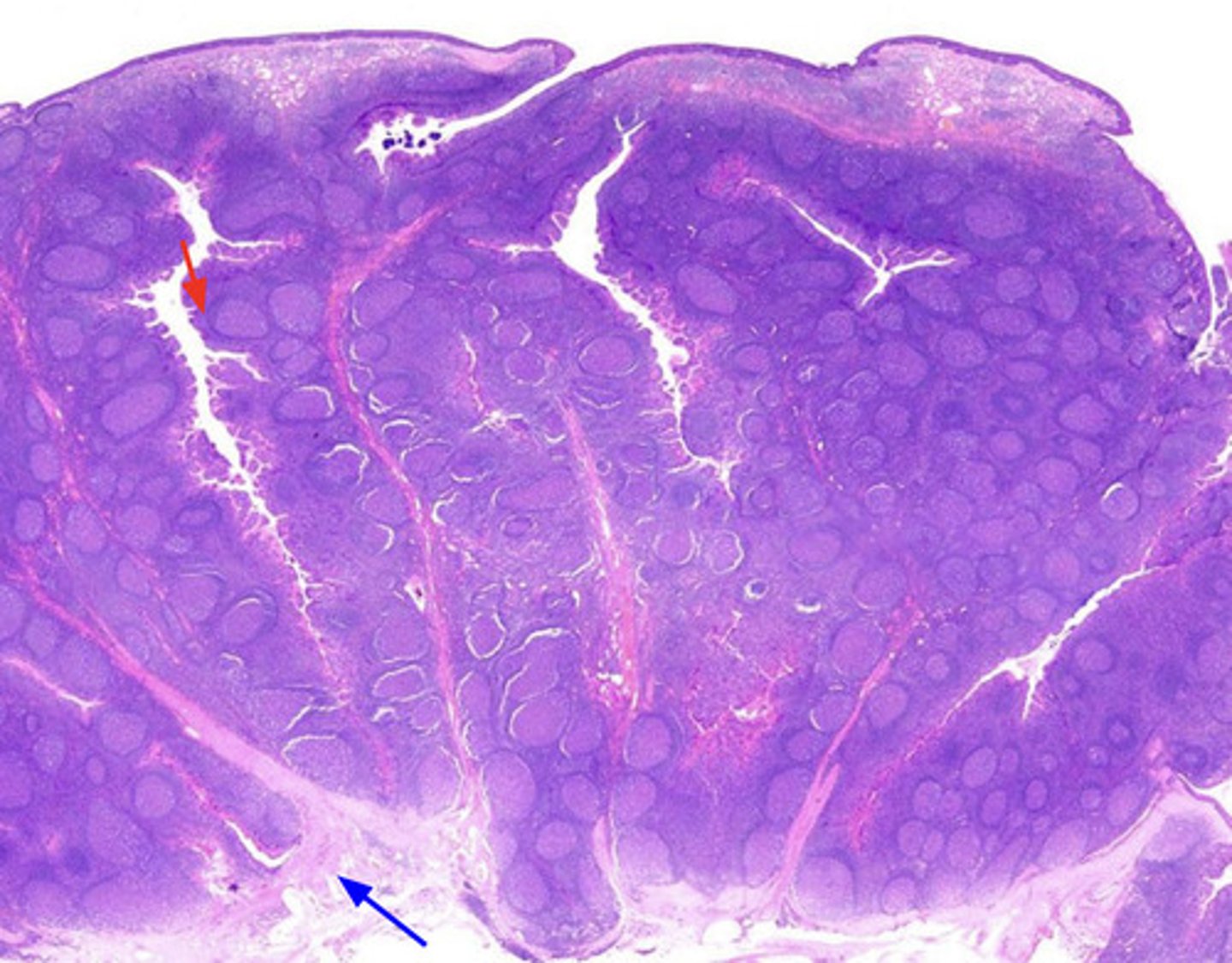
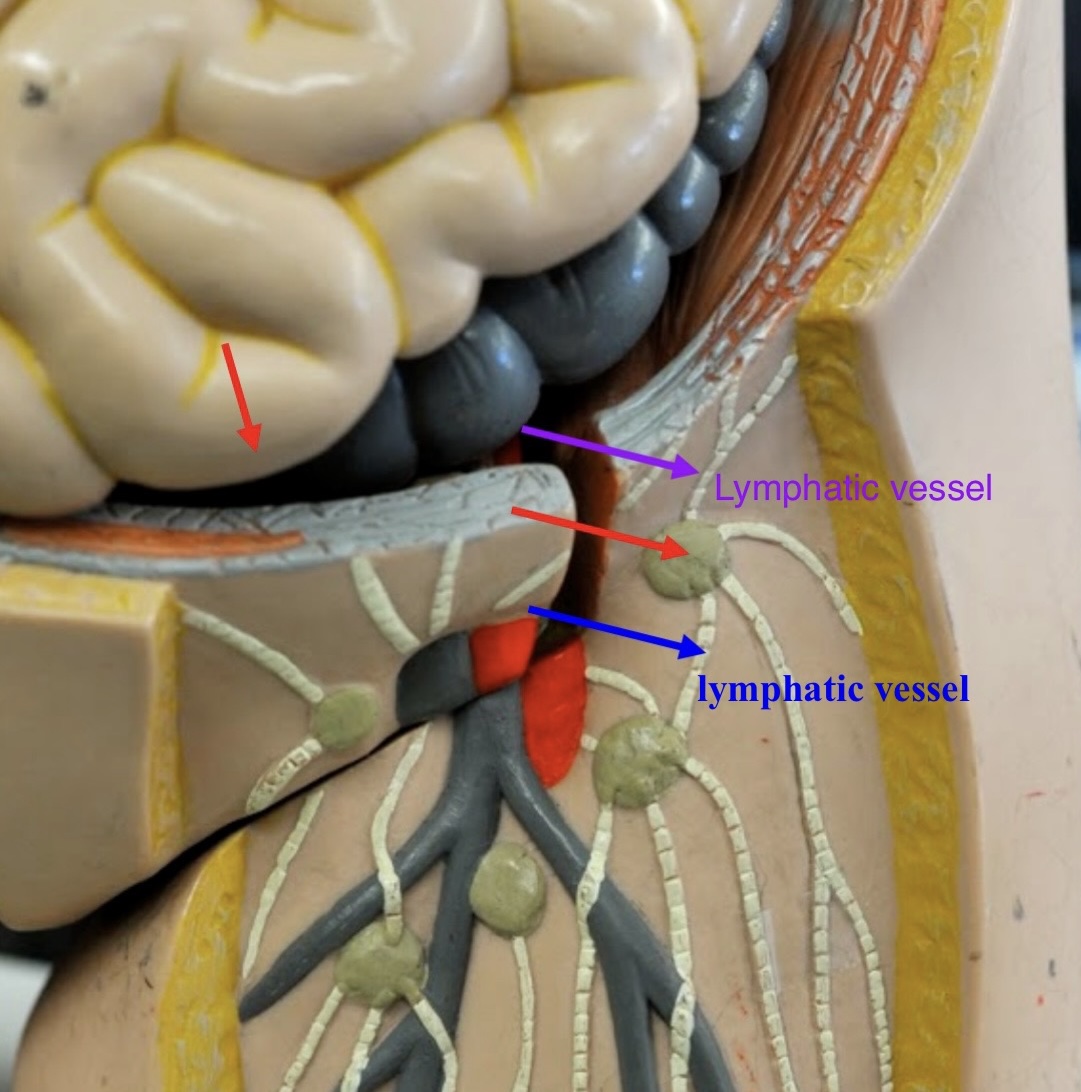
lymphatic vessels
large vessels with valves, which collect and carry lymph to lymph nodes
lymph
fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system, containing white blood cells (mainly lymphocytes), proteins, and other substances
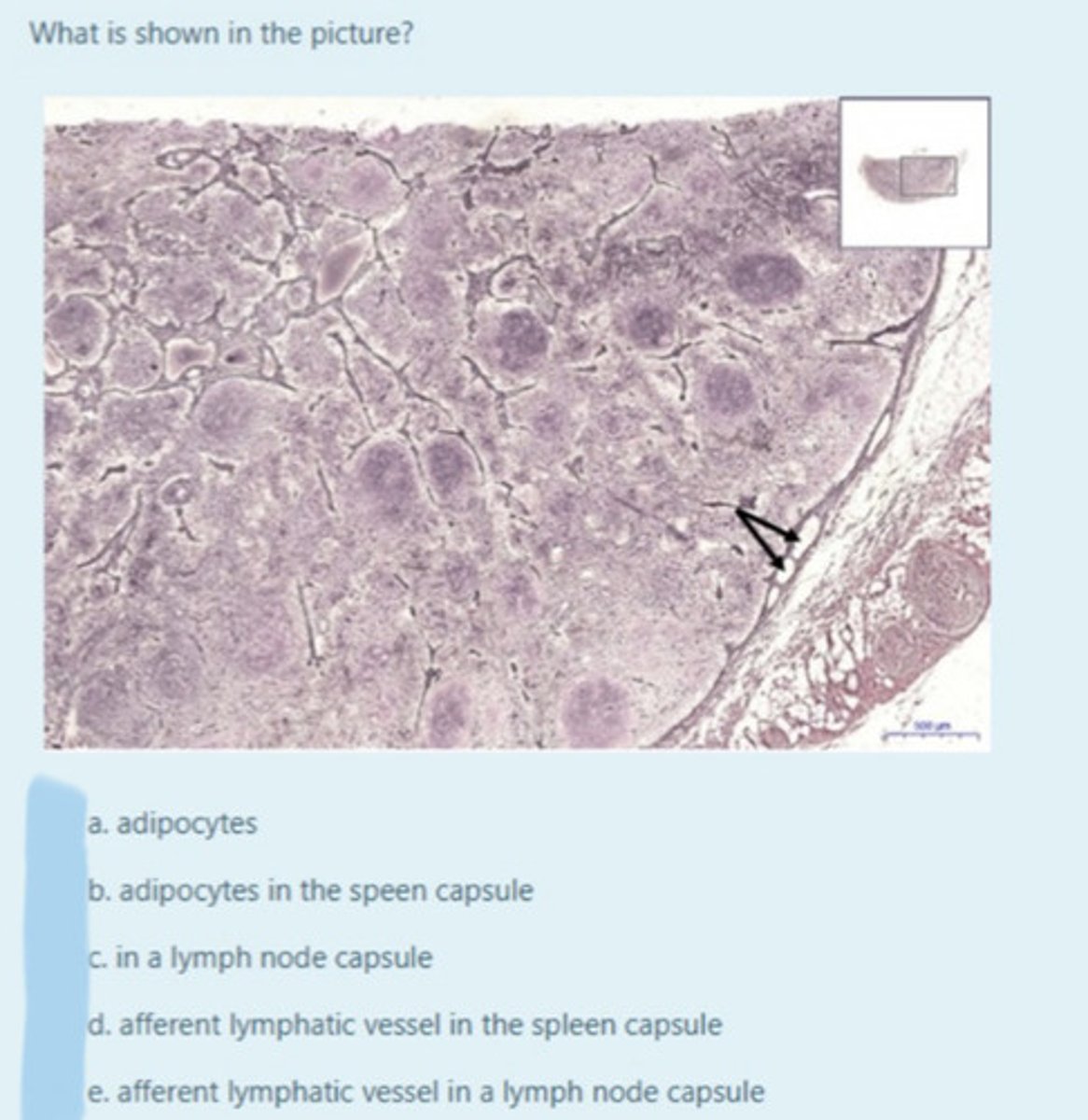
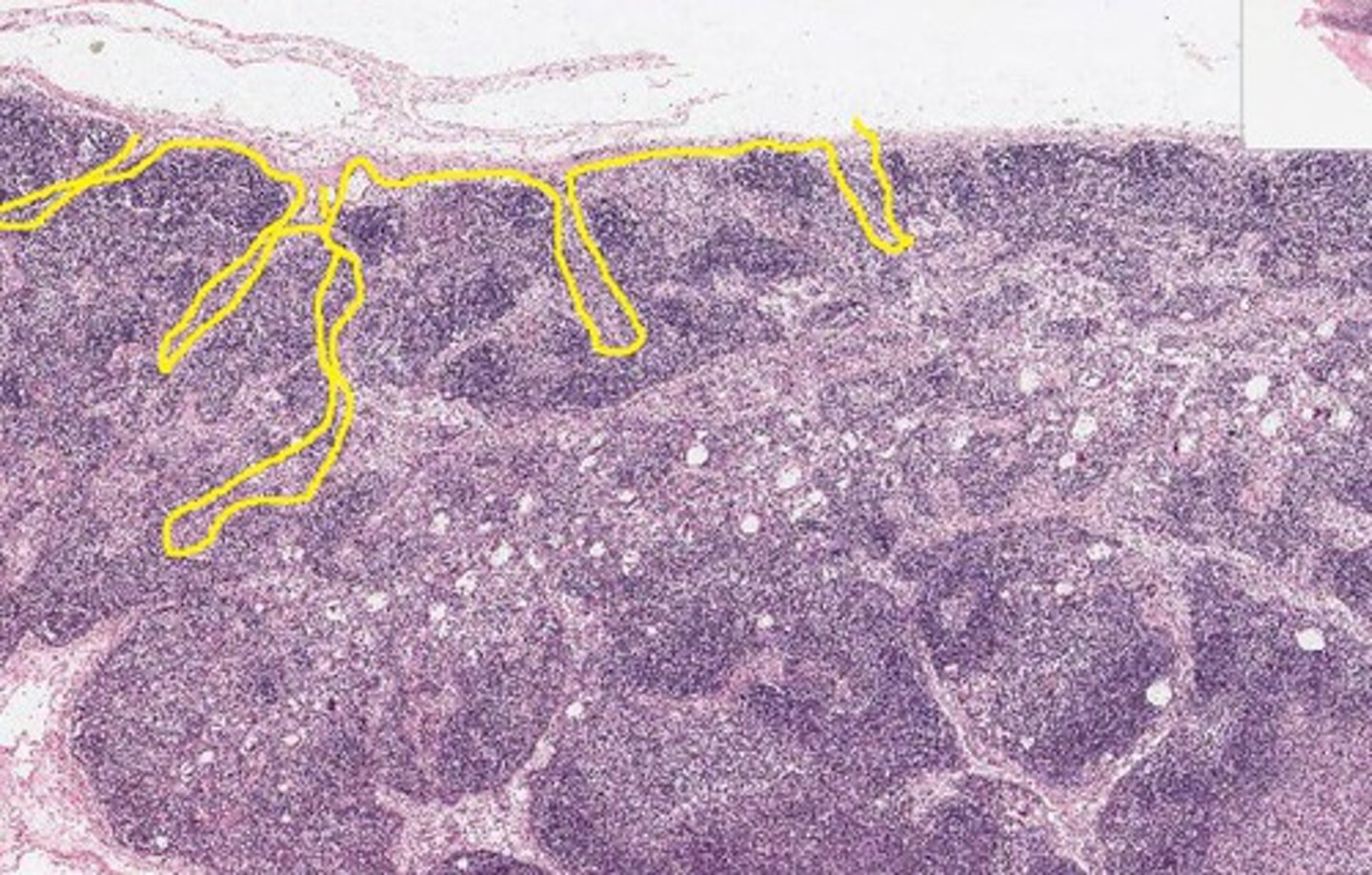
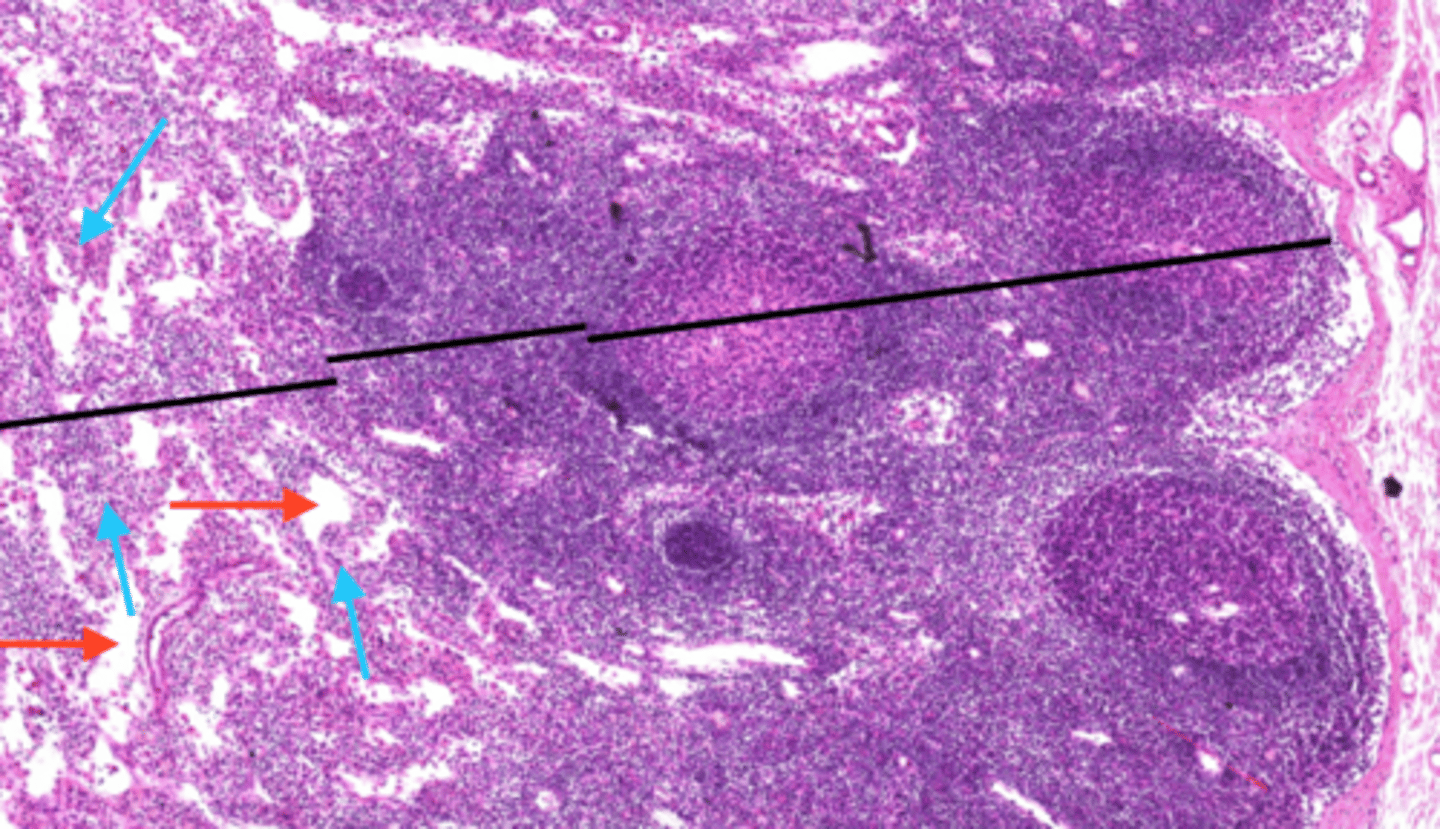
afferent lymphatic vessels (lymph node)
Entrance on the lymph node for lymphatic vessels to bring lymph fluid
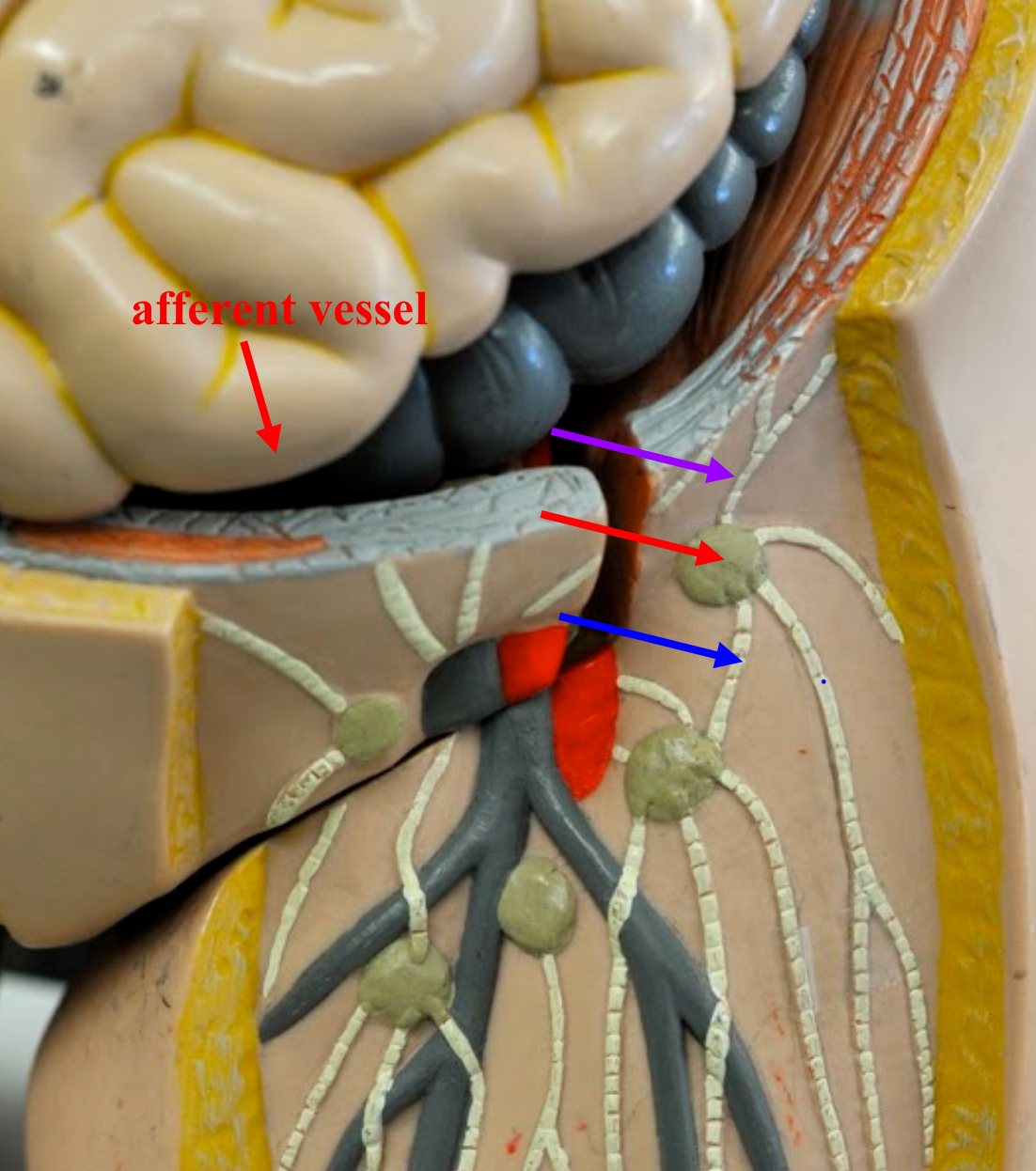
hilum (lymph node)
An indentation where blood vessels and nerves reach the lymph node.
efferent lymphatic vessels (lymph node)
the vessels leaving the concave hilum of the lymph node carry lymph away and onward to the venous system.
Are there more afferent or efferent lymphatic vessels?
Afferent lymphatic vessels generally outnumber efferent lymphatic vessels.
lymphatic capsule (lymph node)
The connective tissue that surrounds and protects the lymph node.
trabeculae (lymph node)
the extends inward and partition the interior of the node.
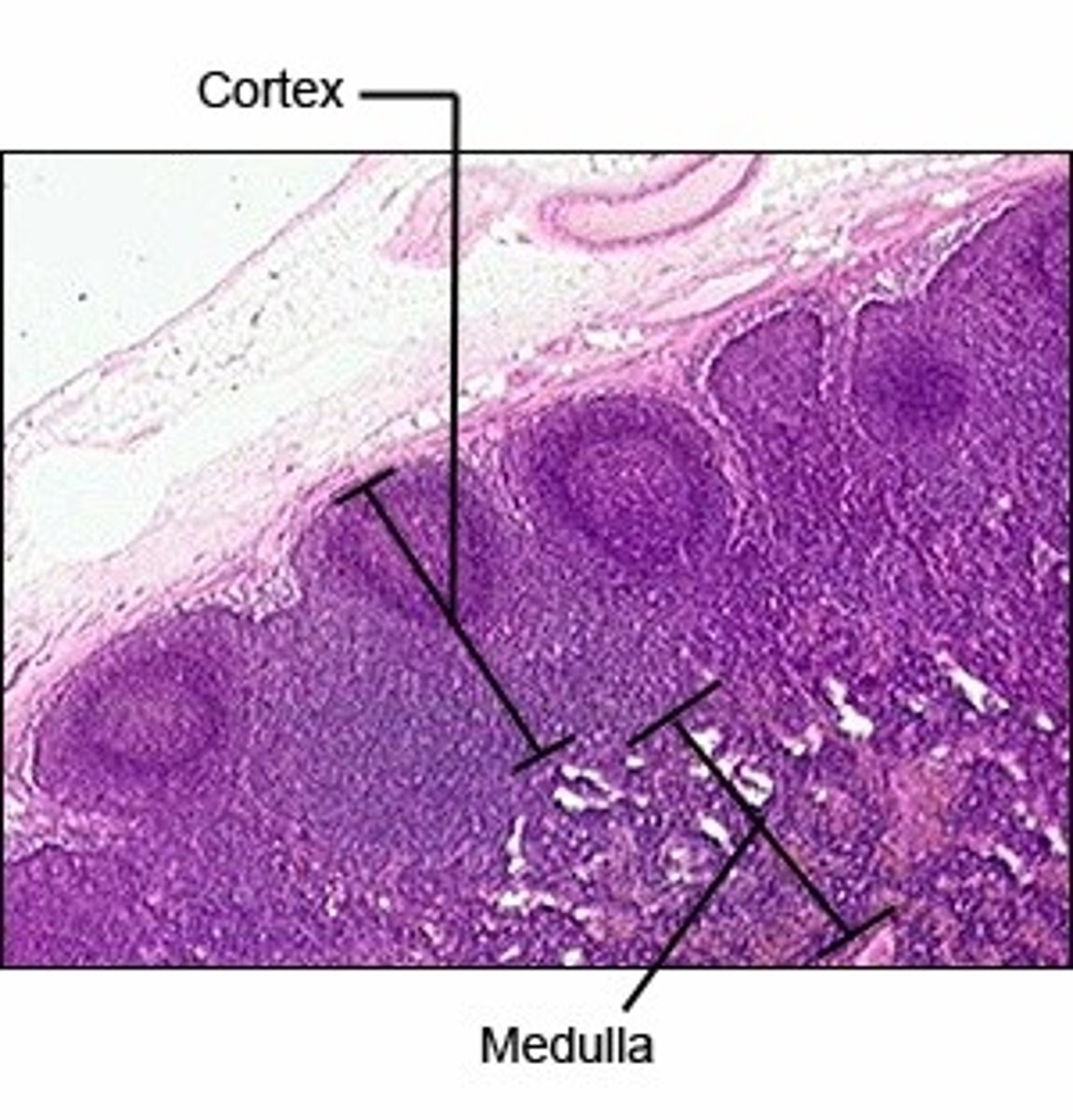
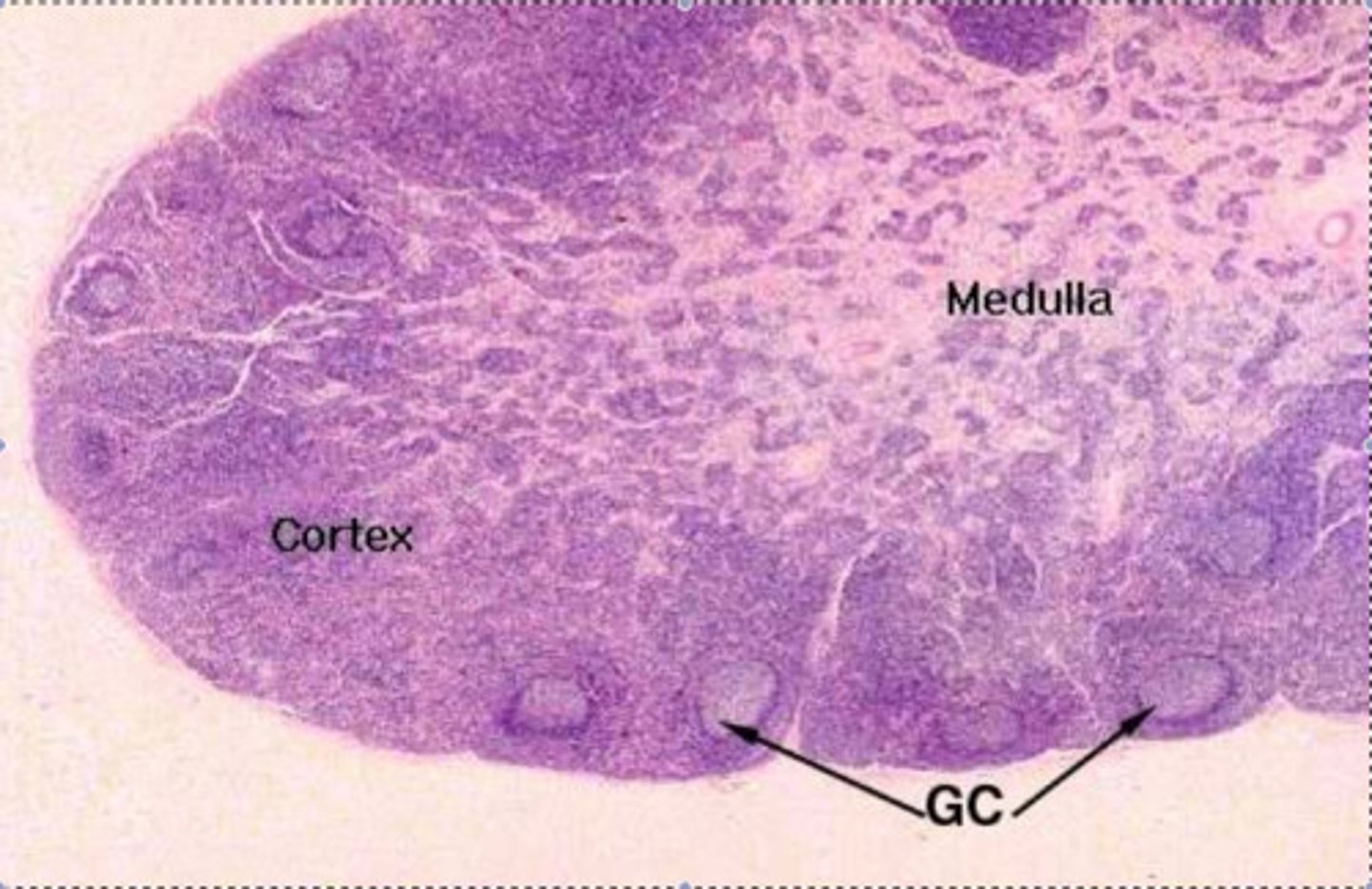
cortex (lymph node)
Contains clusters of lymphocytes. The outer region of a lymph node containing B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages, playing a key role in immune response activation.
sinuses (lymph node)
spaces allowing lymph movement through the node
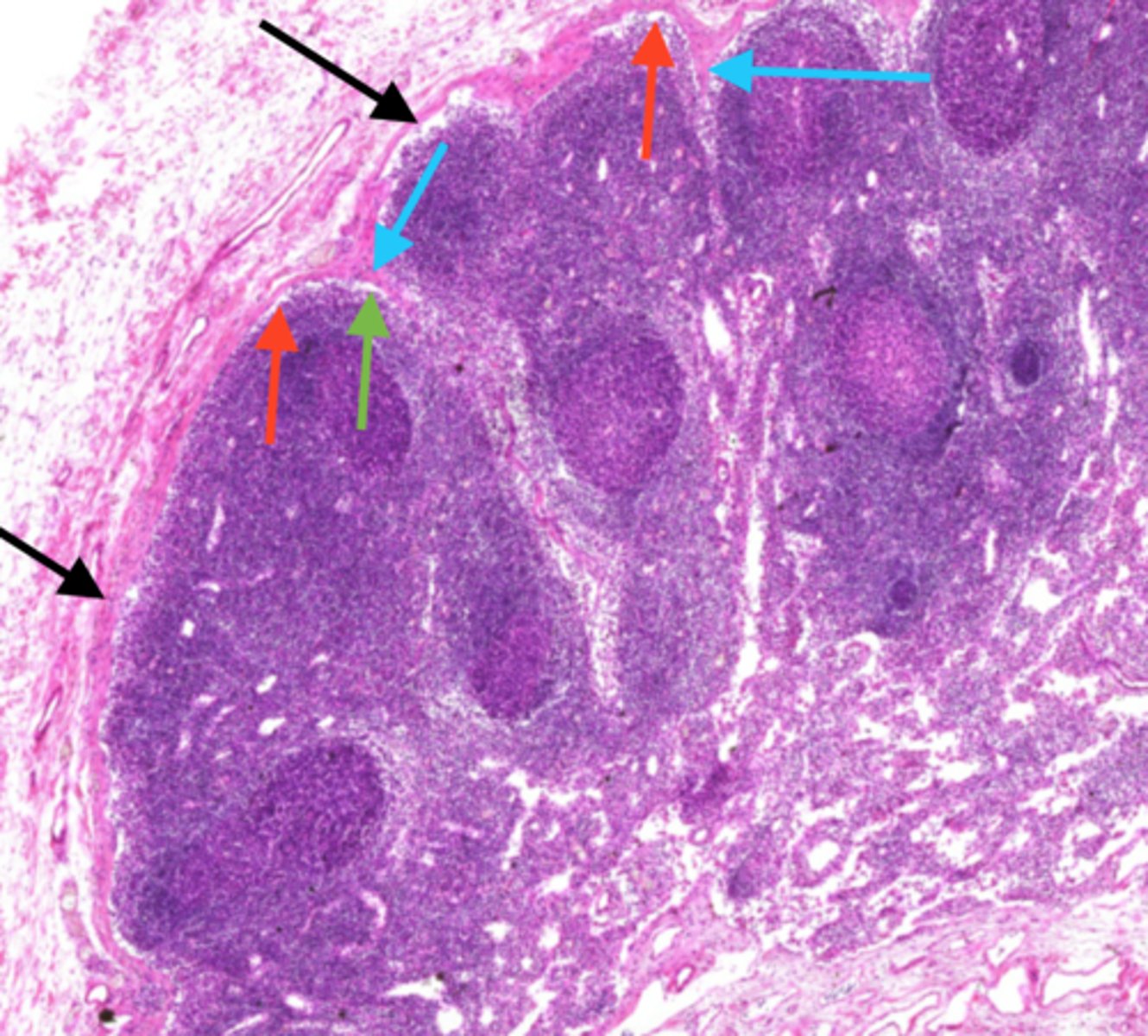
medulla (lymph node)
Medullary cords extend inward from cortex and contain B cells, T cells, and plasma cells
medullary cords (lymph node)
lymphatic tissue in the medulla of a lymph node filled with B cells, plasma cells, and macrophages, playing a role in antibody production and immune response.
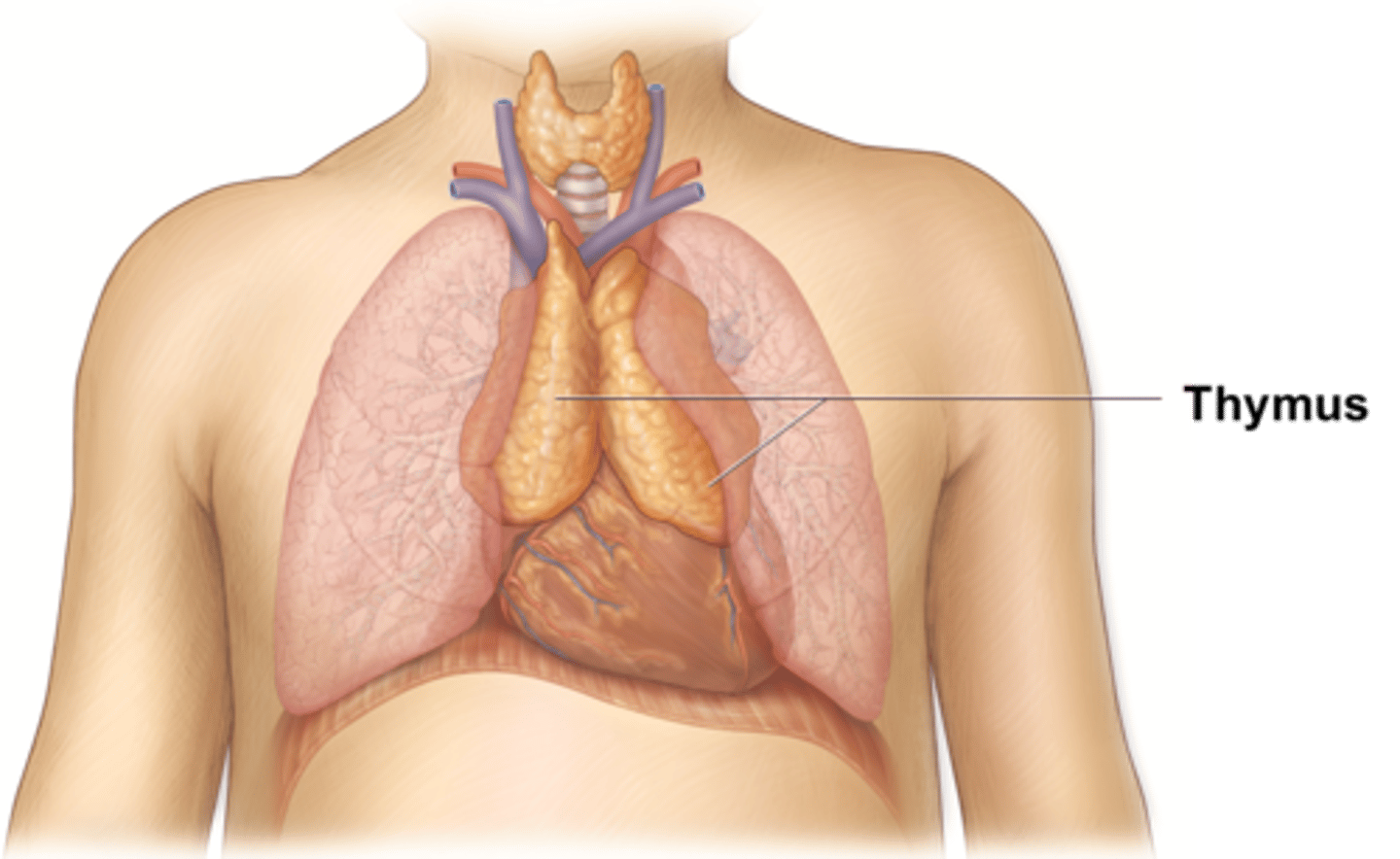
thymus
An immune organ located near the heart. The site of T cell maturation and is larger in children and adolescents.
thymic capsule
A connective tissue covering that surrounds the thymus, appearing as a thin, fibrous outer layer that provides structural support and extends inward to form septa that divide the thymus into lobules.
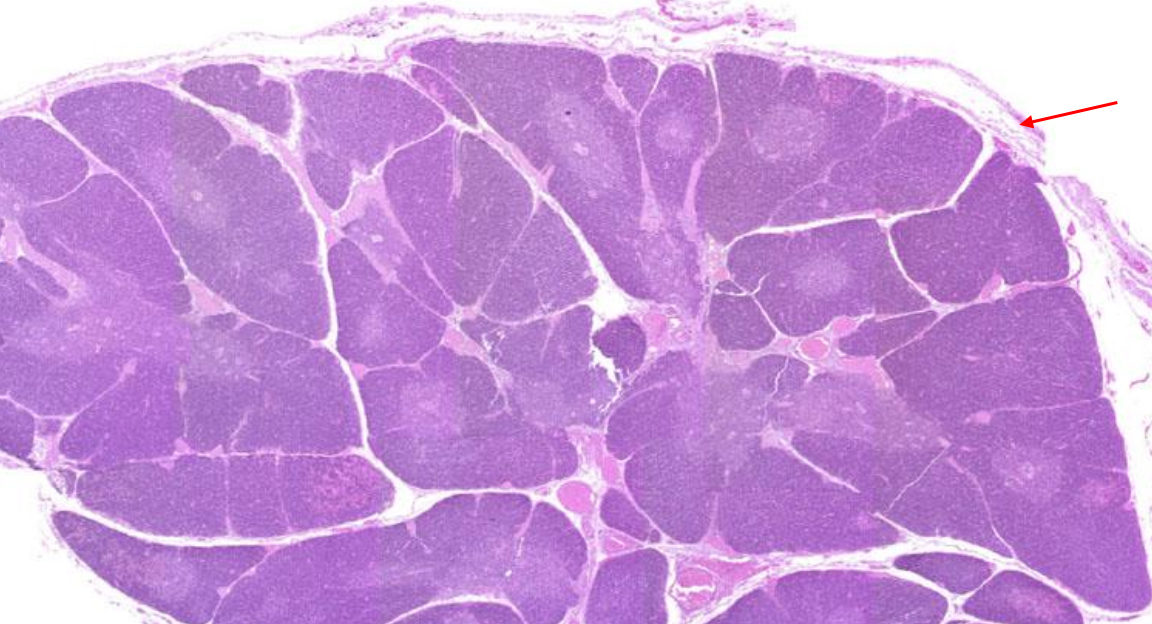
thymic lobules
Each cortex of each lobule exhibits regions of rich purple staining.
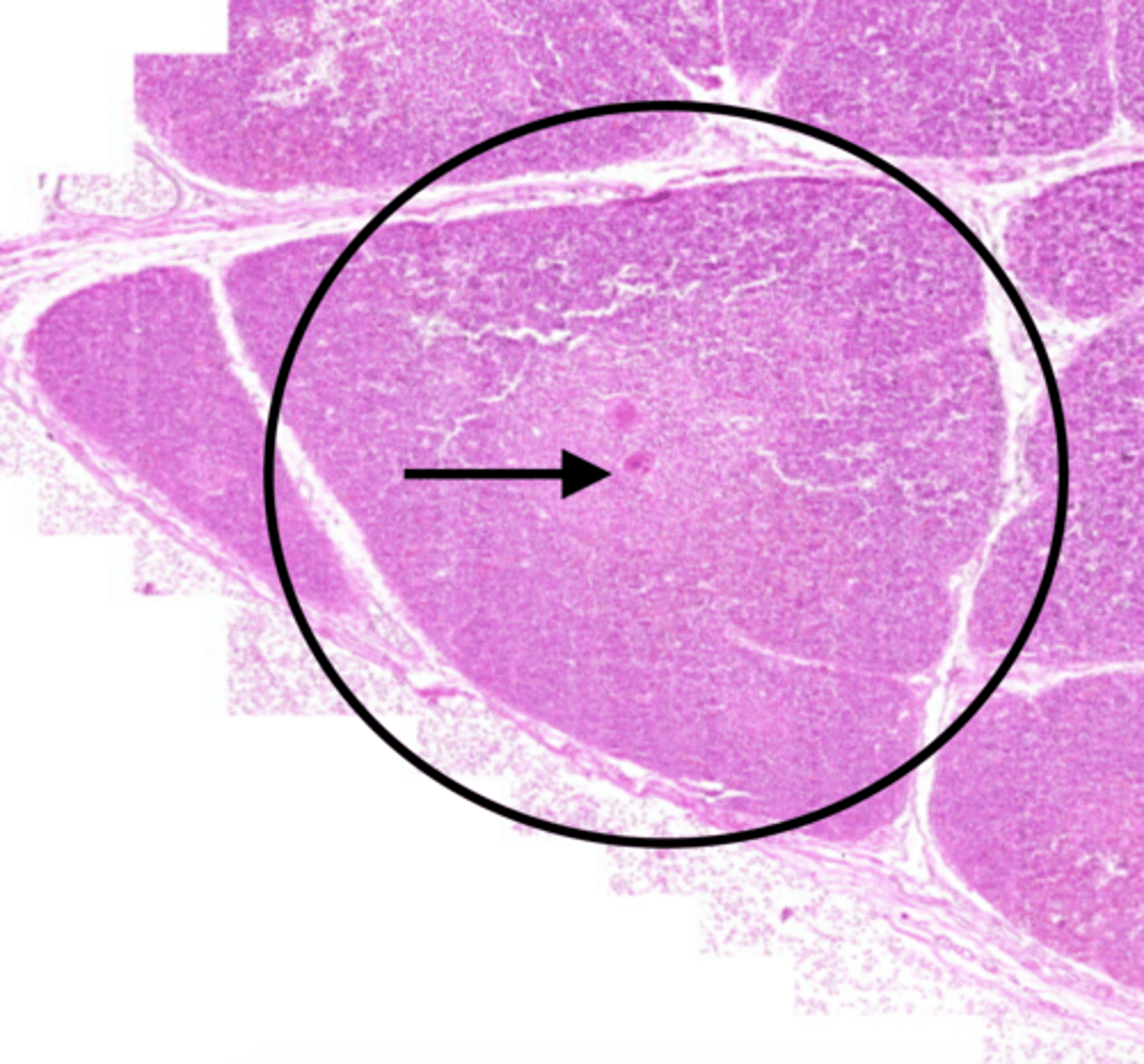
T lymphocytes (thymus)
migrate to the thymus from the bone marrow in order to complete their development and become mature immunocompetent lymphocytes.
helper T lymphocytes (thymus)
secretes chemicals to mobilize and control the entire immune system.
cytotoxic T lymphocytes (thymus)
mature t cells that have "graduated" from the thymus will go on and to kill infected and cancerous cells.
regulatory T lymphocytes (thymus)
suppress any overactivity of immune cells
What makes up the adult thymus?
It contains 𝐚𝐛𝐮𝐧𝐝𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐢𝐩𝐨𝐜𝐲𝐭𝐞𝐬 (fat cells in the subcutaneous layer in the thymus) and 𝐟𝐢𝐛𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐭𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐮𝐞 (tissue that forms the thymic capsule)
How would the average age of red blood cells in the splenic artery compare to the average age of red blood cells in the splenic vein?
The average RBC age will decrease because the spleen would have removed many of the oldest RBC's.
What is the advantage of the fact that afferent lymphatic vessels outnumber efferent lymphatic vessels?
This creates a bottleneck effect that slows down the flow of lymph within the node. This creates more time for examination of the lymph.
Tonsillectomies used to be a common occurrence as a means of dealing with tonsil infections. Such surgeries are no longer performed as often. Why do you suppose this is?
Tonsillectomies remove one of the first lines of defense against inhaled and ingested pathogens.
Humans with a deficient gene known as FOXN1 are born athymic. What are the ramifications of this?
Being athymic would result in depression in every aspect of the immune system (because of the lack of helper T cells) as well as a profound inability to destroy infected cells (because of the lack of cytotoxic T cells)